Photosynthesis -Kreb Cycle
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
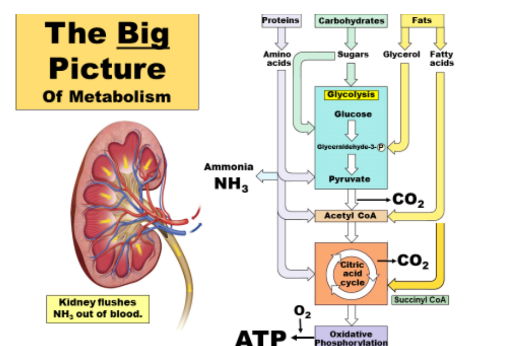
what does it mean if carbon and nitrogen are chemically inert.
That means they are very stable, low-energy molecules.
-It’s hard to get them to react with other chemicals
-t’s hard to transform them into bio-molecules.
-in amino acids, BNA and rDNA basis
how do we make co2 and N2 into useable biochemicals
carbon and nitrogen fixation
Fixation
incorporates C atoms and N atoms into the air so molecules with all cells can use.
why cant Animals fix either C or N for themselves!
They have to rely on plants and bacteria to fix carbon, and on bacteria (and lightning) to fix nitrogen.
How does Carbon Fixation work to get co2 into the air
mainly fixed by photosynthesis, and turned into organic molecules.
How does Nitrogen Fixation work to get N2 into the air
mainly fixed by various bacteria, and turned into molecules of NH3 (ammonia).
Some N2 is also fixed by lightning and turned into nitrogen oxides: NO, NO2, and NO3.
How can nitrogen be used for metabolic pathways.
through the kidney cus it flushes NH3, out of Blood
(Oxygenic) photosynthesis
turns CO2 into fixed carbon (organic molecules), and it also produces free oxygen (O2).
-In plants, oxygenic photosynthesis occurs inside a cell organelle called a chloroplast.
what is The most advanced type of bacterial photosynthesis
carried out in cyanobacteria and chloroplasts.
-Chloroplasts and cyanobacteria do photosynthesis the same way.
-Chloroplasts came from cyanobacteria.
What is photosynthesis role in the earths ecosystem
autotrophs and heterotrophs
autotrophs
make there own food from sunlight
heterotrophs
eat autotrophs and heterotrophs
Photosynthesis in Cyanobacteria & Chloroplasts
1.Superior to other types of photosynthesis.
2.Has two photosystems: PS I & PS II.
3.Splits H2O to get electrons.
4.Makes O2 as a by-product.
light defination
on a spectrum of radiation
color defination
different energy of light molecules
How is the light of energy created
In atoms, electrons can jump to different levels of energy. This absorbs or emits photons of different energies or colors.
-Electrons in atoms and molecules can absorb (and emit) light energy.
what creates the color molecule
absorption of light by electrons.
what is the energy levels of each color
Red is the low-energy end of the visible spectrum, and blue/violet is the high-energy end.
3 pigments in plants
chlorophll a
chlorophll b
caroteniods
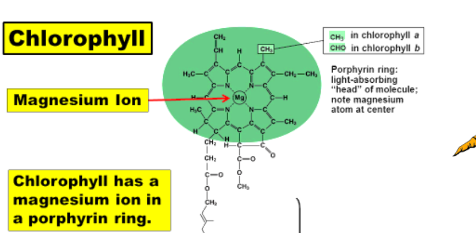
Chlorophylls
a key pigment in photosynthesis and are helped by other pigments called carotenoids and xanthophylls, of which there are many kinds.
-in thylakiods
how do chlorophylls and carotiods raises electrons through high light that are carried over to load the calvin cycle
sunlight
what is the difference between chlorophyll a and b
chlorophyll a has a methonel group and chlorophyll b has an aldehyde
caroteniods
reflect yellows and orange
why does chlorophyll have a magnesium ion in a porphyrin ring
to hold the entier molecule together
Chloroplast
has two outer membranes (lipid bilayer membrane), covering its photosynthetic apparatus. They are transparent like the windows of a greenhouse.
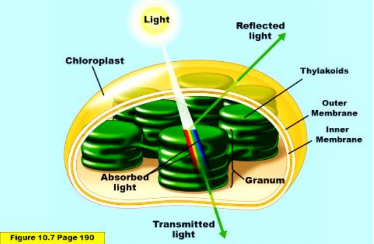
stroma
is all the material surrounding the thylakoids.
