ESS - Topic 3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biodiversity and Conservation
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
1
New cards
environmental pressures
the factors (abiotic or biotic) in an ecosystem which put pressure on an organism's survival and increase competition (whether inter-species or intra-species)
2
New cards
biodiversity
a combination of the species diversity, genetic diversity and habitat diversity of an ecosystem
3
New cards
variation
the differences, either physical or genetic, between individuals of a species
4
New cards
simpson's diversity index
a measure of diversity between similar ecosystems
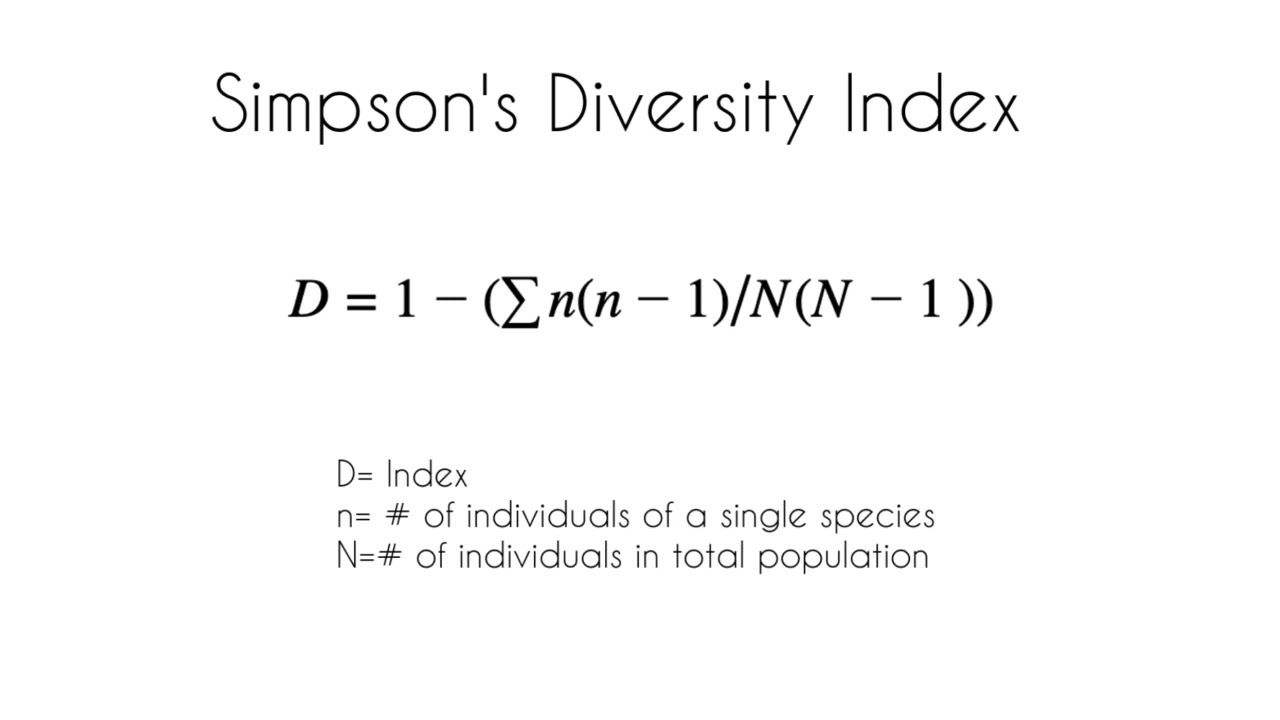
5
New cards
species diversity
the number of species (richness) and their relative proportions (evenness) in a community
6
New cards
genetic diversity
the range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species
7
New cards
random genetic mutations
the small differences which may occur in an organism as a result of reproduction - these small changes may add up to create variation
8
New cards
hotspots
an area of high biodiversity (which is under threat from human activities)
9
New cards
endemic species
the species which only occur in one specific area
10
New cards
speciation
the gradual change in populations of a species over time - often caused by geographical isolations, resulting in new species
11
New cards
evolution
the process by which a species may adapt to environmental pressures through natural selection of favourable variation - caused by random genetic mutations - over thousands of generations
12
New cards
natural selection
survival of the fittest - only the best suited organisms will be able to compete (due to environmental pressures) and so survive long enough to reproduce - their favourable traits are then passed on to new generations
13
New cards
geographical isolation
the separation of populations of a single species - often leads to speciation if populations cannot interbreed for a very long time
14
New cards
physical barriers
e.g. a mountain, ocean or separation of lakes
15
New cards
land bridges
a connection between land masses - often as a result of lowering sea levels e.g. the Bering Straits
16
New cards
continental drift
the movement of the tectonic plates by around 1cm a year causing the change in shape and location of continents
17
New cards
lithosphere
the Earth's crust - the rocky part of Earth
18
New cards
Gondwana
the land mass made up of Africa, New Zealand, Australia and South America, India, Arabia and Antarctica millions of years ago - separated millions of years ago
19
New cards
background extinction rate
the natural rate of extinction of species - around 1 species per million species per year
20
New cards
extinction
the complete loss of a species from Earth - no more individuals of that species exist
21
New cards
mass extinctions
an extinction rate far greater than background extinction rate
22
New cards
Holocene extinction event
the 6th mass extinction occurring for the last 10,000 years, however, much faster in the last 100 years - generally agreed to be as a result of human activity
23
New cards
weedy species
the species (generally plant or animal) which are able to survive the environments we create e.g. urban rats, domesticated animals
24
New cards
Living Planet Report
a report produced by the Worldwide Fund for Nature (WWF) creates on the state of the world's ecosystems
25
New cards
conservation
the act of preserving nature - attempting to save habitats, species and biodiversity in general
26
New cards
2/3
the proportion of living species which are found in tropical rainforests
27
New cards
current extinction rates
approx. 100 species per million species per year
28
New cards
ecosystem complexity
creates stability and resilience to change in an ecosystem - there are many pathways for energy flow
29
New cards
limiting factors
environmental conditions that limit the growth, abundance, or distribution of an organism or a population of organisms in an ecosystem - when there are few of these, biodiversity is likely to be high (and vice versa)
30
New cards
inertia
the ability of an ecosystem to resist change (maintain equilibrium) when subjected to a disruptive force
31
New cards
natural hazards
naturally occurring events which may have a negative impact on the environment e.g. eruption of Mount St Helens in 1980, the 2004 SEA earthquake and subsequent tsunami
32
New cards
habitat loss
the major cause of loss of biodiversity
33
New cards
