AP Human Geo - Unit 4 | 2.0
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
State
Country, political entity
Nation
Groups of people with shared language, religion, ethnicity, and/or heritage, cultural entity
Nation-State
The whole state is one nation
Stateless Nation
When a nation doesn’t have sovereignty
Multistate Nation
A nation spanning more than one country
Multinational State
A country with various ethnicities/ cultures living inside
Perforated (state shape)
State with another state inside it
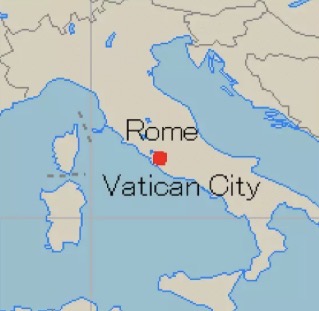
Prorupted (state shape)
Compact state with a long extension (panhandle)
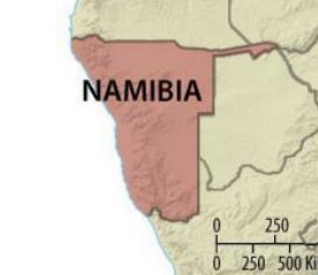
Fragmented (state shape)
One state broken up
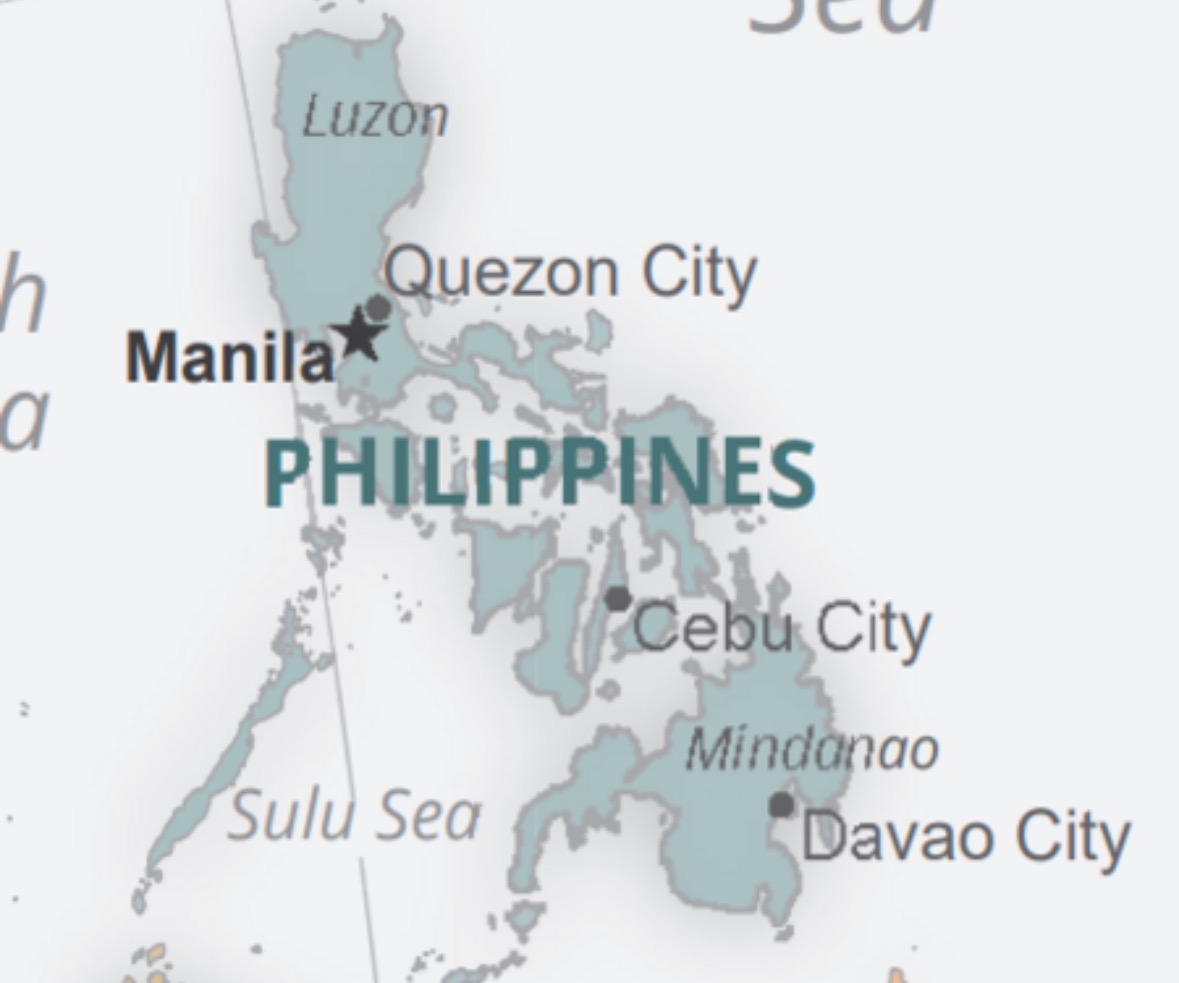
Elongated (state shape)
Long
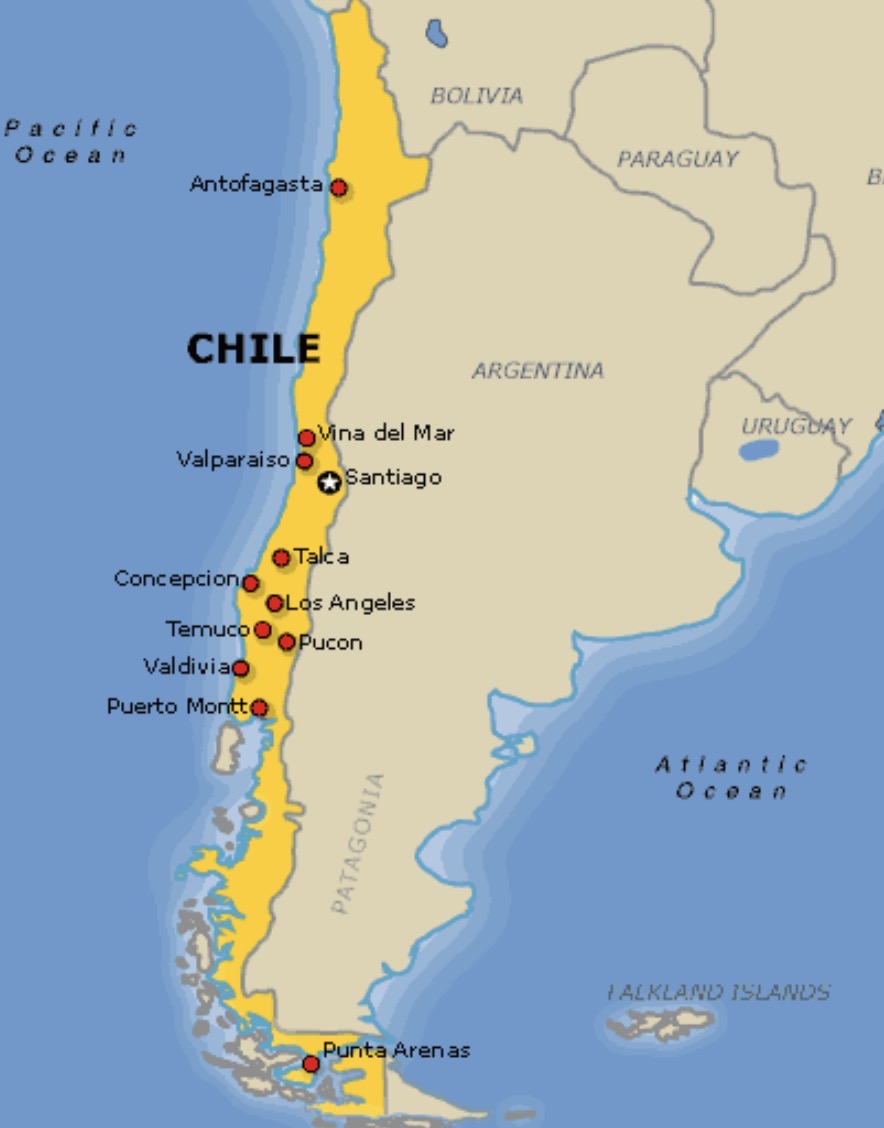
Spratly Islands (location, who disputes it, why)
South China Sea; China, Taiwan, Vietnam, Philippines, Malasia, Brunei; has a lot of natural resources
Antecedent Boundaries
Borders drawn before it was well populated ~Opposite of Subsequent Borders~
Subsequent Boundaries
Borders drawn after the areas are already well settled ~Opposite of Antecedent Boundaries
Consequent Boundaries
Type of Subsequent boundary, Borders drawn based on cultural landscapes
Superimposed Boundary
Borders drawn over existing accepted borders by an outside force (Africa, Berlin Conference)
Geometric boundaries
Mathematical boundaries, typically follow lines of latitude of longitude.
Definition (Creating boundary)
Document is created that indicated exact landmarks
Delineation (Creating boundary)
Cartographers place the boundary on a map
Demarcation (Creating boundary)
Marking the boundary by some method on the ground
UNCLOS
United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea
Exclusive economic zone
The country has exclusive rights over the materials from their coast to 200 nautical miles
UNCLOS states…
A country’s territorial seas extend 12 nautical miles off its coast and it’s exclusive economic zone extends 200 nautical miles from it’s coast
Allocation Dispute
Neighboring states argue over distribution of resources
Definitional Dispute
The legal language of a boundary agreement no longer applies or can get twisted
Locational Dispute
The delineation and possible demarcation of the border is in dispute
Operational Dispute
neighboring states disagree over policies to be applied along a boundary (immigration)
Reapportionment
The seats in the House of Representatives are reallocated to different states because of change in population (different growth speeds, when on state loses people and another gains)
Electoral college
Electors, who were chosen to elect the president
Gerrymandering
Redistricting boundaries to favor one party
Unitary state
Most common, top gov has ultimate power (top-down approach)
Pros and cons of unitary state
Pros: efficient. Cons: government can more easily become corrupted