L8: Personality and well-being
1/88
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
89 Terms
What are the two main dimensions of well-being?
Hedonism
Eudaimonia
What encompasses Hedonism?
- Happiness
- Satisfaction with life
- subjective well-being
What encompasses Eudaimonia?
asks deeper questions about what constitutes well-being
- positive relationships
- autonomy
- purpose
- personal growth
- psychological well-being
What are the 2 main model's that capture well-being in psychology?
- Components of Subjective well-being (Diener, 1984)
- Ryff's (1989) model of psychological well-being
What 2 main dimensions encompass Diener's model/subjective wellbeing?
- Affect (happiness)
- cognition (life satisfaction)
hedonistic approach
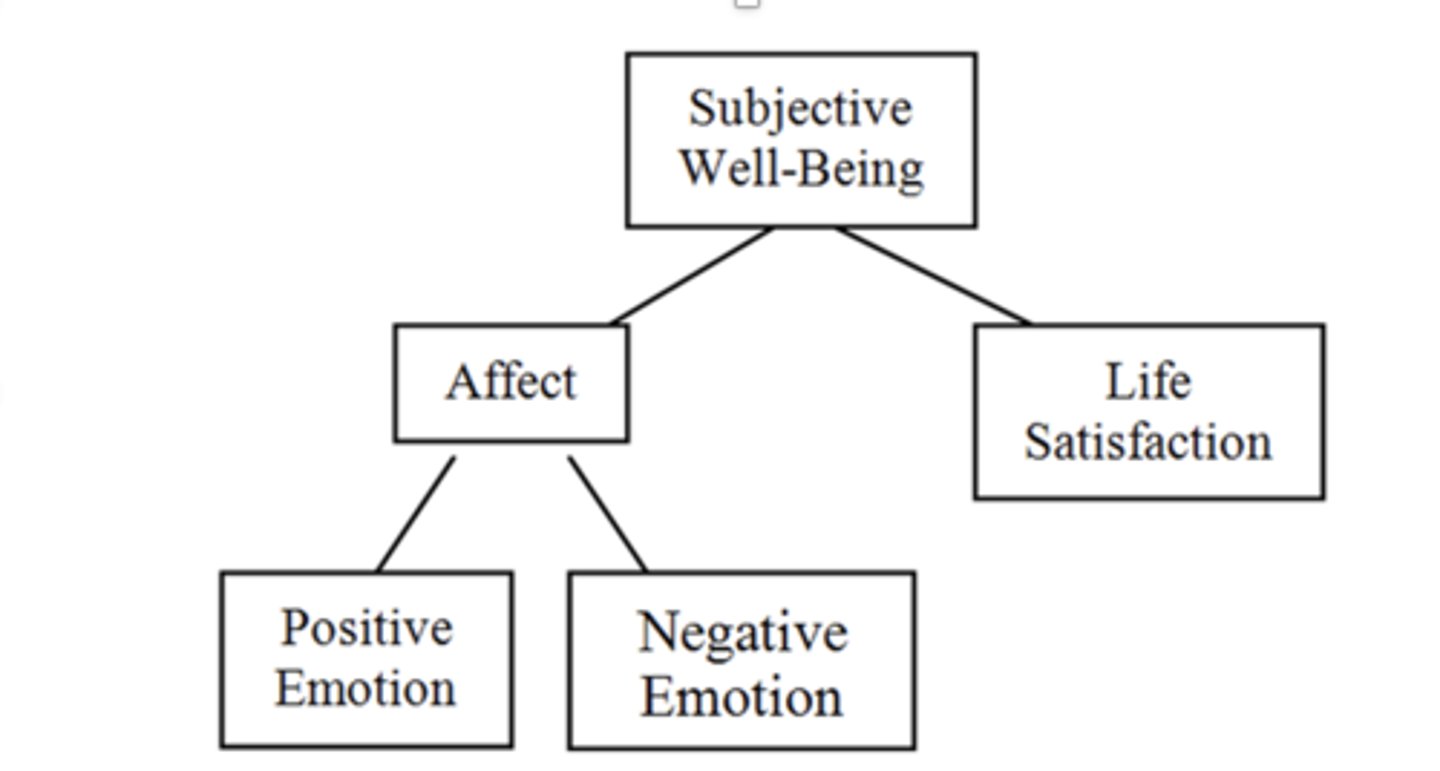
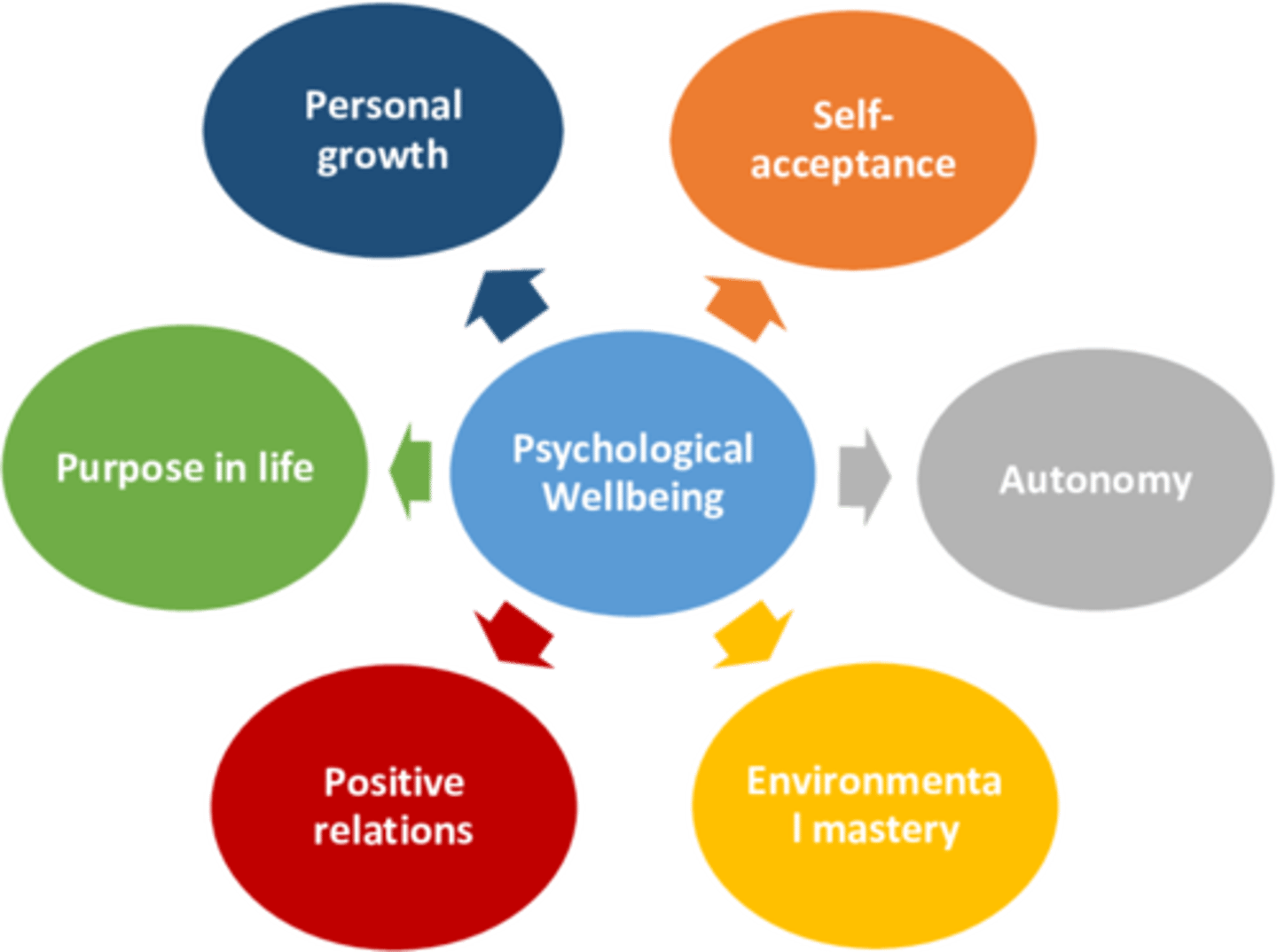
What is Ryff's (1989) model of psychological well-being?
