4.1.8 Exchange rates
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Define an exchange rate
The price of one currency in terms of another
How are floating exchange rates determined?
Markets forces of supply and demand intersect and the equilibrium is the set exchange rate
What causes floating exchange rate appreciations?
Increase in relative interest rates
Speculatiors aniticipate increase in value of the pound
Increase FDI
Increase in income abroad
Increase demand for uk exports
What causes floating exchange rate depreciations?
Decrease in interest rates
Speculators anticipate decrease value of the pound
Firms moving away from UK
Increase incomes domestically increase imports
Define a fixed exchange rate?
A system which the government of a country agreed to fix the value the value of its currency in terms of another currency
To support a fixed exchange rate system the government or central bank requires to hold large sums of currency reserves
What do countries with a fixed exchange rate do when its currency is overvalued?
When currency is overvalued, they sell their donestic currency for foreign currency as increasing supply will depreciate the value of that currency
What do countries with a fixed exchange rate do when their currency is overvalued?
Use foreign currency reserves to but more domestic currency, as increasing demand leads to increasing value bringing back the exchange rate to where it is meant to be
Define a devaluation
When the value of a currency is officially lowered
Define a revaluation
When a country values their currency again ( increase of decrease
What is required to maintain fixed exchange rates?
Government intervention is required
Lots of currency reserves and interest rate manipulation. ( for example increasing interest rates lead to hot money inflows leading to increased demand for currency and appreciation")
What are the negative impacts of an appreciation?
Lower economic growth
Potential current account deficit
Increased unemployment in domestic industries
What are the positive impacts of an appreciation?
Decreased inflation due to lower cost push inflation
Increased living standards due to cheaper imports
What are the positive impacts of a depreciation?
Increased employment in exporting industries
Increased economic growth
Current account deficit is reduced
What is the negative impact of a depreciation?
Higher inflation due to cost push and demand pull
What are some judgement points to the impacts of currency appreciation or depreciations?
Extent to which the exchange rate changed
PED of imports or exports( Marhsall Lerner and J curve)
Restriction on trade or trade barriers
What is the Marshal Lerner condition?
A depreciation in a currency onlt corrects a current account deficit if the
PEDx + PEDm > 1
Draw the J curve
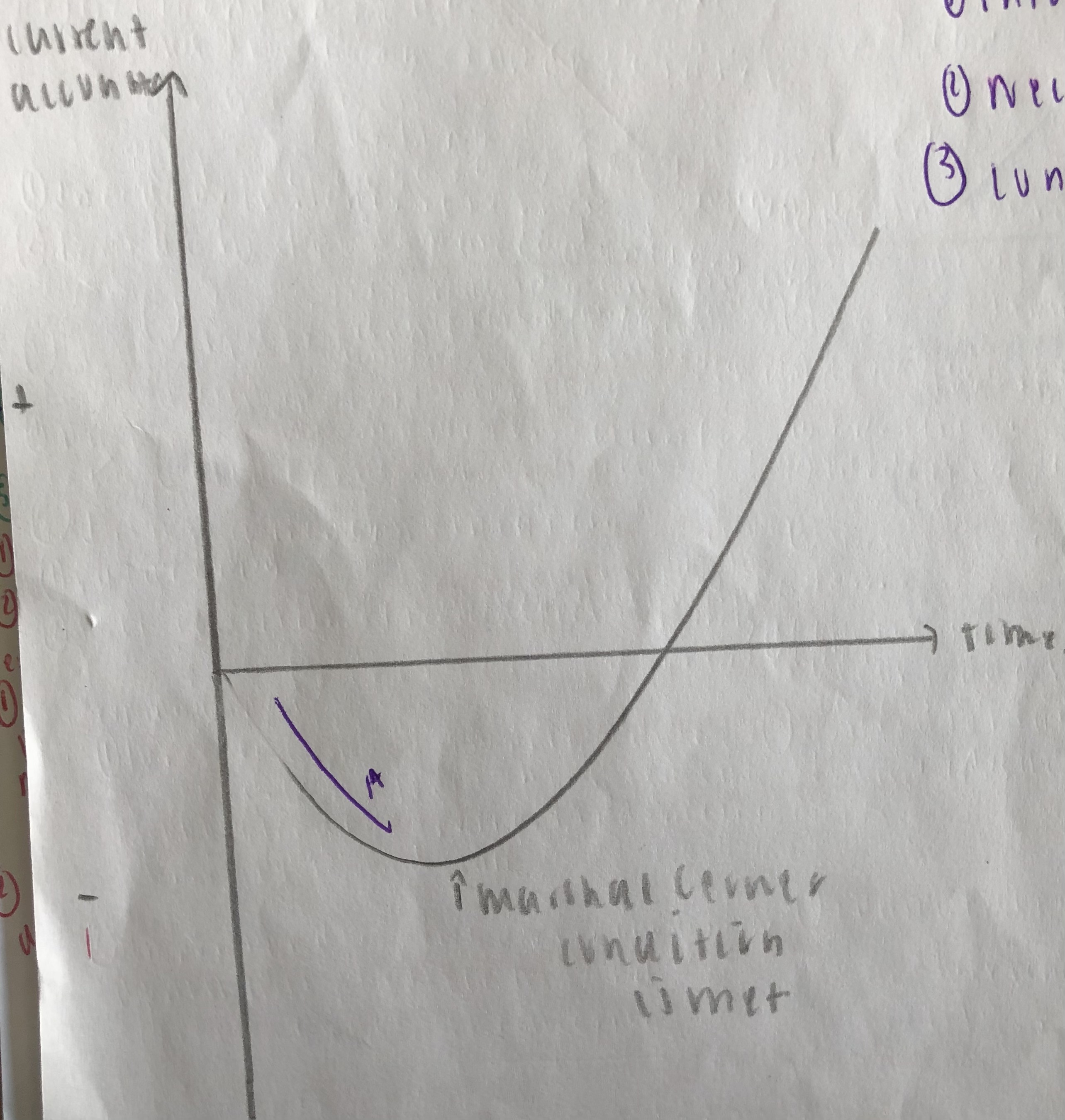
On point A of the diagram on the J Curve, what causes the current account to worsen before it improves when the currency depreciates?
Information failure
Necessity status
Contracts
What is the argument for a fixed exchange rate?
PARTIAL AUTOMETIC CORRECTION FOR TRADE DEFICIT. The self correction of a deficit is unlikely as speculation has greater influence
Freedom of domestic monetary policy. Freedom is not always effective if economy is weak. Liquidity trap during recession like Japan stuck in liquidity trap called “lost decade”
Volatility or currency creates uncertainty for firms reduced FDI or exports demanded. Other factors like unit labour costs or infrastructure override uncertain currency and would still lead to FDI
What is the argument for a fixed exchange rate?
Increased consumer welfare as firms must improve non price competitveness. However price competitveness has greater influence and little incentive for firms to be non price competitive if low exchange rate strategy is working effrctively in price sensitive markets
Leads to decreased economic growth as manipulating interest rates may lead to economic growth and low unemployment being sacrificed. However greater certainty of prices attarcts firms and FDI as they can predict future costs and profits which a floating exchange rate cannot do
define a managed exchange rate.
Also known as a dirty float. Value of a currency is determind by demand and supply but the central bank will try to prevent large changes in the exchange rate on a day to day basis. This is done by using foreign currency reserves and interest rates