Animal Nutrition
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards covering key vocabulary related to animal nutrition, including definitions and important concepts from the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
Essential Nutrients
Materials required by an organism that cannot be synthesized from simpler organic molecules and must be obtained from the diet.
Four classes
Essential amino acids
Essential fatty acids
Vitamins
Minerals
Essential Amino Acids
The amino acids that animals must obtain from their food, which cannot be synthesized in sufficient quantities.
All organisms require 20 amino acids
Essential Fatty Acids
Certain unsaturated fatty acids that cannot be synthesized by the body and must be obtained through the diet.
Vitamins
Organic molecules required in the diet in very small amounts, essential for various physiological functions.
13 vitamins are essential for humans
Minerals
Simple inorganic nutrients generally required in small amounts for various biological processes.
Variation due to diets
Herbivores dine mainly on plants or algae
Carnivores mostly eat other animals
Omnivores regularly consume animals and plants or algae
Malnutrition
A failure to obtain adequate nutrition, which can lead to health issues and physiological impairments.
Undernourishment
A condition resulting from a diet lacking sufficient chemical energy, leading to the use of stored fat and protein, loss of muscle mass
Food processing
Ingestion-act of eating or feeding
Digestion-process of breaking food down and into molecule small enough to absorb
Mechanical digestion-chewing or grinding, increases the surface area of food
Chemical Digestion-splits food into small molecules can pass through membranes
Absorption-is uptake of small molecules by body cells
Elimination-is the passage of undigested material out of the digestive system
Peristalsis
The process of alternating waves of smooth muscle contraction and relaxation that pushes food through the esophagus.
Sphincters-valves that regulate the movement of material between compartments
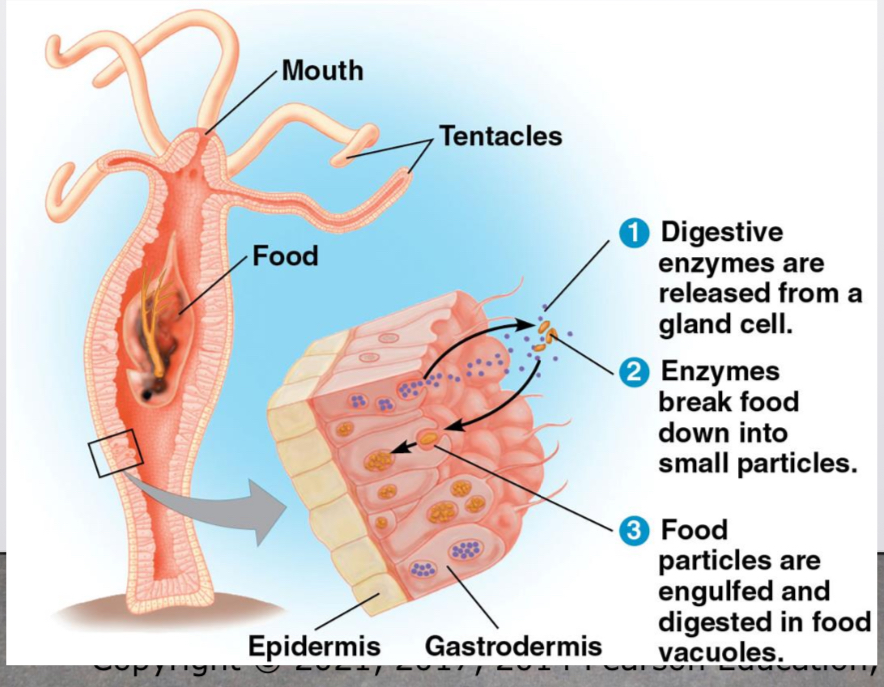
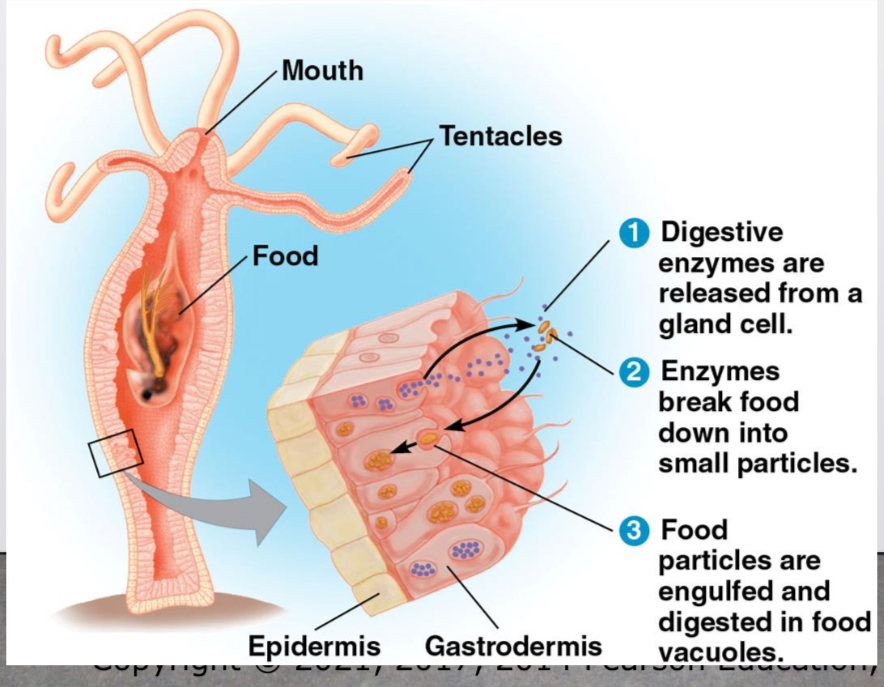
Gastrovascular cavity
For animals with a simple body plan functions in both digestion and distribution of Nutrients
Alimentary Canal
The complete digestive tract
Mouth
Pharynx
Esophagus
Stomach
Small and large intestines
Rectum
Anus
Accessory glands
Secrete digestive juices through ducts through into the alimentary Canal
Salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder
Oral Cavity, Pharynx, and Esophagus
Oral cavity-where food processing begins
Salivary glands-deliver saliva to lubricate food and which contains mucus of viscous mixture of water, salt and cells and glycol proteins, and also contains amylase, which breaks down starch