developed in response to Diener's model in how we define wellbeing by arguing that there is more to wellbeing than happiness and how it can be tested emprically (what it means to live a meaningful life)
how many dimensions are in Ryff's (1989) model of psychological well-being?
6 dimensions
- the higher you are on the dimensions the higher your psychological wellbeing is overall
- e.g self-acceptance, autonomy, personal growth, purpose, pos relationships and environmental mastery
What is the difference between Hedonia and Eudaimonia?
There is a philosophical nature of difference rather than empirical.
- cross cultural study showed minimal discriminant validity in their association with correlates of well-being (Disabato et al)
What are the 3 main ways the 2 constructs differ?
- Temporal focus
- Motivational drivers
- Social vs personal dimension.
How do Hedonic and Eudaimonic wellbeing differ in terms of Temporal focus?
Hedonic = more closely tied to momentary states and emotional experiences, more aligns to traits like E and N
Eudaimonic = long-term pursuits and goals, more aligned with traits like C
How do Hedonic and Eudaimonic wellbeing differ in terms of Motivational Drivers?
Hedonic = aligns with sensation seeking and reward sensitivity (high E, low N) reward
Eudaimonic = aligns with intrinsic motivation and self-determination (C,A) reflective.
How do Hedonic and Eudaimonic wellbeing differ in terms of social and personal dimensions?
Hedonic = depends on external circumstances and social interactions
Eudaimonic = inwardly-focussed, aligns with personal values and self-reflection.
What % of genetics accounts for Subjective well-being?
around 50% of the populations variance in SWB is accounted for by genetics.
what is 'set-point' and its influence on happiness?
A chronic happiness that is stable over time and immune to influence or control (biological/genetic factors)
- High heritability for happiness 'set-point'
How does our neurobiology influence our set-point?
happiness set point reflects our intrapersonal, temperamental affective personality traits rooted in neurobiology
What did Weiss et al (2008) find?
There is a common general genetic factor underlying both FFM traits and subjective well-being
- correlation between Mz much stronger than Dz twins.
- down to shared genetic characteristics.
- genetic influence on SWB is fully mediated by personality traits.
What particular personality traits have a shared variance with SWB?
Extraversion, Neuroticism and Conscientiousness.
what did Pelt et al (2024) find about FFM and SWB?
- Don't find a complete overlap but find an overlap between N, E AND C (to an extent the levels of these different personality traits explain our wellbeing)
How does Neuroticism relate to subjective well-being? (Costa & McCrae 1980)
Neuroticism was found to be a negative predictor of subjective well-being over a 10 year period.
How does Extraversion relate to subjective well-being? (Costa & McCrae 1980)
Extraversion was found to be a positive predictor of subjective well-being over a 10 year period. (temporal consistency)
How did Pavot et al (1990) support (Costa & McCrae 1980) findings?
136 college students using self report and peer reported measures (robust) - observed higher levels of positive affect and life satisfaction among high Extraverts
- over a 2 week period.
