Topic 1 AQA A Level
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
77 Terms
What is a monomer / 1
Smaller, repeating unit from which polymers are made
Give 2 features of DNA and explain why each one is important in semi conservative replication of DNA/2
"1. Weak easily broken H bonds allowing strands to separate 2. Two strands so can both act as template 3. Complementary base pairing allows accurate replication"
Describe how a peptide bond is formed between 2 amino acids to form a dipeptide/2
Condensation reaction (loss of water) ; between amine and carboxyl
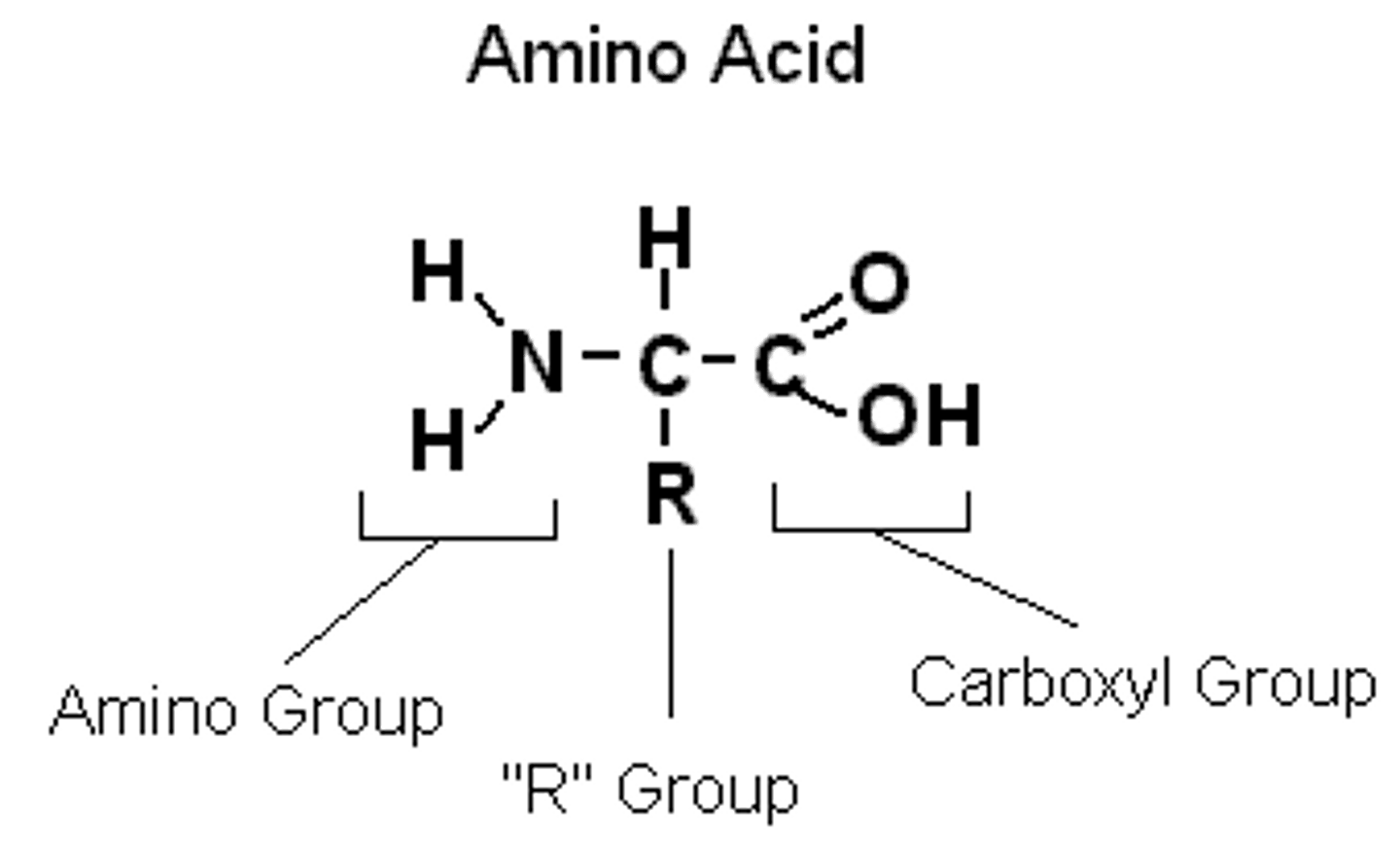
Draw the general structure of an amino acid/2
Amine group; carboxyl group; central carbon with H and R group
Name the bond found between 2 DNA nucleotides in a single strand
Phosphodiester
Describe the function of DNA helicase/1
Breaking H bonds between DNA strands
Describe the function of DNA polymerase/1
Joins adjacent nucleotides with phosphodiester bonds
Contrast ATP and a DNA nucleotide/3
ATP has ribose and DNA nucleotide has deoxyribose; ATP has 3 phosphats and DNA one; ATP base is always adenine and DNA nucleotide base can vary
Describe two differences between the structure of a cellulose and glycogen molecule / 2
1. Cellulose is made up of beta glucose and glycogen of alpha glucose. 2. Cellulose molecule has straight chain and glycogen is branched. 3. Cellulose molecule has straight chain and glycogen is coiled 4. Glycogen has 1,4 and 1,6 glycosidic bonds and cellulose has only 1,4 glycosidic bonds
Describe and explain two features of starch that make it a good storage molecule/2
1. Insoluble so doesn't affect water potential. 2. Branched/coiled so makes molecule compact. 3. Polymer of alpha glucose so provides glucose for respiration. 4. Branched so more ends for fast enzyme action. 5. Large so cannot cross cell membrane
Give the two types of molecule from which a ribosome is made / 2
