pt 4 during the First 3 Year: Prenatal development - Birth and Physical Development
1/162
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
163 Terms
Prenatal Development
Gestation
- the approximate 38-week period of development between conception and birth.
The normal range being 38 and 42 weeks old.
other source: ▪ Between 37 and 41 weeks
Gestational age
is usually dated from the first day of an expectant mother's last menstrual cycle.
Stages of Prenatal Development
1. Germinal Stage (Fertilization to 2 Weeks)
2. Embryonic Stage (2 to 8 weeks)
3. Fetal Stage (8 weeks to Birth)
1. Germinal Stage (Fertilization to 2 Weeks)
the zygote divides, becomes more complex, and is implanted in the wall of the uterus.
Within 36 hours, it enters mitosis. This mass will then differentiate into three layers:
o Differentiation
specialization of the cells to perform various tasks
o Blastocyst
fluid-filled sphere which floats freely in the uterus until 6th day after fertilization then it implants itself in the uterine wall
o Trophoblast
outer layer of cells that later provides nutrition and support for the embryo
(1) the ectoderm
- outer layer of the skin (becomes outer layers
of skin, nails, hair, teeth, sensory organs, and the nervous system)
(2) the endoderm
- digestive system, liver, pancreas, salivary glands, and respiratory system
(3) the mesoderm
- inner layer of skin, muscles, skeleton, and excretory and circulatory systems.
o Amniotic Sacs
encloses the developing embryo, protecting it and giving it a room and grow.
o Placenta
allows oxygen, nourishment, and wastes to pass between mother and embryo.
o Umbilical Cord
connects the embryo to the placenta.
2. Embryonic Stage (2 to 8 weeks) (first 2 months)
by this time, the organs and major body systems— respiratory, digestive, and nervous—develop rapidly. This is also when the embryo is most vulnerable to destructive influences (critical period) in the prenatal environment. The most severely defective embryos usually do not survive beyond the first trimester.
Organogenesis
o Major body systems (respiratory, digestive, and nervous system) develop
2a. ➢ Spontaneous abortion
commonly called a miscarriage, is the expulsion from the uterus of an embryo or fetus that is unable to survive outside the womb.
2b. ➢Stillbirth
miscarriage occurred after 20 weeks of gestation (approx. 5 months)
o Males are more likely to be spontaneously aborted or to be stillborn
3. Fetal Stage (8 weeks to Birth)
the appearance of the first bone cells. During this period, the fetus grows rapidly to about 20 times its previous length, and organs and body systems become more complex.
They also begin to breathe, kick, turn, flex their bodies etc... development of olfactory systems and response systems are also present
3. Fetal Stage (8 weeks to Birth)
o Responds to mother’s voice
o Fetuses know when they approach the near end of the pregnancy
o Grasping reflex
o 6 months or more fetuses can survive outside the womb
o 24-37 months babies need help in breathing
at 36 weeks
o Facial expressions of pain.
3a. ➢ Ultrasound
- the use of high-frequency sound waves to detect the outline of the fetus.
Environmental Influences: Maternal Factors
Teratogenic
birth defect-producing
Paternal Factors
o Exposure to lead, marijuana, tobacco, radiation, pesticides, etc may result in abnormal or poor quality sperm
Birth and Physical Development during the First 3 Years
The Birth Process
Labor
Parturition
Uterine Contractions
Braxton-Hicks Contractions
Labor is an apt term for the process of giving birth.
parturition
a series of uterine, cervical, and other changes—which typically begins about two weeks before delivery, when sharply rising estrogen levels stimulate the uterus to contract and the cervix to become more flexible.
Braxton-Hicks contractions
false contractions, mild irregular compared to actual contractions.
o Real labor contractions are more frequent, rhythmic, and painful, and they increase in frequency and intensity
o Midwifery
profession that provides health care to women during pregnancy, birth, and even postpartum period.
o Doula
caregiver who provides continuous physical, emotional, and educational support for the mother before, during, and after childbirth.
1 STAGES OF CHILDBIRTH
Labor takes place in three (3) overlapping stages:
A. Stage 1: Dilation of the Cervix
B. Stage 2: Descent and Emergence of the Baby
C. Stage 3: Expulsion of the Placenta
A. Stage 1: Dilation of the Cervix
1. First stage, the longest, typically lasts 12 to 14 hours.
o Regular and increasingly frequent uterine contractions—15 to 20 minutes apart at first.
o Toward the end of the first stage, contractions occur every 2 to 5 minutes.
o Cervix is fully open (10 centimeters, or about 4 inches).