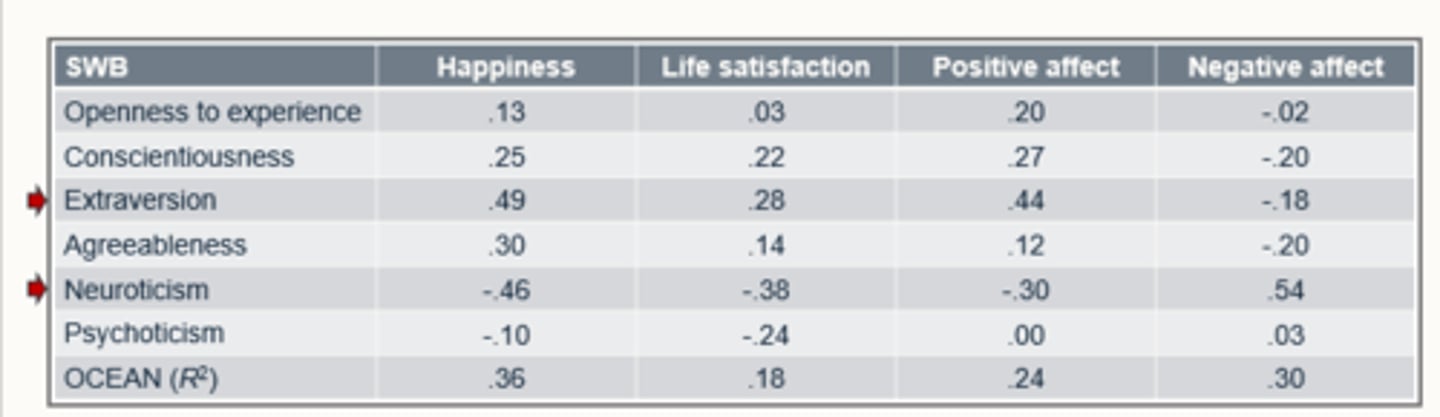
What did a meta-analysis find about the big 5 personality traits and their connection to wellbeing? (Steel, Schmidt & Shultz, 2008)
146 studies
- Big 5 traits account for a significant variance in wellbeing indicators (18%-36%) of indications of subjective wellbeing can be explained by personality traits.
- E and N = strongest predictors.
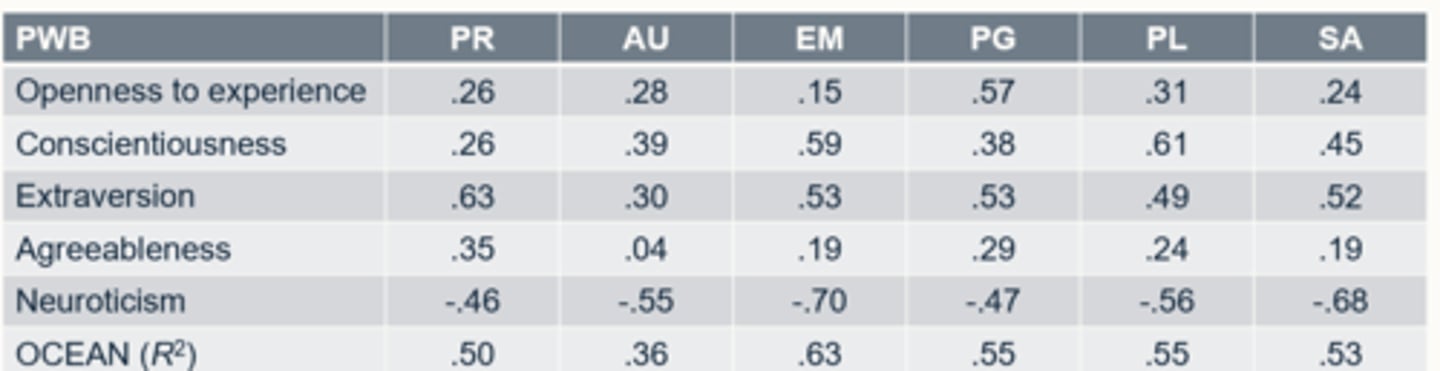
How may Ryff's (1989) model of psychological well-being correlate with personality traits? (Anglim et al 2020)
Meta-analysis
- Extraversion is a positive predictor for Personal relationships (outgoing/sociable)
- high in neuroticism has a negative relationship with PR as well as the other dimensions.
