biology - human nutrition (digestive system)
1/3
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
4 Terms
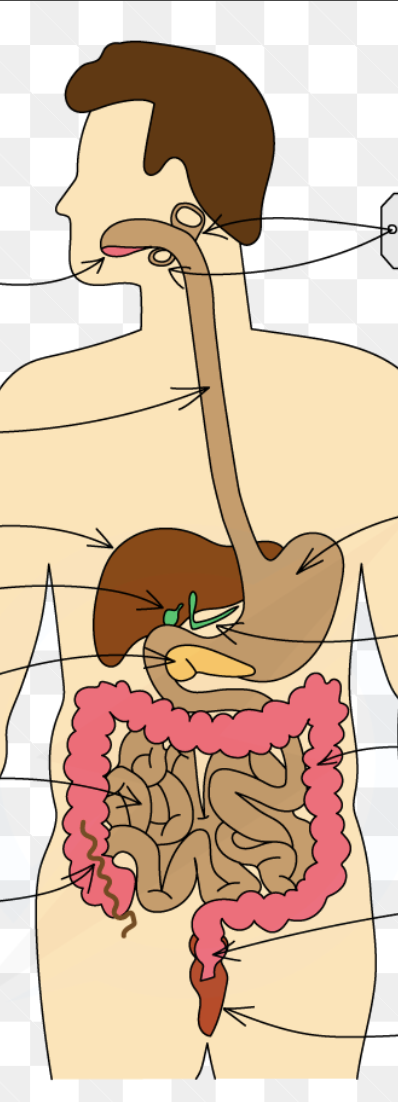
Identify in diagrams and images the main organs of the digestive system
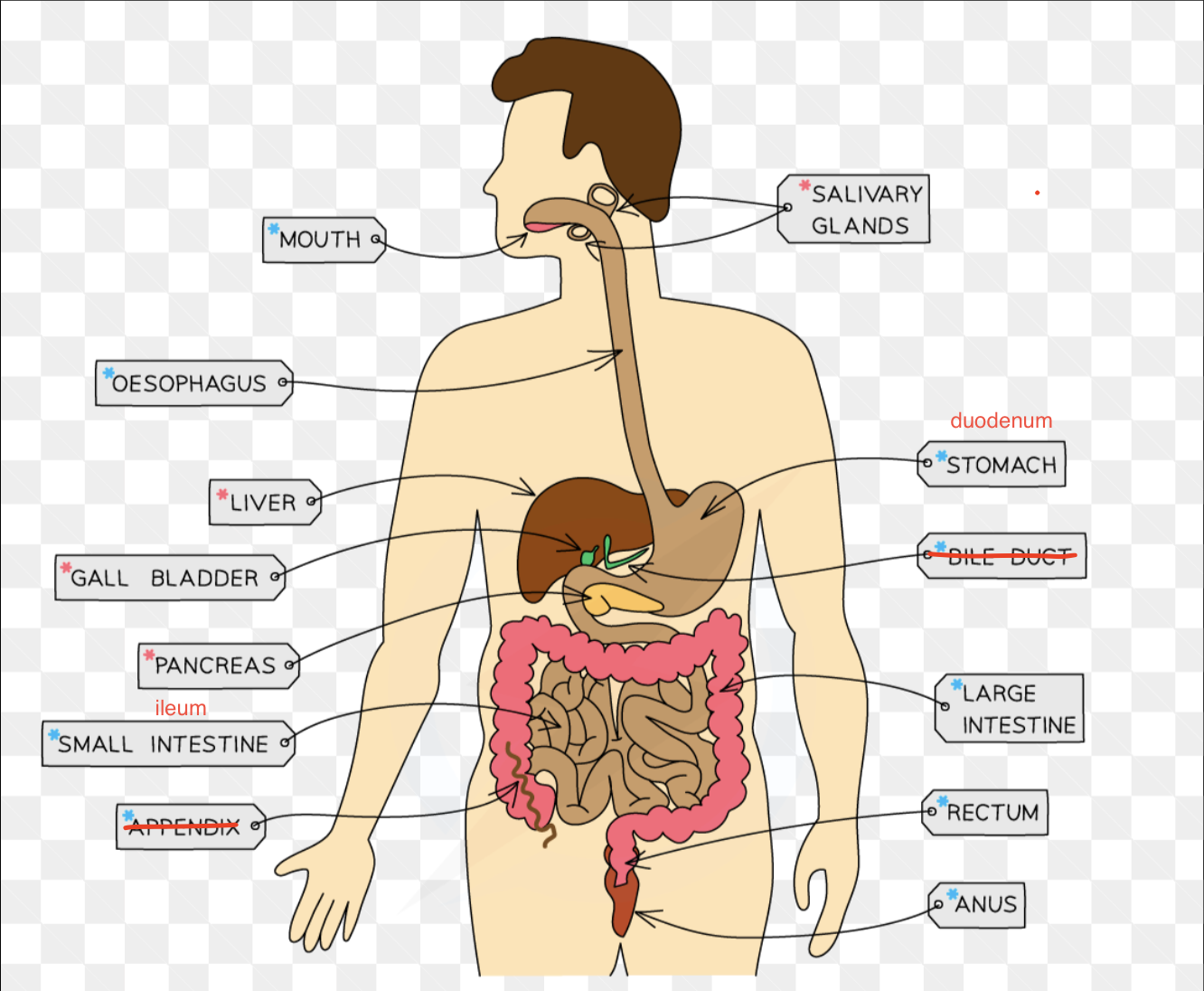
Describe the functions of the organs of the digestive system
ingestion – the taking of substances, e.g. food and drink, into the body
teeth: physically break down food and increases surface area so it’s easier for enzymes to break it down
salivary glands: release saliva which contains amylase and digests starch into maltose
oesophagus: contractions of the walls of the oesophagus force the food downwards; this is peristalsis
digestion – the breakdown of food
stomach: contracts muscular walls, protease enzymes break down proteins into amino acids, and hydrochloric acid is produced which kills bacteria
pancreas: amylase, protease and lipase enzymes are produced