B. Stage 2: Descent and Emergence of the Baby
2. Second stage, typically lasts up to an hour or two, contractions become stronger and closer together. The baby's head begins to move through the cervix into the vaginal canal, ends when the baby emerges completely from the mother's body.

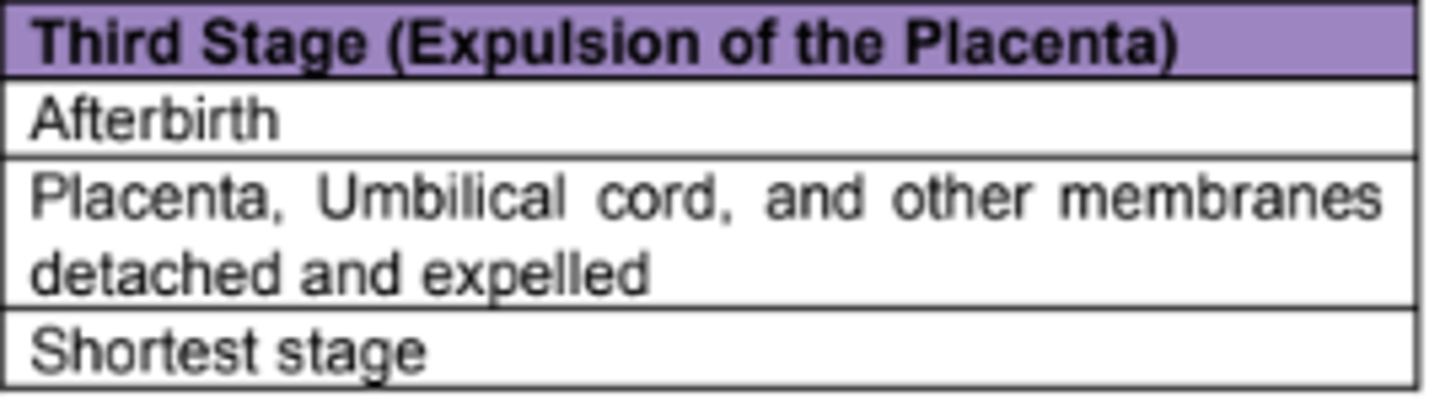
C. Stage 3: Expulsion of the Placenta
3. Third Stage, lasts about 10 to 60 minutes, placenta and the remainder of the umbilical cord are expelled from the mother.
Methods of Childbirth
o Electronic Fetal Monitoring
o Vaginal Delivery
o Cesarean Delivery
o Medicated vs. Nonmedicated delivery
Electronic Fetal Monitoring
can be used to track the fetus' heartbeat during labor and delivery and to indicate how the fetal heart is responding to the stress of uterine contractions. Monitoring it can detect and serious problems/signal when the fetus needs help.
▪ extremely high false-positive rate
o Bradley Method
husbands as coaches, relation for easier birth and prenatal nutrition and exercise
Vaginal Delivery
The usual method of childbirth
Cesarean Delivery
delivery can be used to surgically remove the baby from the uterus through an incision in the mother's abdomen.
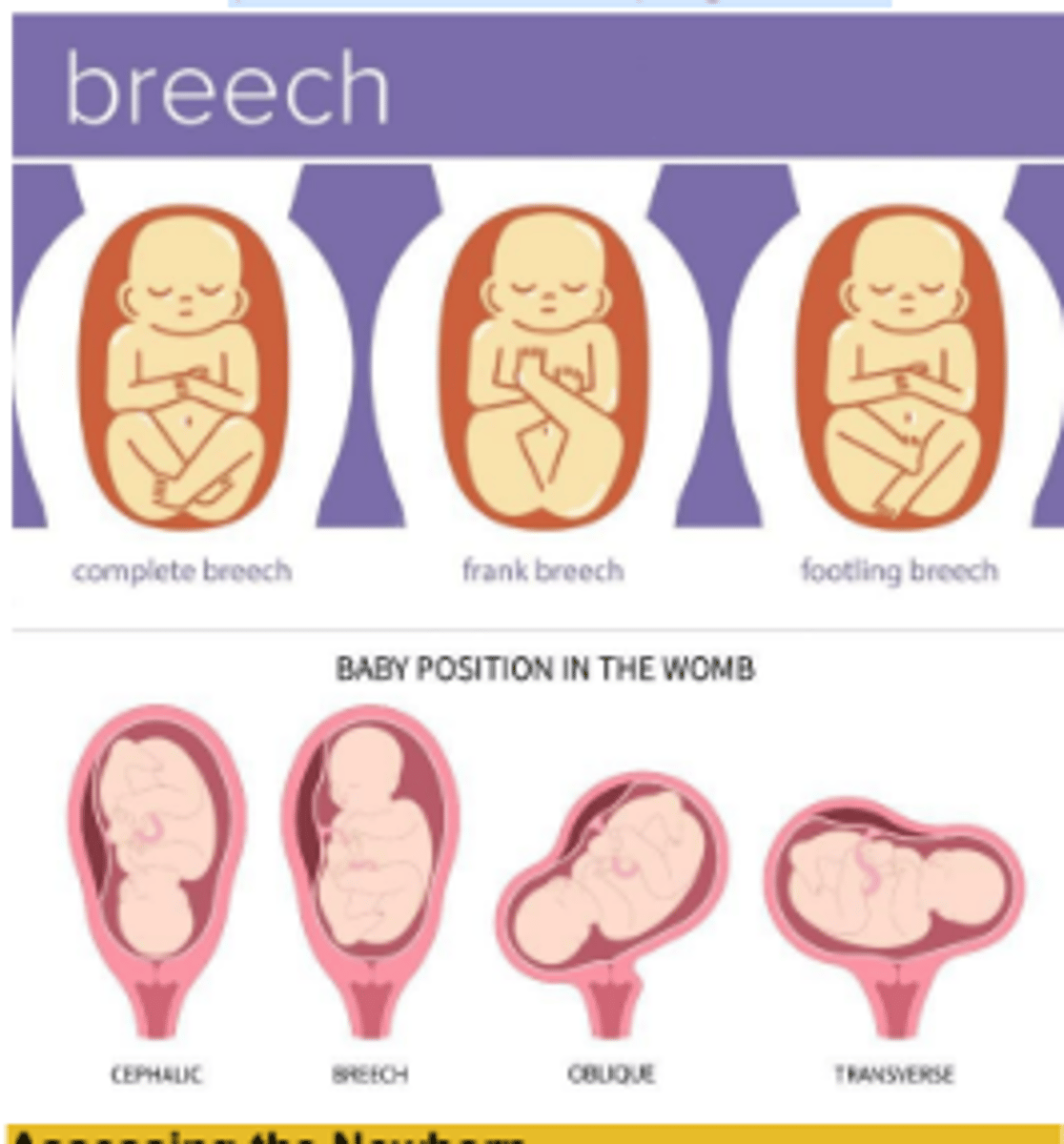
▪ Performed if the baby is
▪ Breech Position: feet or buttocks first
▪ Transverse Position: lying crosswise in the uterus.
▪ The head is too big to pass through the mother’s pelvis.
Cesarean Delivery
▪ Not recommended prior to 39 weeks of gestation unless there is an indication of fetal lung maturity.
• Vaginal Birth After Cesarean (VBAC)
▪ Breech Position
