reproduction
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
groups of vascular plants
pteridophytes - ferns, horsetails (spores)
seed plants → angiosperms (most abundant) and gymnosperms
reproduction
production of new individuals
can be new genets or ramets
genets
sexually formed, genetically distinct
ramets
asexually formed, clones
angiosperms - forms of reproduction
separate sexes, self-fertilization → sexual reproduction
apomixis
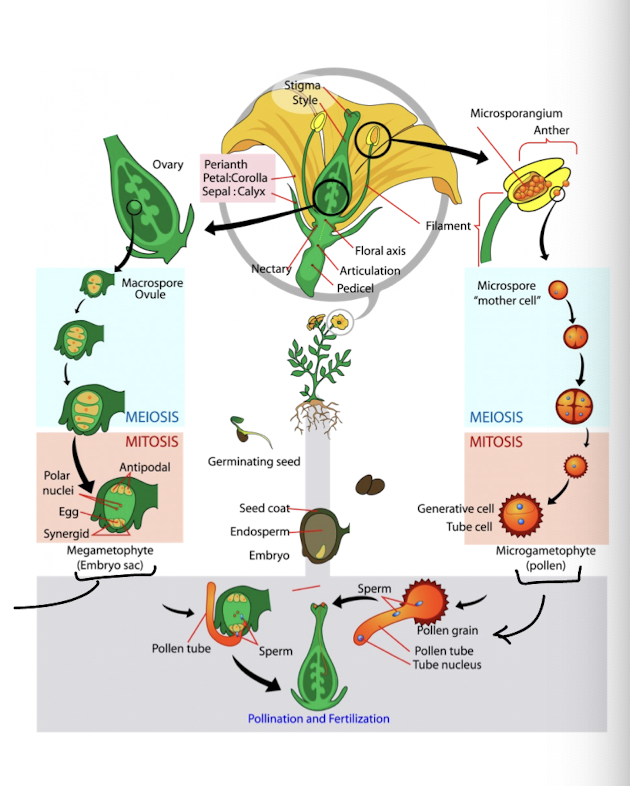
sexual reproduction in angiosperms - meiosis
in meiosis diploid parent cell, macrospore or microspore, divides into four haploid cells (spores)
macrospore → haploid cell develops into four cells, embyronic sac cell and 3 degenerate cells
microspore → haploid cell develops into four cells, pollen tetrad
spores are gametophyte generation - will form embryo sac or pollen grain
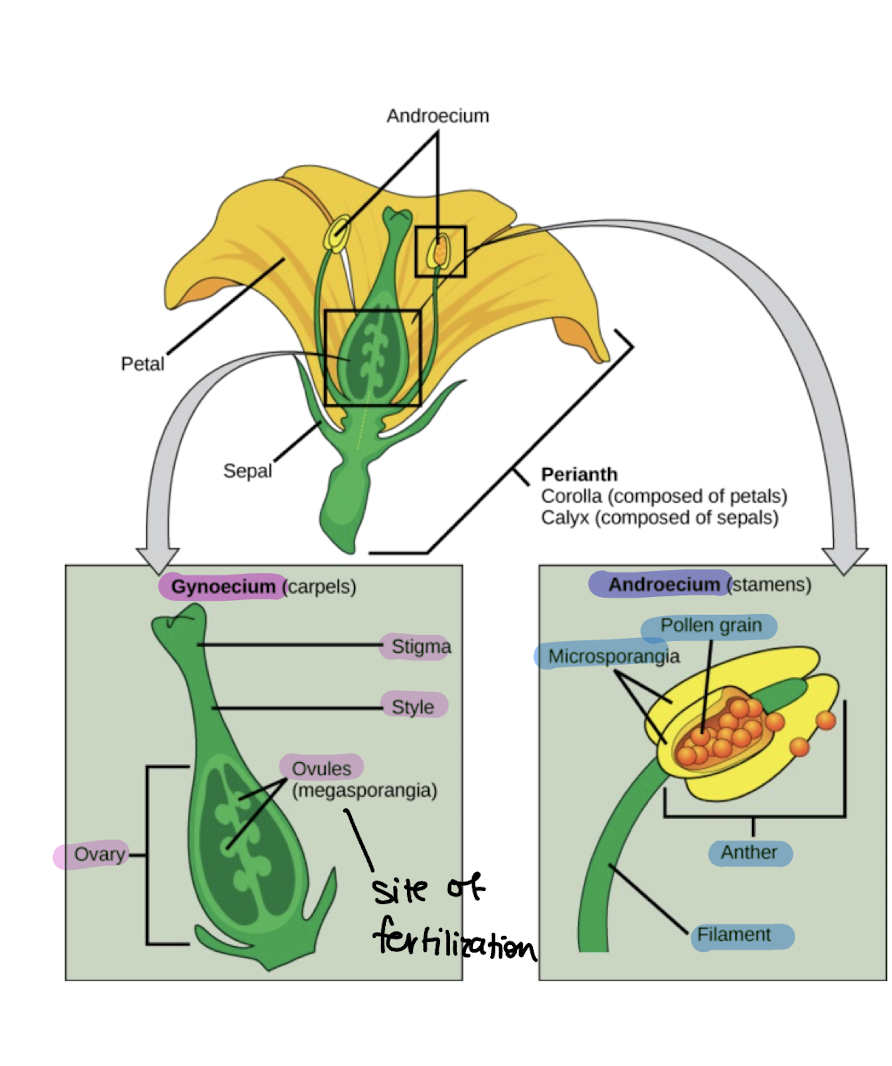
gynoecium
ovary
macrospore/ovule found within
undergoes meiosis and mitosis to form the megagametophyte/embryo sac
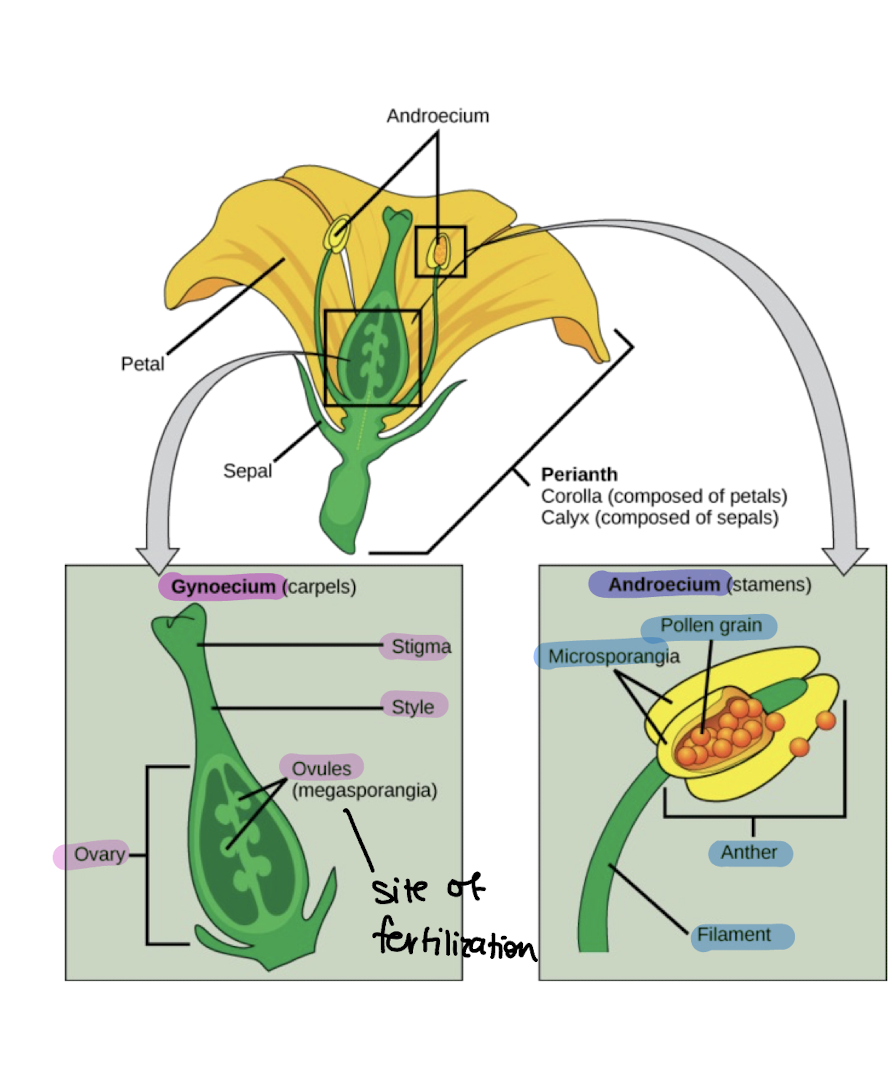
androecium
anther
microspre divides into pollen tetrad during meiosis, then microgametophyte is formed via mitosis - pollen (then pollen tube and pollen grain develop)
sexual reproduction in angiosperms - mitosis
haploid gametophyte (spore) grows by producing egg, antipodal cells, polar nuclei, and synergid (megagametophyte)
as well, the pollen tetrad falls apart and each cell (haploid gametophyte spore) grows into two cells → 1-2 generative and 1 tube cells (microgametophyte)
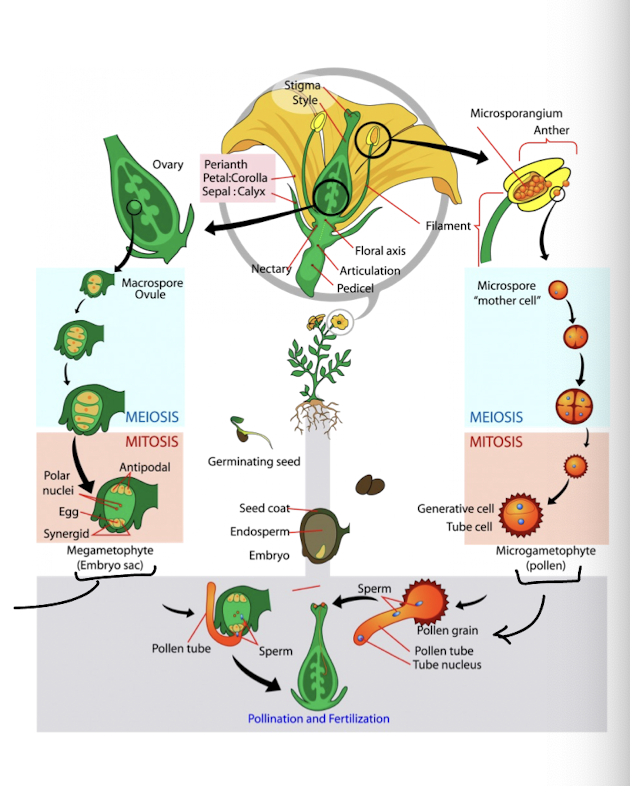
sexual reproduction in angiosperms - fertilization
pollen lands on stigma and the pollen tube forms, reaching to the ovary to reach the ovule where the egg is
sperm cell 1 fuses with the egg to form the zygote