- see links with personality with this construct of wellbeing too
What 3 mechanisms explain the link between personality and wellbeing
- Emotion regulation
- coping strategies
- interpersonal relations
What is emotional regulation?
Emotions have a range of adaptive functions including facilitating decision making, learning etc
- rapid motor responses + tailoring attention to situational demands.
How may emotions be unhelpful?
- we can have inappropriate emotional responses for the situation we are dealing with (e.g conflict at work - do not want an angry attack in that moment)
- inaccurate responses
- trigger responses that conflict with important goals
What does Emotional regulation involve?
Modifying positive and negative emotions in such a way as to bring them in alignment with the goals of an individual.
How does emotional regulation link to personality to wellbeing?
personality traits often shape your preference for particular emotional regulation strategies (suggesting particular strategies have implications for your well-being)
How does neuroticism influence emotional regulation? (Ng & Diener, 2009)
People high in N expressed more negative emotions to unpleasant stimuli and less decrease in negative emotions when the unpleasant scenario was improved (opportunity for repair)
- do not respond as well to repaired situation
How does Extraversion influence emotional regulation? (Ng & Diener, 2009)
High E individuals felt more positive about repaired situations and showed a tendency to savour positive emotions - less affected by negative situations.
what do the results from (Ng & Diener, 2009) suggest?
Differences in emotional regulation are explained by personality.
- 'savouring' - high E - fixate on this and enjoy the positives more
What are adaptive strategies to emotionally regulate?
- Reappraisal (see negative as a positive challenge)
- problem solving
- associated with pos outcomes like reduced stress and increased life satisfaction
What are maladaptive strategies to emotionally regulate?
- suppression of negative emotion.
- avoidance
- linked with negative outcomes such as heightened anxiety, depression, lower wellbeing
What personality traits are positively correlated with adaptive strategies? (Baranczuk, 2019)
E, C, A, O
- problem solving, re-appraisal and mindfulness
What personality traits are negatively correlated with maladaptive strategies? (Baranczuk, 2019)
Extraversion - negatively related to rumination, worry and suppression.
What personality trait is negatively correlated with adaptive strategies? (Baranczuk, 2019)
Neuroticism - neg correlation with re-appraisal, problem solving and mindfulness
What personality trait is positively correlated with maladaptive strategies? (Baranczuk, 2019)
Neuroticism - worry, suppression, avoidance and rumination
What did Yang et al (2020) find on personality and emotional regulation?
Biological evidence
how did Yang et al (2020) study biological evidence?
They got people to complete a cognitive appraisal task whilst in a MRI scanner.
- task images were either neutral or negative (injury, accidents etc)
- asks ptps to either look at image and respond with emotion rating or to down regulate their emotions.
Yang et al (2020) personality findings
people high in N were less able to regulate negative responses to stimuli in cognitive appraisal task.
Yang et al (2020) biological findings
People High in N was associated with higher amygdala activity and lower dmPFC activity - part of brain known to down regualate activity of amygdala (dorsomedial prefrontal cortex) activity.
What do Yang et al (2020)'s biological findings suggest?
There's evidence that people High in N are physically less able to modulate emotional responses - leads to negative well-being outcomes.
What is Coping defined as?
'Cognitive and behavioural efforts to manage specific external demands that are appraised as taxing or exceeding the resources of the person.
What is Coping specifically concerned with?
- concerns responses to stressful situations only
- can only occur during or after a stressful event
- coping is aimed at reducing stress and managing demands of a situation (goals)
What is problem focussed coping?
It's directed at the stressor - aim is to minimise the stress by directly dealing with the problem causing the stress
What is emotion focussed coping?
Aims to minimise the distress caused by the stressors rather than addressing the source of the problem.
What is meaning-focussed coping?
