lab 4 axial skeleton
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
What is surrounding bone
Extra cellular matrix mainly made of calcium salts and surrounding collagen fibers
What is the Haversian system in compact bone
Repeating osteons each have a concentric bone lamellae arranged around an osteonic canal
What is lacunae
Small spaces in bone contains osteocytes
What are osteocytes
Mature bone cell which maintains metabolism like exchange of nutrients and waste in blood. Dosent do cell division
What is concentric lamellae
Inside ostenoic canal circular plates of mineralized ECM surrounded by blood vessels and nerves
What is canaliculi
Network of minute canals containing process of osteocytes. Acts as route for nutrients to reach osteocytes and for waste to leave them
What is trabeculae
In spongy bone contains colum of bone trabeculae
which contain bone lamellae, osteocytes, bone lacunae, and
bone canaliculi. Spaces filled with red bone marrow
How do osteocytes, osteoblasts and osteoclasts work together to maintain the skeletal
system?
Osteoprogenitor cell (develops into an osteoblast) Osteoblast
(functions in bone deposition, the buildup of bone extracellular matrix) Osteocyte (maintains bone tissue) Osteoclast
(functions in bone resorption, the breakdown of bone extracellular matrix
What is the function of the osteocytes cytoplasmic extensions
Calcification
Where is compact bone found
In diaphysis and epiphysis
Where is sponges bone found
Interior of bone, in hips, ribs, sternum, vertebrae, skull, proximal ends of femur and humerus (where red bone marrow is stored as well)
Where do the osteocytes of spongy bone obtain their nutrients and oxygen, since there is no
central (Haversian) canal?
Between bone trabeculae lined with endosteum and bone marrow
How is red and yellow bone marrow different
Red produced blood cells and yellow has adipose tissue
What is the epiphyses of long bone
Proximal and distal ends of bone
What is the metaphyses and epipyseal line of long bone
Region between epiphysis and diaphysis. In growning bone it has a layer of hyaline cartilage. When it stope growing its replaced by bone forming a epiphyseal line
What is the periosteum in long bone