Pharynx(throat)-junction that opens to both the esophagus and trachea
Esophagus connects to the stomach
Trachea(windpipe) leads to the lungs
Digestion in the stomach
Stomach-store food and process it into a liquid suspension and secretes gastric juice and mixes it with food through churning action
Chyme-The mixture of ingested food and gastric juice in the stomach, which is then passed to the small intestine.
Gastric Juice is made up of
Hydrochloric Acid
Pepsin-a protease, breaks peptide bonds to cleave proteins into smaller polypeptides
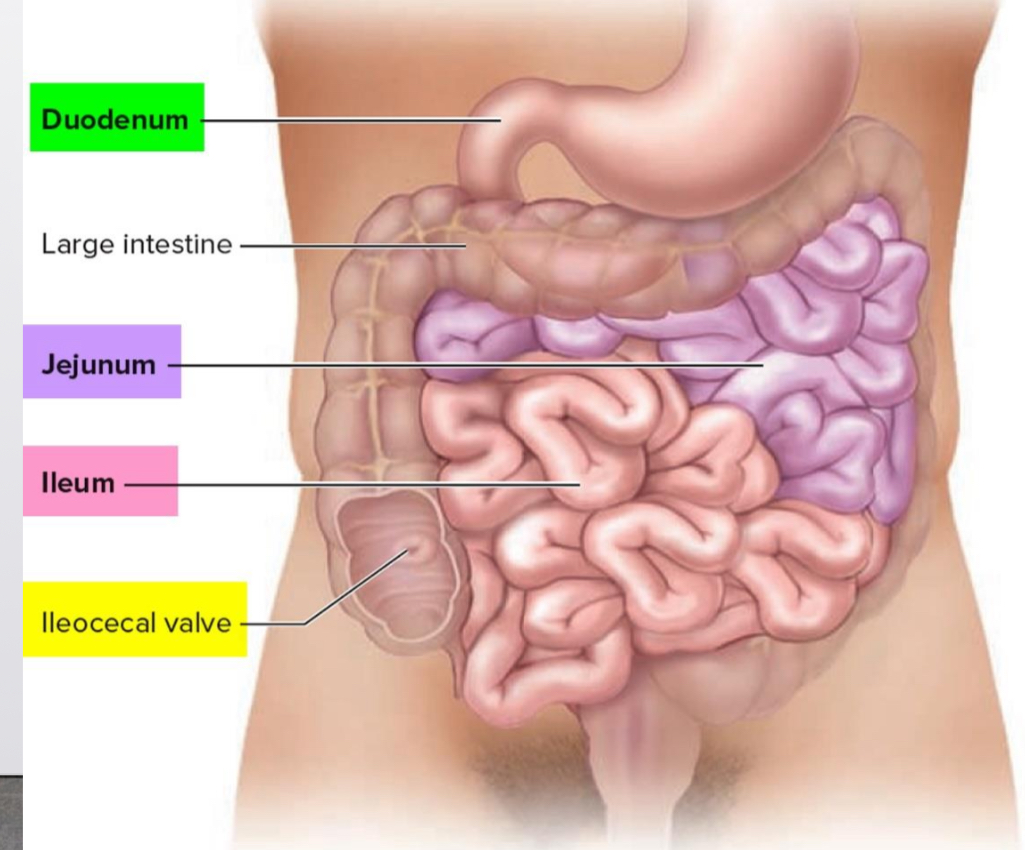
The Small Intestine
Small intestine-longest compartment of the alimentary canal
Duodenum-the first portion of the small intestine
The Jejunum second portion of small intestine for nutrient absorption
Ileum the third portion of small intestine for nutrient absorption
Ileocecal Valve- the portion of the small intestine where it connects to the large intestine
Huge surface area due to villi and microvilli that are exposed to the intestinal lumen
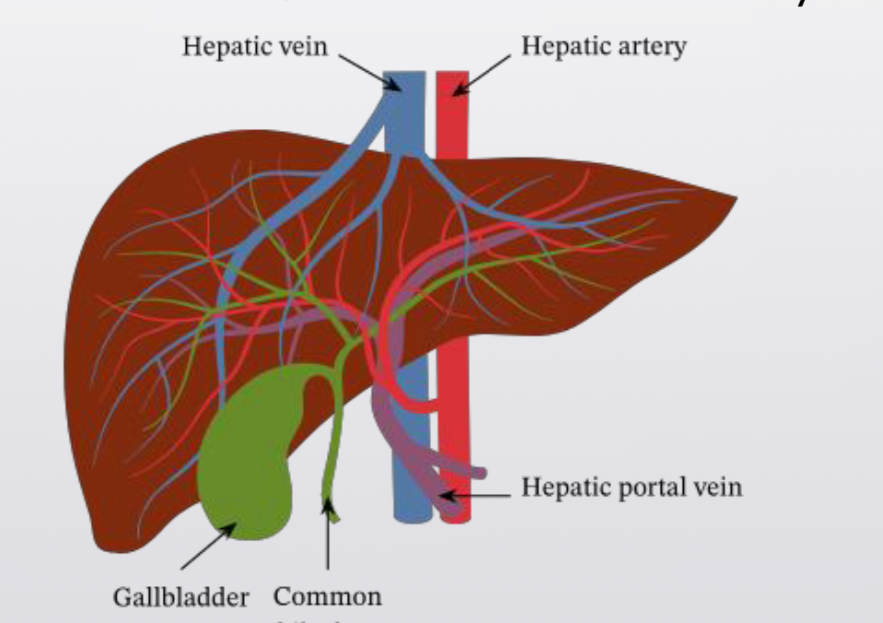
Absorption in the Small Intestine
• The hepatic portal vein carries nutrient-rich blood from the capillaries of the villi to the liver, then to the heart