Ribosomal RNA ; polypeptide/protein
Describe the role of a ribosome in the production of a polypeptide. (not include transcription in answer)/3
1. mRNA binds to ribosome. 2 two codon binding sites. 3. Allows tRNA with anticodons to bind. 4. Formation of peptide bond between amino acids (held by tRNA molecules. 5. Moves along mRNA to the next codon.
In eukaryotes why might the base sequence of mRNA be different from pre mRNA? /2
1. Introns in pre mRNA. 2. Removal of sections of pre mRNA / splicing
Describe the structure of glycogen /2
1. Polysaccharide/polymer of alpha glucose 2. Glycosidic bonds / branched structure
Name 2 enzymes involved in the semi conservative replication of DNA / 2
(DNA) helicase and (DNA) polymerase
Explain the meaning of a) degenerate b) overlapping with regards to the genetic code /2
a) more than one triplet for each amino acid b) each base is part of only one triplet
Give 2 properties of water that are important in the cytoplasm of cells/4
1. Polar molecule; acts as a universal solvent. 2. Solvent; reactions occur faster in solution. 3. Reactive; takes place in hydrolysis/condensation. Marks for property with explanation (need two)
Compare and contrast the process by which water and inorganic ions enter cells / 3
1. Both move down concentration gradient. 2. Both move through protein channels in membranes (aquaporins for water). 3. Ions can move against the concentration gradient by active transport whereas water cannot
Give 2 ways in which the nucleotides of DNA are different to that of RNA/2
1. DNA contains thymine and RNA contains uracil. 2. DNA contains deoxyribose and RNA contains ribose
Explain how the organic bases help to stabilise the structure of DNA/2
H bonds between the base pairs hold two strands together; Many H bonds provides strength
Scientists determined that a sample of DNA contained 18% adenine. What were the % of thymine and guanine in this sample of DNA?