Tough connective sheath associated with blood supply. Surrounds bone surface wherever it’s not covered by articular cartilage, protects and nourishes bone. Site of attachment for tendons and ligaments
What is the medullary cavity in long bone
Hollow space in diaphysis with yellow bone marrow and blood vessels. Makes bone lighter
What is the endosteum in long bone
This membrane lining medullary cavity and internal space of spongy bone. Has many osteoprogenitor cells
4 functions of skeletal system
Support, protection, assistance in movement and mineral homeostasis
What is the axial division of skeleton
Skull,vertebrae, sternum, lower ribs and hyoid bone
What is the appendicular skeleton
Pectoral girdle, pelvic girtdle, upper and lower limbs
What is a foramen/ foramina bone marking
Opening in which blood vessels nerves or ligament pass
What is fossa bone marking
Shallow depression
What is a meatus bone marking
Tubelike opening
What is a process bone marking
Projections/outgrowth on bones at joints or attachment points of connective tissue
What is a condyle bone process
Large round protuberance with smooth articulate surface at end of bone.
What is a crest bone process
Prominent ridge or elongated projection
What is a facet of bone
Smooth flat slightly concave/convex articulated surface
What is the head of the bone
Rounded articular projection of bone supported on neck of bone
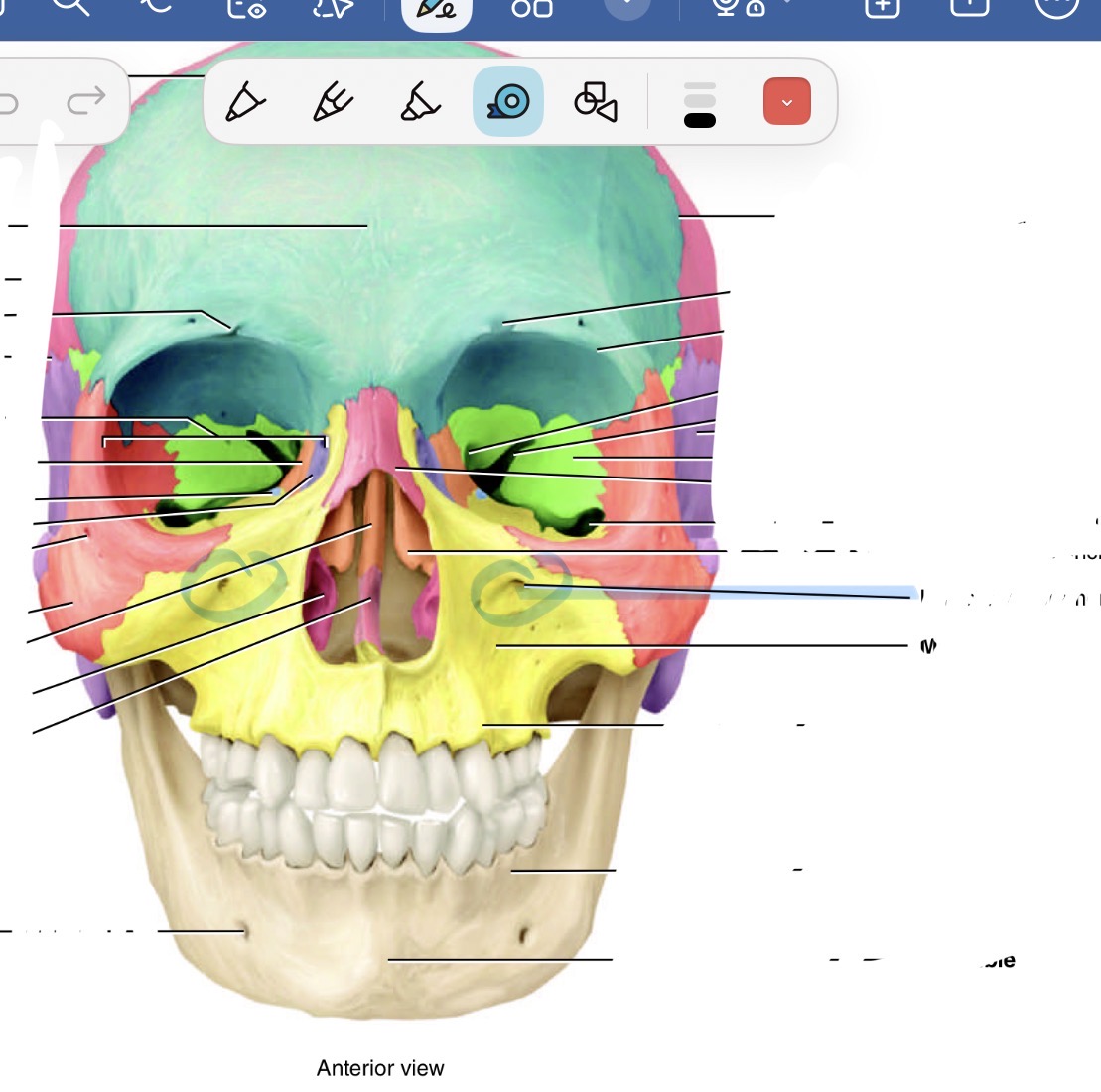
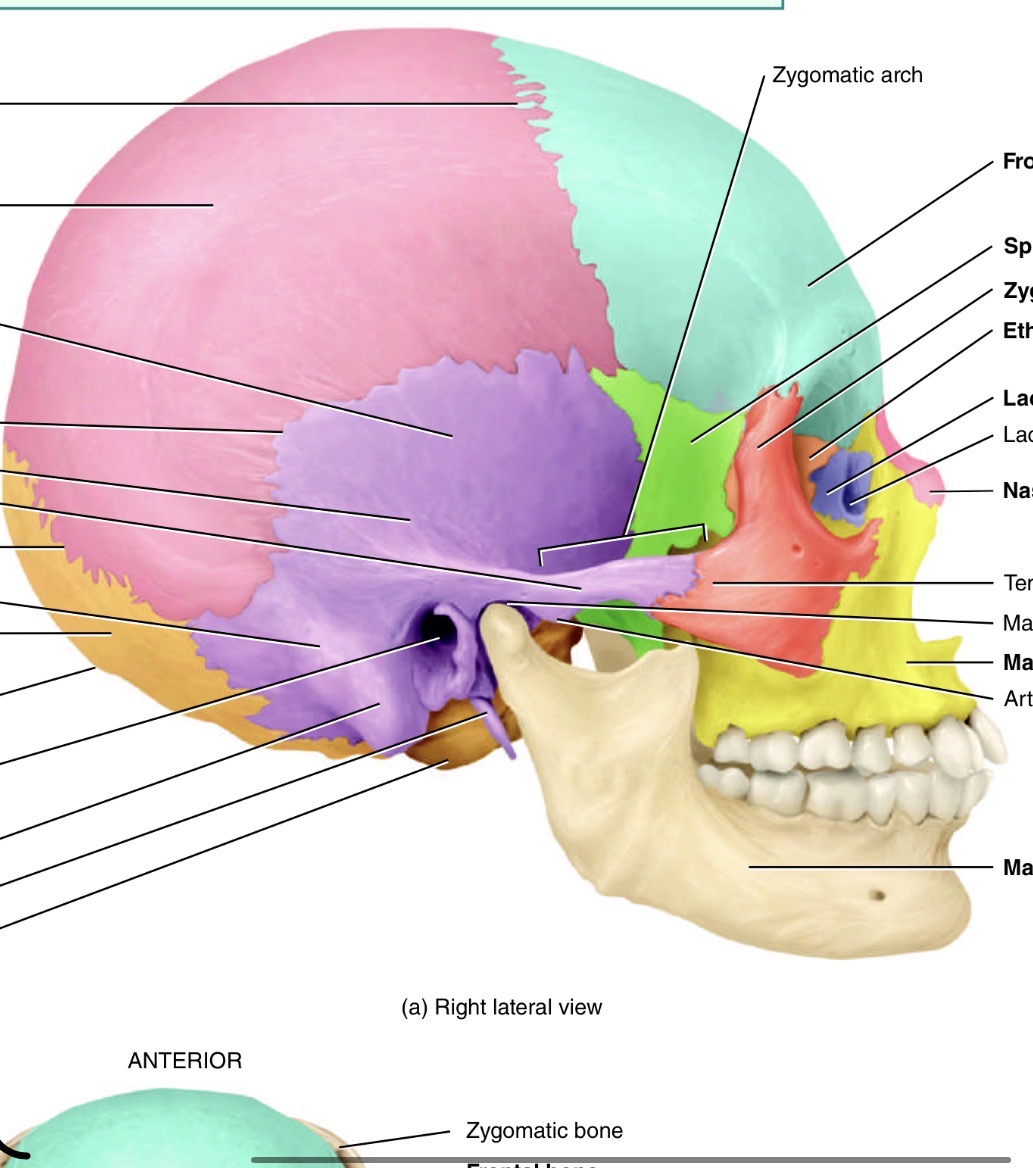
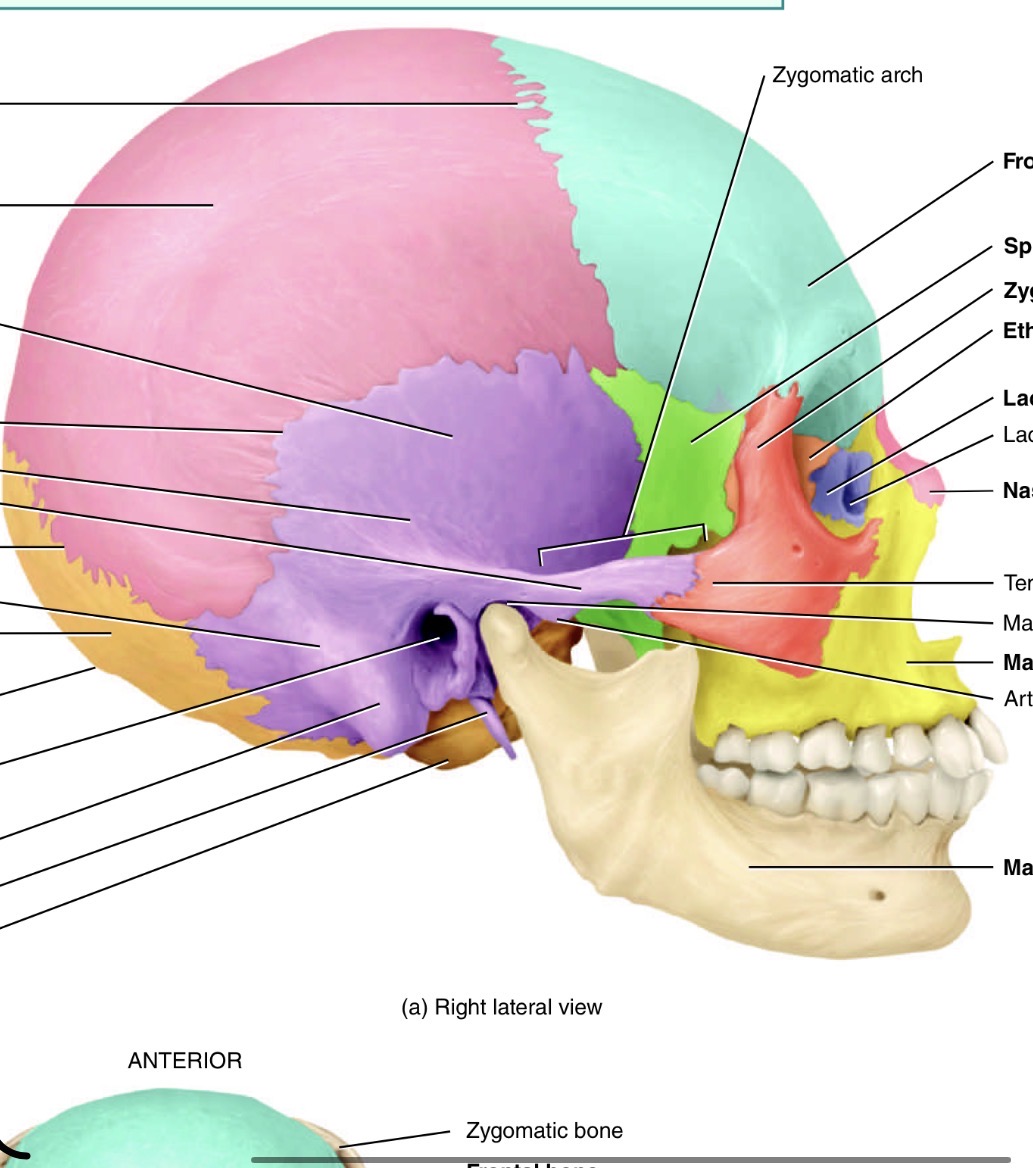
What forms the facial bones
Orbit and sinuses
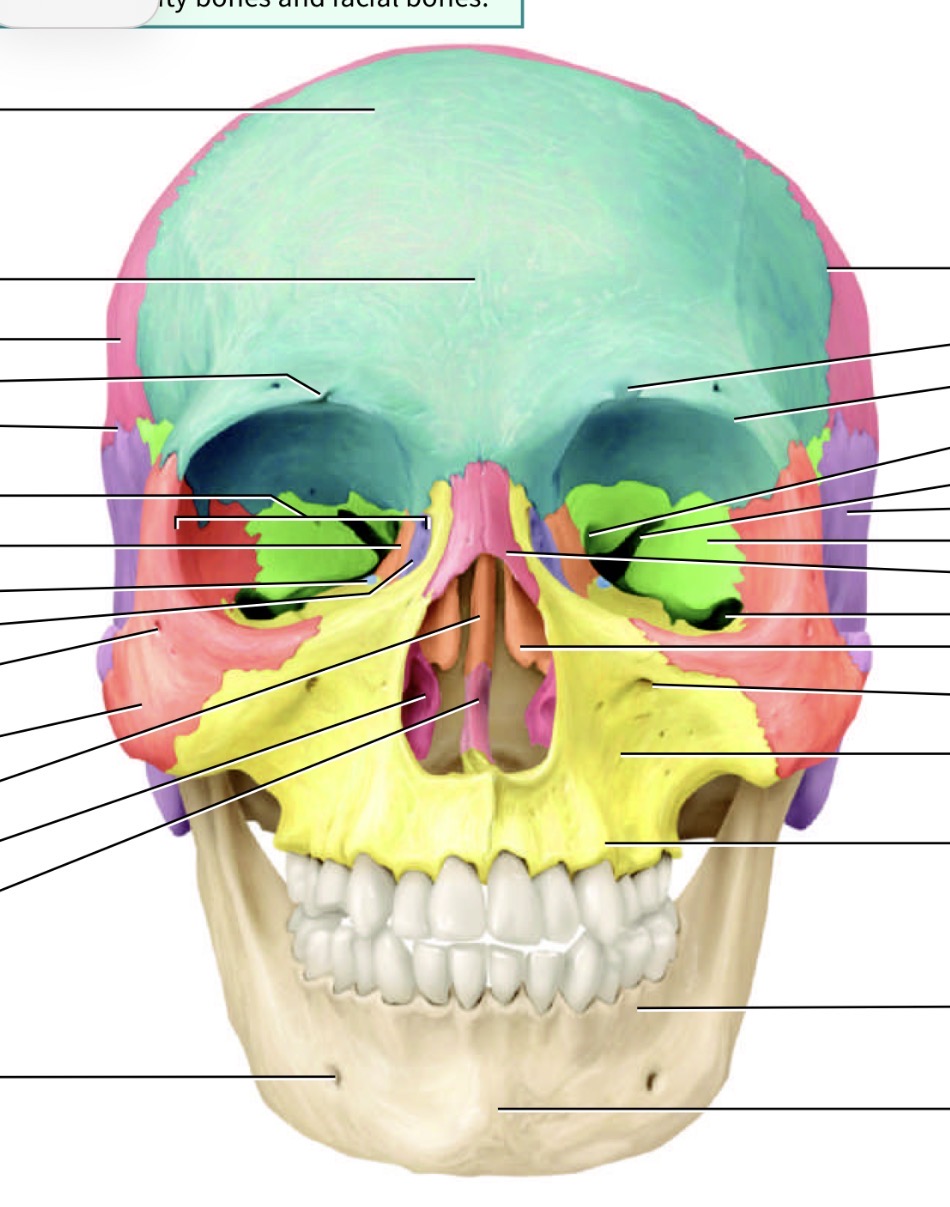
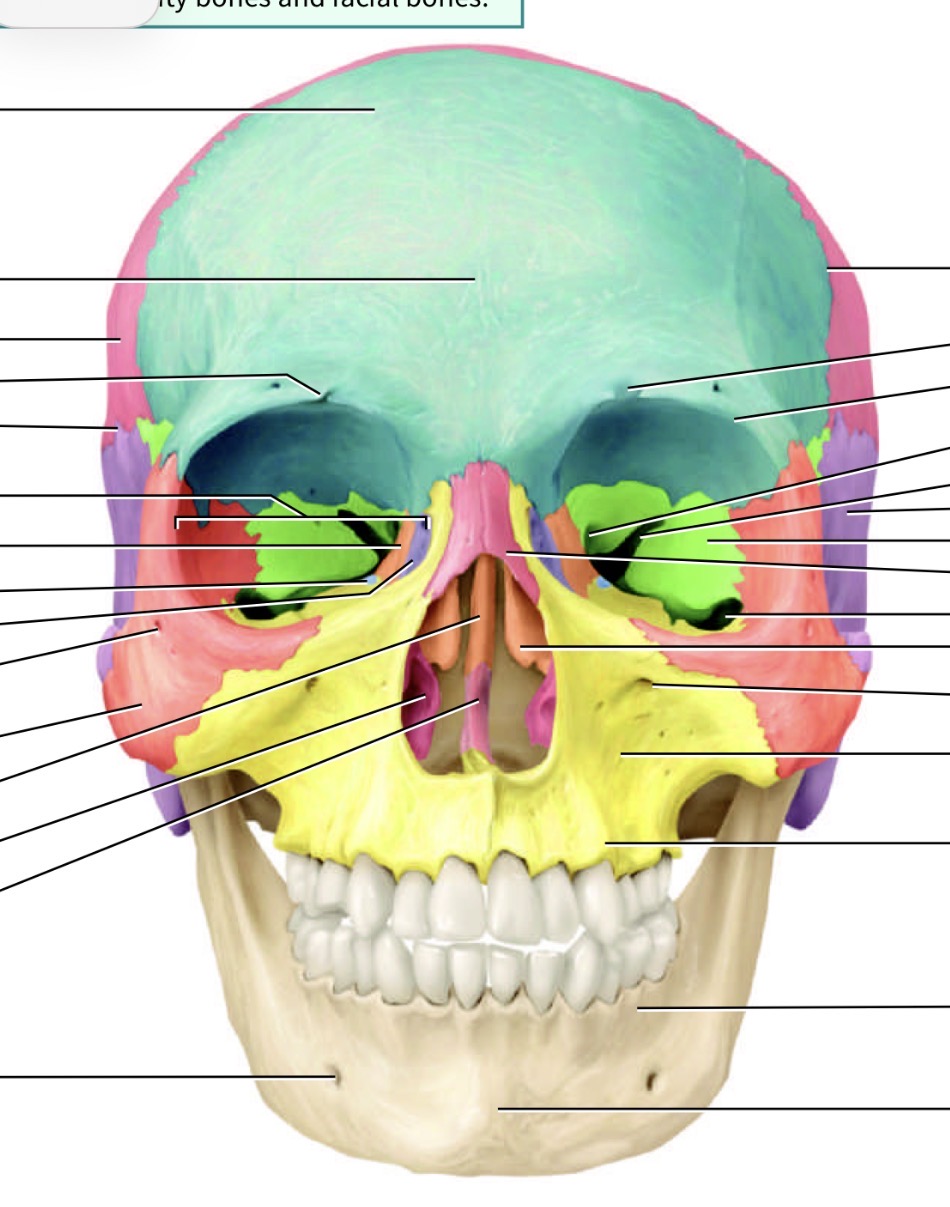
Which bone is the blue one and where is its marking and name
Frontal bone, supraorbital foramen just above eye cavity
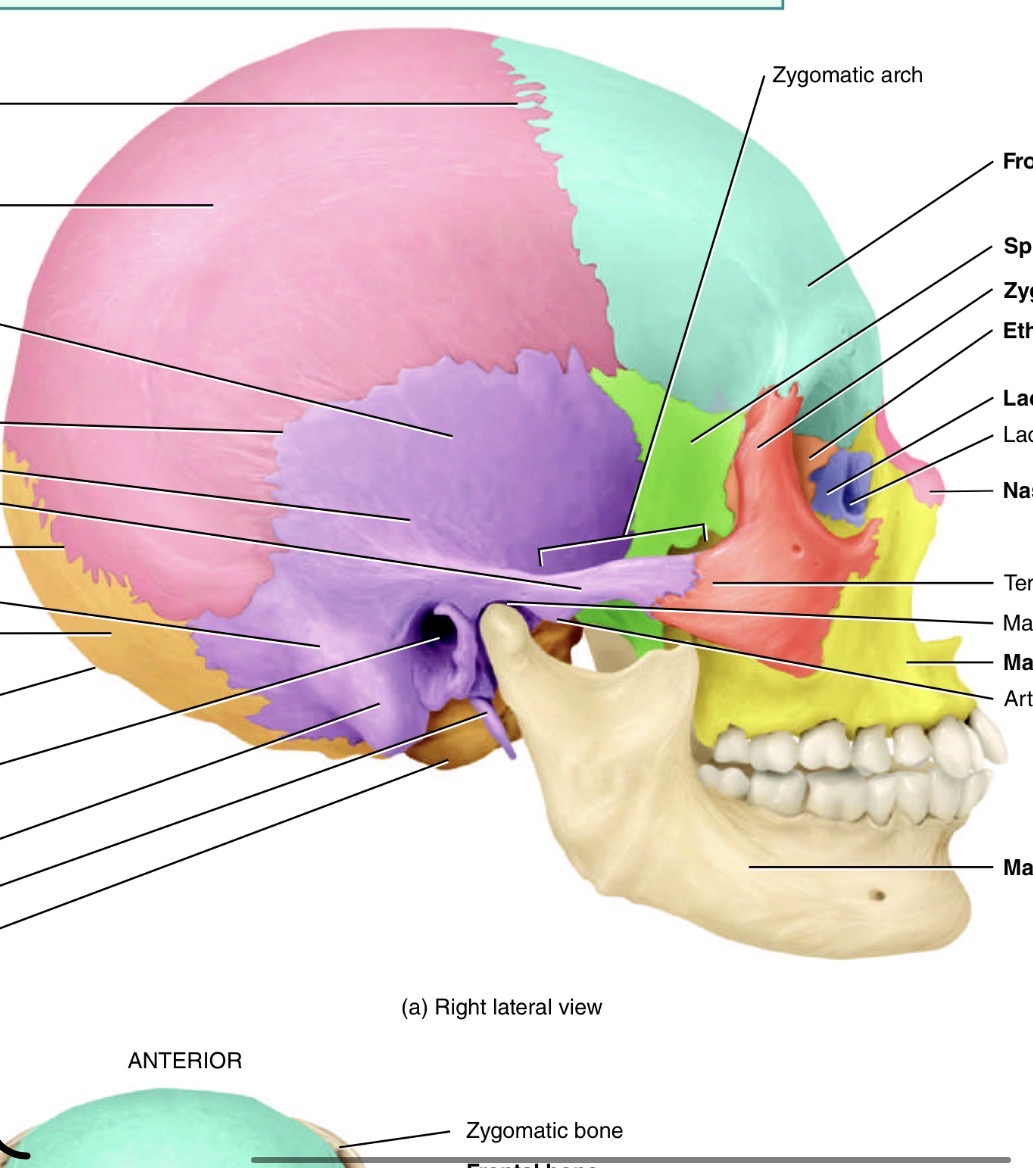
Which is the orange bone by the eye
Ethmoid bone
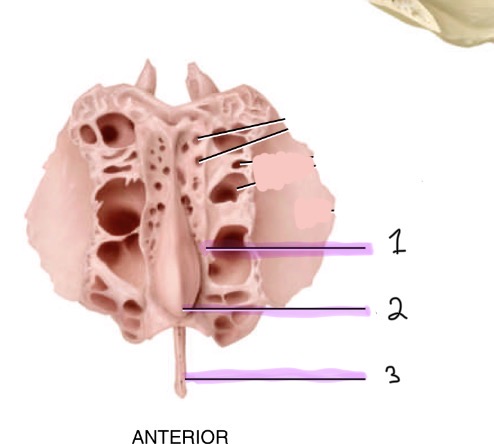
Identify the ethmoid bone markings (anterior view)
Cribriform plate, 2. Crista galli, 3. Perpendicular plate
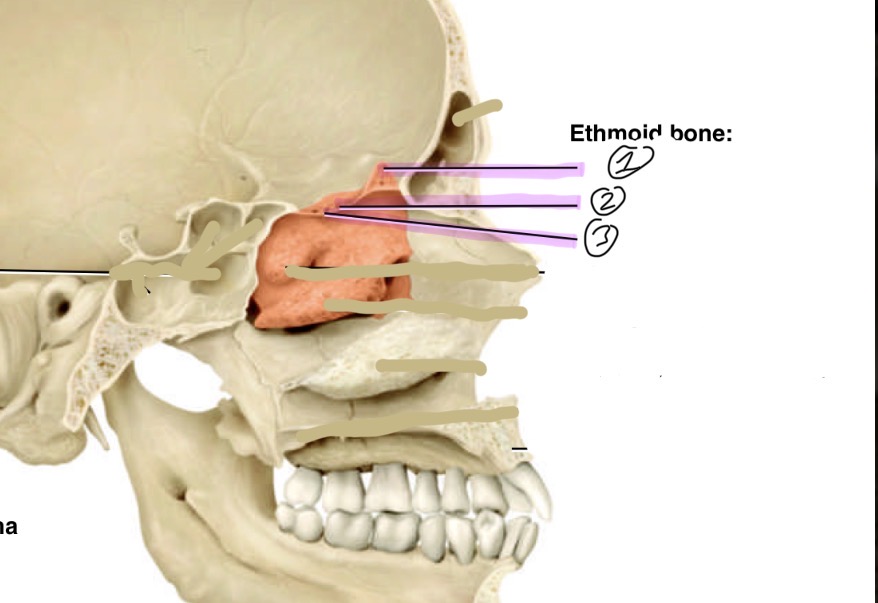
Identify the ethmoid bone markings
Crista galli, 2. Olfactory foramen, 3. Cribriform plate.
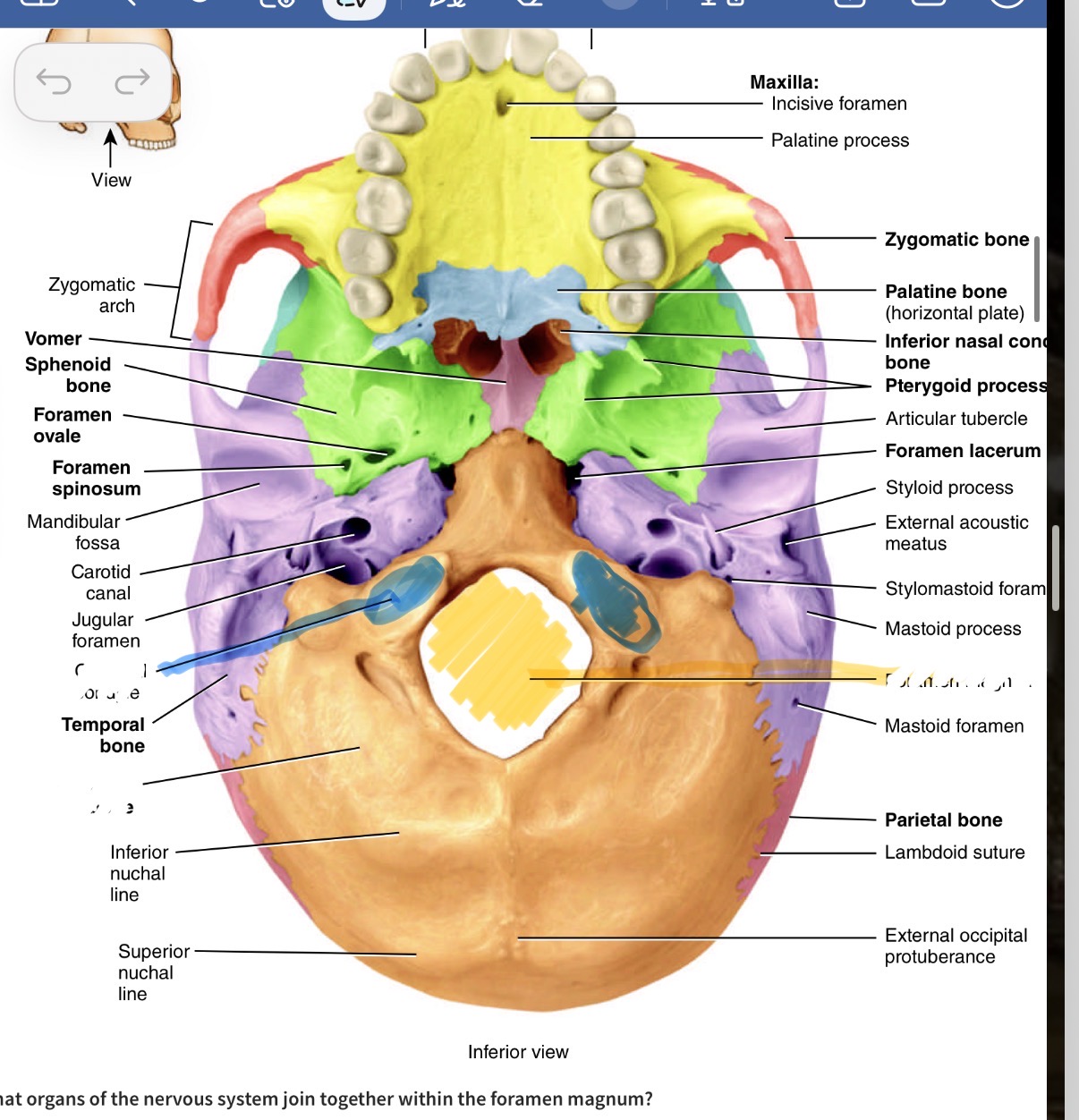
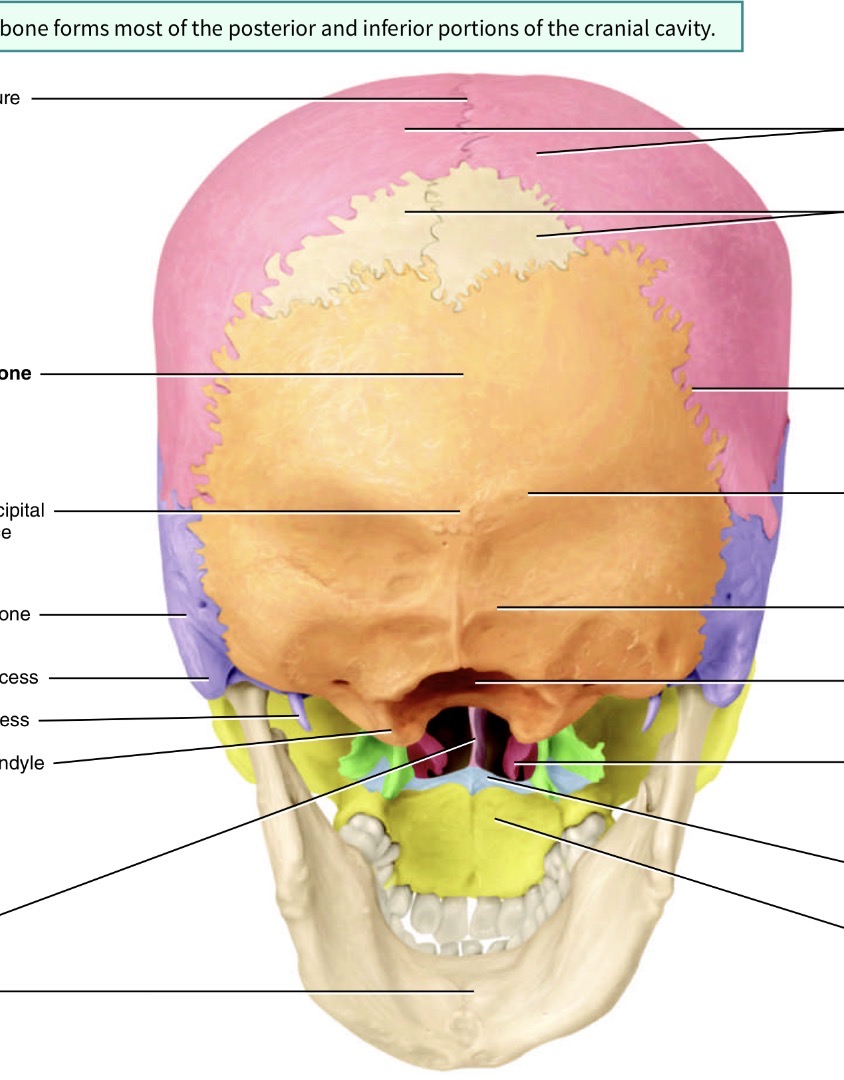
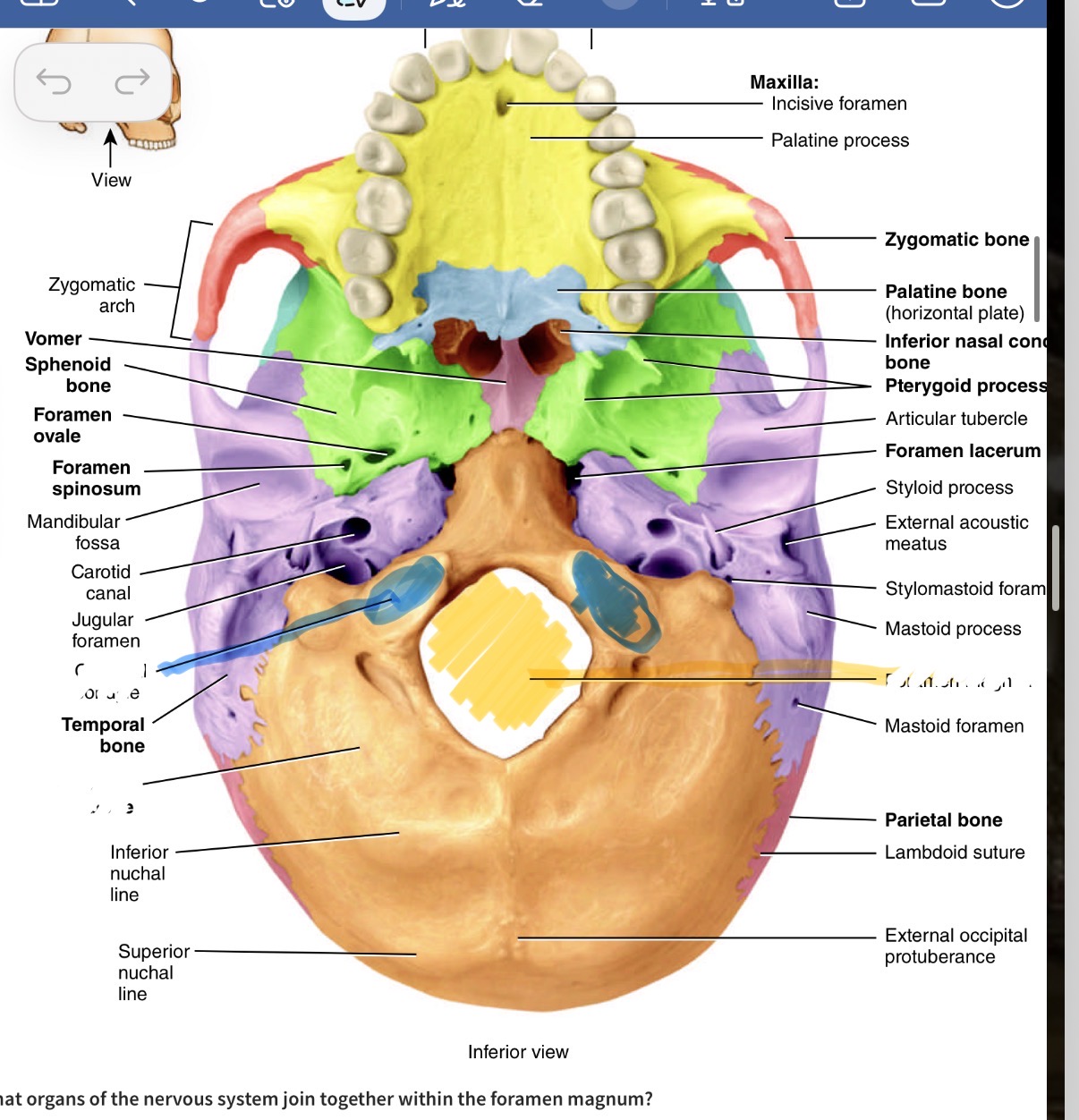
Which bone is the bog orange one and what are its marking s