habitat fragmentation
when a large area of habitat is broken into many smaller areas, often physically divided by roads, towns, factories, power lines etc - leads to the loss of biodiversity
34
New cards
overexploitation
the overuse of a resource to the point that is has a negative impact on the ecosystem e.g. deforestation
35
New cards
introduction of non-native species
when a species which is not naturally occurring in an ecosystem is introduced and may out-compete the native species - this may lead to a loss of biodiversity e.g. rabbits, cane toads, red foxes, camels in Australia
36
New cards
lungs of the Earth
rainforests - they are called this because they are thought to produce around 40% of the oxygen that animals breath
37
New cards
narrow geographical range
a small area that a species inhabits - makes a species prone to extinction
38
New cards
low genetic diversity
caused by small populations or declining diversity - makes a species prone to extinction as they may not be able to adapt to change
39
New cards
low population density
some species need a large area to hunt - if there are only a few organisms over a large territory this may make them prone to extinction, especially if habitats become fragmented
40
New cards
large body
due to the 10% rule, it is much more difficult for big organisms to find enough food - this makes them prone to extinction e.g. wolves, tigers
41
New cards
low reproductive potential
reproducing slowly and/or infrequently - this makes a species prone to extinction as it may take a long time for a population to recover its numbers
42
New cards
seasonal migration
the movement between different areas at different seasons - this makes a species prone to extinction as they rely on more than one habitat - if one is destroyed, they will not survive
43
New cards
poor dispersers
a species which cannot move easily to new habitats - this makes them prone to extinction - for example plants which rely on a slow dispersal of seeds, flightless birds of New Zealand
44
New cards
specialised feeders
a species which requires a specific food and cannot eat others e.g. giant pandas eat bamboo shoots, koalas eat eucalyptus leaves - this makes them prone to extinction if their food source becomes scarse
45
New cards
minimum viable population size
the lowest number of individuals of a species needed for a population to be able to recover - if a population is lower than this number, they may become extinct
46
New cards
IUCN
The International Union for the Conservation of Nature and Natural resources - often known as the World Conservation Union
made up of government agencies, states, non-governmental organisations (NGOs) and scientists and experts - their goal is to conserve nature and increase sustainability of resource use
made up of government agencies, states, non-governmental organisations (NGOs) and scientists and experts - their goal is to conserve nature and increase sustainability of resource use
47
New cards
IUCN Red List
the conservation status of species based on: population size, degree of specialisation, distribution, reproductive potential, geographic distribution and fragmentation, habitat quality, trophic level and therefore, the probability of extinction
48
New cards
extinct (EX)
IUCN Red List Status - no reasonable doubt that the last of a species has died
49
New cards
extinct in the wild (EW)
IUCN Red List Status - a species is known only to survive in cultivation, captivity or outside of its past range
50
New cards
critically endangered (CR)
IUCN Red List Status - at extreme risk of extinction in the wild
51
New cards
endangered (EN)
IUCN Red List Status - facing a very high risk of extinction in the wild
52
New cards
vulnerable (VU)
IUCN Red List Status - facing a high risk of extinction in the wild
53
New cards
near threatened (NT)
IUCN Red List Status - likely to qualify as vulnerable or endangered in the near future (but does not yet)
54
New cards
least concern (LC)
IUCN Red List Status - widespread and abundant
55
New cards
data deficient (DD)
IUCN Red List Status - when there is insufficient data to determine a species' status
56
New cards
not evaluated (NE)
IUCN Red List Status - when a species has not been evaluated against the criteria
57
New cards
UN
United Nations
58
New cards
UNEP
United Nations Environmental Program
59
New cards
CITES
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
60
New cards
UNDP
United Nations Development Program
61
New cards
WWF
Worldwide Fund for Nature
62
New cards
WRI
World Resource Institute