T=18%, G=32%
Two glucose molecules join together to form a disaccharide. Name the products/2
Water and maltose
Name the type of reaction that joins glucose molecules together/1
Condensation
Describe the test you could use to check if food in a diet contained starch / 2
Add iodine / potassium iodide solution; blue-black colour (with starch)
Explain how digestion of starch in the gut leads to an increase in the concentration of glucose in the blood (do not need co-transport details) /3
Hydrolysed by enzymes/amylase/maltase; produces glucose; small enough to cross the gut wall into the blood
Describe the difference between the structure of a triglyceride molecule and the structure of a phospholipid molecule/1
In phospholipid one fatty acid replaced by a phosphate
Describe how you would test for the presence of a lipid in a sample of food/2
Add ethanol, then add water; white emulsion
Describe how a saturated fatty acid is different from an unsaturated fatty acid/1
Saturated single/ no double bonds OR unsaturated as has at least one double bond (between carbons)
Describe how ATP is resynthesised in cells/2
From ADP and phosphate; By ATP synthase; During respiration/photosynthesis
Give two ways in which the hydrolysis of ATP is used in cells/2
To provide energy for other reactions / named process; To add phosphate to other substances and make them more reactive/change their shape
Name the products of the hydrolysis of sucrose/2
Fructose and glucose
Explain how a mutation of a protein receptor gene may lead to a non functional protein receptor/4
Change in DNA base/nucleotide sequence; Change in amino acid sequence; alters position of H/ionic/disulfide bonds; change in 3ry structure of receptor
Trypsin is a protease - name the part of a pancreatic cell that produces the inactive form of trypsin/1
Ribosome/ rough endoplasmic reticulum (ignore RER)
Name the type of bond hydrolysed when the short chain of amino acids is removed/ 1
Peptide bond
Sometimes trypsin can become activated inside a pancreatic cell. A competitive inhibitor then binds to it and stops it working. Explain how a competitive inhibitor stops trypsin working /3
Inhibitor is a similar shape to the substrate; blocks or binds to active site / complementary to active site; substrate cannot bind to active site so fewer ES complexes formed
What term is used to describe the structure of a protein made of two or more polypeptides/1
Quaternary
Alpha polypeptide has 141 amino acids. Calculate the minimum number of DNA bases needed to code for the number of amino acids in one alpha polypeptide/1
423
Maltose is hydrolysed by the enzyme maltase. Explain why maltase catalyses only this reaction/3
Active site has a specific shape/tertiary stucture complementary to substrate/maltose; only maltose can bind/fit; To form E-S complex
Give 2 ways in which the structure of starch is similar to cellulose/2
1. Are polymers/polysaccharides of monomers/monosaccharides 2. Contain glucose/carbon, hydrogen and oxygen 3. Contain glycosidic bonds. 4. Have 1-4 links. 5. H bonding wihtin structure
Give 2 ways in which the structure of starch is different from cellulose/2
1. Starch contains alpha glucose - cellulose beta. 2. Starch helical/coiled/compact/branched not straight 3. 1,6 bonds whereas cellulose does not. 4. Glucoses same way up. 5. No H bonds between molecules. 6. No microfibrils
Describe the role of DNA polymerase in DNA replication / 1
Joins nucleotides to form a new strand
Other than being smaller, give 2 ways in which prokaryotic DNA is different from eukaryotic DNA/2
1. Circular/non linear 2, Not associated with proteins/histones 3. No introns/ no non coding DNA
An enzyme catalyses only one reaction. Explain why / 2
Enzyme has active site; only subsrate fits
Name the monosaccharides from which the following are composed: a) sucrose b) lactose /2
a) fructose and glucose b) glucose and galactose
Give one feature of starch and explain how this feature enables it to act as a storage substance / 2
One of 1. Coiled so compact / can fit in small space 2. Insoluble so no osmotic effect/ does not affect water potential. 3. Large molecule/long chain so does not leave cell. 4 Branched chains so easy to remove glucose
Two ways in which the structure of cellulose is different from the structure of starch/ 2
1. Starch 1-4 and 1-6 bonds but cellulose 1,4 bond only. 2. Starch all gluclose same way up, cellulose alternate glucose upside down. 3. Starch helix/coiled/compact. Cellulose straight. 4. Starch alpha glucose, cellulose beta glucose. 5. No microfibrils, cellulose has them
Explain one way in which the structure of cellulose is linked to its function/2
H bonds / microfibrils; provide strength/rigidity
Describe how you could use the emulsion test to show that a seed contains lipids/3
Crush/grind; with ethanol; then add water; forms emulsion/goes white/cloudy
The structure of a phospholipid molecules is different from that of a triglyceride. Describe how a phospholipid is different/2
Phosphate; instead of one of the fatty acids
What is an unsaturated fatty acid?/2
Double bonds; between carbon
Describe how you could use the biuret test to distinguish a solution of the enzyme, lactase from a solution of lactose./1
Add Biuret reagent to both solutions (no mark) Lactase will give purple / lactose will remain blue
Starch was present in the cells of potato tissue. Describe how the student could find out where in the cells the starch was present/ 2
Add iodine/ stain to the slide; blue-black
Sucrase is an enzyme. It hydrolyses sucrose during digestion. Name the products of this reaction/2
Fructose and glucose
Sucrase does not hydrolyse lactose. Use your knowledge of the way in which enzymes work to explain why/2
Lactose has a different shape/structure; does not fit/bind to active site of enzyme OR active site of enzyme has a speciic shape.
