Operations Management
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
Operations management
Set of activities that creates goods and services by transforming inputs into outputs
Operations
A function or system that transforms inputs into outputs of greater value
Operations management
The design, operation, and improvement of manufacturing and service system
Value chain
A series of activities from supplier to customer that add value to a product or service
4 Types needed for operations
Finance, marketing, Human Resources, suppliers
Focus of OM
Efficiency and effectiveness of processes
What operations managers do
Plan, organize, staff, lead, control
Vision
What do we want to accomplish ultimately
Mission
How do we accomplish our goals
Values
Ethical standards and norms that govern the behavior of individuals within a firm
Tools for operation decision making
SWOT, business model canvas
Eisenhower decision matrix
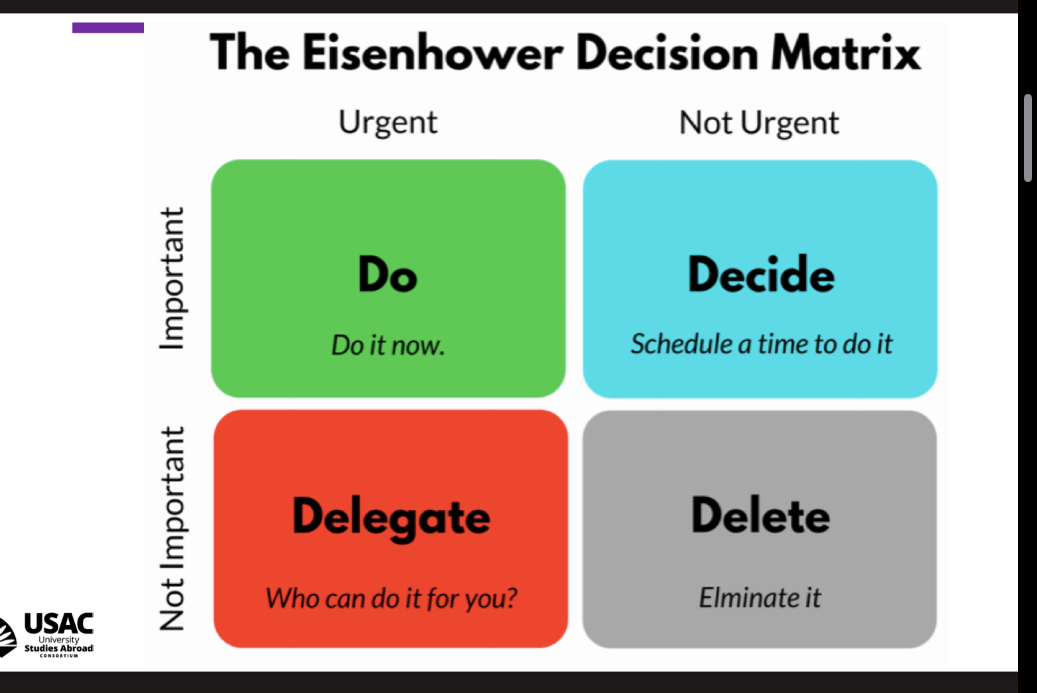
Why is time management important
Time is a scarce resource that must be used well; prevents procrastination, reduce stress, achieve your goals faster, prioritize your work
Value adding time
The moments when the product or service is actually being transformed in a way the customer is willing to pay for (assembling a component coding software)
Non value adding time
Time spent waiting, moving, inspecting, or sitting in inventory
Timeboxing
Production method that involves allocating a fixed amount of time to complete a specific task
Benefits of timeboxing
Increased productivity , improved time management, reduced procrastination, better prioritization, reduced stress
Tips for timeboxing
Set realistic goals, take breaks, be flexible, use a time management tool
Black swan events
Incidents that describe highly improbable but high impact events
Elements of project plan
Objectives, project scope, contract requirements, schedules, resources, personnel, control, risk and problem anaylsis
Gannt Chart
Graph with a bar representing time for each activity in the project being analyzed. Visual display of project schedule
Human Resources
People who work in an organization
Human Resources management
Process of managing these people to achieve organizational goals
Importance of HR
Attract, develop, and retain employees
Motivation
A willingness to work hard because that effort satisfies an employee need
Maslow hierarchy of needs
Physiological, safety, social, esteem, self-actualization
