15- Tissue & Organ System Physiology
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Tissue
A group of cells with similar structures that work together to perform a specific function
Tissue changes are the result of
Development, growth, aging, trauma, and disease
Four primary tissue types
-Epithelial
-Connective
-Muscle
-Nervous
Epithelium
-Covers internal and external surfaces
-Forms most glands
-Consists almost entirely of cells with little extracellular matrix between them
Epithelium characteristics
-Free surface = Layer of cells with one surface not in contact with other cells
-Basement membrane = Attaches cells to underlying tissues (Protein/carbohydrate secretion made by epithelial and underlying cells)
-Blood vessels do not extend from the underlying tissues into the epithelium
Major functions of epithelial tissue include
Protecting underlying structures
-Minimizes abrasion risk to underlying structures
Acting as barriers
-Prevents entry of many substances and organisms into the body
Selective permeability
-Allows movement of certain substances through the epithelium
Secreting/absorbing substances
-Release of sweat, mucus, or enzymes into outer environment
-Contain carrier molecules that regulate the absorption of materials
Epithelial classification is based on
Number of cell layers –
-Simple = A single layer of cells
-Stratified = More than one layer of cells stacked on top of each other
Shape of the cells –
-Squamous = Flat cells
-Cuboidal = Cubelike cells
-Columnar = Column-like (tall and thin)
What type of name is given to epithelia?
Compound name
-(e.g., simple squamous, simple columnar, etc.)
-When stratified: Name according to the cell shape at the free surface (e.g., stratified squamous)
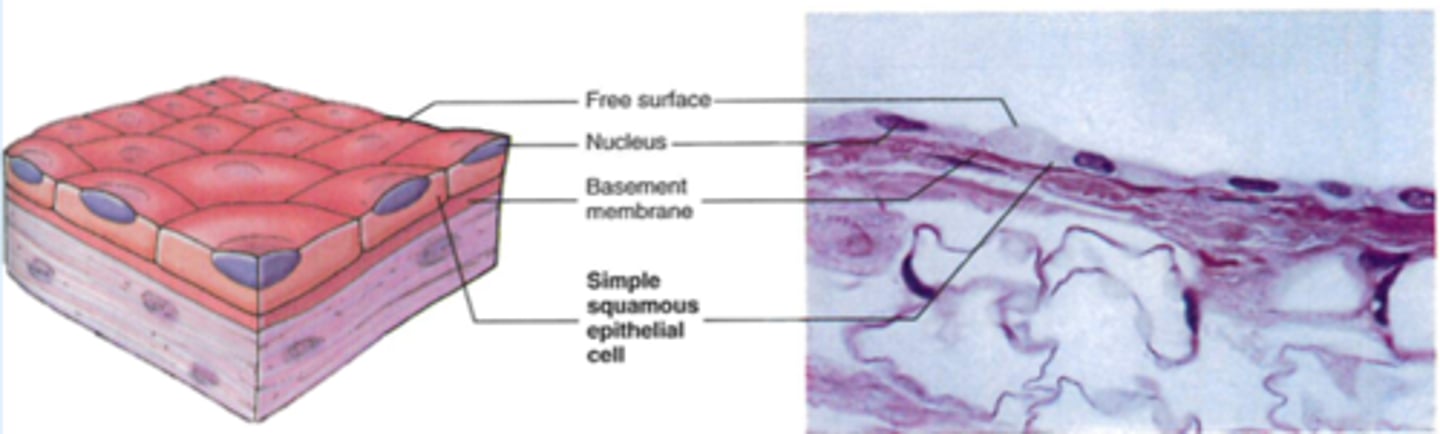
Simple Squamous epithelium
-Location: Blood vessel lining, heart, serous membranes, alveoli
-Structure: Single layer of thin, flat cells
-Function: Diffusion, filtration, and friction protection
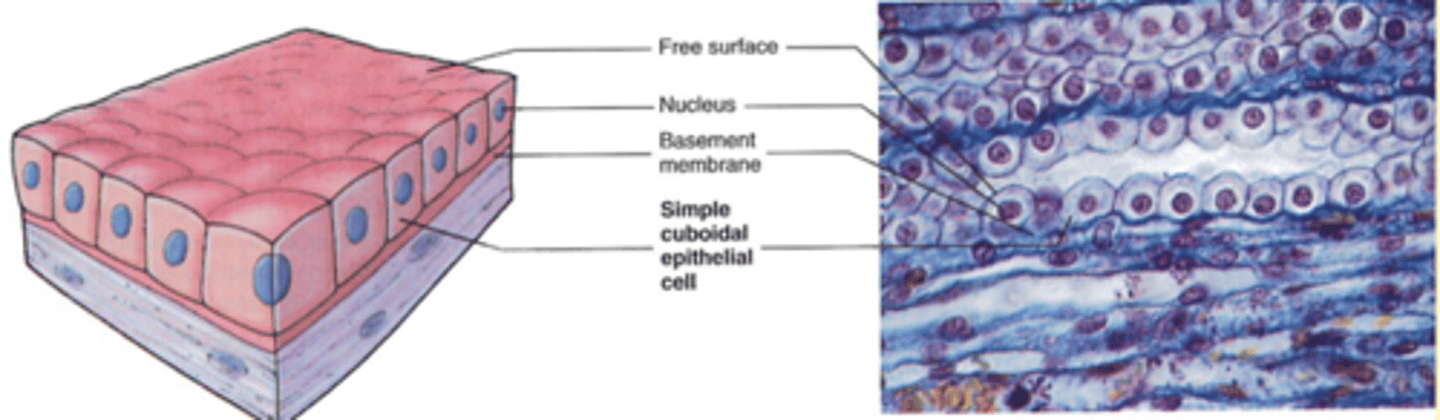
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
-Location: Kidney tubules, glands, bronchioles, choroid plexus (brain)
-Structure: Single layer of cube-shaped cells; some have cilia
-Function: Secretion & absorption (Via active transport & facilitated diffusion); mucus movement (via cilia/microvilli)
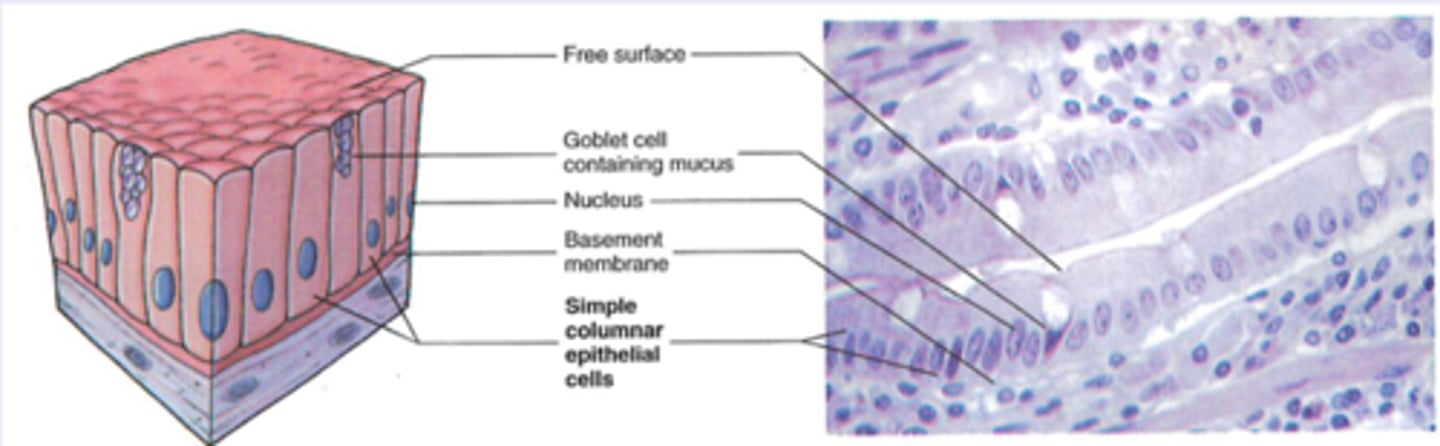
Simple columnar epithelium
