Chapter 14
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
In cattle, roan coat color (mixed red and white hairs) occurs in the heterozygous (Rr) offspring of red (RR) and white (rr) homozygotes. Which of the following crosses would produce offspring in the ratio of 1 red:2 roan:1 white?
roan × roan
A black guinea pig crossed with an albino guinea pig produced twelve black offspring. When the albino was crossed with a second black animal, six blacks and six albinos were obtained. What is the best explanation for this genetic situation?
Albino is recessive; black is dominant.
Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio for a particular trait. This ratio suggests that ________.
the parents were both heterozygous for the particular trait
Mendel studies seven different traits in the garden pea. What genetic term is used to describe an observable trait, such as those studied by Mendel?
phenotype
In certain plants, tall is dominant to short. If a heterozygous plant is crossed with a homozygous tall plant, what is the probability that the offspring will be short?
0
In cats, black fur color is caused by an X-linked allele; the other allele at this locus causes orange color. The heterozygote is tortoiseshell. What kinds of offspring would you expect from the cross of a black female and an orange male?
tortoiseshell females; black males
In humans, male-pattern baldness may be assumed to be controlled by an autosomal gene that occurs in two allelic forms. Allele B determines nonbaldness, and allele b determines pattern baldness. In males, because of the presence of testosterone, allele b is dominant over B. If a man and woman both with genotype Bb have a son, what is the chance that he will eventually be bald?
75 percent
The individual with genotype AaBbCCDdEE can make many kinds of gametes. Which of the following is the major reason?
different possible assortment of chromosomes into gametes
When Thomas Hunt Morgan crossed his red-eyed F1 generation flies to each other, the F2 generation included both red- and white-eyed flies. Remarkably, all the white-eyed flies were male. What was the explanation for this result?
The gene involved is on the X chromosome.
Suppose two AaBbCc individuals are mated. Assuming that the genes are NOT linked, what fraction of the offspring are expected to be homozygous recessive for the three traits?
1/64
In the cross AaBbCc × AaBbCc, what is the probability of producing the genotype AABBCC?
1/64
In humans, blue eyes are inherited as a recessive autosomal trait and color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A woman with blue eyes and normal color vision whose father was color-blind marries a man who also has normal color vision. He has brown eyes, but his mother had blue eyes. Which of the following would you expect to be TRUE for their sons?
One-fourth of their sons will be color-blind and have blue eyes, one-fourth of their sons will be color-blind and have brown eyes, one-fourth of their sons will have normal color vision and blue eyes, one-fourth of their sons will have normal color vision and brown eyes.
Radish flowers may be red, purple, or white. A cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant yields all-purple offspring. The part of the radish we eat may be oval or long, with long being the dominant trait. If true-breeding red long radishes are crossed with true-breeding white oval radishes, the F1 will be expected to be which of the following?
purple and long
A man has extra digits (six fingers on each hand and six toes on each foot). His wife and their daughter have a normal number of digits. Having extra digits is a dominant trait. The couple's second child has extra digits. What is the probability that their next (third) child will have extra digits?
1/2
Assuming independent assortment for all gene pairs, what is the probability that the following parents, AABbCc × AaBbCc, will produce an AaBbCc offspring?
1/8
Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F1 individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and location assort independently. Among the F2 offspring of a dihybrid cross, what is the probability of plants with white axial flowers?
3/16
Albinism is an autosomal (not sex-linked) recessive trait. A man and woman are both of normal pigmentation, but both have one parent who is albino (without melanin pigmentation). What is the probability that their first child will be an albino?
1/4
Which of the following is an example of polygenic inheritance?
skin pigmentation in humans
Use the figure and the following description to answer the question(s) below.
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D. Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A true-breeding, dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted outcome of the F2 is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square.
D d
D 1 2
d 3 4
Which of the boxes marked 1—4 correspond to plants with a HETEROZYGOUS genotype?
2 and 3
Mendel crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants and then allowed the offspring to self-pollinate to produce an F2 generation. The results were as follows: 6022 yellow and 2001 green (8023 total). The allele for green seeds has what relationship to the allele for yellow seeds?
recessive
The work of Gregor Mendel provided an answer to two prevailing hypotheses popular at the time. What were these two hypotheses?
The two major hypotheses of the time were blending inheritance and inheritance of acquired characteristics.
In tigers, a recessive allele causes a white tiger (absence of fur pigmentation). If one phenotypically normal tiger that is heterozygous is mated to another that is phenotypically white, what percentage of their offspring is expected to be white?
50 percent
Different ratios occur in crosses with single gene pairs or two gene pairs. What types of ratios are likely to occur in crosses dealing with a single gene pair?
3:1, 1:1, 1:2:1
In humans, blue eyes are inherited as a recessive autosomal trait and color blindness is an X-linked recessive trait. A woman with blue eyes and normal color vision whose father was color-blind marries a man who also has normal color vision. He has brown eyes but his mother had blue eyes. Which of the following would you expect to be TRUE for their daughters?
