CMSC 137 - Internet Protocol
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
Internetworking
connecting multiple different networks together to make one big network — like the Internet
[The Internet at the Network Layer] datagram
uses the _____ approach to packet switching
[The Internet at the Network Layer] universal
uses the _____ address defined in the network layer to route packets from the source to the destination
[The Internet at the Network Layer] connectionless
communication is _____
[The Internet at the Network Layer] independently
treats each packet _____
[IPv4 Datagram Format] Version (VER)
4-bit field that defines the version of the IPv4 protocol
[IPv4 Datagram Format] Header Length (HLEN)
4-bit field that defines the total length of the datagram header in 4-byte words
[IPv4 Datagram Format] Service
previously called service type, now called differentiated service
[IPv4 Datagram Format] Precedence
3-bit subfield that defines the priority of datagram in issues such as congestion
[IPv4 Datagram Format] Type of Service (TOS) Bits
4-bit subfield with each bit having a special meaning
[Differentiated Services] codepoint
the first 6 bits make up the _____ subfield, the last 2 bits are not used
[Differentiated Services] when the 3 rightmost bits are 0s
the 3 leftmost bits are interpreted the same as the precedence bits
[Differentiated Services] when the 3 rightmost bits are NOT all 0s
the 6 bit define 64 services based on the priority assignment by the Internet or local authorities
[IPv4] Total Length
16-bit field that defines the total length of the IPv4 datagram in bytes
[IPv4]
Identification
Flags
Fragmentation Offset
used in fragmentation
[IPv4] Time to Live (TTL)
used to control the maximum number of hops (routers) visited by the datagram
[IPv4] Protocol
8-bit field that defines the higher-level protocol that uses the services of the IPv4 layer
[IPv4] Checksum
for error checking, covers only the header
[IPv4] Source Address
32-bit address that defines the IPv4 address of the source
[IPv4] Destination Address
32-bit address that defines the IPv4 address of the destination
[IPv4] Options
maximum of 40 bytes, used for network testing and debugging
[IPv4 - Options] No Operation
1-byte option used as a filler between options
[IPv4 - Options] End of Option
1-byte option used for padding at the end of the option field
[IPv4 - Options] Record Route
used to record the Internet routers that handle the datagram (up to 9 router addresses)
[IPv4 - Options] Strict Source Route
used by the source to predetermine a route for the datagram as it travels through the Internet
[IPv4 - Options] Loose Source Route
similar to strict source route in which each router in the list must be visited, but the datagram can visit other routers as well
[IPv4 - Options] Timestamp
used to record the time of datagram processing by a router
[Fragmentation] Maximum Transfer/Transmission Unit (MTU)
each data link protocol has its own frame format in most protocol, where one of the fields defined in the format is the maximum size of the data field
[Fragmentation] less than
when a datagram is encapsulated in a frame, the total size of the frame must be _____ the MTU, which is defined by the restrictions imposed by the hardware and software used
[Fragmentation] Identification
16-bit field that identifies the datagram originating from the source host
[Fragmentation] Flags
3-bit field
1st bit — reserved
2nd bit — do not fragment bit
3rd bit — more fragment bit
[Fragmentation] Fragmentation Offset
13-bit field that shows the relative position of the fragment with respect to the whole datagram
IPv6
Internetworking Protocol, Version 6
To overcome deficiencies of IPv4
Address depletion is a long-term problem
Internet must accommodate real-time audio and video transmission
Internet must accommodate encryption and authentication of data
IPng (Internetworking Protocol, next generation)
IPv6 is also known as this
[IPv6] Advantages
Larger address space
Better header format
New options
Allowance for extension
Support for resource allocation
Support for more security
[IPv6] Payload
The payload can contain:
A transport layer segment (like TCP or UDP)
Or extension headers (used for extra options, like routing or security)
Or sometimes even other packets
[IPv6 - Base Header] Version
4-bit field that defines the version number of the IP
[IPv6 - Base Header] Traffic Class
8-bit field that distinguishes different payloads with different delivery requirements
[IPv6 - Base Header] Flow Label
20-bit field that is designed to provide special handling for a particular flow of data
a flow is a sequence of packets that share the same characteristics
[IPv6 - Base Header] Payload Length
2-byte field that defines the length of the IP datagram excluding the base header
[IPv6 - Base Header] Next Header
8-bit field defining the type of the first extension (if present) or the type of data that follows the base header
[IPv6 - Base Header] Hop Limit
8-bit field that serves the same purpose of TTL field in IPv4
[IPv6 - Base Header] Source Address
16-byte IP address that identifies the original source of the datagram
[IPv6 - Base Header] Destination Address
16-byte IP address that identifies the final destination of the datagram
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] header
the length of the _____ is fixed in IPv6
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] priority and flow label
the _____ fields together take over the function of the service type field in IPv4
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] payload
the total length field is eliminated in IPv6 and replaced by the _____ length field
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] fragmentation extension header
the identification, flag, and offset fields are eliminated from the base header in IPv6, they are now included in the _____
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] hop limit
the TTL field in IPv4 is called _____ in IPv6
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] next header
the protocol field in IPv4 is replaced by the _____ field in IPv6
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] checksum
the header _____ in IPv4 is eliminated in IPv6 because it is already provided by upper-layer protocols
[IPv4 vs. IPv6 Header] extension headers
the option fields in IPv4 are implemented as _____ in IPv6
Transition from IPv4 to IPv6 Strategies
Dual Stack
Tunneling
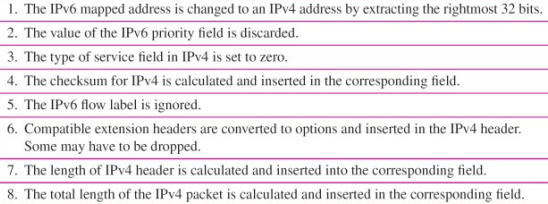
Header Translation
[Transition from IPv4 to IPv6 Strategies] Dual Stacking
station must run IPv4 and IPv6 simultaneously
[Transition from IPv4 to IPv6 Strategies] Tunneling Strategy
the IPv6 packet is encapsulated in an IPv4 packet when it enters the region and it leaves the capsule when it exits the region
[Transition from IPv4 to IPv6 Strategies] Header Translation