-Location: Lining of stomach, intestines, glands, ducts, auditory tubes
-Structure: Single layer of tall narrow cells; some have microvilli/cilia
-Function: Secretion; mucus movement (via cilia/microvilli)
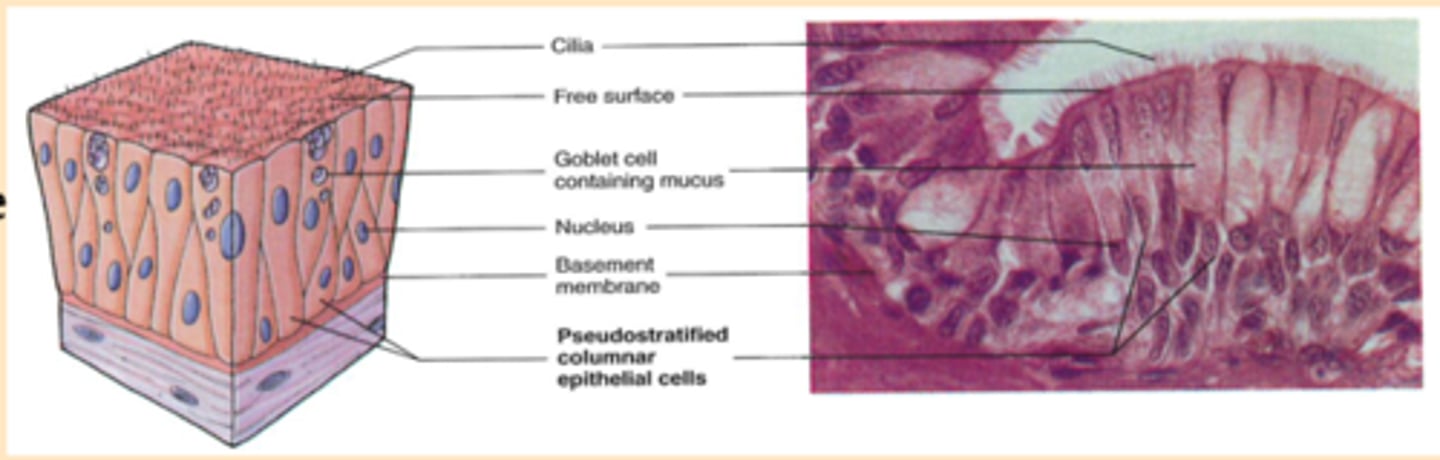
Pseudo-stratified columnar epithelium
-Location: Lining of the nose, sinuses, pharynx, trachea, bronchi
-Structure: Single layer of irregularly-sized cells (some reach the free surface; others do not); ciliated and associated with goblet cells
-Function: Secretion (mucus); mucus movement (via cilia)
Stratified squamous epithelium
-Location: Skin, cornea, lining of mouth, throat, esophagus
-Structure: Many layers of cells; basal layer is cuboidal/columnar; cells become flattened at the free surface
-Function: Abrasion protection; infection barrier; prevents H2O loss

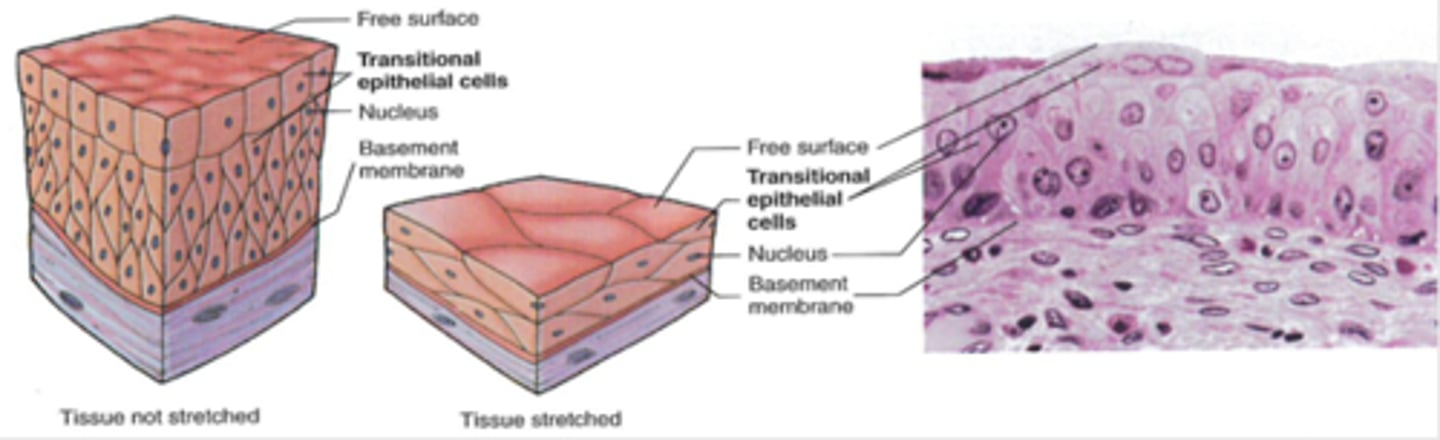
Transitional epithelium
-Location: Lining of urinary bladder, ureters/urethra
-Structure: Stratified cuboidal when at rest (not stretched); squamous when stretched
-Function: Accommodates fluid volume fluctuations in an organ or tube; protects against caustic effects of urine
How are epithelial cells connected to one another?