HR and Maslow
Helps decide how benefit packages should be made to meet employee needs
Job performance
Function of motivation combined with ability
Sustainable workplace
Adopting practices that promote environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and economic viability
7 points of compensation
Hourly wage, piece-rate wages, salary, commission, bonus, profit sharing, stock options
Social dimension of OM
Impact of operations on people, including employees, customers, and the broader community
Corporate social responsibility (CSR)
Taking responsibility for the impact of operations on society and the environment
Creating a product
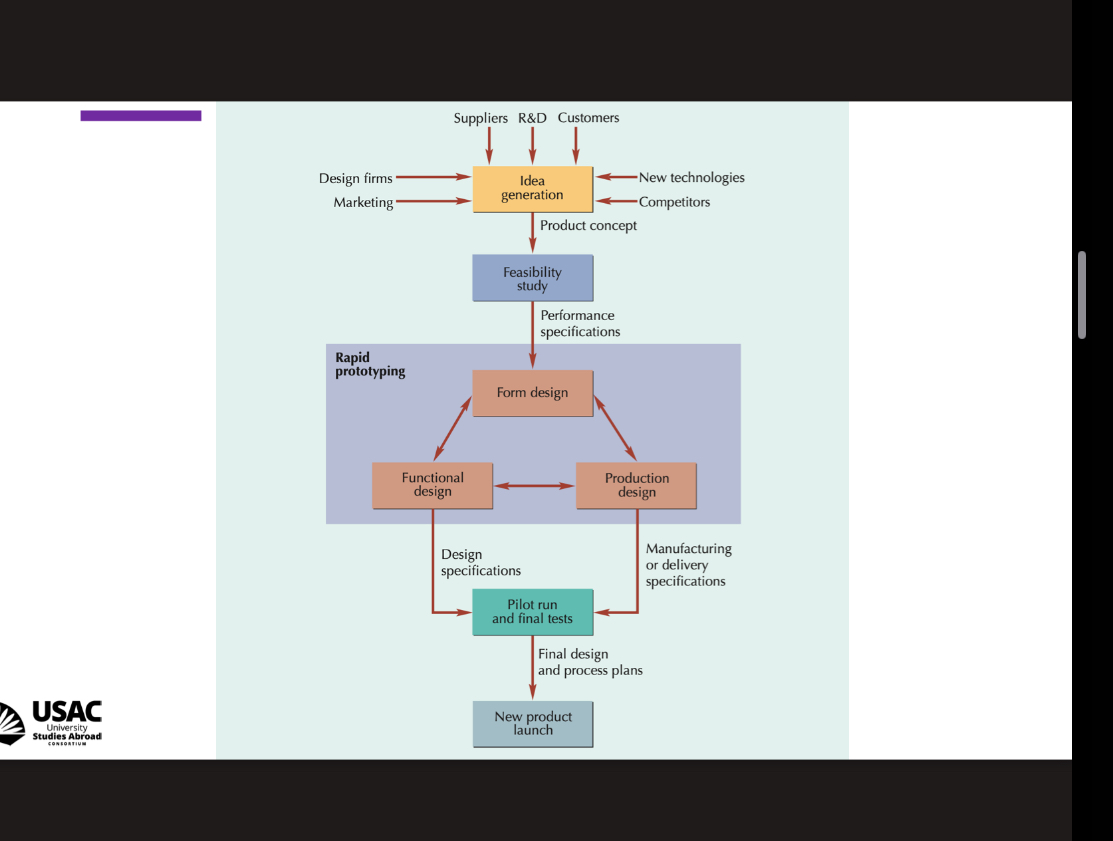
Types of concurrent design
Form design, functional design, and product design
Form design
Physical appearance of a product
Functional design
How the product performs; reliability, maintainability, and usability
Production design
How the product will be made
Reliability
Product will perform its intended function for a specified period of time
Maintainability
Ease/ cost with which a product or service is maintained/repaired
Usability
Ease of use of a product or service
Concepts of product design
Understanding customer needs and preferences, creating a product that is functional and aesthetically pleasing, considering the product life cycle, environmental impact, ensure the product can be manufactured
Simplification
Attempt to reduce the number of parts, assemblies, or options in a product
Standardization
The process in which commonly availed and interchangeable parts are used
Modular design
The process that combines standardized building blocks, or modules, to create unique finished products
Design of manufacture
Process of designing a product so that it can be produced easily and economically
Service design
Process of designing and delivering services that meet the needs of customers and the organization providing the service
Goods vs services
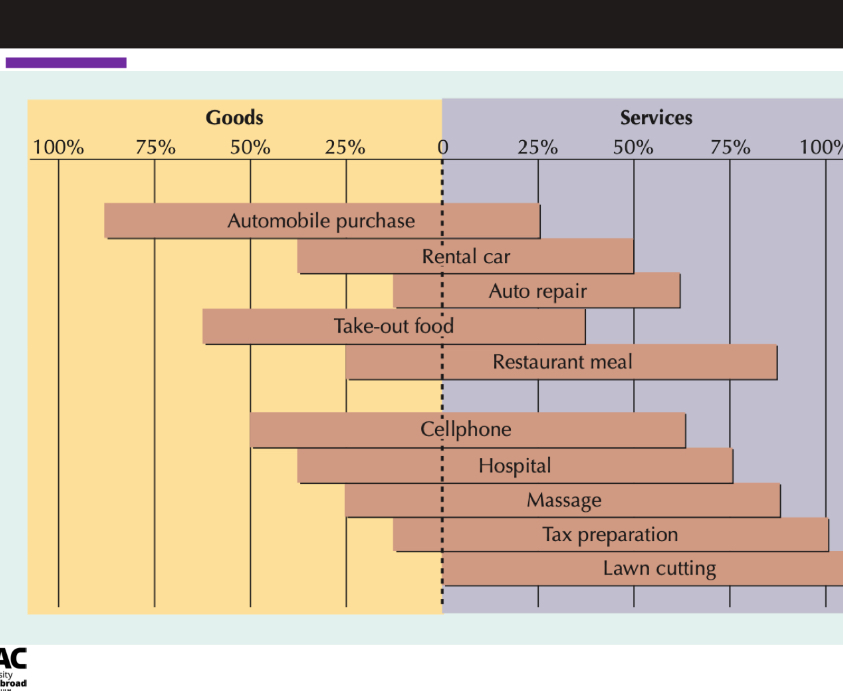
Aspects of serivce design
Developing a service concept, defining the service package, determining performance, design and delivery specifications
Elements of service
Time, human interaction, customization, support
Quality
Degree to which a product meets the design specifications offering a satisfaction factor that fulfills all the expectations that a customer wants
Quality management