One-half of their daughters will have normal color vision and brown eyes; one-half of their daughters will have normal color vision and blue eyes.
When Mendel crossed yellow-seeded and green-seeded pea plants, all the offspring were yellow seeded. When he took these F1 yellow-seeded plants and crossed them to green-seeded plants, what genotypic ratio was expected?
1:1
Two true-breeding stocks of pea plants are crossed. One parent has red, axial flowers and the other has white, terminal flowers; all F1 individuals have red, axial flowers. The genes for flower color and location assort independently. If 1000 F2 offspring resulted from a dihybrid cross, approximately how many of them would you expect to have red, terminal flowers?
190
What do we mean when we use the terms "monohybrid cross" and "dihybrid cross"?
A dihybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for two characters that are being studied, and a monohybrid cross involves organisms that are heterozygous for only one character being studied.
Gray seed color in peas is dominant to white. Assume that Mendel conducted a series of experiments where plants with gray seeds were crossed among themselves, and the following progeny were produced: 302 gray and 98 white.(a) What is the most probable genotype of each parent?(b) Based on your answer in (a) above, what genotypic and phenotypic ratios are expected in these progeny? (Assume the following symbols: G = gray and g = white.)
a) Gg × Gg; (b) genotypic = 1:2:1, phenotypic = 3:1
Albinism is an autosomal (not sex-linked) recessive trait. A man and woman are both of normal pigmentation and have one child out of three who is albino (without melanin pigmentation). What are the genotypes of the albino's parents?
Both parents must be heterozygous.
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is a serious condition caused by a recessive allele of a gene on the human X chromosome. The patients have muscles that weaken over time because they have absent or decreased dystrophin, a muscle protein. They rarely live past their twenties. How likely is it for a woman to have this condition?
One-half of the daughters of an affected father and a carrier mother could have this condition.
Cinnabar eyes is a sex-linked, recessive characteristic in fruit flies. If a female having cinnabar eyes is crossed with a wild-type male, what percentage of the F1 males will have cinnabar eyes?
100 percent
Use the figure and the following description to answer the question(s) below.
In a particular plant, leaf color is controlled by gene locus D. Plants with at least one allele D have dark green leaves, and plants with the homozygous recessive dd genotype have light green leaves. A true-breeding, dark-leaved plant is crossed with a light-leaved one, and the F1 offspring is allowed to self-pollinate. The predicted outcome of the F2 is diagrammed in the Punnett square shown in the figure, where 1, 2, 3, and 4 represent the genotypes corresponding to each box within the square.
D d
D 1 2
d 3 4
Which of the boxes marked 1—4 correspond to plants that will be true-breeding?
1 and 4 only
When crossing an organism that is homozygous recessive for a single trait with a heterozygote, what is the chance of producing an offspring with the homozygous recessive phenotype?
50 percent
Hutchinson—Gilford progeria is an exceedingly rare human genetic disorder in which there is very early senility and death, usually from coronary artery disease, at an average age of 13 years. Patients, who look very old even as children, do not live to reproduce. Which of the following represents the most likely assumption?
The disorder may be due to mutation in a single protein-coding gene.
Which of the following describes the ability of a single allele to have multiple phenotypic effects?
pleiotropy
Two plants are crossed, resulting in offspring with a 3:1 ratio for a particular trait. This ratio suggests that ________.
