
Looks like no one added any tags here yet for you.
PCB (PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARD)
Refers to the system of components, power, and signal sources that enable the current to flow around
OPEN CIRCUIT
A type of electrical circuit where the continuity is broken, preventing current from flowing.
INCOMPLETE (Gap somewhere in the path)
CLOSE CIRCUIT
A type of electrical circuit that allows current to flow freely due to an unbroken path.
(current flows) Implies that the circuit is complete
BULB
Connected to an electric power supply
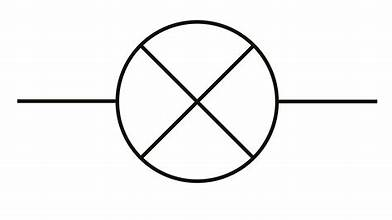
CELL (DC SOURCE)
Generates electricity
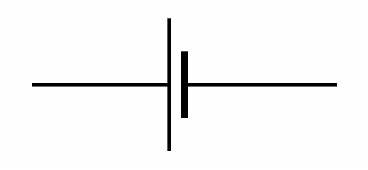
BATTERY
2 or more electrochemical cells connected together to provide a voltage source.
CONNECTING WIRE
A conductor that allows electric current to flow between components in a circuit.
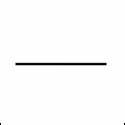
CAPACITOR
2 terminal electrical component for energy storage
KINDS:
POLARIZED
STANDARDIZED
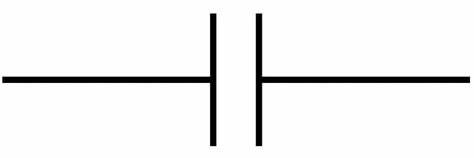
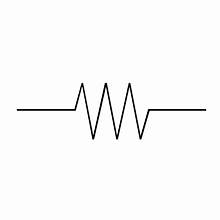
RESISTOR
An electric current that limits and controls the flow of current in a circuit
measured in OHMS
DIODE
A semi conductor device that allows current to flow in one direction
KINDS:
STANDARD DIODE
LED

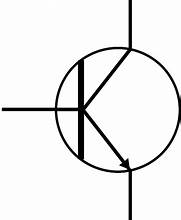
TRANSISTOR
Amplify/switches electronic signals and power
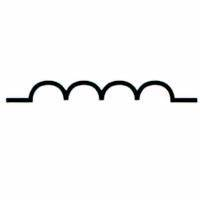
INDUCTOR
Resist AC while permitting DC to pass
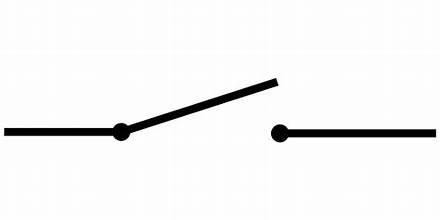
SWITCH
Turn on and off the electricity
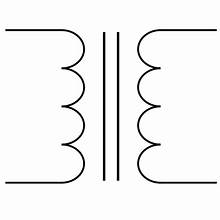
TRANSFORMER
Trades voltage for current/vice-versa
AMMETER
Device used to measure current
SYMBOL: (A)
VOLTMETER
Used to measure potential difference
SYMBOL: (V)
TYPES OF CIRCUIT
Series Circuit
Parallel Circuit
SERIES CIRCUIT
Components are connected end-to-end, one after another
makes a simple loop
damage isa, damage all
PARALLEL CIRCUIT
Components are connected side by side
current has routes
damage isa, dili ma-damage all
MEASURING CURRENT
Electric current is measured in amps (A) using an ammeter connected in series in the circuit
MEASURING CURRENT (SERIES CIRCUIT)
Current is the same at all points in the circuit.
MEASURING CURRENT (PARALLEL CIRCUIT)
Current is shared between the components
MEASURING VOLTAGE
The ‘electrical push’ which the cell gives to the current is called the voltage. It is measured in volts (V) on a voltmeter
Different cells produce different voltages. The bigger the voltage supplied by the cell, the bigger the current.
Unlike an ammeter a voltmeter is connected across the components
Scientist usually use the term Potential Difference (pd) when they talk about voltage.
MEASURING VOLTAGE (SERIES CIRCUIT)
Voltage is shared between the components
MEASURING VOLTAGE (PARALLEL CIRCUIT)
Voltage is the same in all parts of the circuit