sperm cell 2 fuses with the polar nuclei to form the endosperm (food storage)
selfing in plants
ex Stipa capillata - needle grass which is facultative
can pollinate via cleistogamy or wind pollination
adaptation to severe weather? or ensures reproduction
cleistogamy
self reproduction with closed flowers, instead it remains in leaf sheath to allow self pollination
consequences of selfing in plants
- : reduction of genetic variability, and ability to colonize
+: significantly less resource allocation to reproduction, reproductive insurance
for ex mean pollen grains produced in cleistogamous or obligate selfer plants is quite lower
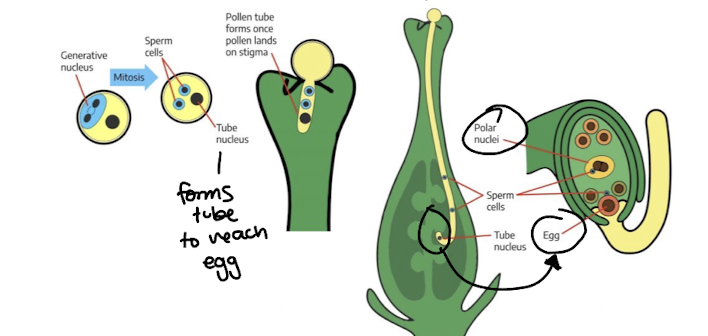
apomixis
form of asexual reproduction - not vegetative
clonal reproduction of seeds, offspring is genetically similar to mother plant
ex diplospory
diplospory
meiosis is skipped, instead mother cell multiplies to diploid megaspore (and degenerative cell)
then there is mitosis of megaspore cell
pseudogamy (resulting in embryo identical to mother) OR autonomous endosperm (no fertilization by pollen)
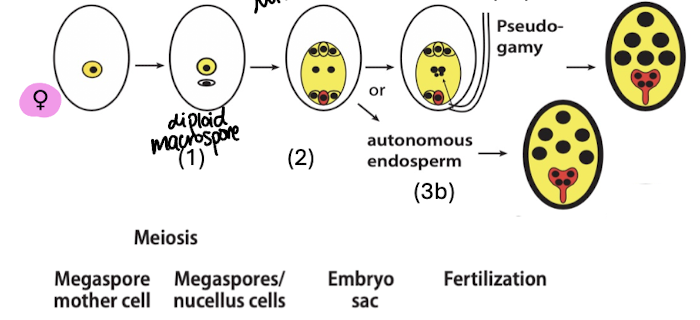
pseudogamy
fertilization of endosperm by pollen, but not the egg
as occurs in diplospory
diplospory example
common among taraxacum species (dandelion)
seeds are the genetic clone of mother plant - genetic differences occur by mutation or hybridization
generations are clonal lineages which can become microspecies
theres about 3000 microspecies, which are commonly divided into aggregate groups as not many people can see the differences
clonal growth
production of genetically identical ramets through growth of stems, roots or leaves
ramets can remain connect or become independent
benefits: vegetative reproduction, forage potential, resource storage, response to disturbance, resource sharing, genet longevity