Occipital bone. Yellow hole is the foramen magnum, blue is the occipital condyle
What bone is the green one and its marking
Sphenoid bone with the optic canal/foramen
Which bones are the pink ones
Parietal
Which bone is the purple one
Temporal bone
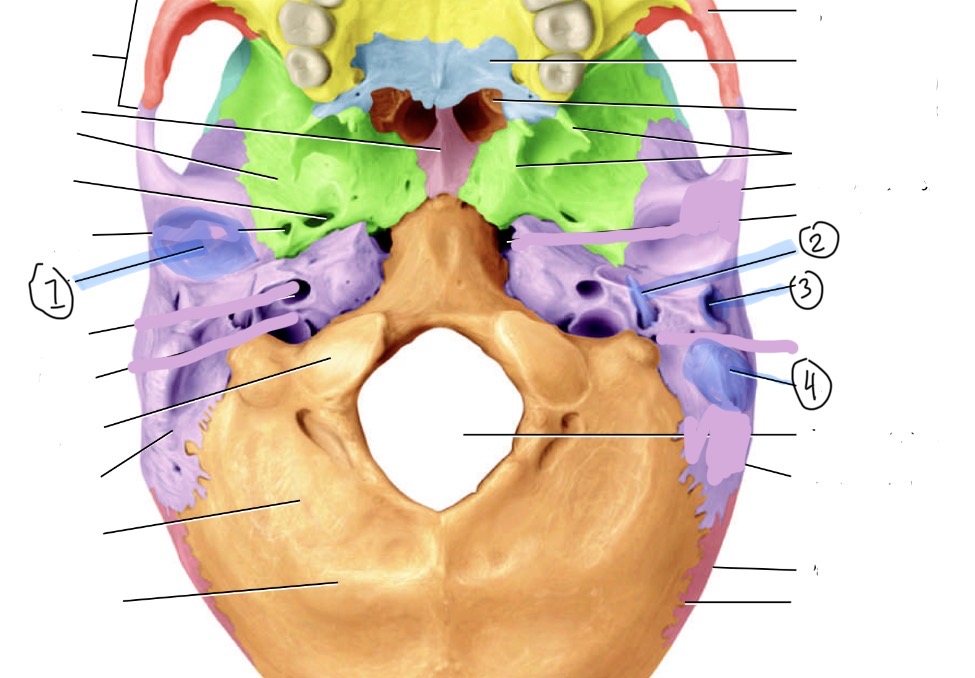
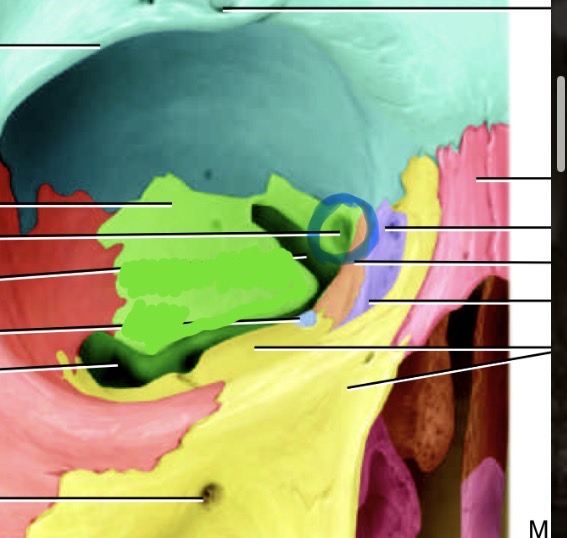
Label these temporal bone markings
Mandibular fossa, 2. Styloid process,3. External acoustic meatus 4. Mastoid process
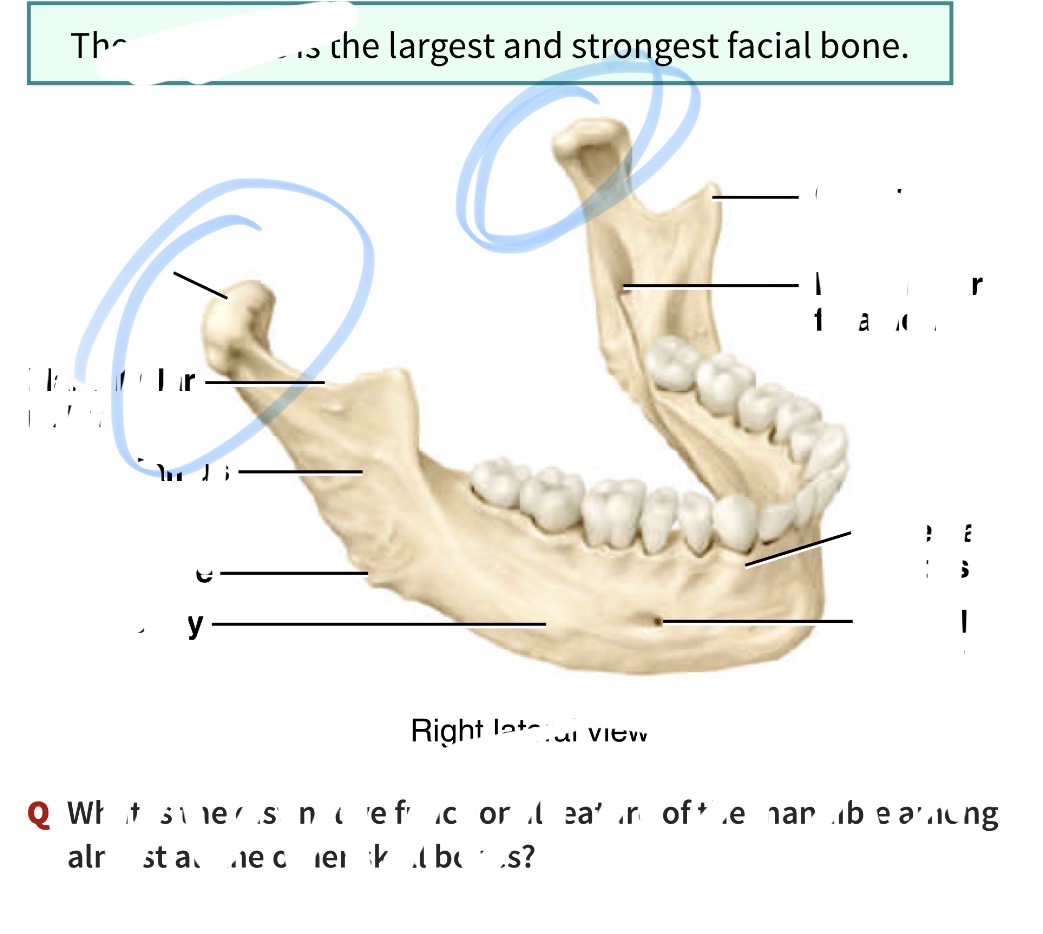
Which bone is this and what is its marking
Mandible. Has a condylar process
What bone is this and its marking
Maxilla showing the infraorbital foramen
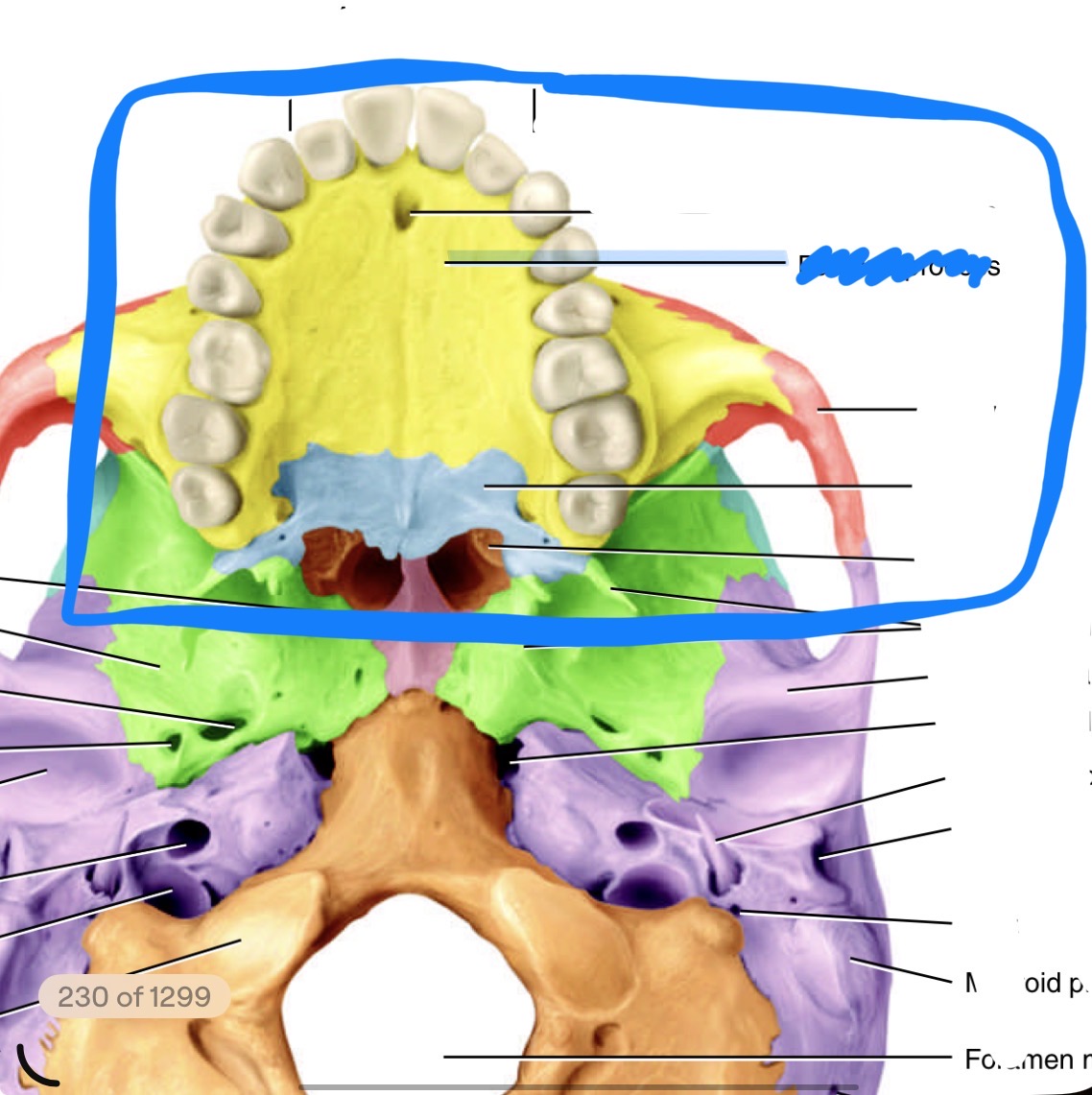
What is the name of tho marking on the maxilla bone
Palatine process
What is the red bone by the cheek
Zygomatic
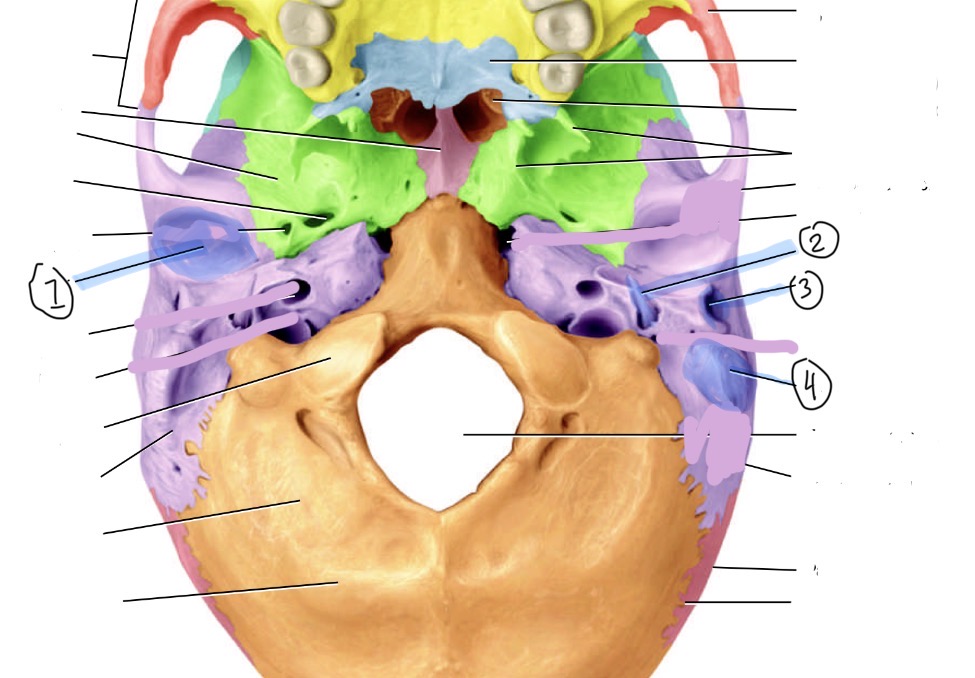
What is the blue bone behind the mouth
Palatine bone
What is the smaller pink bone in the middle
Vomer
Which bone is this
Inferior nasal concha bone
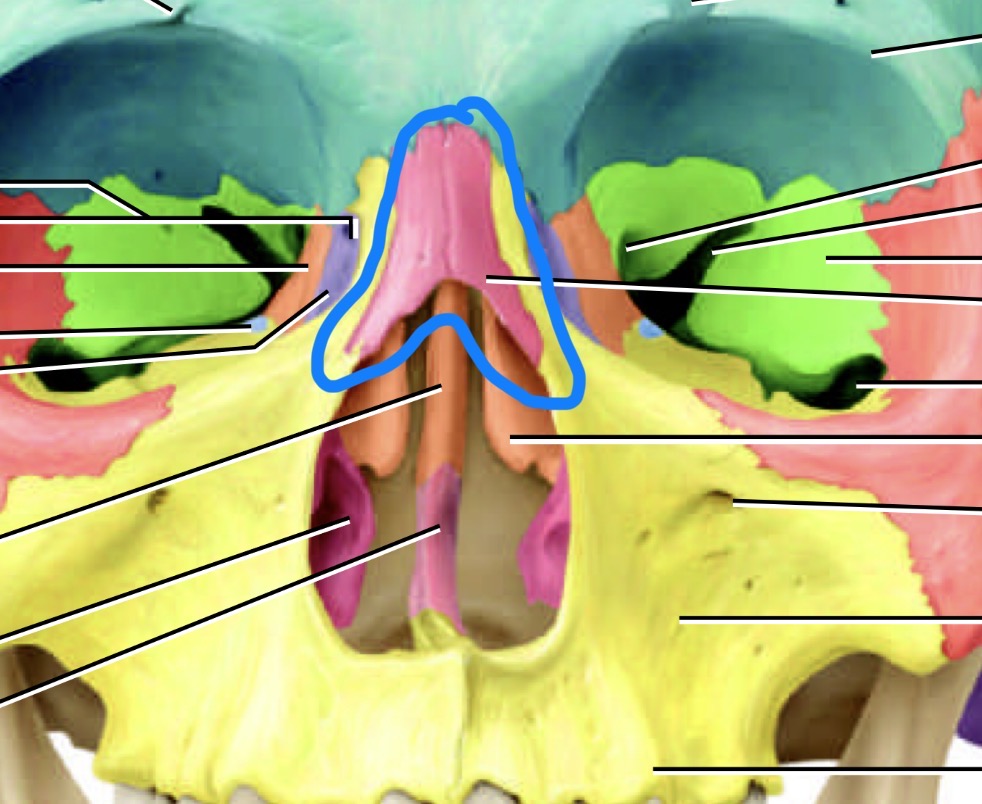
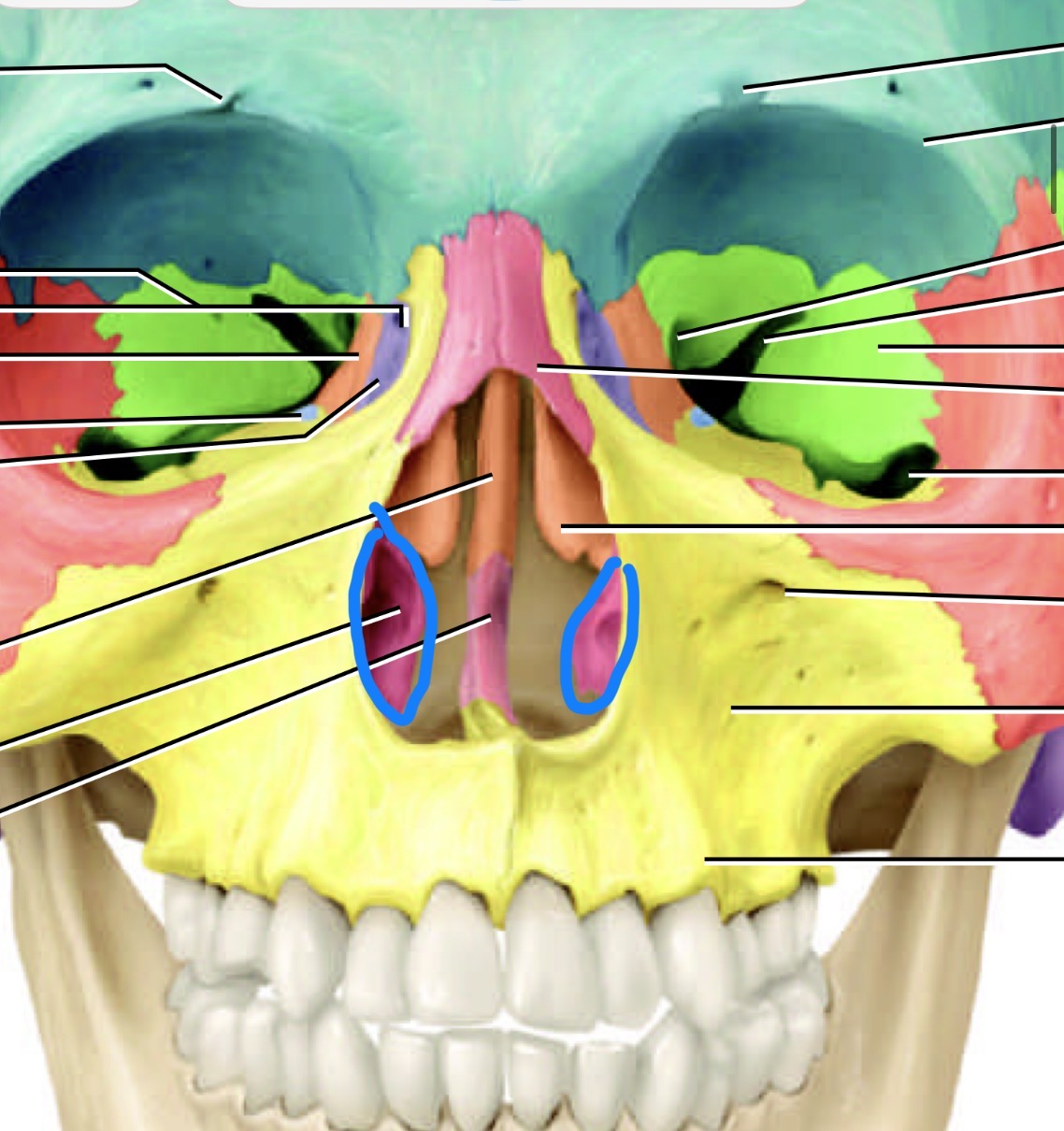
What is this bone
Nasal bone