Finding benefit and meaning in adverse experiences
What is proactive coping?
pre-emptive actions before threats or stress arise (scanning horizon for emerging threats)
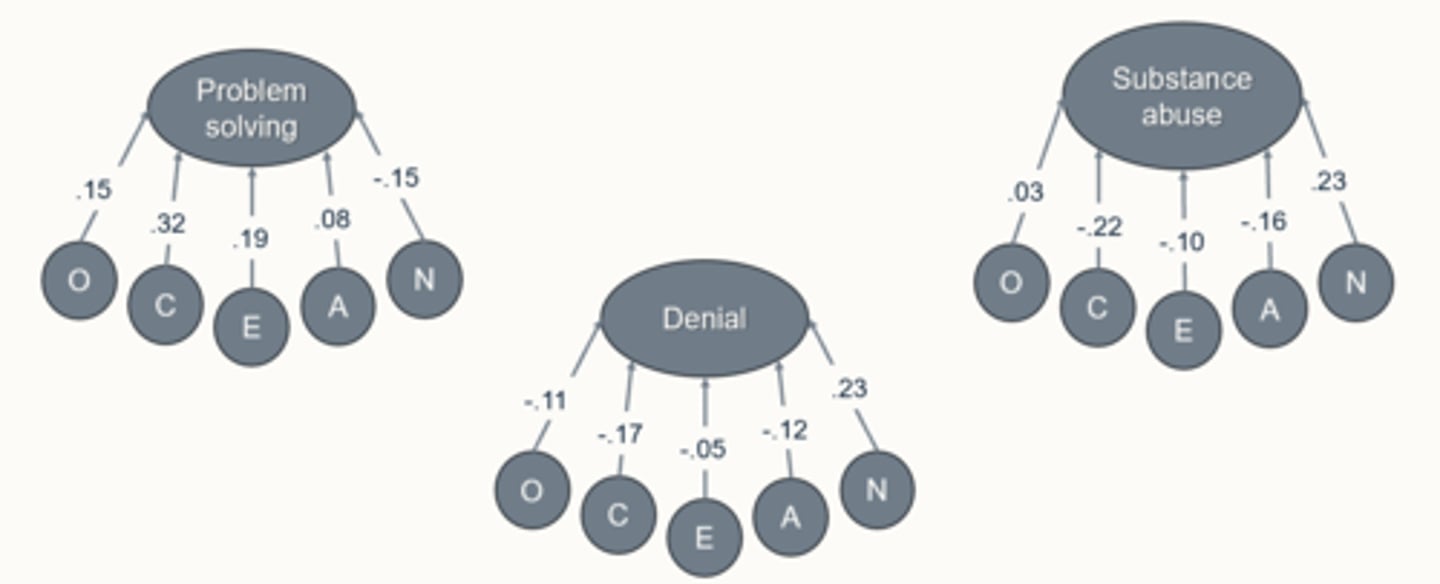
Connor-Wood & Flachsbart, 2007 (personality and coping)
problem solving = C, O, E
Denial = N
Substance abuse = N
What other factors does the relationship between personality and coping strategies vary depending on?
- Age
- stressor severity type
- Situational vs dispositional coping
How does age influence the relationship between personality and coping strategies?
- personality is more likely to influence your coping strategies when you are younger compared to older.
- acquire more knowledge to manage situations and problem solve as you get older so temperament has lees of an effect.
How does stressor severity type influence the relationship between personality and coping strategies?
- personality is more closely related to coping among people experiencing severe stress (cancer, pain, divorce). as influences multiple life domains.
- low stressors elicit less coping variability
How does Situational vs dispositional coping influence the relationship between personality and coping strategies?
- personalty plays more of a role in dispositional coping (large range of scenarios) better than response to specific stressors.
How do interpersonal relations explain the link between personality and wellbeing
- positive social relationships are integral to psychological wellbeing through belonging, social support and self-esteem.