stolons
type of clonal growth
above ground growth
ex fragaria
epigeogenous rhizomes
type of clonal growth
partly above ground, shorter, more storage capacity and buds
hypogeogenous rhizomes
type of clonal growth
all underground growth, long reach, less storage capacity
ex elymus repens
tubers and bulbs
type of clonal growth
very large storage capacity
tulips, lilies
bud bearing roots
type of clonal growth
full root system where the buds grow from the roots
CLO-PLA
worldwide database of clonal growth in plants
built on publications and quantify clonal traits
clonal vs non clonal plant reproductive output
used data for different plant species across central europe, compared reproductive output
clonal plants devote less to sexual reproduction and therefore have lower output - no reliance, splitting resources
monocarpic species have the highest rate as they undergo only on reproduction event
but this paper did not test the significance between groups just btw
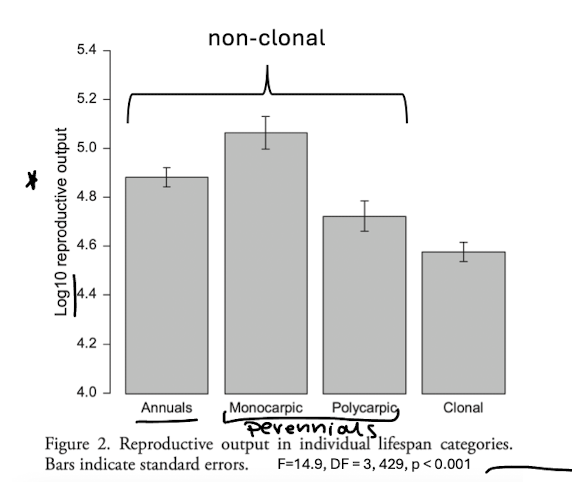
reproductive output
product of seed output and seed mass
exclusion of clonal growth organs
bud bank
collection of dormant vegetative buds above or below ground - as shown in raukiners life forms
allow for regrowth capacity post fire or disturbance, and stabilize population size fluctuations
death can always be accounted for w regrowth
traits include size and depth (not well studied)
costs and benefits of bud bank size
smaller size: low carbohydrate sink, low survival rate
larger: high carb sink, high survival rate
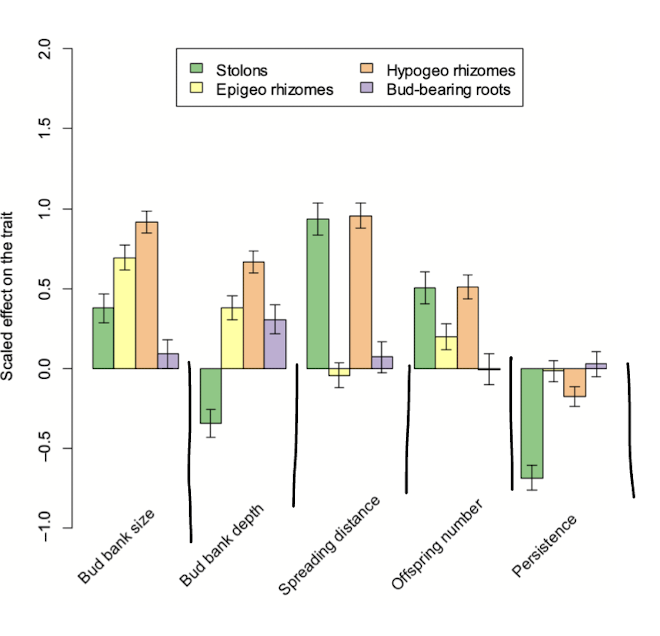
bud bank comparisons
comparisons of the four types of bud banks relative to control plants (no clonal growth)
compares various factors such as bud bank size, bud bank depth, spreading distances, offspring number and persistence