Thylakiods
Their role is to help absorb sunlight for photosynthesis to occur.
Thylakoids are membrane-bound disks, like flattened vesicles. Inside each thylakoid is the very thin “thylakoid space,” filled with more material.
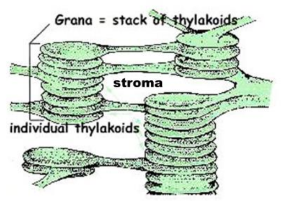
why are thylakiods green
because all theChlorophylls is in there membrane
Anthocyain
break down of Chlorophylls causing fall colors
-have pH
OXYGENIC PHOTOSYNTHESIS equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
-con go both ways between reactants and products though the sun and fire
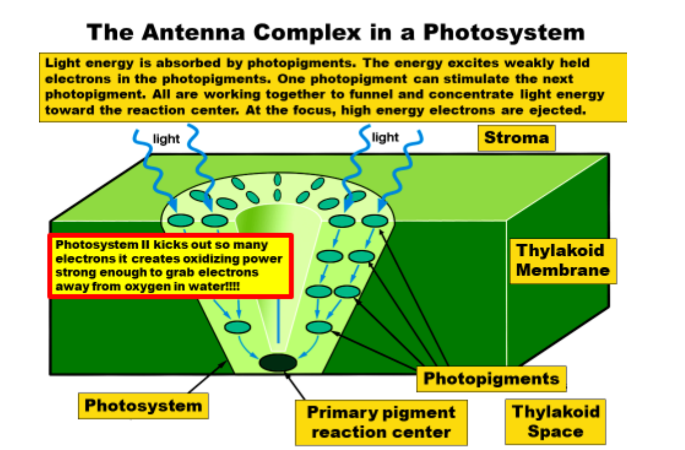
What are the sinifigant events within Tylakiod membrane
there is a photosystem
they get light through electrons and can jump from molecule to molecule.
3.Eletrons get kicked out of the primary pigment reaction in the center of the photosystem
-example P1 and is another kind of ETC
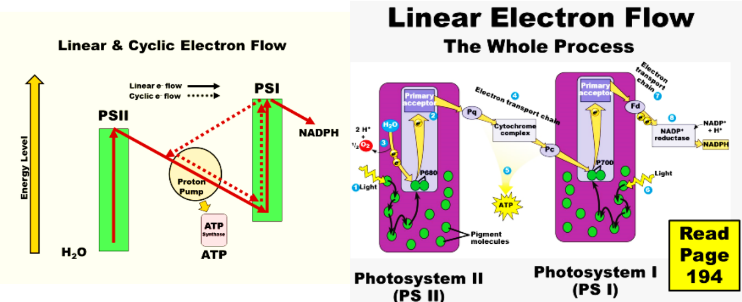
what is the linear electron flow of the light reactions
light goes into chlyorophyll
in P2 the electrons go into the e- acceptors, goes through a ETC, into another chylorphyll
for P1, that other chlyorophll emits electrons into another e- acceptors and produces NADPH and NADP+
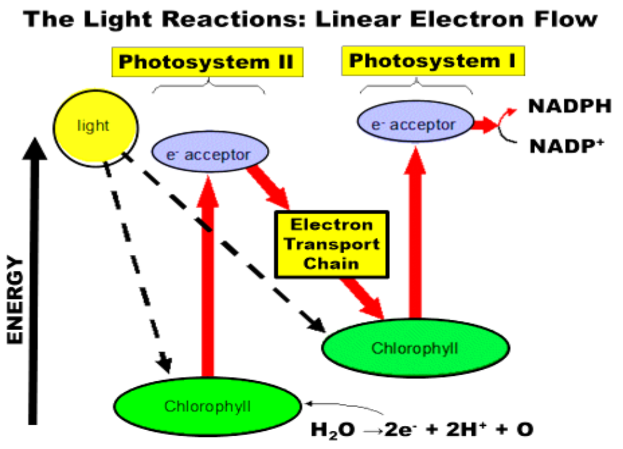
where do the elctrons come from
busted up water molecules that rob eachothers electrons constantly
-oxidizes oxygen
photosystem
giant protein cone that absorbes light and it is where the green actually is
- ejects hot electrons.
How does PSll replace electrons
If it’s PSII it replaces the electrons by stealing them from water, leaving O2 behind.
