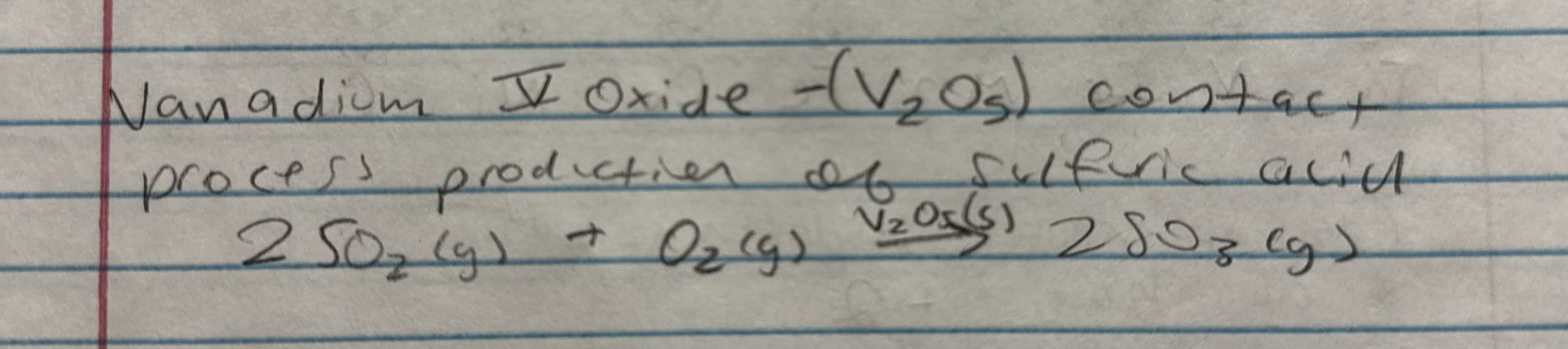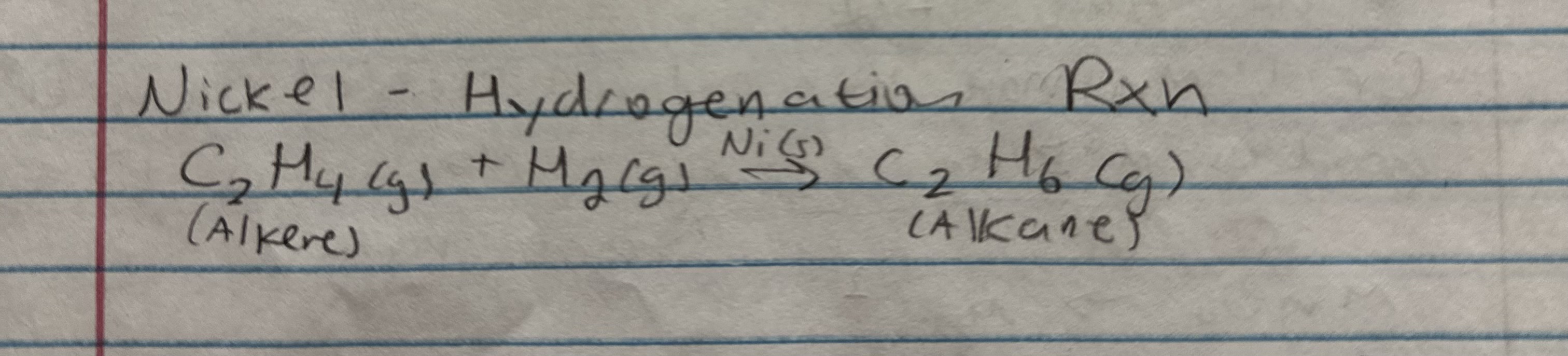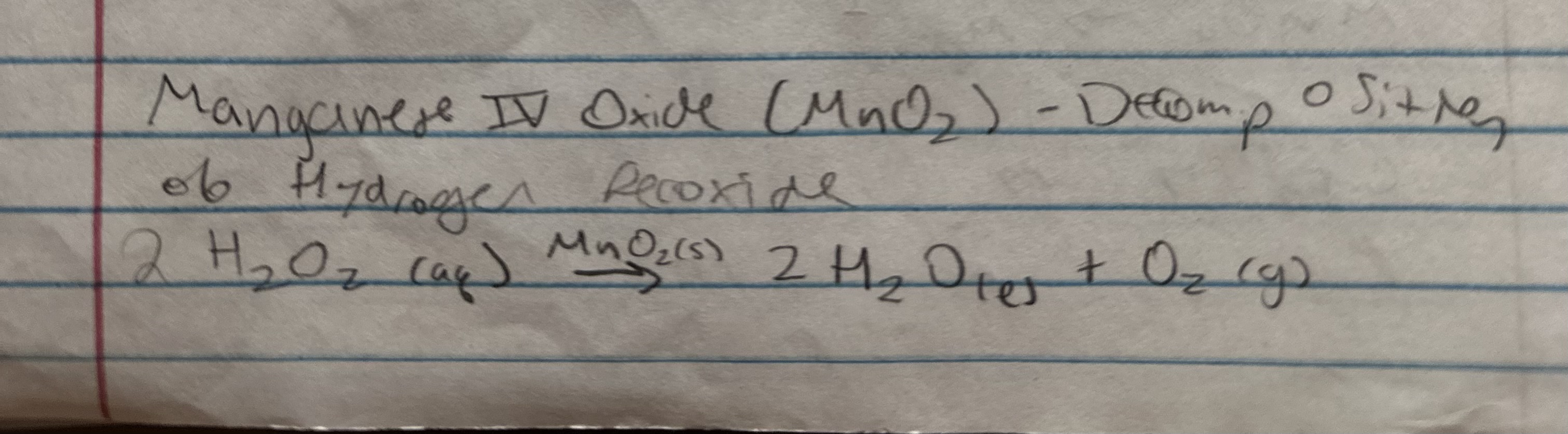U1 - IB Chem
1/47
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
48 Terms
e- transition from n=1 to n=infinity
e- has been removed
1st ionizaiton energy
1st ionization energy
energy needed to remove 1 mole of e- from 1 mole of gaseous atoms in the ground state
ionization energy trends
down group - dec
across period - ince
is 1st or 2nd ionization energy greater
2nd is greater
continuous spectrum
shows wavelengths of visible light
absorption spectrum
continuous spectrum with black lines to represent energy abosorbed by e-
emission spectrum
shows energy of the light emitted as e- falls down
Hydrogen Emission Spectrum
LBP
Lynman Series - ultraviolet - e- falls to n=1
Balmer Series- visible light - e- falls to n=2
Paschen Series - infared light - e- falls to n=3
units for frequency
s-1 , hertz
units for wavelength in equation
use nm (1×109 nm = 1 m)
units for energy in equation
Joules
pauli exclusion principle
every orbital holds a max of 2 e-
the e- have opposite spins
aufbau principle
e- are placed in lowest energy level possible
hund’s rule
every orbital within a sublevel gets one e- before any orbital gets two
s sublevel
circle shape
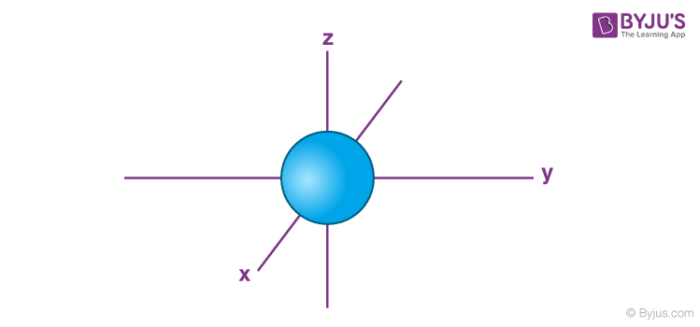
p sublevel
dumbbell shape - on x or y or z axis
exceptions for electron configuration
copper, chromium
copper electron configuration
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s¹ 3d¹⁰
one 4s e-
chromium electron configuration
1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s1 3d⁵
one 4s e-
What determines color of transition metal?
the color of light transmitted is the complmetary color of the color it absorbs
presence of partially filled d orbitals
Colorless ions
Sc3+ [Ar]
Zn2+ [Ar]3d10
Cu1+ [Ar]3d10
degenerate
d orbitals of equal energy in a free ion
location of 5 d orbitals
3 between axis
2 along axis
what happens to d orbitals when ligand comes in?
the lone e- repel the 2 orbitals along the axis, causing them to split.
what does more splitting (from ligand) of d orbitals mean?
greater energy gap, more energy needed to excite electron
What causes change of color
anything that changes splitting
What factors affect splitting of ligands