ex plants with stolons or rhizomes have larger spreading distance but lower depth
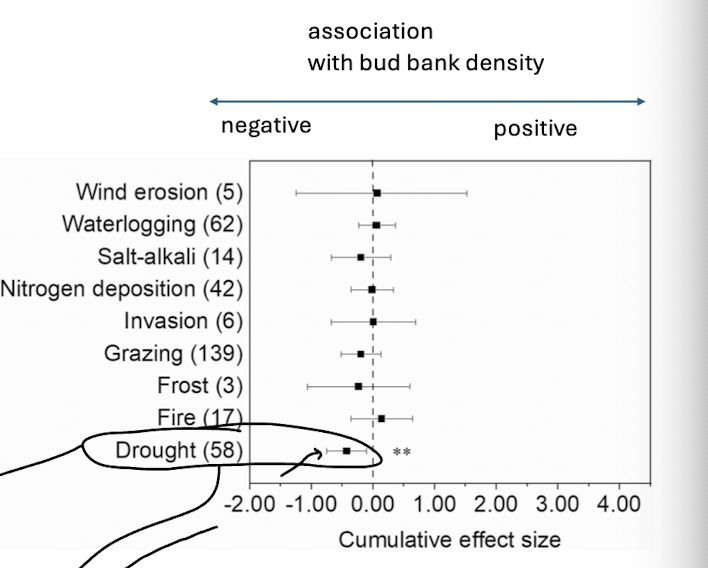
disturbance association with bud bank density
positive association is predicted, but meta analysis showed otherwise
no significant results, except a negative…
consider resource allocation, what is more costly under periods of stress - survival not reproduction, or perhaps regeneration rather than supporting buds
missing water availability and bud bank density controlled…
diaspore
dispersal unit consisting of seed, plus tissue to aid dispersal
ex pappus in dandelion and fruit flesh in strawberry
cypselae
exterior shell containing a seed
as seen in sunflower seed, dandelion
barochory
dispersal via gravity
for example acorns and heavy seeds are intended to fall on the ground, since they are heavy they are not expected to travel via wind
ballochory
ejection of seeds post desiccation
for ex caragana will violently eject seeds
hydrochory
disperse in water
ex coconuts
anemochory
dispersal via wind, various divergent tissues to aid
for ex dandelion seeds with the pappus
or maple seeds with helicopter like samara
endozoochory
seeds dispersed through animal ingestion often have fleshy attachments
or in grasslands the leaf is the “fruit”
epizoochory
seeds disperse by adherence to animals
ex fur, clothes
ex burdock
seed dispersal information
reduces spread of undesired plants - noxious weeds, introduced species
raise awareness about invasive species
ex boot brush station
seed dispersal vectors
air, wind, insects, animals, water, cars, boats, trailers, socks, mud, shoes
can be passively transported or actively
seed retention in human clothes
studied how types of fabric impact seed retention in different species