baby's buttocks are the first part to emerge from the vagina
which can cause respiratory problems
▪ Complications: bleeding, infection, damage to pelvic organs, post-operative pains, riskier future pregnancies
o Medicated vs. Nonmedicated delivery
1. Natural Childbirth
2. Prepared Childbirth
3. Alternative Method of Natural Childbirth or Prepared Childbirth
1. Natural Childbirth
method that aims to reduce the mother's pain by decreasing her fear by providing information about childbirth and teaching her and her partner to use breathing methods and relaxation techniques during delivery.
1. Natural childbirth
first introduced as childbirth without fear; method of childbirth that seeks to prevent pain by eliminating the mother's fear through education about the physiology of reproduction and training in breathing and relaxation during delivery.
2. Prepared childbirth
- uses instruction, breathing exercises, and social support to induce controlled physical responses to uterine contractions and reduce fear and pain.
3. Alternative Method of Natural Childbirth or Prepared Childbirth
o Lamaze Method
o Leboyer Method (1970's)
o Michael Odent
o Bradley Method
o Lamaze Method
(French obstetrician Fernand Lamaze; late 1950's)
▪ Teaches expectant mothers to work actively with their bodies through controlled breathing.
▪ The woman learns to relax her muscles as a conditioned response to the voice of her coach who attends classes with her, takes part in the delivery, and helps with the exercises.
➢ LeBoyer Method (1970's)
- the woman gives birth in a quiet room under low lights, to reduce stress, and the newborn is gently massaged to ease crying.