What is the little purple bone by the sides of the nose
Lacrimal bone
What is the line separating the blue forehead part and the pink back of the head part
Coronal suture
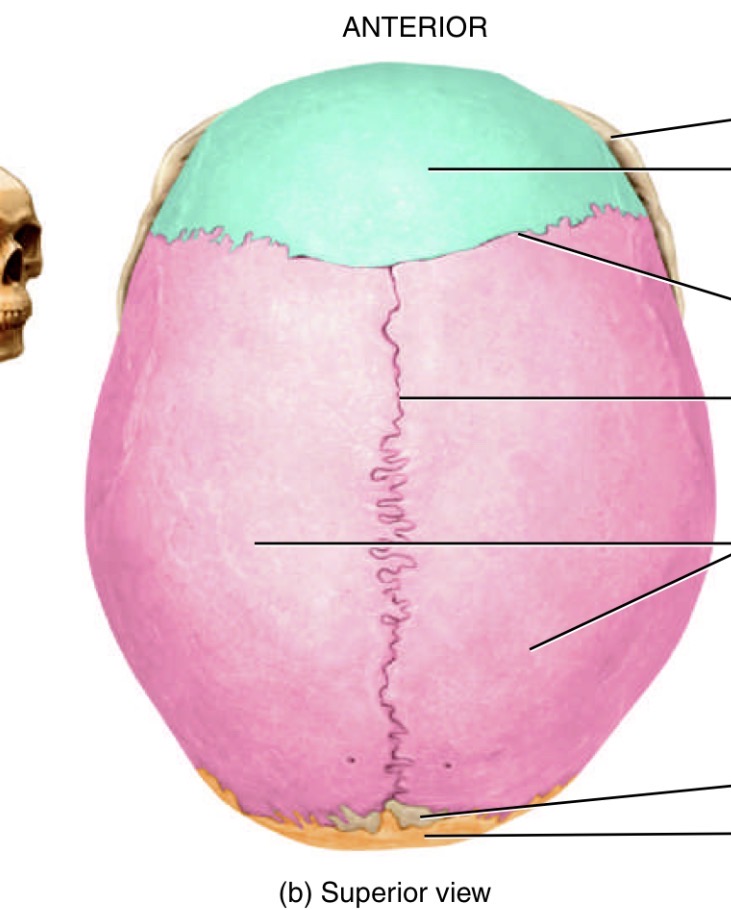
What is the line in the middle of the head
Sagittal suture
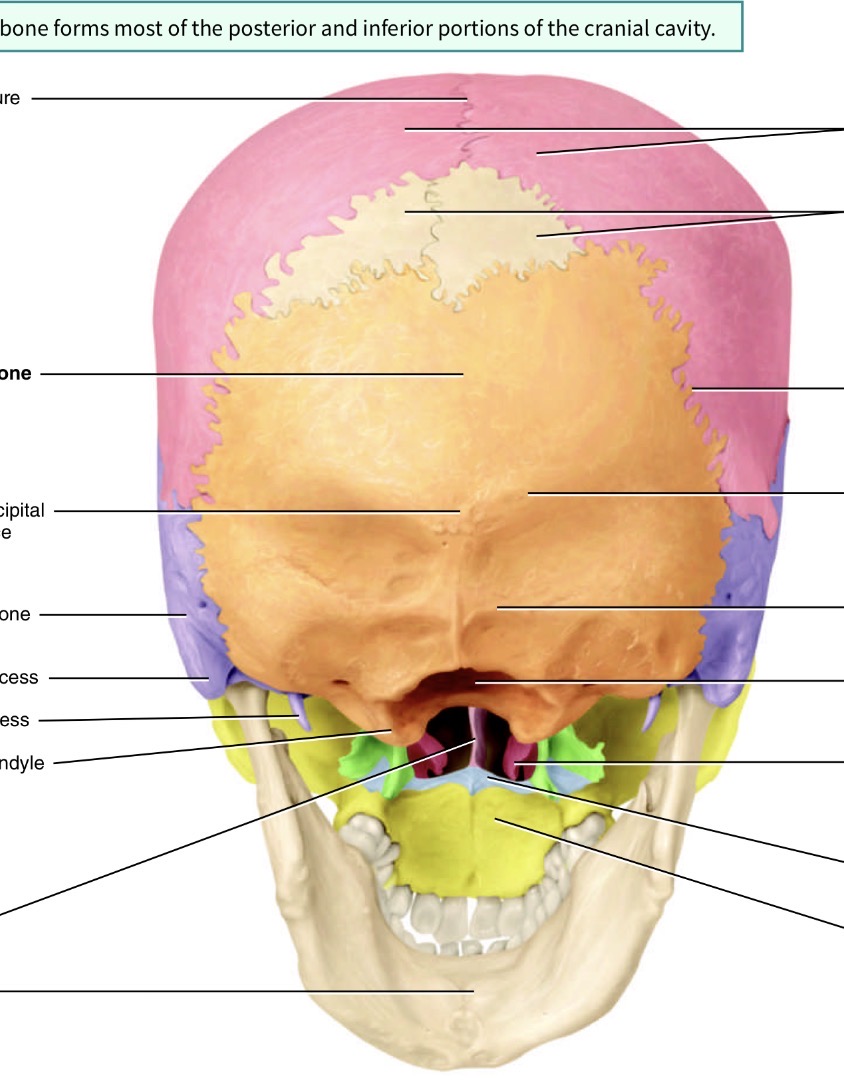
What is the line separating the orange and pink
Lambdoid suture
What is the line seperating pink and purple
Squamous suture
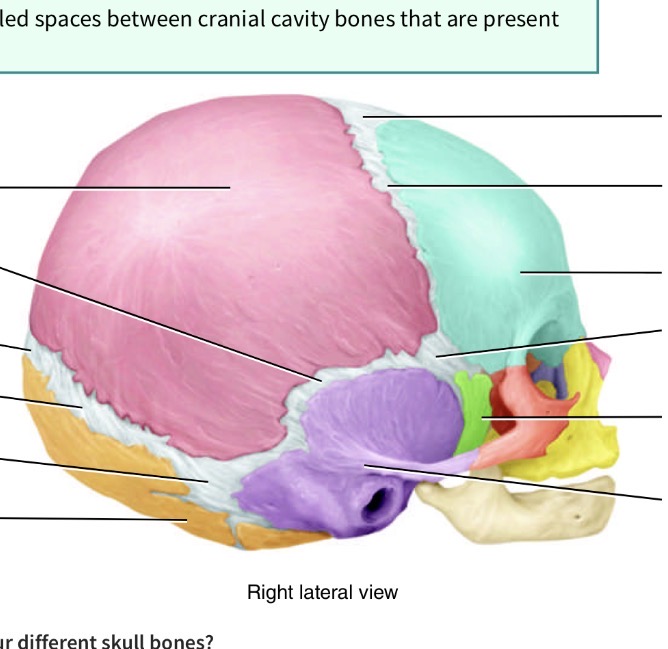
What is the fontanel( spot spot) seperating blue and pink
Anterior fontanel
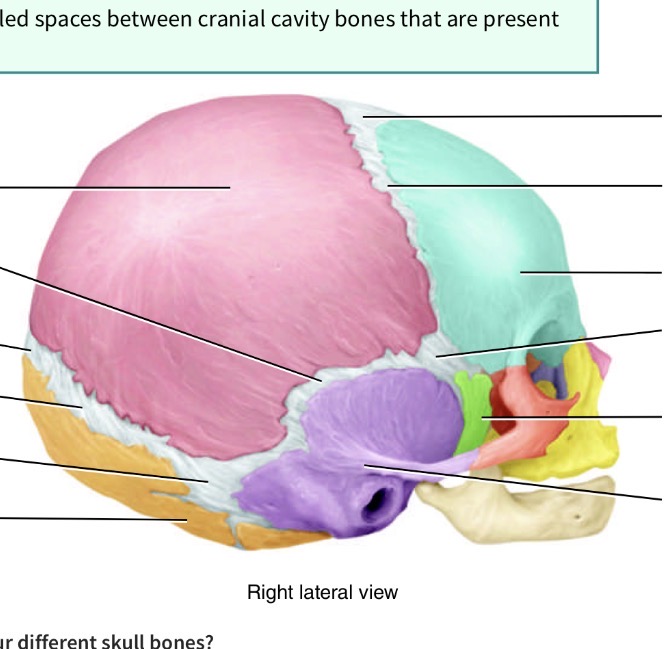
What is the fontanel( spot spot) seperating pink and orange
Posterior fontanel
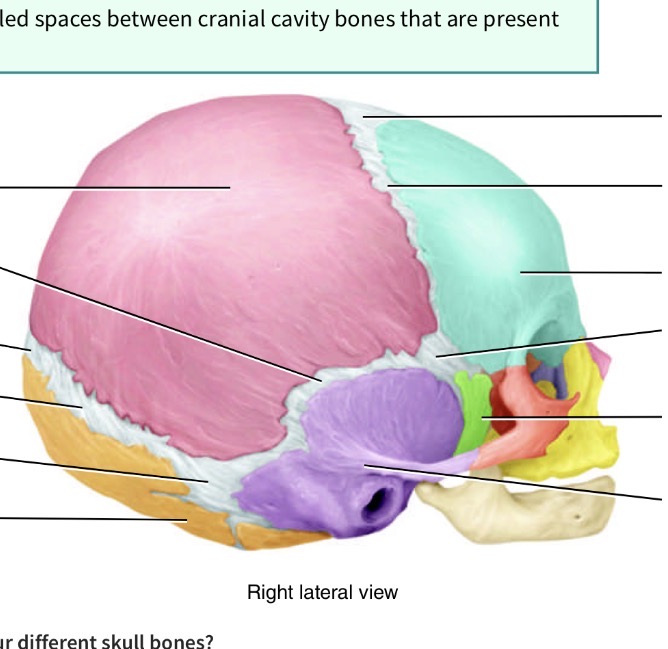
What is the fontanel( spot spot) in the junction toward back of head seperating pink, orange and purple
Posterolateral fontanel
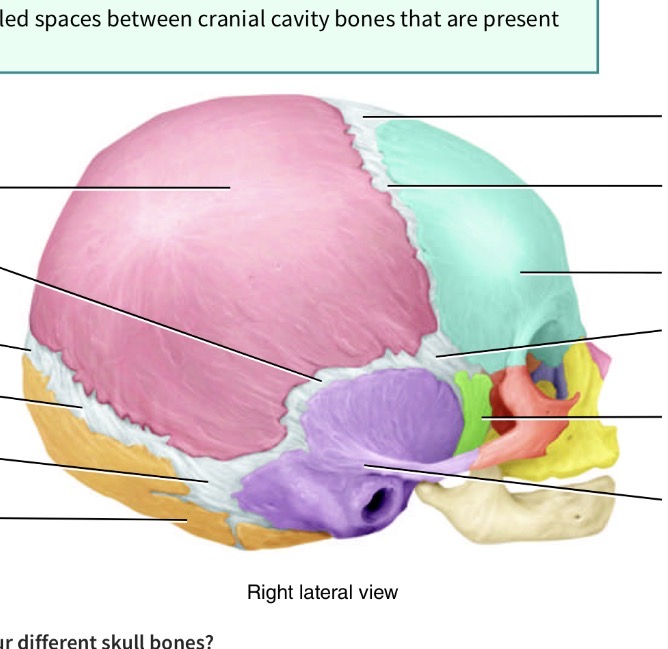
What is the fontanel( soft spot) toward the front of the head in the junction of blue purple pink and green
Anterolateral fontanel
What bones make up the sinuses
Frontal, sphenoid, ethmoidal and maxillary
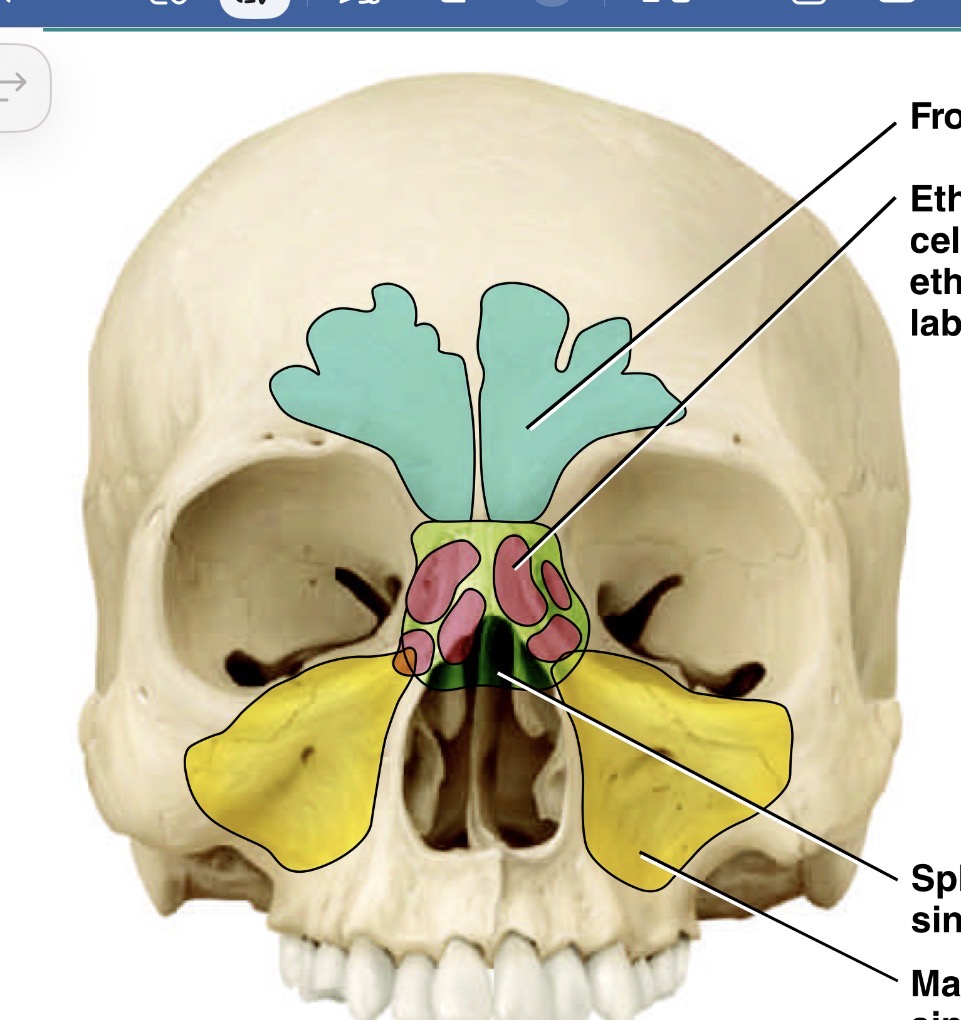
What is the blue sinus
