amines
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
what is a primary amine? (2)
a primary amine has one carbon atom bonded to the nitrogen atom
represented as RNH₂
provide an example of a primary amine (1)
CH₃NH₂
what is a secondary amine? (2)
a secondary amine has two carbon atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom
represented as R₂NH
provide an example of a secondary amine (1)
(CH3)2NH
what is a tertiary amine? (2)
a tertiary amine has three carbon atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom
represented as R₃N
provide an example of a tertiary amine (1)
(CH3)3N
what is a quaternary ammonium salt? (2)
a quaternary ammonium salt has four carbon atoms bonded to the nitrogen atom
represented as R4N+
provide an example of a quaternary ammonium salt (1)
(CH3)4N+
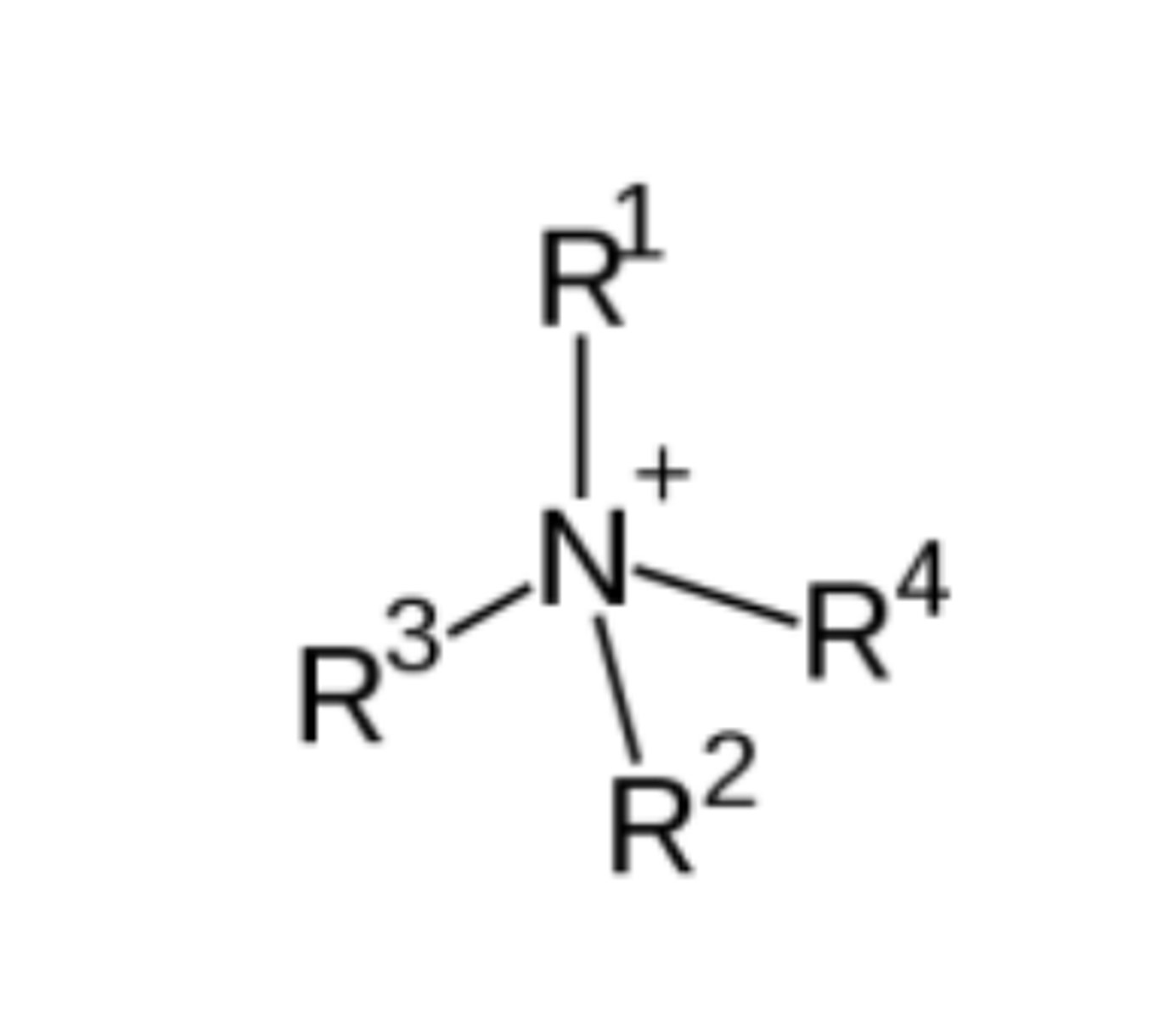
draw the general structure of quaternary ammonium salts (3)
what property allows primary, secondary, and tertiary amines to act as bases? (1)
the nitrogen atom has a lone pair, which can accept a proton, allowing them to act as bases
how does the availability of the lone pair affect the strength of amines as bases? (2)
the strength of amines as bases increases
with the availability of the lone pair on nitrogen for protonation
how do amines and ammonia behave as bases in water? (2)
they partially dissociate in water
for example: NH3 + H2O ⇌ NH4+ + OH-
arrange the following in increasing base strength: aromatic amines, ammonia, aliphatic amines (1)
aliphatic amines > ammonia > aromatic amines
why are aromatic amines weaker bases? (3)
the lone pair on nitrogen overlaps with the delocalised ring
this makes the lone pair on nitrogen less available
this is called the negative inductive effect
why are aliphatic amines stronger bases? (3)
the R group pushes electrons towards the nitrogen atom
this makes the lone pair on nitrogen more available
this is called the positive inductive effect
why can amines act as nucleophiles? (1)
they can donate their lone pair of electrons to a δ+ carbon
why do quaternary ammonium salts not react? (1)
they have no lone pair on the nitrogen atom
why are short-chain amines soluble in water? (1)
because they form hydrogen bonds with water molecules
what is the shape of an amine molecule and why? (2)
amines are pyramidal in shape
due to three bonding pairs and one lone pair of electrons
what is the shape of quaternary ammonium salts? (1)
tetrahedral
why do amines generally have lower boiling points than alcohols with the same carbon chain length? (2)
amines have weaker hydrogen bonds compared to alcohols
resulting in lower boiling points
what are the two methods for preparation of aliphatic amines? (2)
nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes
reduction of a nitrile
what is the general equation and conditions for the preparation of amines by nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes? (1)
RX + 2NH3 → RNH2 + NH4X
with excess of concentrated ammonia and dissolved in ethanol
what is the general mechanism for the preparation of amines by nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes? (1)