A protein molecule contains 151 amino acids. What is the total number of peptide bonds in this molecule?/1
150
A sample of xanthine oxidase was tested by mixing with biuret reagent. Describe and explain the result of this test./2
Lilac / purple / mauve / violet; Xanthine oxidase is a protein;
Explain why an enyzyme is able to catalyse one reaction but it is not able to catalyse other reactions./2
Substrate has specific shape; Allows binding / fitting / forms ES complex with active site; OR active site has specific shape; allows binding to form ES complex with substrante
Explain how a decrease in temperature decreases the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction./2
"molecules moving less / slower; reduces chance of collision (between enzyme and substrate) / of enzyme-substrate complexes being formed"
Urea breaks hydrogen bonds. Explain how the addition of urea would affect the rate of an enzyme-controlled reaction./3
1. these bonds hold / maintain tertiary / globular structure (of enzyme); 2. enzyme denatured / tertiary structures destroyed; 3. (shape of) active site distorted / changes; 4. substrate no longer fits / enzyme-substrate complex not formed;
Explain how a non competitive inhibitor would decrease the rate of reaction catalysed by an enzyme/3
1. idea that non-competitive inhibitor(C) binds at a site not the active site; 2. binding causes a change in the shape of the active site; 3. substrate is no longer able to bind to the active site;
Name the bonds that join amino acids in the primary structure./1
Peptide bonds
Explain why the replication of DNA is described as semi-conservative/2
each strand copied / acts as a template; (daughter) DNA one new strand and one original / parent strand;
Name the monomer present in cellulose/1
Beta glucose
Name the type of reaction that converts cellulose to its monomers/1
Hydrolysis
Cotton is a plant fibre used to make cloth. Explain how cellulose gives cotton its strength/3
1. straight / unbranched chains; 2. (idea of more than 1) chains lie side by side / form (micro)fibrils; 3. idea of H bonds holding chains together;
Explain how a change in the primary structure of a globular protein may result in a different three-dimensional structure./3
1. sequence of amino acids changes; 2. tertiary structure changes / folds in a different way; 3. bonds form in different places
Explain how DNA replicates./4
1. hydrogen bonds broken; 2. semi-conservative replication / both strands used (as templates); 3. nucleotides line up complementary / specific base pairing / A and T / C and G; 4. DNA polymerase;
Explain why a mutation involving the deletion of a base may have a greater effect than one involving substitution of one base for another./3
1. deletion causes frame shift / alters base sequence (from point of mutation); 2. changes many amino acids / sequence of amino acids (from this point); 3. substitution alters one codon / triplet / one amino acid altered / code degenerate / same amino acid coded for;
How are the two strands of the DNA molecule held together?/1
Hydrogen bonds
Give one advantage of DNA molecules having two strands./1
Stability/ protects bases/replication
The sequence of bases on one strand of DNA is important for protein synthesis. What is its role?/1
determines (sequence of) amino acids / specific protein produced / mRNA formation;
Describe how a saturated fatty acid differs in molecular structure from an unsaturated fatty acid./2
1. absence of a double bond; in the (hydrocarbon) chain; 2. unable to accept more hydrogen / saturated with hydrogen
Explain how the shape of an enzyme molecule is related to its function./3
1. specific 3D tertiary structure / shape; 2. substrate complementary shape; 3. (reject same shape) substrate (can bind) to active site / can fit into each active site;
Bacteria produce enzymes which cause food to decay. Explain how vinegar, which is acidic, can prevent the action of bacterial enzymes in some preserved foods/3
1. (bacterial) active site / enzymes / proteins denatured / tertiary 3D structure disrupted / changed; 2. (ionic) bonds broken (reject peptide bonds) 3. no enzyme substrate complex formed / substrate no longer fits
A sample of DNA was analysed. 28% of the nucleotides contained thymine. Calculate the percentage of nucleotides which contained cytosine
22%
What is an enzyme?/2
1. Protein 2. catalyst 3.lowers activation energy
Describe how in DNA replication, after the parent DNA strand is separated how the second strand of DNA is formed. /3
1. Semi-conservative replication; 2. Complementary pairing; 3. Hydrogen bonding (of bases/nucleotides); 4. Condensation/described of nucleotides; 5. DNA polymerase involved