Frontal sinus
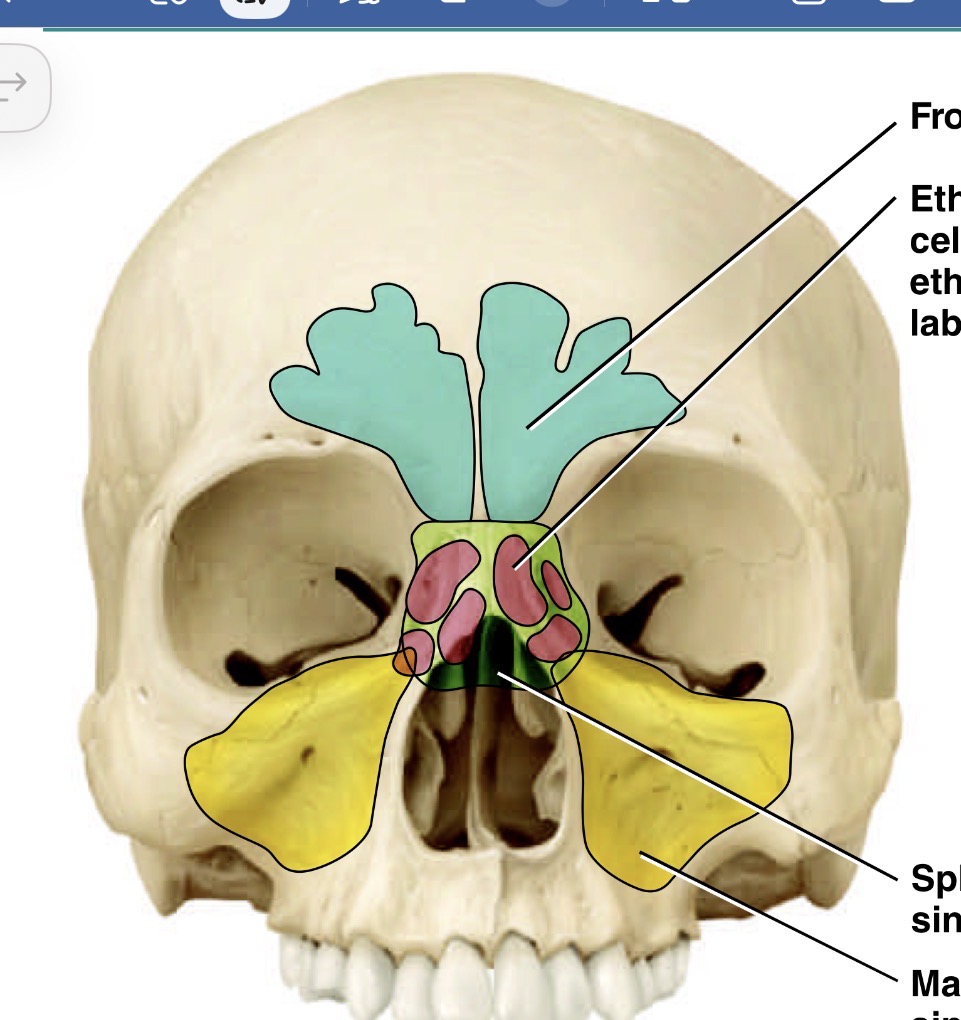
Which is the green sinus
Sphenoid sinus
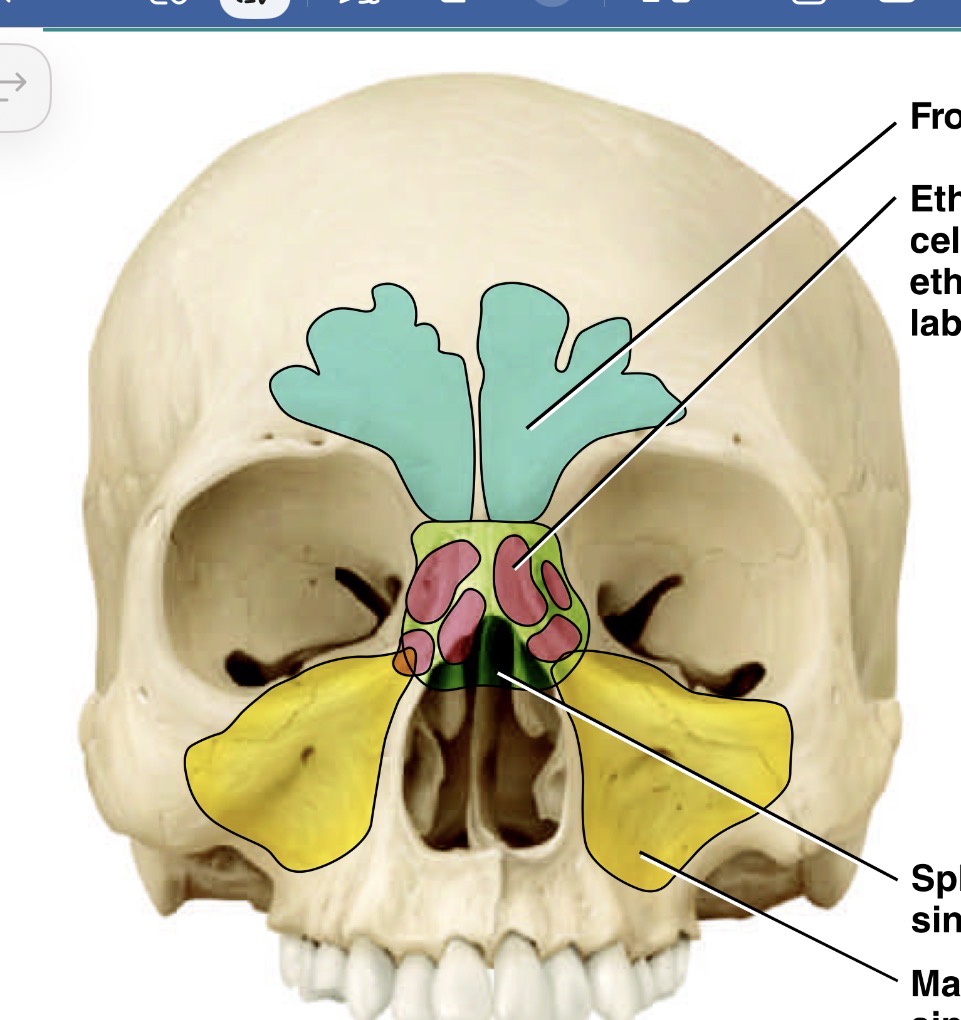
Which is the pink sinus
Ethmoid sinus
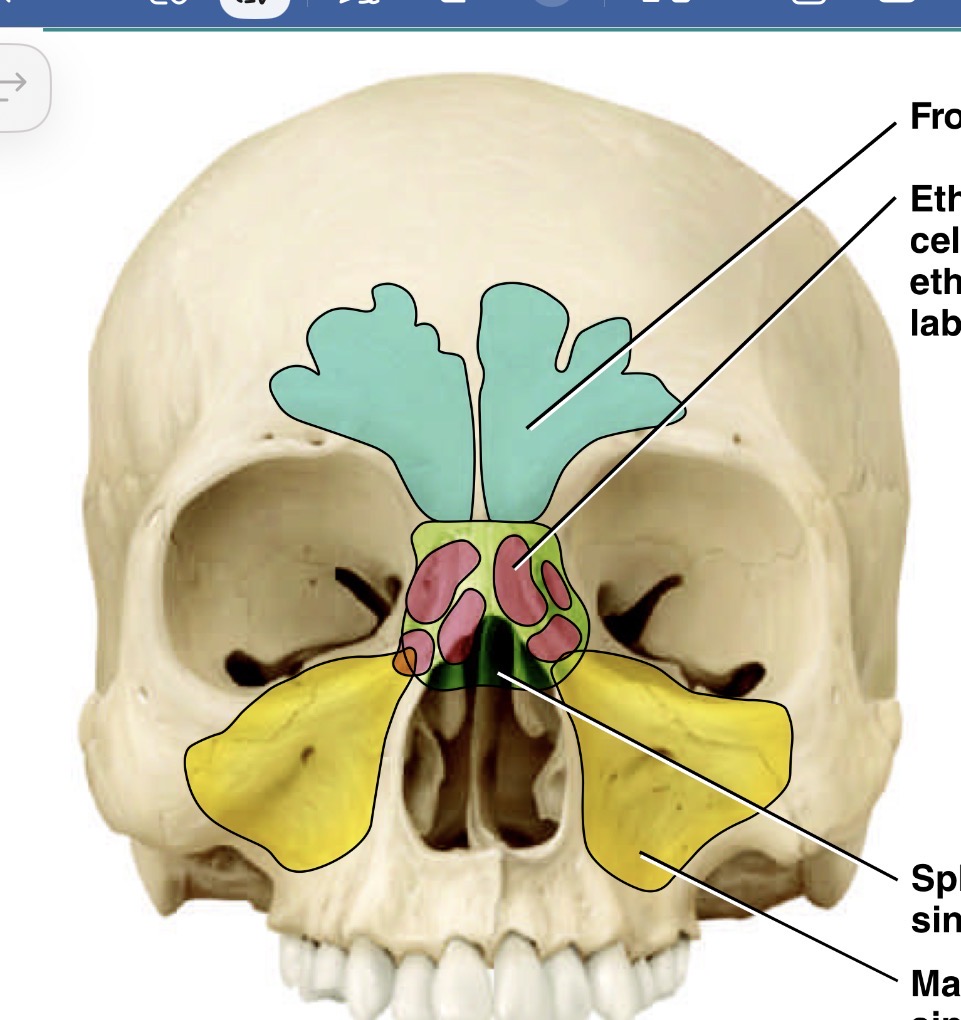
What is the yellow sinus
Maxillary sinus
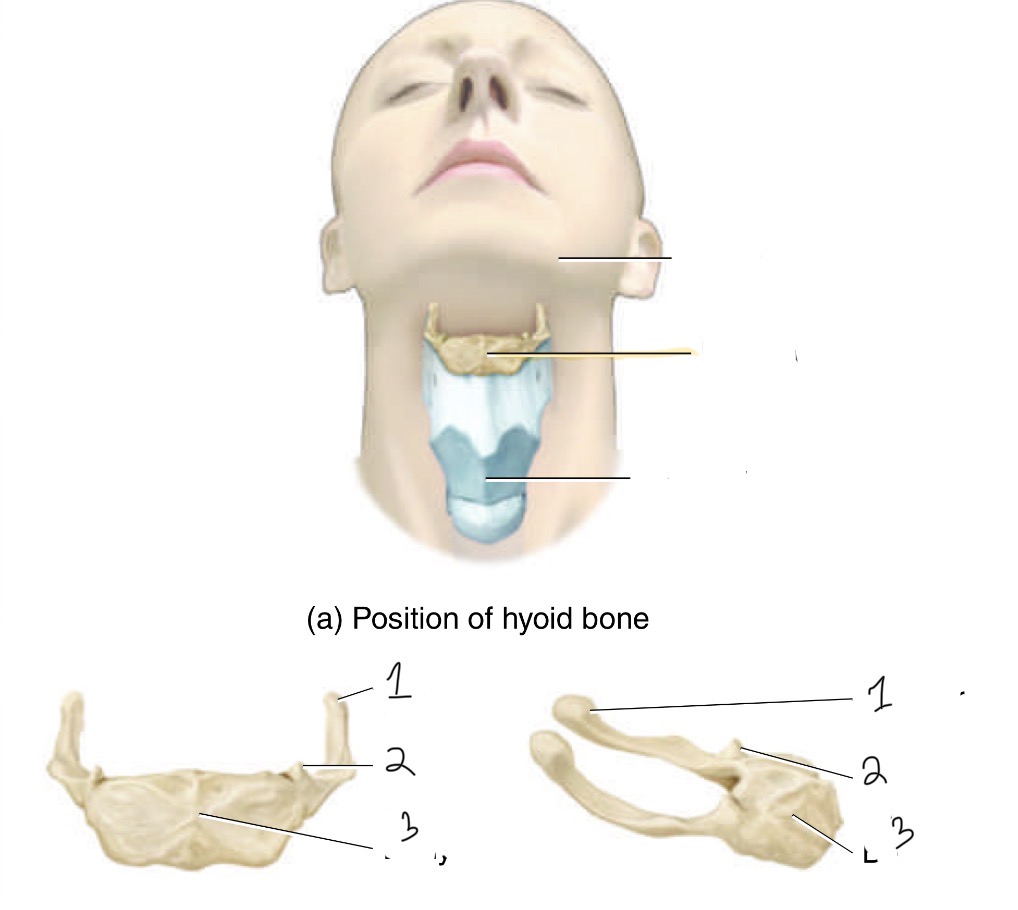
What bone is this and it’s parts
Hyoid bone. 1. Greater horn, 2. Lesser horn, and 3.body
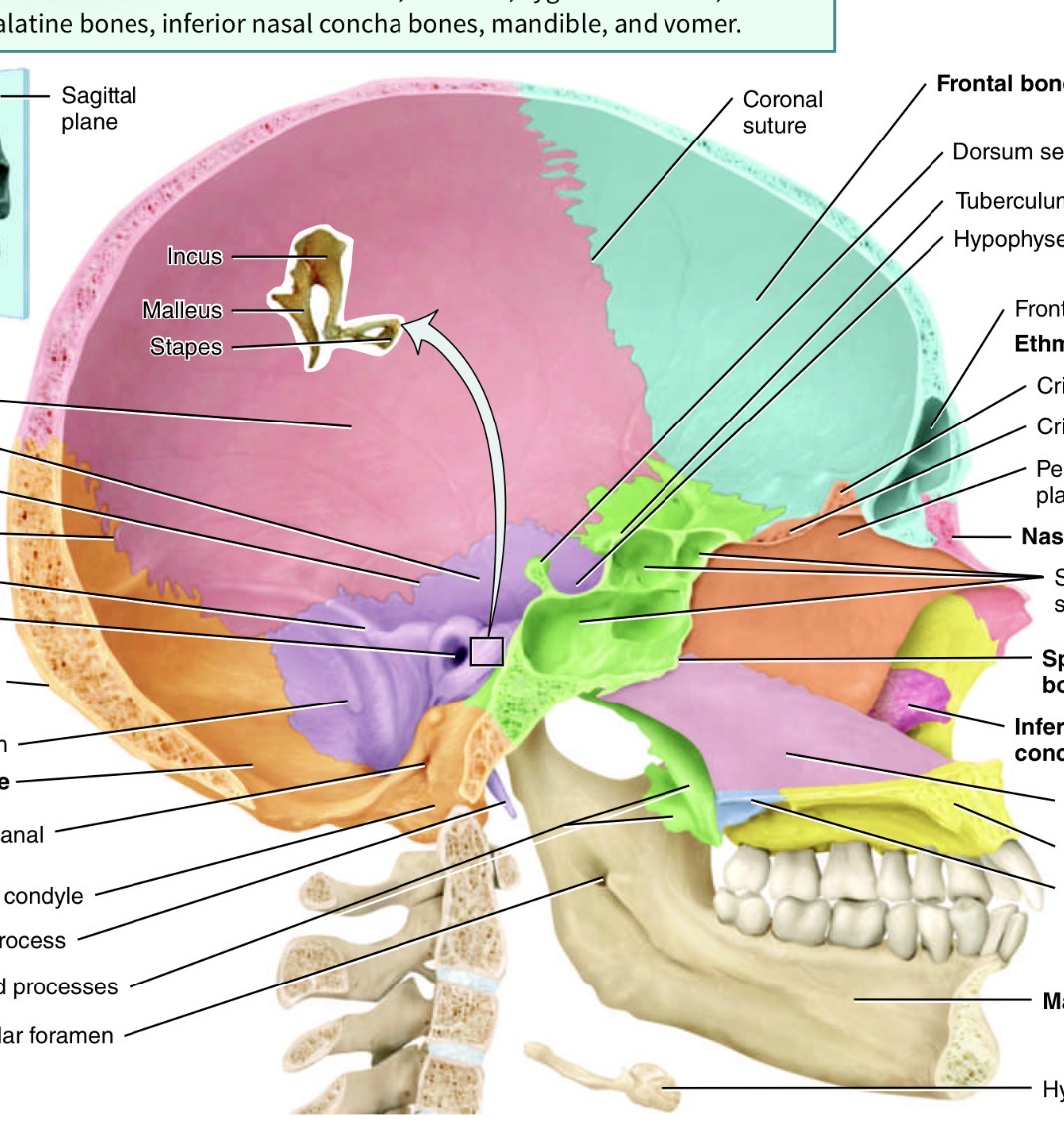
Ossicles are the bones found in the ear name the three bones
Malleus (attached to incus),incus (tear drop shapes)and stapes (donut shaped)
What is in between vertebrae
Intervertebral discs made of fibrocartilage to causation and absorb shock
What is the vertebral foramen
Spaces in between adjacent vertebral body
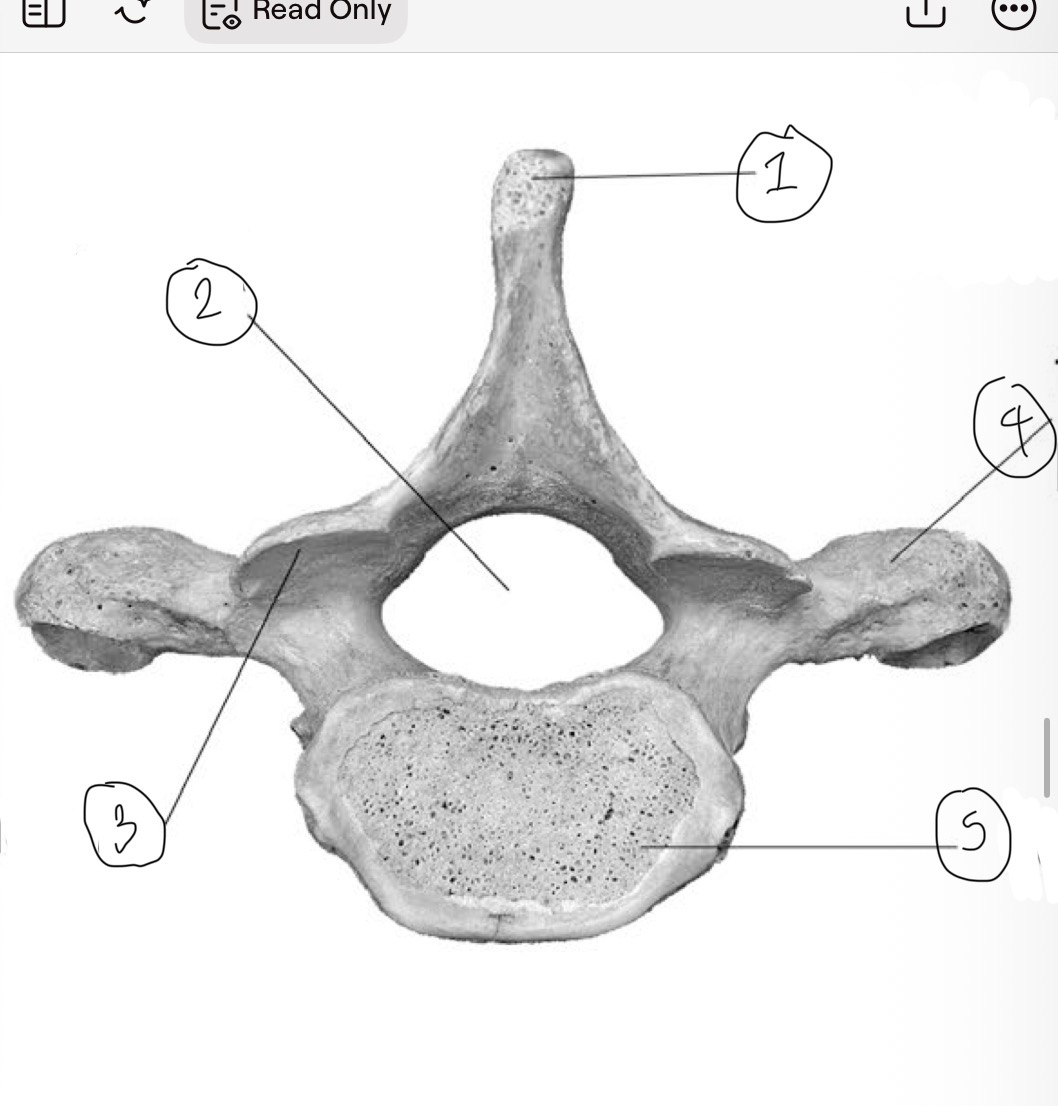
What is 1
Spinous process
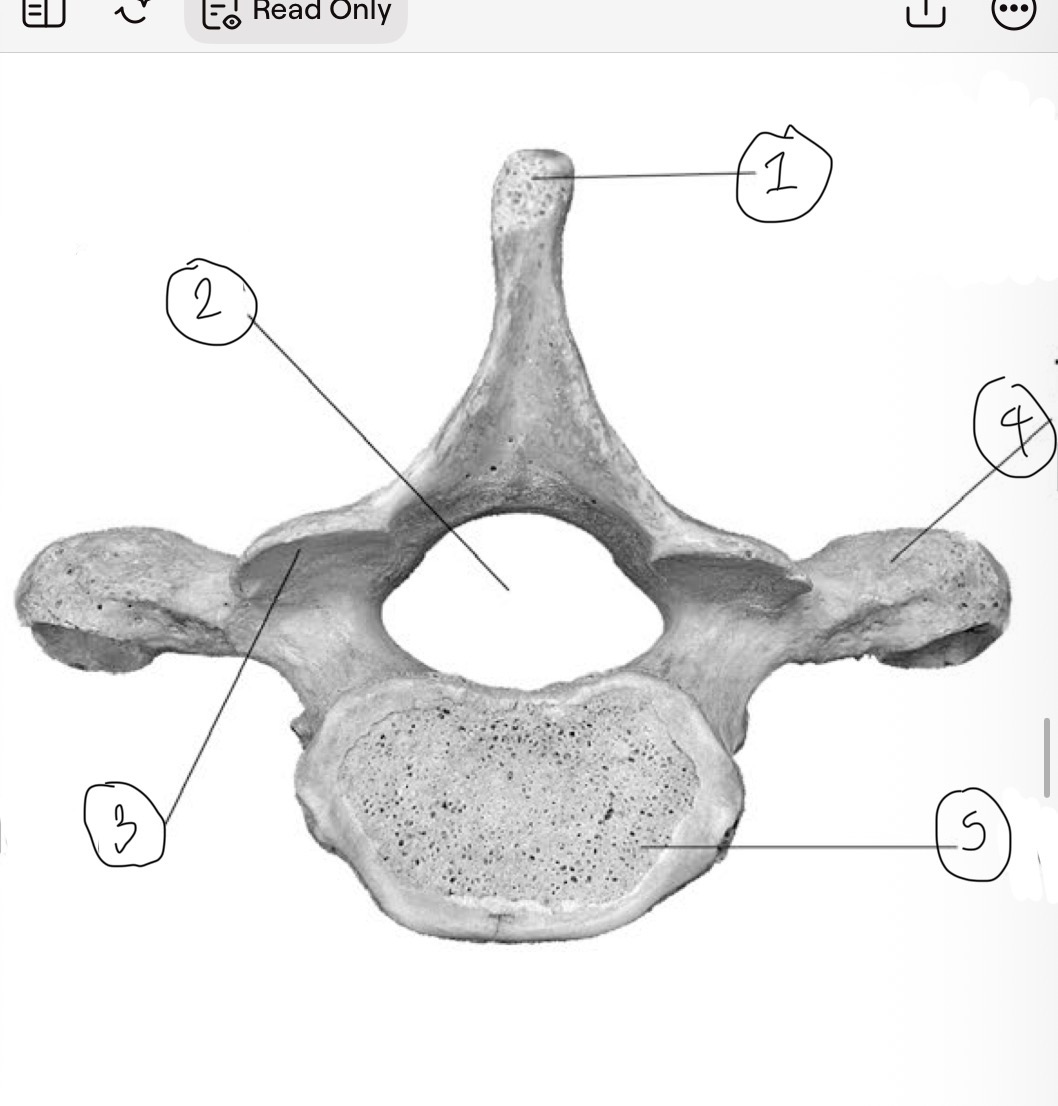
What is 2
Vertebral foramen
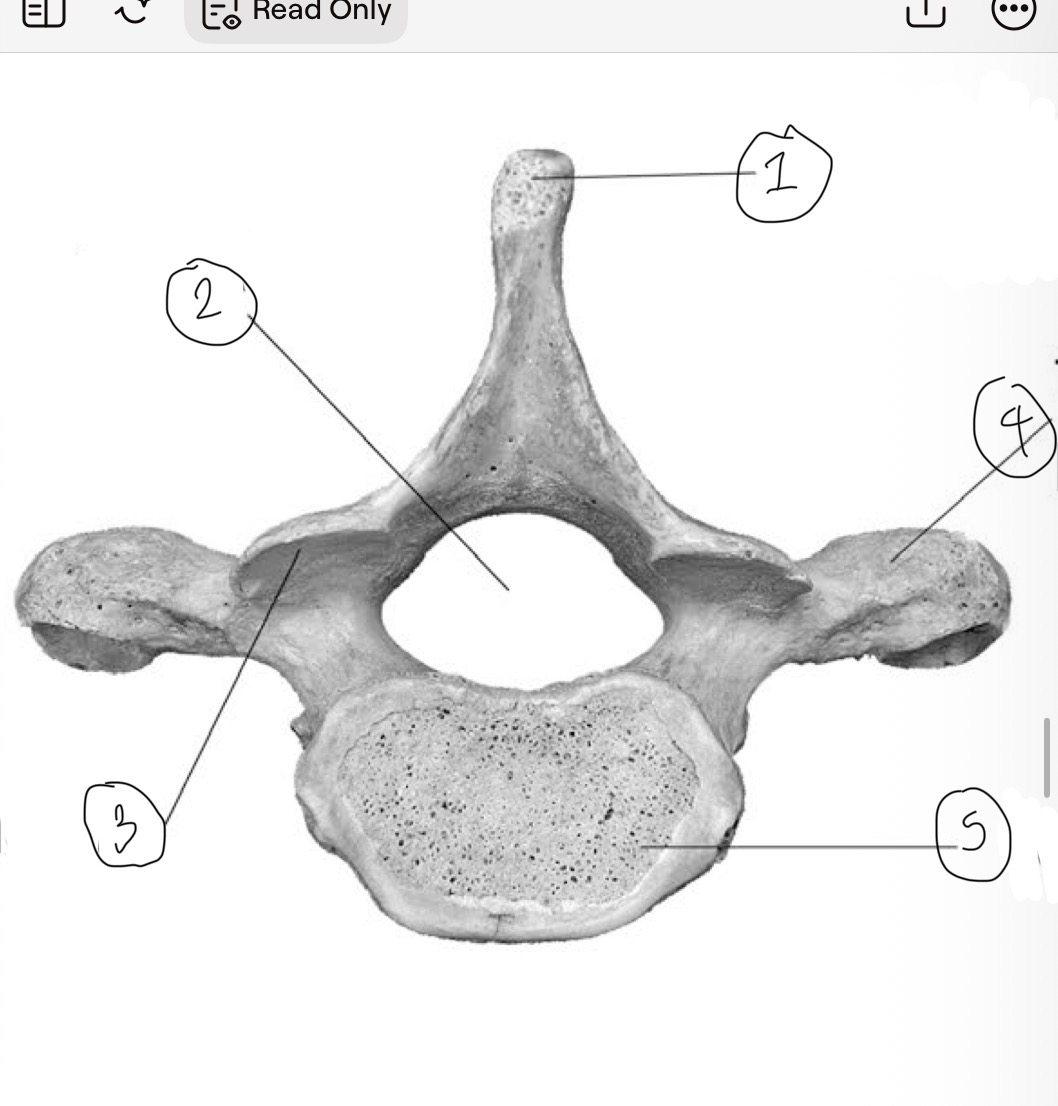
What is 3
Inferior articular facet
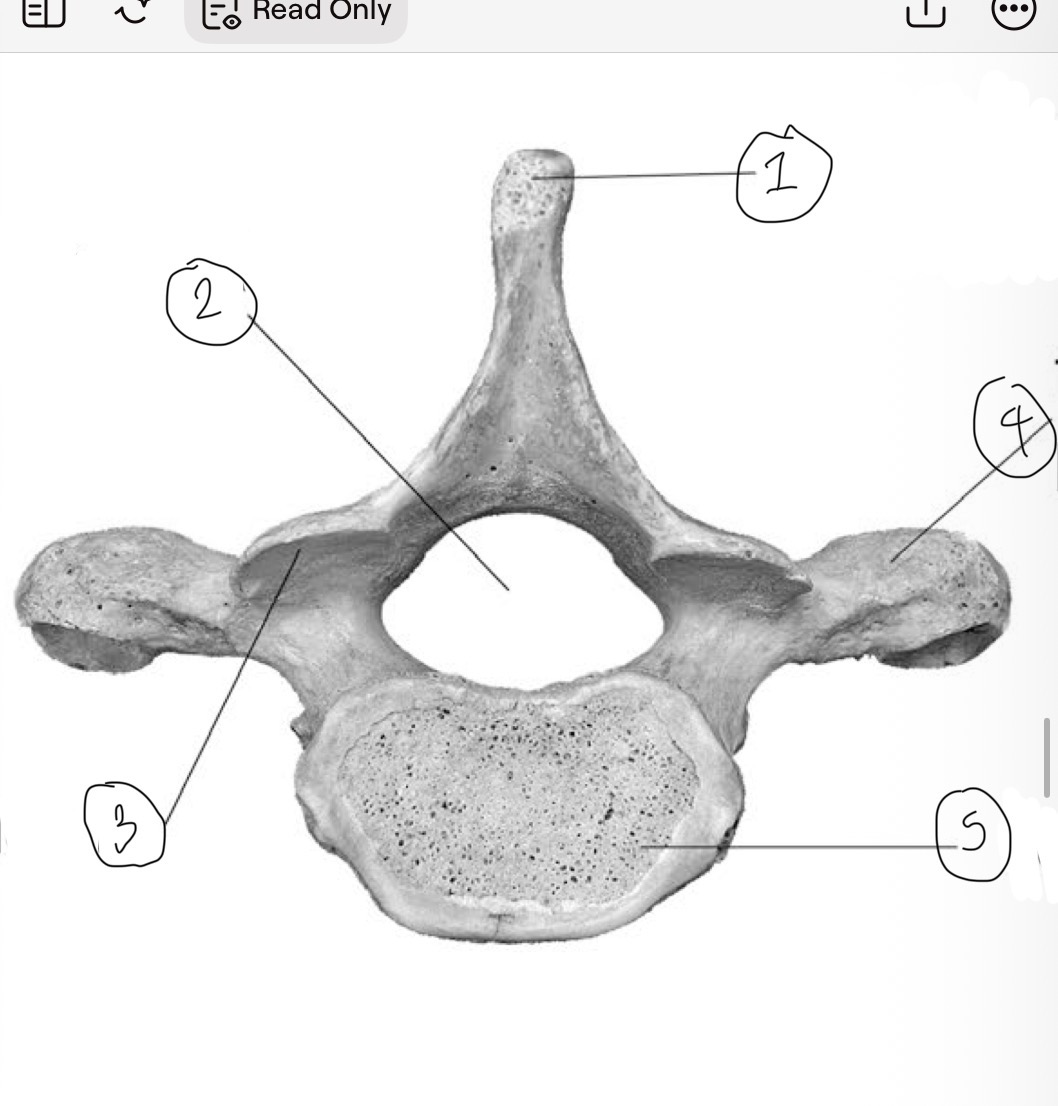
What is 4
Transverse process
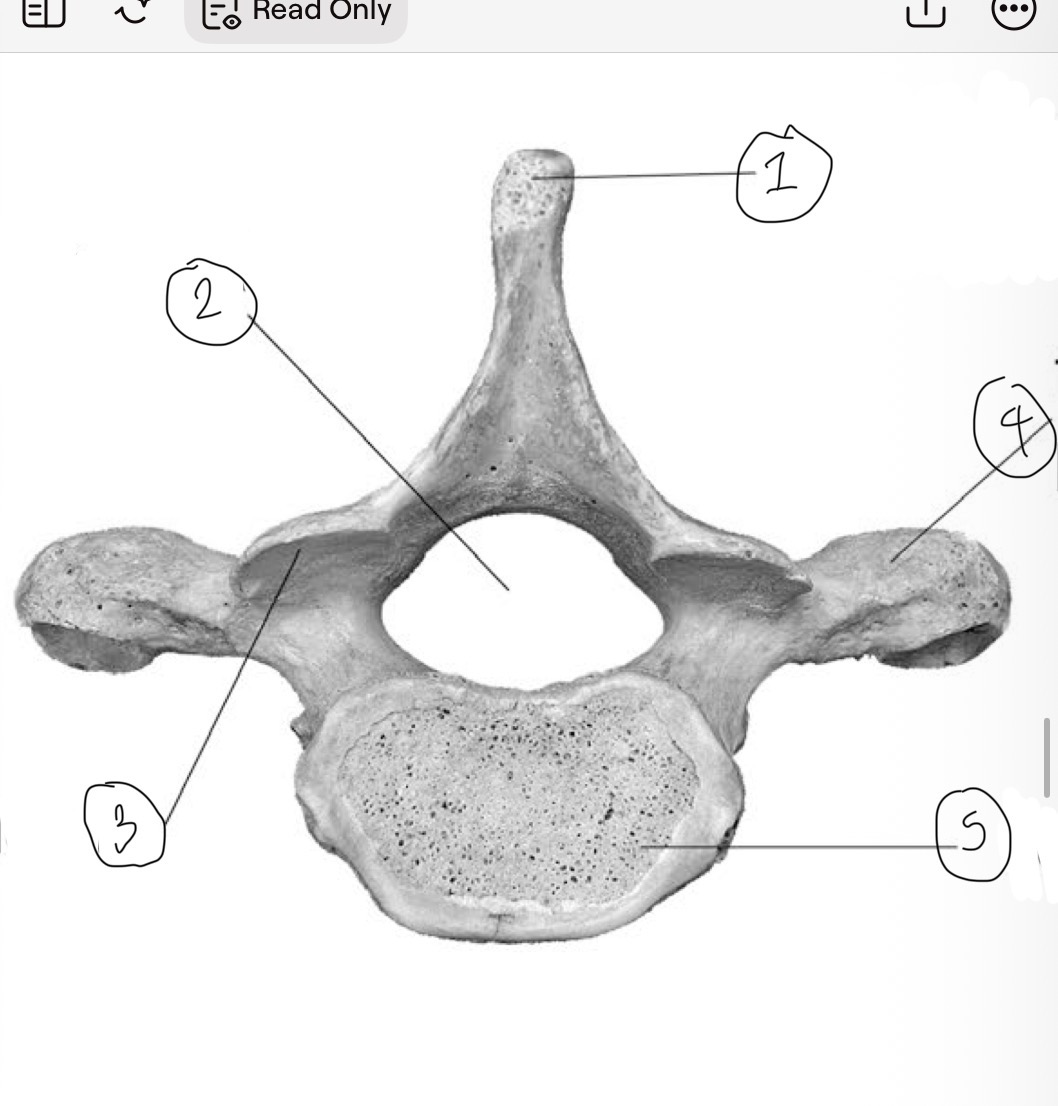
What is 5
Centrum
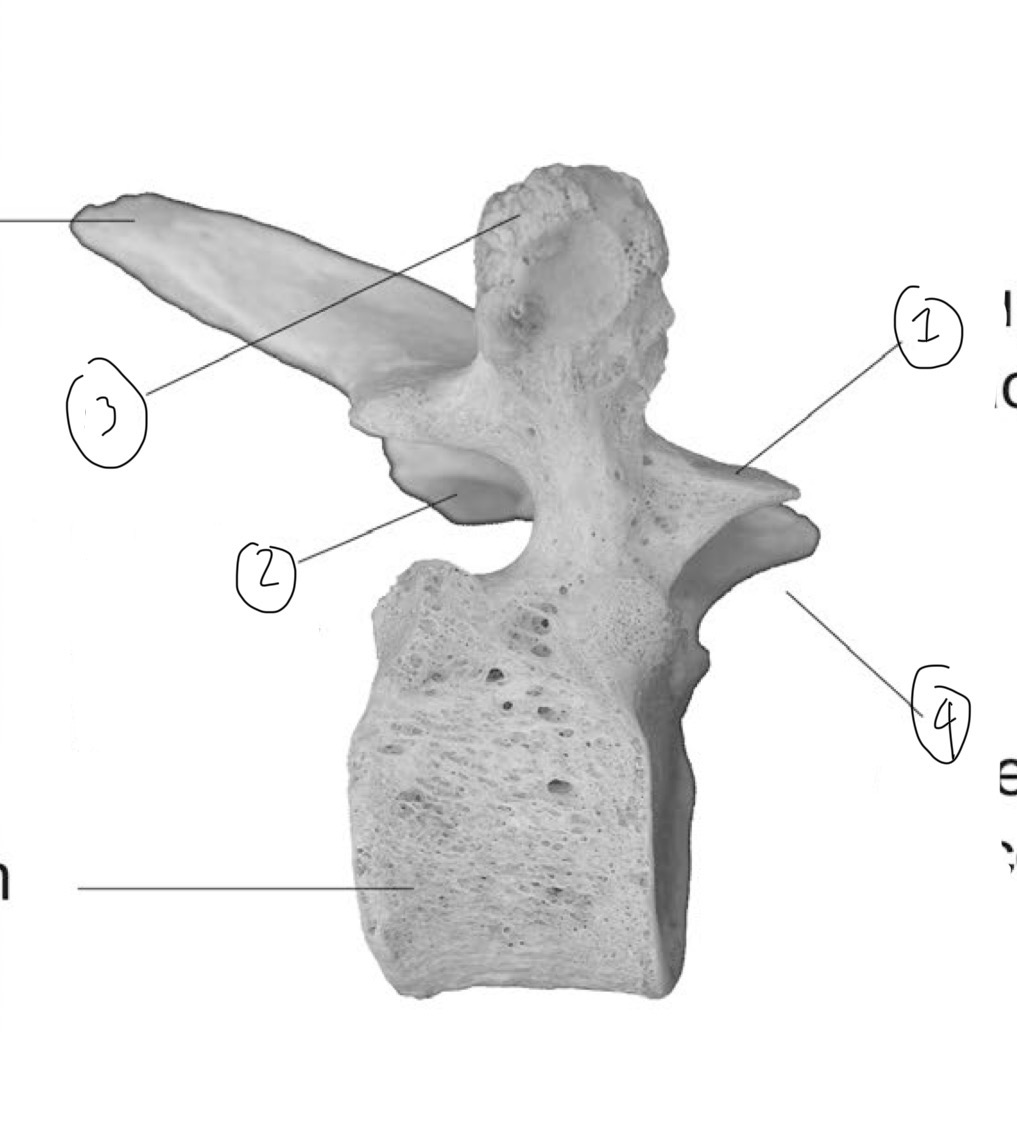
