Chapter 4: Graphing Family Processes
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
socio-generational principle
close family members of the previous generation (mother, father, grandparents, etc.l) significantly influence how children approach their social world and develop ideological orientation, understand and respond to emotions, develop and use intellect, and learn to navigate interpersonal relationships
parentified child (parentification)
the transformation of a child into a parent - the overburden, the loss of trust as the parent turn to the child - the special bond of commitment is destroyed
pedigree chart
diagram that visualizes how a specific trait or disorder is passed down through generations
genogram
introduced by Murray Bowen (psychiatrist), and developed by scholars McGoldrick and Randy Gerson, not a pedigree chart or a family tree, index person, includes family chronology, goes back 2-4 generations (ever changing), description of family relationships and family processes
uses
describing family relationships, and describing family processes
importance
they can help us better understand the desirable and the undesirable influences
that earlier generations have had on us which can help us enjoy and appreciate the desirable
effects, and sometimes find ways to minimize and change some of the undesirable effects,
we can also use genograms as family scientists to help others better understand their lives,
their families, and the options they have to grow and improve their lives
figure 4.1
simple three generation genogram of the Sandra jones family

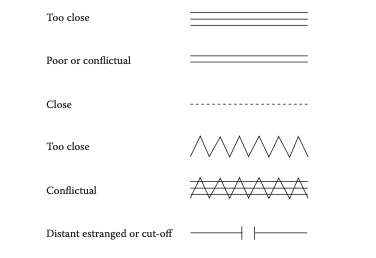
relationship symbols figure 4.4
genogram symbols
male
depicted as a box
female
depicted as a circle
death symbols
X inside of a box or circle
index person
based on fact and perception
generational transmission principle
families tend to transmit their style of life to each new generation, quality of marriage - conflict (child of divorce)