what is the primary disadvantage of using nucleophilic substitution of haloalkanes for producing aliphatic amines? (2)
a mixture of amine products is formed due to the product also acting as a nucleophile
resulting in a low yield of primary amine
what are the steps in the 2-step method for producing an amine from reduction of a nitrile?
formation of a nitrile from a haloalkane
reduction of a nitrile to form an amine
what is the general equation for the formation of a nitrile from a haloalkane? (2)
RX + KCN → RCN + KX
(nucleophilic substitution in aqueous ethanol)
what is the general equation for the reduction of a nitrile to from an amine? (2)
RCN + 2H2 → RCH2NH2
(catalytic hydrogenation)
which catalyst and conditions are required in the reduction of nitriles to amines? (1)
nickel catalyst and heat
why does the 2-step method for producing amines yield a purer product compared to the 1-step method? (1)
it increases the length of the carbon chain and reduces the formation of by-products
why can’t phenylamine be made by the reaction of bromobenzene with ammonia? (3)
the carbon atom bonded to the halogen is in the delocalised ring
so nucleophiles wont be attracted to it
benzene ring repels nucleophiles as high electron density
what are aromatic amines/arenes? (1)
they contain a benzene ring
how are aromatic amines formed? (2)
by the reduction of nitrobenzene
using HCl and tin as the catalyst
write the balanced equation for the reduction of nitrobenzene to aromatic amines (1)
C6H5NO2 + 6[H] → C6H5NH2 + 2H2O
what happens to the product of nitrobenzene reduction in the presence of HCl? (1)
the aromatic amine reacts with HCl
to form a salt, C6H5NH3Cl
how is the free aromatic amine liberated from its salt? (2)
by adding sodium hydroxide (NaOH)
resulting in C6H5NH2 + H2O + NaCl
write the balanced equation for the liberation of free aromatic amine from its salt (1)
C6H5NH3Cl + NaOH → C6H5NH2 + H2O + NaCl
write the equation for what happens when ammonia reacts as a base with a proton (1)
NH3 + H+ → NH4+
what is the reaction of phenylamine with H⁺? (1)
C6H5NH2 + H⁺ → C6H5NH3+
what is formed when amines react with acyl chlorides? show the general equations by drawing the organic compounds (4)
an amide and HCl
then further reaction of second molecule of amine reacts with HCl to form a salt

what is the general mechanism for the acylation of amines?

what is formed when amines react with acid anhydrides? (2)
an amide and a carboxylic acid
then further reaction of second molecule of amine reacts with carboxylic acid to form a salt
what are amines used for in the manufacture of synthetic materials? (1)
used in the manufacture of nylon, dyes, and drugs
what are quaternary ammonium salts used for? (1)
as cationic surfactants in fabric softening and hair products
how do quaternary ammonium salts function in hair conditioners? (2)
they attract to the negative charges on wet hair surfaces
forming a coating that prevents static electricity and flyaway hair
why are quaternary ammonium salts effective as fabric softeners? (1)
they keep the fabric surface smooth by preventing the build-up of static electricity