What is 1
Superior articular facet
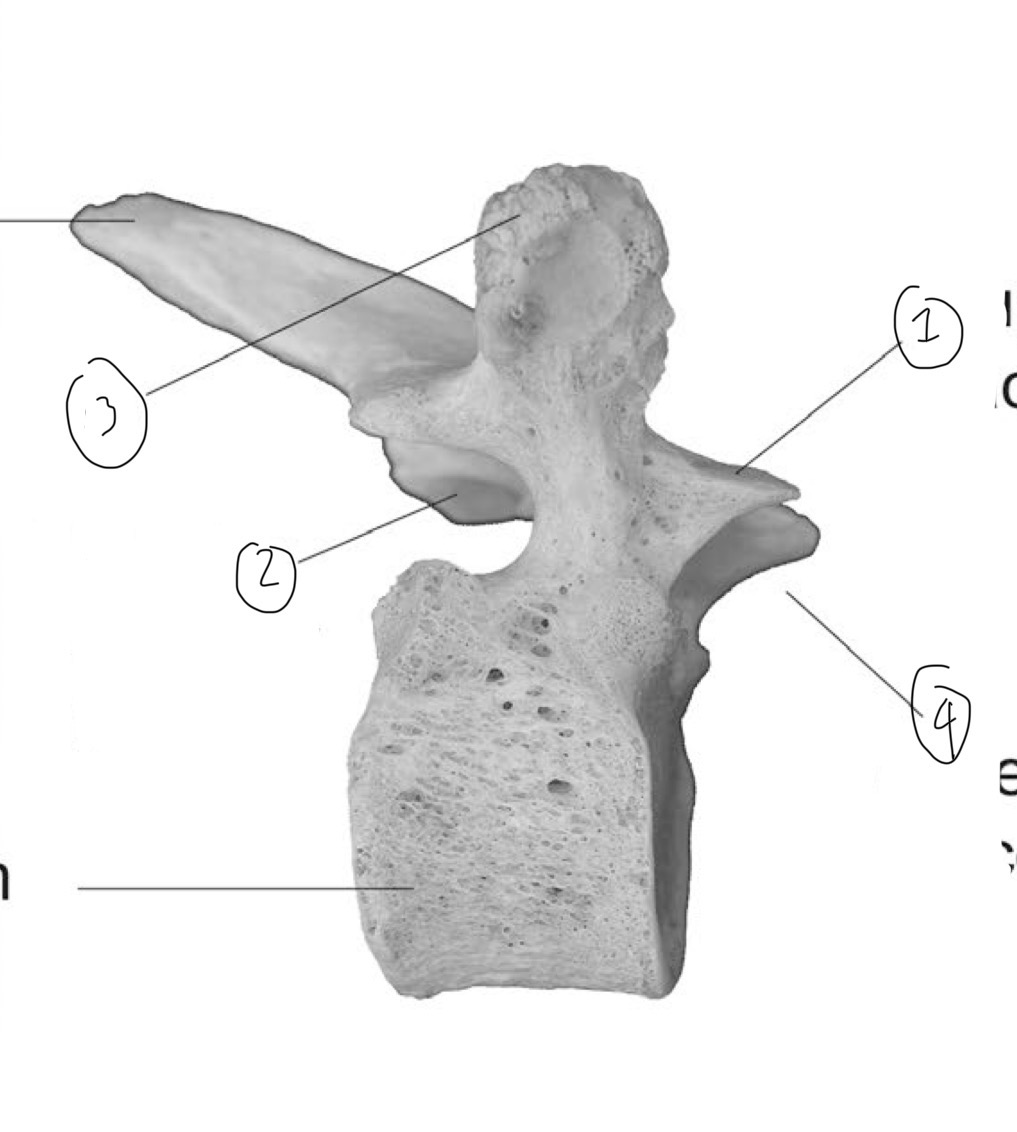
What is 2
Inferior articular facet
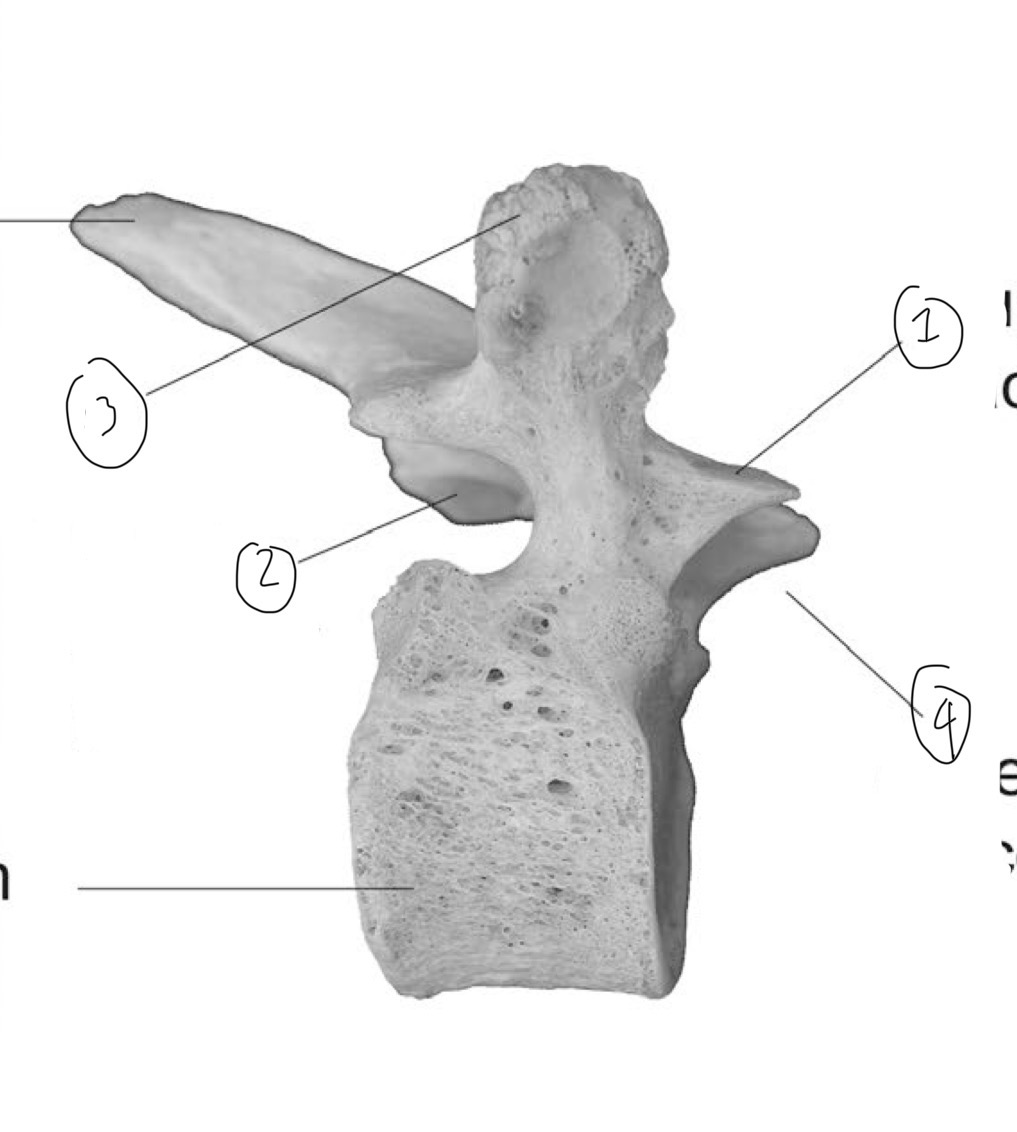
What is 3
Transverse process (side view)
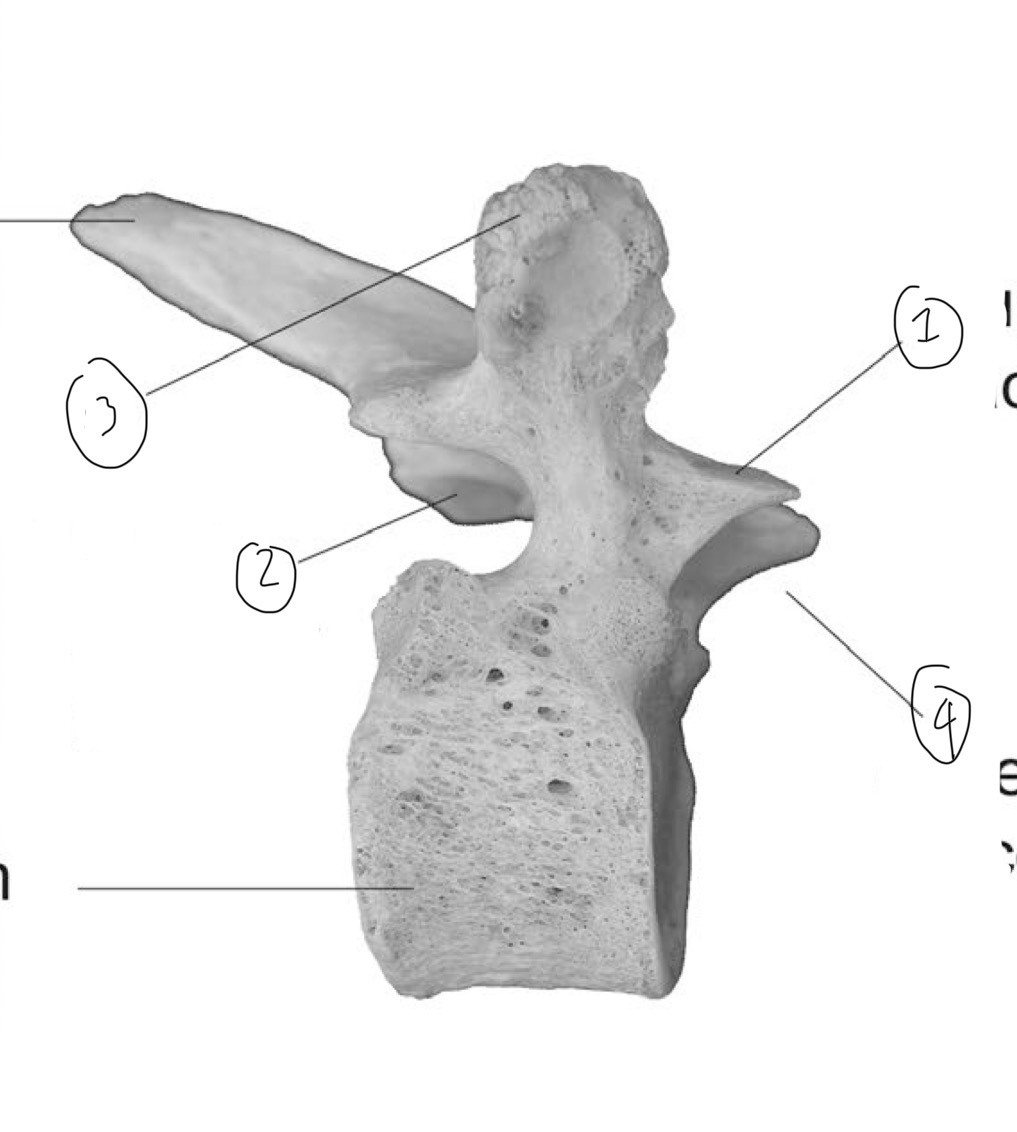
What is 4
Superior articular process
What are the 5 regions of vertebral column
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar, sacrum and coccyx
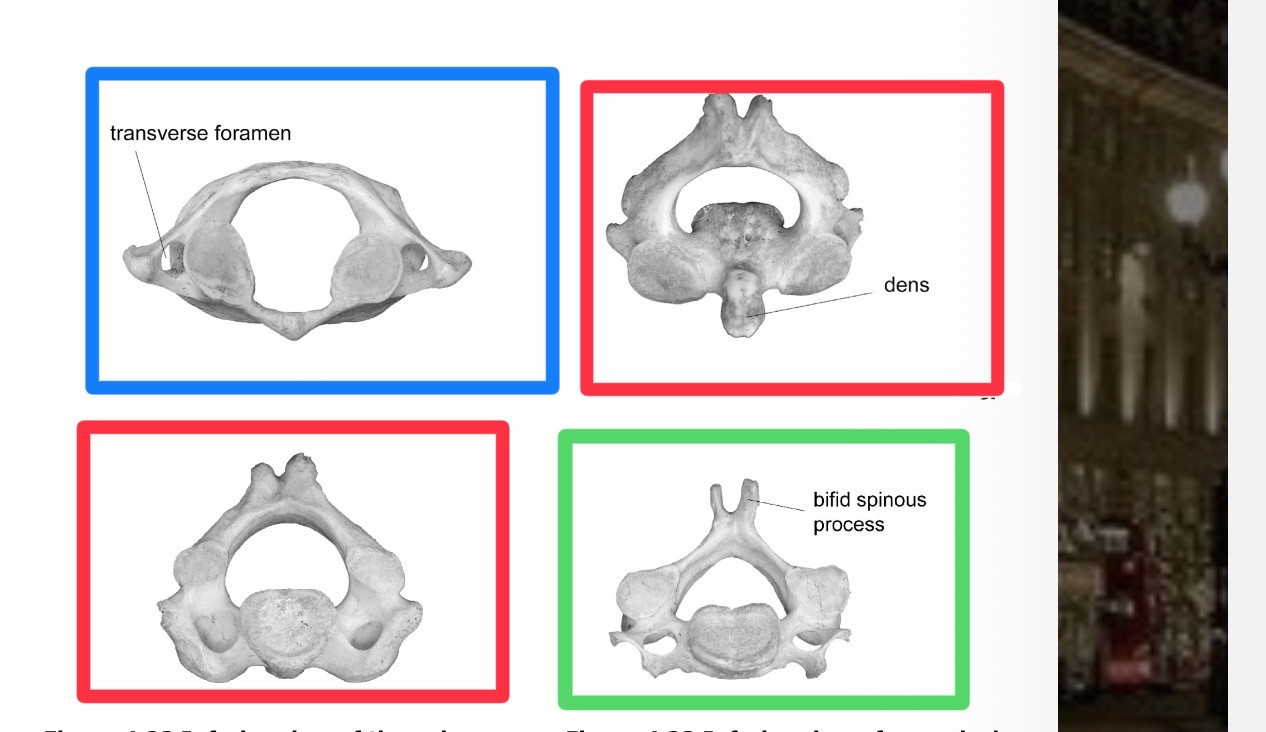
Which is the blue one and which region
Atlas in cervical vertebrae
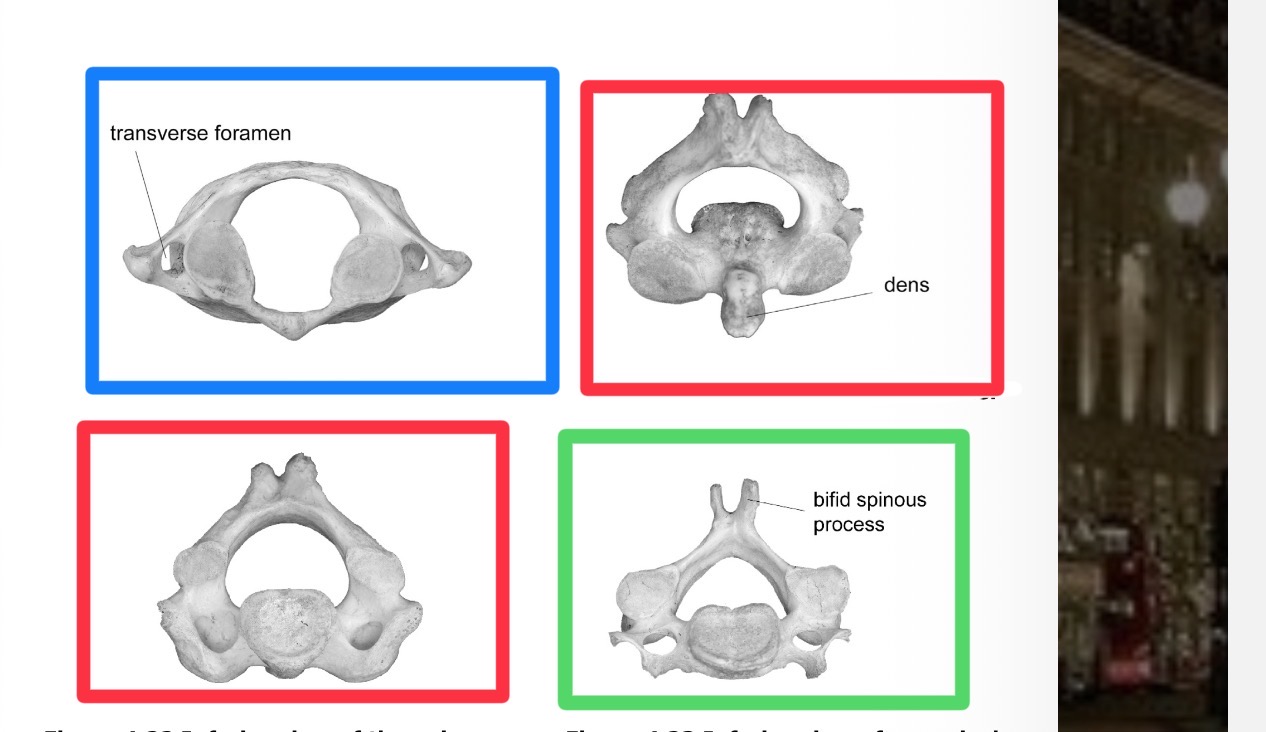
Which is red and which region
Axis in the cervical vertebrae
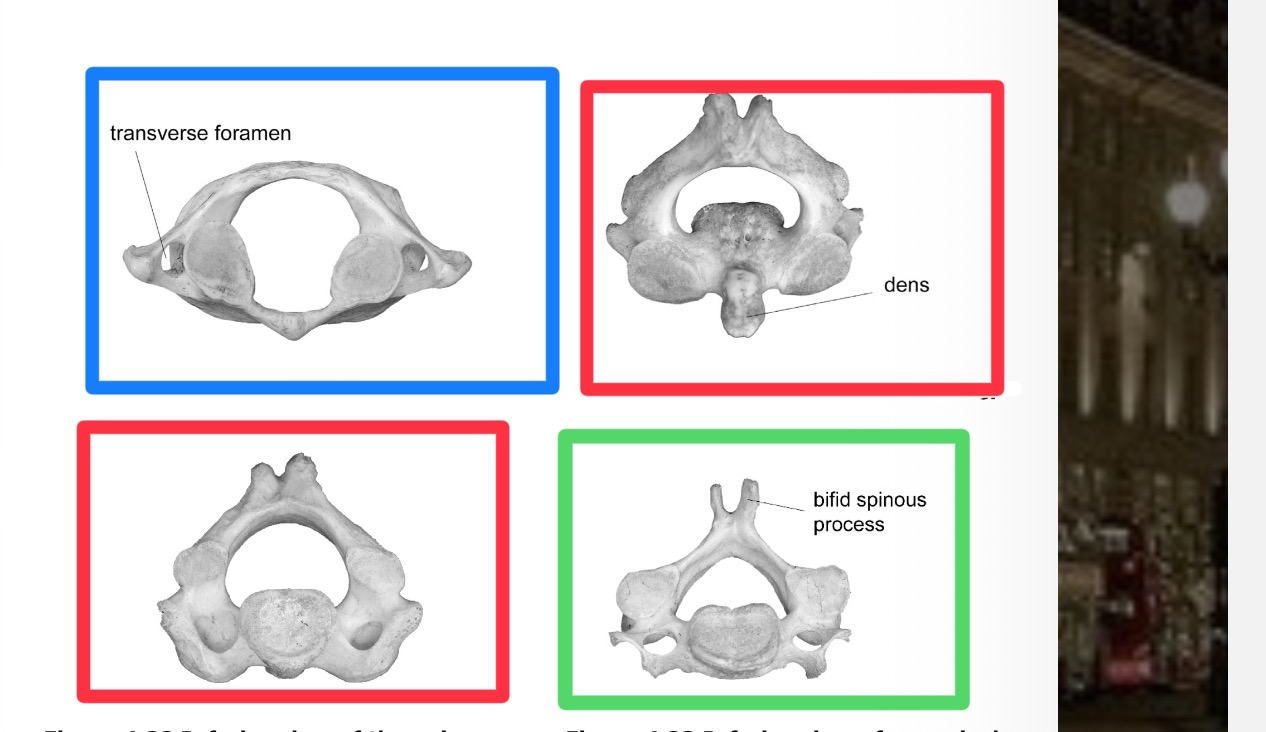
Which is green
Cervical vertebrae
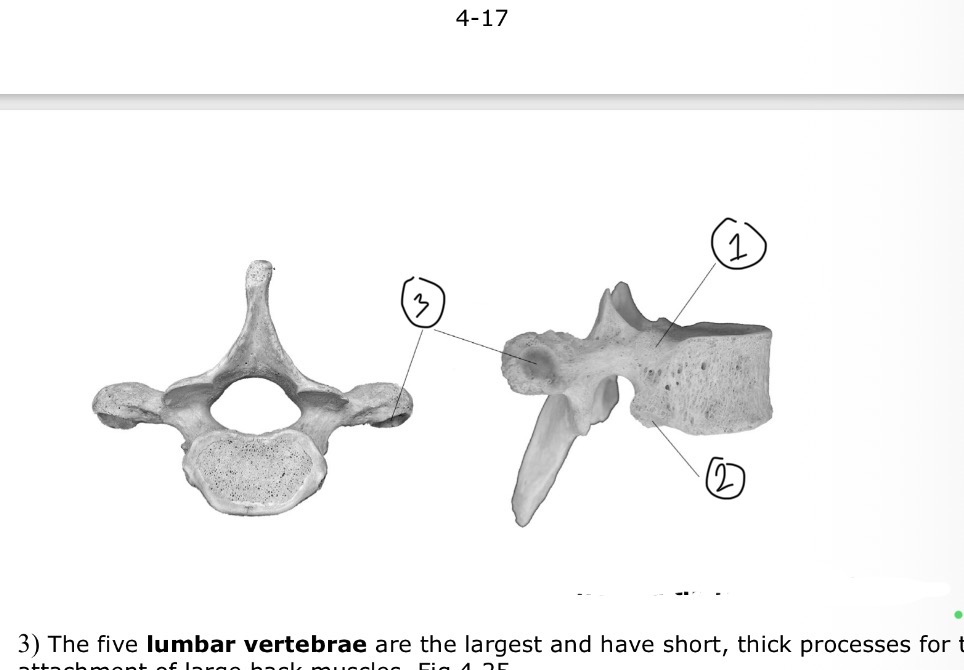
Which vertebrae and its parts
Thoracic vertebrae 1. Superior demifacet, 2.inferior demifacet, 3. Facet for ribs
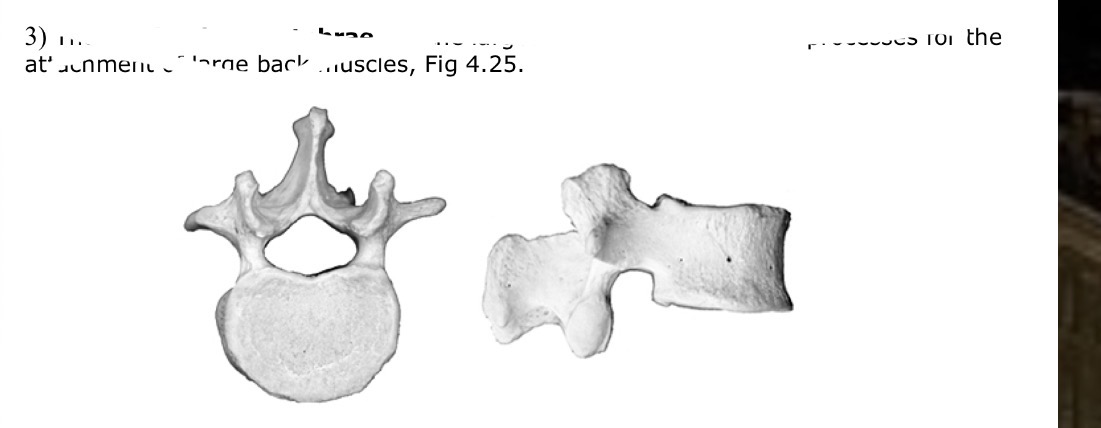
Which vertebrae
Lumbar vertebrae
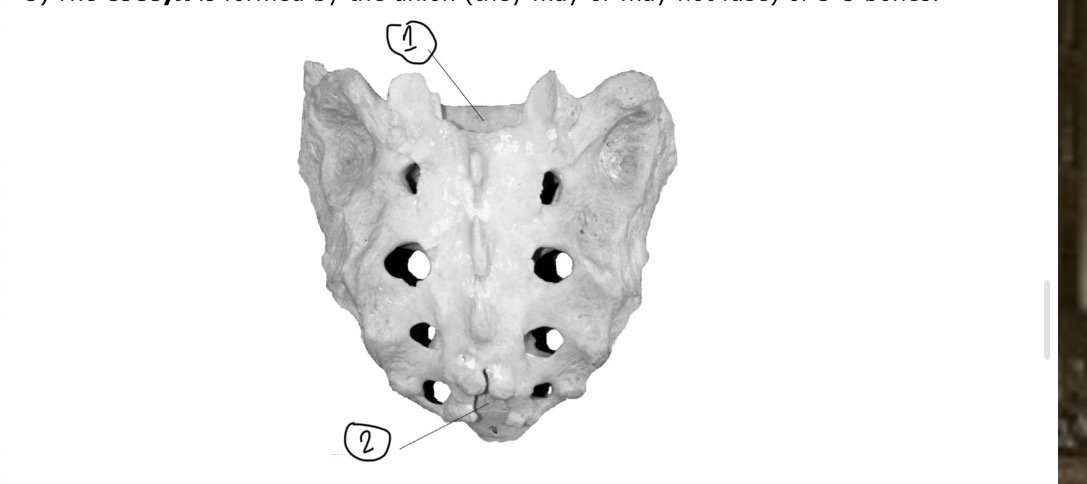
What is this an ids parts
Sacrum. 1. Sacral canal 2. Sacral hiatus
What makes the thoracic cage
Sternum, ribs and costal cartilage
What 3 parts of sternum
Manubrium, body and xiphoid process