reflections of adaptations to attach to furs, etc
then compared fate after washing (under different conditions) and germination stayed possible
interesting case study
importance of seed dispersal
potential to obtain new resources
escape from competition, predation and disease
connections of populations via gene flow
problems of studying seed dispersal
seeds are very small, detachment and dispersal are fast processes (hard to track), can be long distance (logistical issues)
methods of seed tracking approaches
emphasis can either be on dispersal or arrival in different places
seed inventory sample selection
seed trap - wind or gravity, animal dung - animal vectors, soil core, fur shearing, sticky traps (problems with insects), vacuuming, washing, picking up
methods of seed species identification
seedling emergence - on top of sterilized soil, but potential of other seeds, or missing strict growth requirements
extraction and visual ID - microscope, but can be too small, hard to ID or visual similarities
genetic methods - DNA, in early stages of practice
different methods come up with different species richness…
experiment methods of seed dispersal
feeding seeds to animals - analyze content, viability
attachment to fur or clothes, case study example
release and tracking, wind tunnel, etc
seed bank
a collection of seeds in natural or artificial settings - soil, aquatic, aerial (ex birds nest) or canopy (ex in pine trees)
importance of soil seed bank
increases resilience of plant communities to disturbance, shapes population dynamics - esp in annuals, important consideration in ecological restoration
influences weed emergence in crop settings
and helps identify historic vegetation composition, potential for re-establishment
seed banks and restoration