Comprehensive, organization-wide approach to ensuring that company’s products, services, and processes consistently meet or exceed customer expectations
Dimesnions of quality for manufactured products
Performance, features, realizability, conformance, durability, serviceability, aesthics, safety
Dimensions of quality for services
Time, completeness, courtesy, consistency, accessibility, accuracy, responsiveness
Jidoka
Any worker can stop the production line if they spot a defect, preventing the problem from moving down the line
Edward’s deming wheel
Plan, do, study/check, act
Importance of Quality management
To improve customer satisfaction, to reduce costs, to increase market share, to comply with regulations
Blockchain
Transparency and security to supply chain
Goals of blockchain
Decentralization, traceability, disintermediation, transparency and verfiability, immutability of the register(data can’t be changed), programmability of transfers
Smart contract advantages
Certainty of the execution of contractual obligations visible to all participants, transparency of contractual obligations, immutability of recorded transactions, possibility of reaching an agreement in the absence of trust
Classes of artificial intelligence
Autonomous vehicle, autonomous robot, intelligent object, virtual assistant and chatbot, recommendation, image processing, language processing, intelligent data processing
Big data
Private data for marketing, business analysis, security
Internet of things
Path in technological development on the basis of which, through the internet, potentially every object of daily experience acquires its own identity in the digital world. Connection of intelligent objects
Trend
Gradual long-term up or down movement of demand
Types of trends
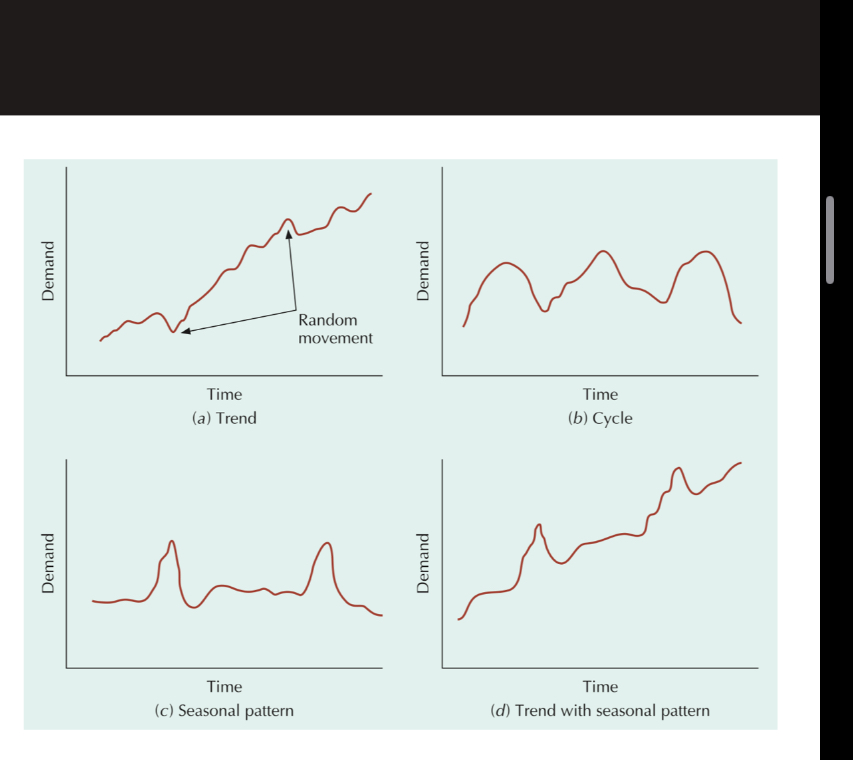
Random variations
Movement in demand that do not follow a patter
Cycle
An up and down movement in demand
Seasonal pattern
Up and down repetitive movement in demand occurring periodically
Time series methods
Statistical techniques that use historical demand data to predict future demand
Regression methods
Attempt to develop a mathematical relationship between demand and factors that cause it to behave the way it does
Qualitative methods
Qualitive forecasting methods use management judgement, expertise, and option to make forecasts
Data mining
Process for analyzing large amounts of data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships in groups