Through tight junctions, desmosomes/hemidesmosomes, and/or gap junctions
Tight junctions
-Bind adjacent cells together; form permeability barriers
-Prevent the passage of materials between epithelial cells
Desmosomes/hemidesmosomes
-Mechanical links that bind cells together (desmosomes)
-Modified desmosomes that anchor cells to the basement membrane (hemidesmosomes)
Gap junctions
-Small channels allowing the exchange of small molecules, ions, and electric potentials to pass from one cell to an adjacent cell
-Acts as communication signals to coordinate cell activity
Gland
a multicellular structure that secrets substances onto a surface, into a cavity, or into the blood
What are glands mostly comprised of?
epithelium
Types of glands
Exocrine and Endocrine
Exocrine glands
glands with ducts
-Simple = No branches
-Compound = Branches
-Tubular = Tube-shaped
-Acinus – Sac-like structure (grapelike)
-Alveolus – Small cavity
Endocrine glands
glands without ducts
-Hormones = carried by blood to other parts of the body
Connective tissue
-Extracellular materials that separate cells from one another
-Extracellular matrix = Consists of protein fibers, ground substance, and fluid
What are the protein fiber types found in connective tissue?
Collagen, Reticular, and Elastic
Collagen
Protein fibers grouped into bundles; flexible but resist stretching
Reticular
Very fine, short collagen fibers that branch to form a supportive network
Elastic
Stretchable coil-like fibers that are grouped into anastomosing bundles
How is connective tissue named?
Named according to their functions.
-Blast cells = Produce the extracellular matrix
-Cyte cells = Maintain the extracellular matrix
-Clast cells = Break down the extracellular matrix or remodel it
What tissue are immune system cells associated with?
connective tissue
Macrophages
ingest microorganisms found in the connective tissue
Mast cells
release histamine following stimulation with pro-inflammatory cytokines
Major functions of connective tissue include
Enclosing, separating, and storing
-Forms layers that separate tissues and organs; adipose tissue stores energy; bones store minerals
Connecting tissues together
-Tendons (attach muscle to bone), ligaments (attach bone to bone)
Supporting, moving, and transporting
-Bones and cartilage provide support for the body and joints for movement; blood transports substances throughout the body
Protecting, cushioning, and insulating
-Protects underlying tissues from injury; immune cells in blood protect against pathogens
§Adipose tissue cushions and protects tissues from trauma; also insulates the body to retain heat
Connective tissue classification
fibrous, special, cartilage, bone, and blood
Organ systems
A collection of anatomical structures (organs) that cooperate to carry out a specific task
What are the eleven organ body systems?
-Respiratory
-Lymphatic
-Cardiovascular
-Nervous
-Integumentary
-Reproductive
-Digestive
-Urinary
-Muscular
-Skeletal
-Endocrine
What does it mean that organ systems are interdependent?
They rely on each other to maintain overall body function and homeostasis
-A failure of one organ system can disrupt the function of others
--Can lead to severe health problems or death
Respiratory and Circulatory
-Work together to provide oxygen to the body cells and remove carbon dioxide waste
-Respiratory = Brings in oxygen; removes carbon dioxide
-Circulatory = Transports oxygen to tissues/cells; transports carbon dioxide away from tissues/cells
Digestive and Circulatory
-Work together to break down and deliver nutrients to the body cells
-Digestive = Breaks down ingested food to usable material (nutrients) for tissues/cells
-Circulatory = Transports nutrients to tissues/cells