• The liver regulates nutrient distribution, interconverts many organic molecules, & detoxifies many organic molecules
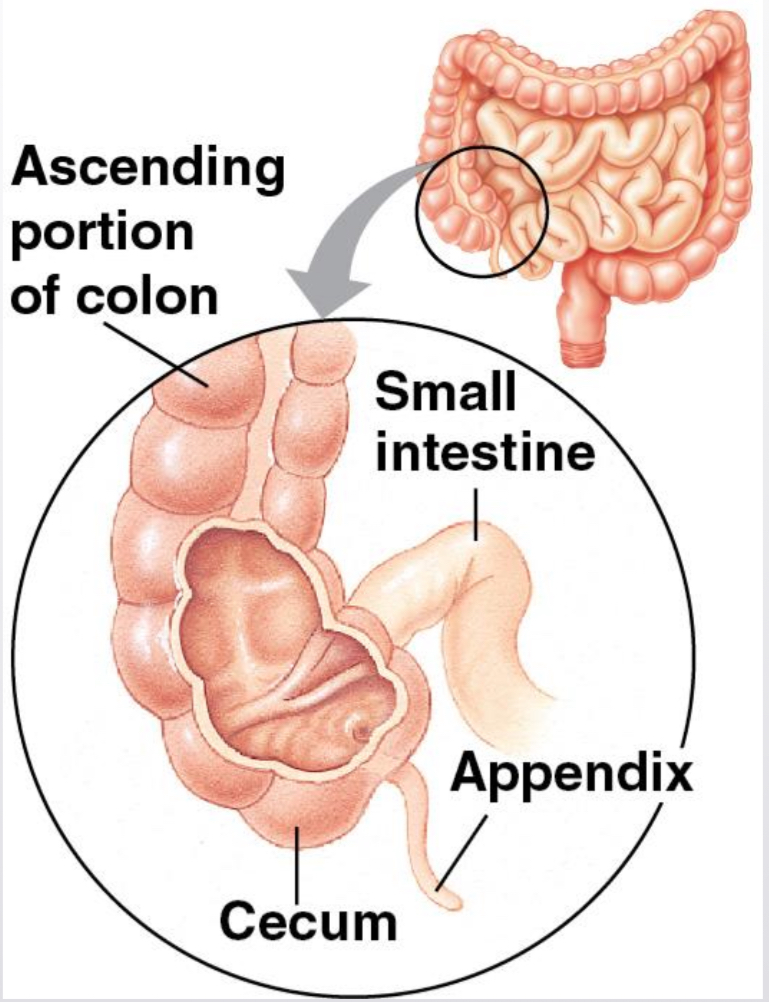
Processing in the Large Intestine
Large intestine ends the alimentary canal
Cecum aids in the fermentation of plant material & connects where the small & large intestines meet
has an extension called the appendix, which plays a minor role in immunity
Processing in the Large Intestine pt2
Colon completes the recovery of water that began in the small intestine
Feces, the wastes of the digestive system, become more solid as they move through the colon
Rectum store feces until they can be eliminated through the anus
Two sphincters between the rectum & anus control bowel movements (one voluntary & one involuntary)
the first part is the ascending colon, then transverse colon, and then the descending colon.
Microbiome
collection of the microorganisms living in and on the body
Regulation of energy storage
The body stores energy not needed for metabolism right away
Energy is stored first in the liver & muscle cells as glycogen
Excess energy is stored in fat in adipose cells
Glucose Homeostasis
relies on the opposing effects of two hormones,
Insulin & glucagon
regulate the breakdown of glycogen into glucose
Liver is the site for glucose homeostasis
Diabetes Mellitus
Deficiency of insulin or decreased response to insulin in target tissues