➢ Michael Odent's method
- submersion of the laboring mother in a soothing pool of water.
o Three kinds of drugs are used for labor:
a. Analgesia
b. Anesthesia
c. Oxytocin
a. Analgesia
pain reliever such as tranquilizers, barbiturates, and narcotics
Reduces the perception of pain by depressing the activity of the central nervous system.
b. Anesthesia
used in the late first stage/ second stage labor and during delivery to block sensation in an area of the body or to block consciousness.
▪ Epidural Block – regional anesthesia that blocks the lower part of the body
▪ Pudendal Block – vaginal anesthesia
c. Oxytocin
hormone that promotes contraction (Pitocin)
The Newborn Baby
1. SIZE AND APPEARANCE
2. BODY SYSTEMS
3. MEDICAL AND BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT
4. STATES OF AROUSAL
• Doula
o An experienced mentor who furnishes emotional support and information for a woman during labor.
neonatal period
the first four weeks of life
is a time of transition from the uterus, where a fetus is
supported entirely by the mother to an independent existence
New babies have distinctive features
the head may be long and misshapen because of the molding that eased its passage through the mother's pelvis, this occurs because the infant's skull bones are not yet
fused and will not be completely joined for 18 months.
Neonate
Newborn baby, up to 4 weeks old.
1. SIZE AND APPEARANCE
Neonate
Fontanels
Lanugo
Vernix Caseosa
Witch's Milk
Neonate
About 20 inches long and weighs about 71⁄2 pounds.
Fontanels
Areas on their heads where the bones of the skull do not meet.
• Covered by a tough membrane that allows for flexibility in shape, which eases the passage of the neonate through the vaginal canal.
Lanugo
A fuzzy prenatal hair.
Vernix Caseosa
"Cheesy varnish", an oily protection against infection that dries within the first few days.
Witch's Milk
A secretion that sometimes leaks from the swollen breasts of newborn boys and girls around the 3rd day of life.
2. BODY SYSTEMS
Anoxia
Hypoxia
Umbilical Cord & Placenta
Neonatal Jaundice
Most babies start to breathe as soon as they are exposed to air.
If breathing has not yet begun within five minutes, the baby may suffer permanent brain injury caused by anoxia - lack of oxygen, or hypoxia - a reduced oxygen supply.
Umbilical Cord & Placenta
Gets oxygen through the umbilical cord.
Bring food from the mother and to carry fetal body wastes away.
Neonatal Jaundice
their skin and eyeballs look yellow; is caused by the immaturity of the liver but is usually not serious
3. MEDICAL AND BEHAVIORAL ASSESSMENT
A. Apgar Scale (Dr. Virginia Apgar)
B. Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS) (Dr. T. Berry Brazelton)
APGAR Scale
Pic
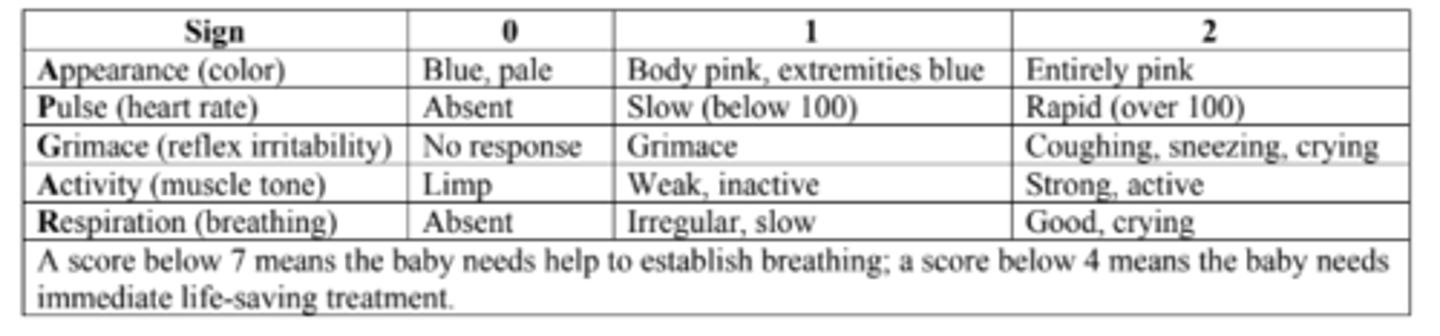
APGAR Scale
Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS)
(NBAS) is used to help parents, health care providers, and researchers assess neonates' responsiveness to their physical and social environment, to identify strengths and possible vulnerabilities in neurological functioning, and to predict future development. performed within 24-36 hrs after birth.
APGAR Scale
• Standard measurement of a newborn's condition.
• Assess one minute after delivery, and then again 5 minutes after birth.