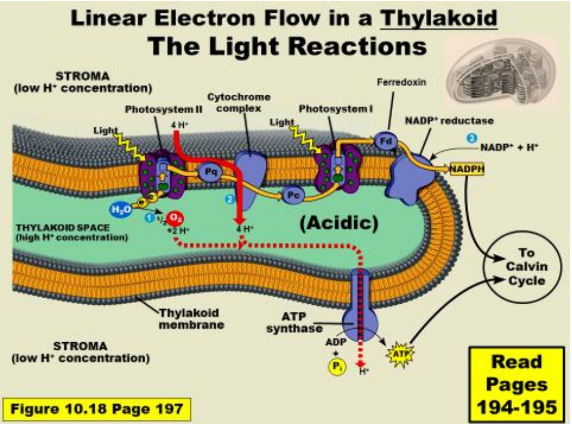
explain this graph
:)
what are the 3 types of “phosphorylation,” meaning ATP production in these cases?
1. Substrate-Level Phosphorylation
2. Oxidative Phosphorylation
3. Photophosphorylation
OEC oxygen evolving complxe
catalyzes the oxidation of water into dioxygen, protons and electrons
-in ps2 and has maganese
-can get high electron chanrge
difference between Oxygenic Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
1.Cellular Respiration harvests high energy electrons from sugar and shuttles them to the electron transport chain to drive ATP synthesis.
2.sunlight energizes electrons and they are shuttled to a process that creates sugar.
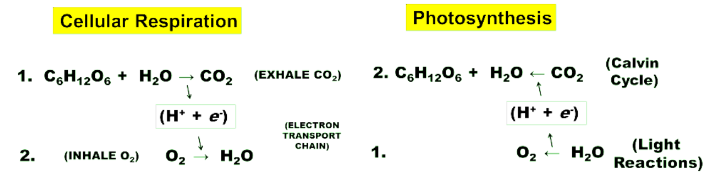
what does photosyntheis consist of
light reactions and calvin cycle
light reactions funtion
1. The light reactions produce NADPH and ATP, which supply energy, electrons and protons.
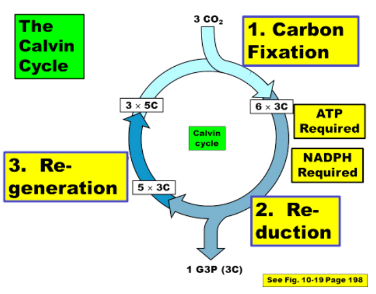
what does the use calvin cycle
2. The Calvin cycle uses the NADPH and ATP to turn CO2 into G3P (glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate).
what does photosynthesis require and where does it come from
ATP and NADPH are made in the light reactions, then are used for calvin cycle to make sugar
what are the processes all occur inside the chloroplast.
1. The light reactions take place in the membranes of the thylakoids.
2. The Calvin cycle takes place in the stroma, and makes G3P.
Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (GP3)
is like glycerol, with one end converted to an aldehyde group, and the other end phosphorylated.
-is a phosphorylated three-carbon sugar.
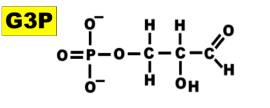
How is G3P converted into glucose
reverse of glycolysis
the funtion of The Photosystems: PS I and PS II
capture light energy (photons of sunlight) and emit free, high-energy electrons that feed into electron transport chains of the thylakoids.
where is PSII and what can it do
first photosystem in the pathway of linear electron flow and it can break apart a water molecule!
how does PSII: work
1.From two water molecules, you get 4 protons and 4 electrons, plus 2 atoms of oxygen, yielding O2.
2.So as protons and electrons are used for G3P synthesis in the Calvin cycle, they can be replaced.
3.You also get a molecule of O2, which for the plant is just a waste product.
PSI:
second photosystem in the pathway of linear electron flow.
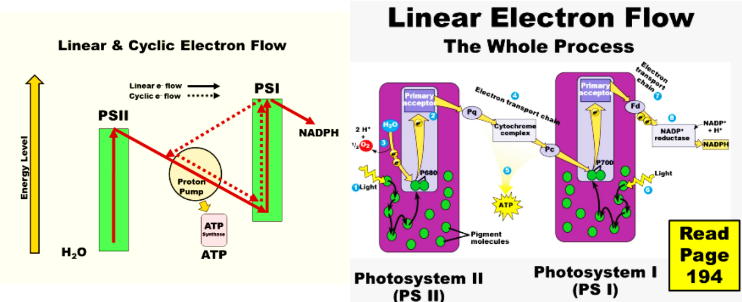
how does PSI:
It jacks up the energy of electrons again, to an even higher level.