liver: bile is produced
gallbladder: releases bile into the small intestine (neutralises acid from stomach and emulsifies lipids)
absorption – the movement of nutrients from the intestines into the blood
small intestines: acidic stomach contents are neutralised by bile, and it is covered in villi which have a huge surface area for diffusion and have a single layer of surface cells
assimilation – uptake and use of nutrients by cells
large intestine: absorbs most of excess water, solid left forms faeces
rectum: faeces are stored here
egestion – the removal of undigested food from the body as faeces
anus: faeces leave the body
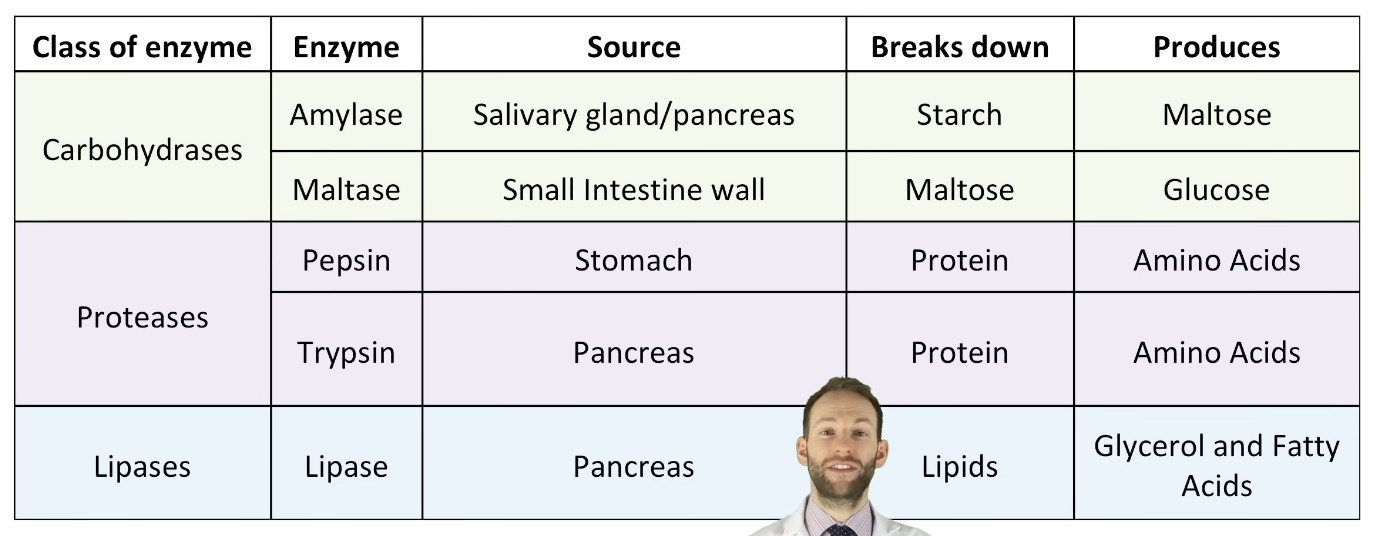
Classes of enzymes
investigating energy content in food (practical)
weigh food sample
place 20cm³ of water in a boiling tube
measure temp of water
light food and hold under boiling tube
continue until it no longer burns
stir water and measure final temp