APGAR Scale
▪ 7 To 10: Good to excellent condition.
▪ Below 5–7: Baby needs help to establish breathing.
▪ Below 4: Baby needs immediate lifesaving treatment.
▪ 0 To 3 At 10, 15, And 20 Minutes After Birth: Increasingly associated with cerebral palsy or other neurological problems.
• Cerebral Palsy: Muscular impairment due to brain damage prenatally or during birth.
Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale
o Suitable for infants up to 2 months old.
o Motor Organization: Behaviors as activity level and the ability to bring a hand to the mouth.
o Reflexes
o State Changes: Irritability, excitability, and ability to quiet down after being upset.
o Attention and Interactive Capacities: General alertness and response to visual and auditory stimuli.
o Central Nervous System Instability: Tremors and changes in skin color.
o Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Network Neurobehavioral Scale
assessment of the newborn's behavior, neurological and stress response, and regulatory capacities.
o Newborn Screening for Medical Conditions
- check for rare genetic, hormone-related, and metabolic conditions that can cause serious health problems
o Boys tend to be slightly longer and heavier than girls.
o First born weigh less that laterborns.
4. STATES OF AROUSAL
• An infant's physiological and behavioral status at a given moment in the periodic daily cycle of wakefulness, sleep,
and activity.
Complications of Childbirth
➢ Low Birth Weight
➢ Postmaturity
➢ Stillbirth
➢ Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
➢ Death from Injuries
➢ Low Birth Weight
Preterm (Premature) Infants
Small-For-Date (Small-For- Gestational-Age) Infants
Immediate Treatment and Outcomes
1. Antiseptic, Temperature- Controlled Crib, Or Isolette
2. Kangaroo Care (KC)
Preterm birth
Babies born before the 37th week of gestation.
• *Typical gestation is 40 weeks.term-93
One condition commonly faced by preterm babies is Respiratory Distress Syndrome wherein there is a lack of surfactant (lung-coating substance) that keeps air sacs from term-98collapsing.
▪ Very Low birth Weight
less than 3 pounds 4 ounces.
▪ Extremely Low Birth
- less than 2 pounds
Pre-term and Low Birth Weight Infants
o Low Birth Weight Infants – weigh less than 5 pounds and 8 ounces at birth
o Very Preterm
less than 33 weeks.
o Extremely Preterm
born less than 28 weeks gestation.
➢ Postmaturity
- when women have not gone into labor after 42 or more weeks' gestation. At that point a baby is considered postmature.
tend to be long and this because they have kept growing in the womb but have had an insufficient blood supply toward the end of gestation.
Shoulder Dystocia
Small-For-Date (Small-For- Gestational-Age) Infants
Born at or around their due dates, but are smaller than would be expected.
• *Refer back to the book for risk factors for LBW.
1. Antiseptic, Temperature- Controlled Crib, Or Isolette
Premature baby lies has holes through which the infant can be examined, touched, and massage.
2. Kangaroo Care (KC)
Method of skin-to-skin contact in which a newborn is laid face down between the mother's breasts for an hour or so at a time after birth.
➢ Stillbirth
- the death of a fetus after the 20th week of gestation, sometimes it is diagnosed prenatally, in other cases, the baby's death is discovered during labor or delivery.
Although the cause of stillbirth is not clearly understood, many stillborn infants are small for their gestational age, indicating malnourishment in the womb.
Shoulder Dystocia
(difficult or obstructed labor)
• A condition in which the baby's shoulders become stuck behind the mother's pelvic bone during delivery.
➢ Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
- is the sudden death of an infant under age 1 which remains unexplained even after a thorough investigation that includes an autopsy.
➢ Death from Injuries
about 90% of all injury deaths are due to one of four causes:
suffocation, motor vehicle traffic, drowning, and residential fires or burns—many of which occur at home.
o Progestin
might help in reducing preterm birth.
Postpartum Period
o Period after childbirth.
o Lasts for about 6 weeks or until the mother's body has completed the adjustment and returned to nearly prepregnant state.
Physical Adjustment
o Loss of sleep that the primary caregiver experiences during this period.
o Sudden and dramatic hormone production
o Estrogen and progesterone levels drop steeply and remain low until the ovaries start producing again.
EARLY PHYSICAL DEVELOPMENT
1. PRINCIPLES OF DEVELOPMENT
2. NUTRITION
3. THE BRAIN AND REFLEX BEHAVIOR
4. EARLY SENSORY CAPACITIES
1. PRINCIPLES OF DEVELOPMENT
Cephalocaudal Principle
Proximodistal Principle