passive ex - soil in crop land holds the seeds of previous plant community, viability may decrease over time but holds onto the memory
active would be introducing new seeds into the soil, ex viability has decreased so much
seed bank global storage
preservation of seeds of important plants to safeguard diversity and future food supply
focusses on diversity of crop and culturally important plants
ex Svalbard Global Seed Vault
why might tundra have lower seed density in seed bank?
most of the year it is too cold for soil penetration, fewer resources to seed development, less biotic dispersal vectors, shorter growing seasons
potentially more vegetative reproduction or perennials rather than annuals producing many seeds
larger seed types, and also shallower soils so less in comparison no matter what
why might tropical forests have lower seed density in seed bank?
no constraints in weather/water and no seasonality means there is few niches for competition
mold and pathogens, seeds are shorter lived, decomp is higher
less stored..
transient seed bank
survival time is up to one year, lack of long term seed dormancy
rapid germination under favourable conditions
short term storage of seeds
continuous turnover of seed composition
persistent seed bank - long term
seed dormancy
prevention of germination during unfavourable conditions - seasonal climates, specific conditions required ex fire in serotinuous cones
long term storage of seeds
bed hedging strategy - increased fitness in stressful conditions
slow turnover of seed composition
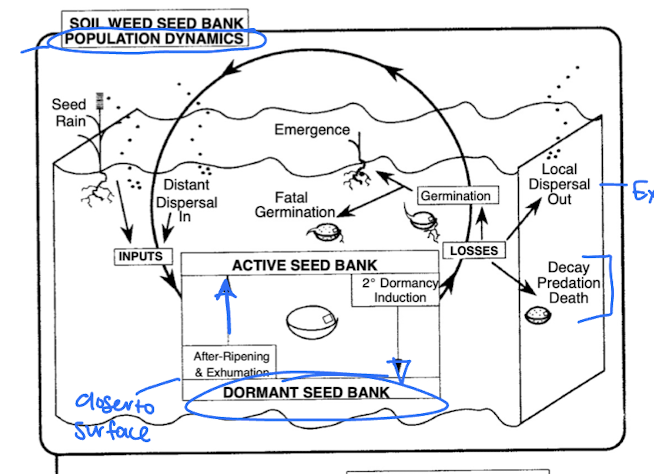
population dynamics and fate in seed banks
inputs from various factors, active and dormant seed banks, ripening ebtween, losses due to decay or predation, germination or dispersal out
fatal germination or emergence and cycle continues