1.) Identity of metal ion - larger metals provide greater splitting - greatter nuclear charge has greater electrostatic attraction to ligand results in more splitting of d orbitals
2.) oxidation state of metal ion - as oxidation state increases splitting of D orbitals increases
3.) Geometry of complex ion
octahedral > tetrahedral > linear
4.) Identity of ligand - stronger ligand, greater splitting
spectrochemical series
I- > Cl- > F- > OH- > H2O > SCN- > NH3 >NO2- > CN- > CO
I clean floors oh water season n-c ho no
Paramagnetic
unpaired electrons
Pulled into magnetic field
Do not retain magnetic properties after field is removed
Where unpaired electrons more attraction
ex paperclip
diamagnetic
paired electrons
weakly propelled by magnetic field
does Not retain magnetic properties after field is removed
Ferromagnetic
contains unpaired electrons that align parallel to each other in domains
Retain magnetic properties after field is removed
Iron cobalt nickel
ex magnet
ligands
species with lone pairs of electrons that form coordinate covalent bonds with central metal ions. Ligands are Lewis bases
monodentant ligands
form cordinate covalent bonds with one long pair of e-
polydentate ligands
contains more than 1 pair of lone e- and can form 2 or more cordinate covalent bonds to the metal ion
bidentant ligands
forms 2 coordinate covalent bonds
hexadentate ligand
has 6 atoms with lone pairs of e-
chelates
2 or more seperate coordinate covalent bonds between ligand and central atom
transition elements
variable oxidation states
incomplete d sublevel as atom or cation
catalytic and magnetic propertiees
what metals are not transition metals
zinc - zn2+ - clear solution
Sn - incomplete d
sc3+ complete d, not transition metal
what transition states Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu have
+2
what elements are good osidizing agents down to 2+ and 3+ because of high oxidation states
Mn and Cr
hetergeneous vs homogenous catalysts
compare phase of catalyst and reactant
homogenous catalyst example
fe3+ heme in blood to transport oxygen
Co3+ in vitamin b12
catalytic converter in car catalyst
Pd (s) or Pt (s)
2CO(g) + 2NO(g) yields 2CO2 (g) + N2 (g)
heterogenous
haber process produciton of amonia catalyst
Fe (s)
3H2 (g) + N2 (g) yields 2NH3 (g)
heterogenous
contact proccess production of sulfuric acid