A 1.1.2 - Hydrogen Bonds
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
**Hydrogen bonds as a consequence of the polar covalent bonds within water molecules.** Students should understand that polarity of covalent bonding within water is due to unequal sharing of electrons and that hydrogen bonding due to this polarity occurs between water molecules. Students should be able to represent two or more water molecules and hydrogen bonds between them with the notation shown to indicate polarity.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
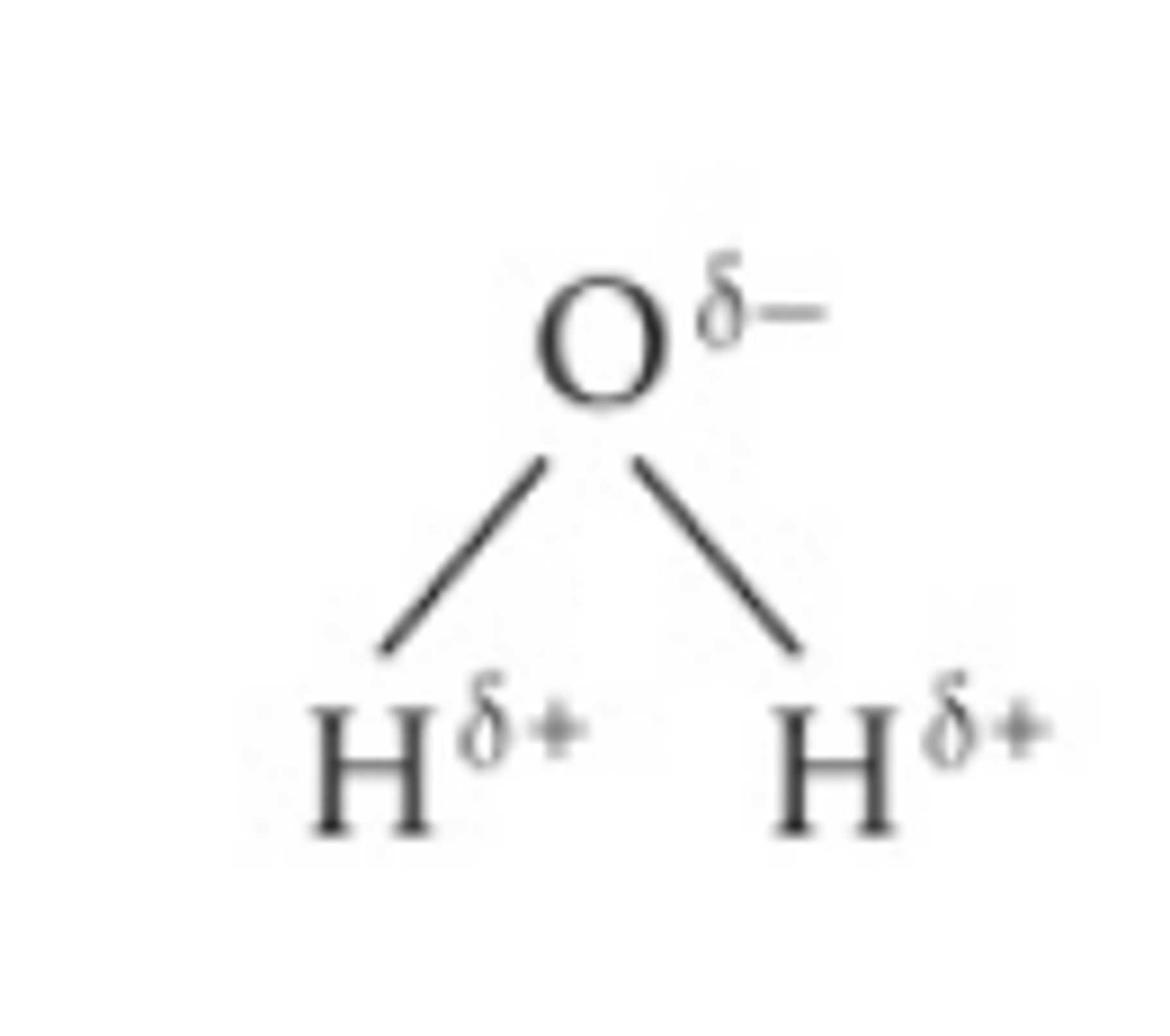
Draw a water molecule with hydrogen bonding including notation.
What are some of the key functions of hydrogen bonding?
the dissolving of solutes in water
the cohesion and adhesion of water molecules
the base-pairing between the two strands of DNA
Interactions between mRNA and tRNA during protein synthesis
Surface effects on membranes between polar phosphate groups and water
How do hydrogen bonds play a role in the structure of proteins?
hydrogen bonds help to form part of the secondary and tertiary levels of structure in proteins.
How do hydrogen bonds give cellulose and collagen their tensile strength?
the hydrogen bonds found between strands of cellulose and collagen give those molecules their tensile strength.
What do the cohesion and adhesion of water molecules allow?
they allow water to move up the trunks of really tall trees.
What does polar covalent bonding result from?
it results from an unequal sharing of electrons
describe the attraction of electrons between hydrogen and oxygen in water.
The oxygen atom attracts the electrons more strongly than the hydrogen atoms, resulting in a weak negatively charged region on the oxygen atom (δ-) and a weak positively charged region on the hydrogen atoms(δ+), this also results in the molecule's asymmetrical shape
what is a dipole
the separation of charge due to the electrons in the covalent bonds being unevenly shared.
what is a polar molecule?
a molecule that has one end that is negatively charged and the other end that is positively charged.
what type of molecule is water
a polar molecule
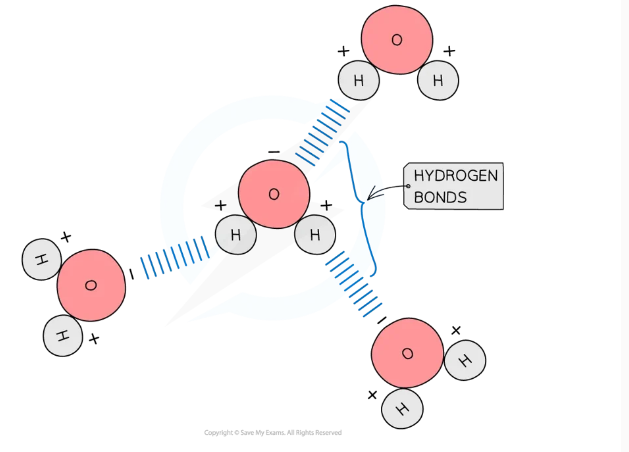
Why do hydrogen bonds form between water molecules?
they form due to the polarity of water, so hydrogen bonds form between the positive and negative charged regions of adjacent water molecules.
Describe the strength of hydrogen bonds.
hydrogen bonds are weak when there are few, so they are constantly breaking and reforming.
however when there are large numbers present they form a strong structure.
Draw a diagram of hydrogen bonds between water molecules.

How much mass of a cell is water?
70% TO 95%