the parents were both heterozygous for the particular trait
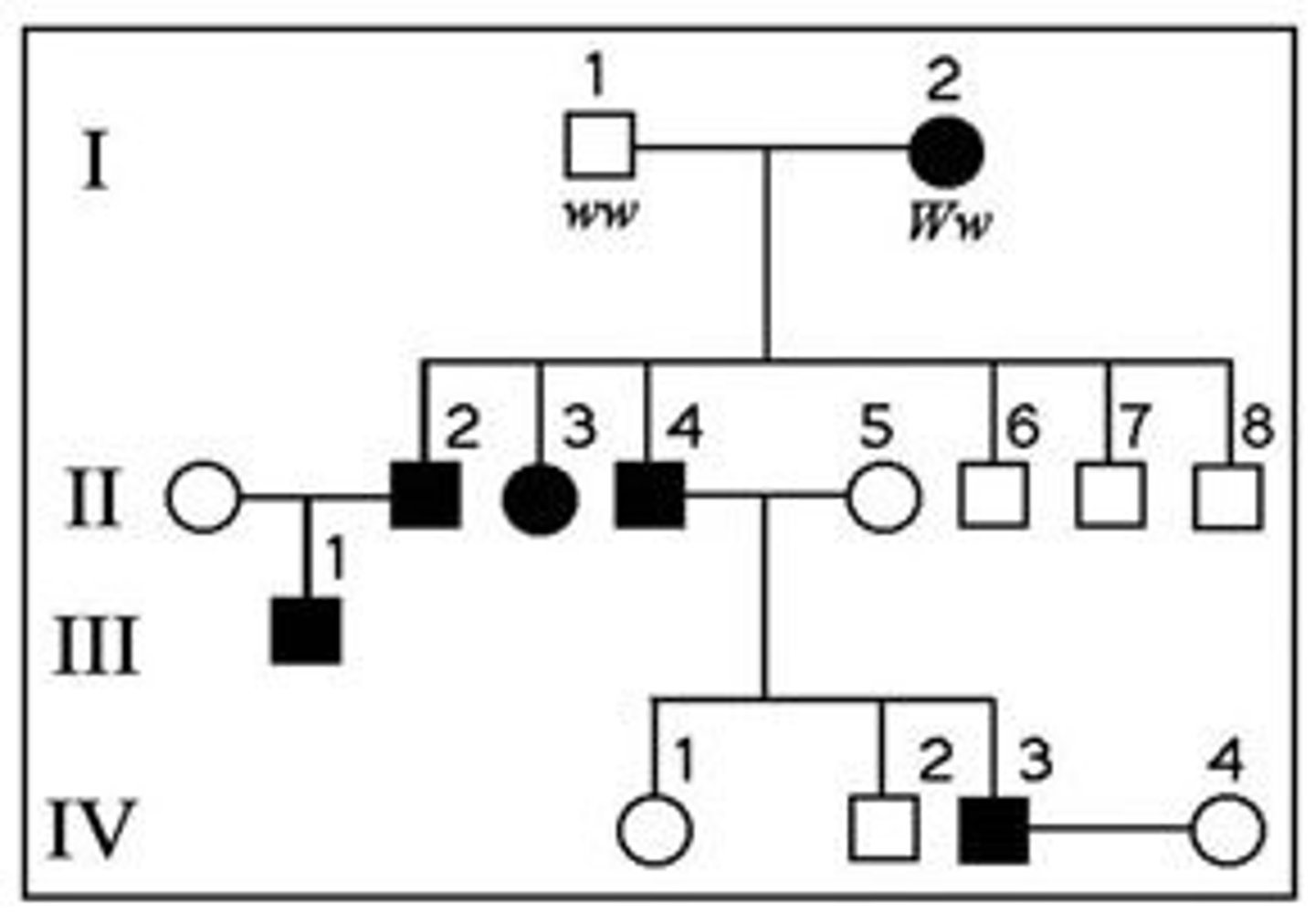
The following question(s) refer to the pedigree chart in the accompanying figure for a family, some of whose members exhibit the dominant trait, W. Affected individuals are indicated by a dark square or circle.
What is the genotype of individual II-5?
ww
Which of the following statements about independent assortment and segregation is correct?
The law of independent assortment requires describing two or more genes relative to one another.
Blending inheritance
The blending of parental traits that leads to offsprings inheriting an intermediate of them
Inheritance of acquired traits
A crucial, and incorrect, aspect of Lamarck's theory of evolution. Lamarck believed that the traits a parent acquired during its lifetime would be passed on to its offspring. (Lamarck's theory)
Polymorphic
A trait that appears in more than one form
Pure lines
Production of identical offspring due to self-fertilization
Hybrids
Mating of two pure lines that differed in one or more traits
Monohybrid cross
Mating parents with 2 different phenotypes for a single trait
Reciprocal cross
A cross done to determine whether sex is a factor in determining the traits inherited by the offspring
Particulate inheritance
Traits do not blend or change through use, & instead, are unchanging units
Autosomal inheritance
The patterns of inheritance of any genes not on sex chromosomes
Test cross
A cross of a homozygous recessive individual and an individual with the dominant phenotype but unknown genotype
Principle of segregation
Alleles are separated into reproductive cells
Dihybrid crosses
Mating between two parents that are both heterozygous
Independent assortment
Alleles of different genes are transmitted independently of each other
Dependent assortment
The transmission of one allele depends on the transmission of the other
Chromosome theory of inheritance
The physical separation of alleles during meiosis 1 that is responsible for Mendel's principle of segregation
Sex linkage
Genes found on sex chromosomes
Sex-linked inheritance
A gene on a sex chromosome that gets inherited
Linkage
The tendency of genes to be inherited together because they are found on the same chromosome
Multiple allelism
More than two alleles of a gene in a population
Codominance
Neither allele is dominant or recessive of the other, instead, heterozygotes display both phenotypes
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygotes display an intermediate phenotype
Pleiotropic
Genes that influence many traits
Autosomal dominant trait
Individuals that are homozygous dominant or heterozygous exhibits the trait
If a trait appears in females as often as it does in males
It is autosomal
If a trait appears in males more than it does in females
The trait is x-linked