- Segrin & taylor (2007) - + relations was associated with SWB and PWB components such as life satisfaction and happiness.
How do Extraverted people relate to social relations?
- larger social networks, seek out social interactions, more positive emotions and experiences in social contexts
= enhanced wellbeing
How do highly agreeable people relate to social relations?
- more cooperative, empathetic and trusting which will leads to more positive and supportive relationships with good quality and trust.
How do highly neurotic people relate to social relations?
- struggle with social relationships due to a tendency towards anxiety, moodiness or conflict which impacts wellbeing.
How do Conscientious people relate to social relations?
they are reliable and organised - strengthen relationships through dependability and trust.
How do people high in openness relate to social relations?
More likely to seek diverse and stimulating interactions, contributing to a sense of fulfilment and wellbeing.
Tov et al 2014 - what predicted higher levels of satisfaction in Extraverted people?
Higher levels of satisfaction with various categories of social relationships, primarily driven by trust (More trusting of other people)
Tov et al 2014 - what predicted higher levels of satisfaction in highly agreeable people?
Higher levels of satisfaction with various categories of social relationships, primarily driven by less frequent negative interactions and conflicts.
What is the explanatory factor for the relationship between extraversion and well-being? (Smillie et al, 2015)
Social wellbeing/interaction
- motivated to socialise, the more opportunity you have to do this the more you'll experience positive affect from the pleasure you get from socialising. leads to a higher level of well-being.
what main component from (Smillie et al, 2015) study was found to drive the effect of extroversion on life satisfaction.
Social contribution - what you bring to the relationship is valued by others - feeds into sense of well-being.
- also found in enacted extraversion - trained people to express more desirable personality traits and gain the well-being benefits that come with it (study 2)
How did the pandemic influence extraverted people? (Anglim and Horwood 2021)
Correlation between extraversion and positive affect was weaker in the pandemic due to people not being able to satisfy motivation to socialise/social interactions to gain well being benefits
- (no differences in other traits)
What did Wijngaards et al (2020) find in people with depression and the tightening of restrictions during the pandemic
Those higher in Neuroticism had improved depressive symptoms. (less anxious staying at home)
- whereas those higher in Extraversion had worsening depressive symptoms (not significant though)
Which personality trait correlates with worse wellbeing from social interactions? (Denissen & Penke, 2008)
Neuroticism
- experience Negative well being benefits from increase social interactions
- may come with a risk of rejection (self esteem decreases in response to relationship conflict/low-quality relationships)
What has been found about digital footprint and personality traits? (Azucar et al 2018)
Personality traits can be reliably predicted from Digital footprint data such as text, images and other material posted online.
What did Woods et al find?
The way you scan a page (eye tracking) for 20 seconds on a social media website/what information you oat attention to can determine your personality traits (can be determined from just 20 seconds of thsis behaviour)
What are the benefits of studying psychological traits using digital footprint data?
- Cost-effective
- Potential use for enhancing personalisation of services and reccomendations systems - leveraged for tailored health messaging and other interventions for public good.
How does Extraversion relate to online behaviours?
Extraverts show parallels between online and offline behaviour = more likely to use social media, post frequently, use positive langauge, and like other's posts
How does Neuroticism relate to online behaviours?
More likely to use negative sentiments in Facebook posts, share personally-identifying information and present an idea or false self online.
What did a study on Spanish adolescents (12-19) find? (Alonso & Romero, 2017)
They observed high neuroticism individuals were more likely to be victims of cyber-bullying.
What is the strong sentiment towards social media and wellbeing?
Among young people, social media is perceived as threat to mental wellbeing (O'Reilly et al 2018)
- inc harm exposure
- social isolation
- cyber bullying
What benefits were found for social media on wellbeing?
it can enhance social connectedness and enable access to supporting communities for people experiencing mental health conditions. (Best et al, 2014)
Is social media bad or good for wellbeing?
No conclusion whether its bad or good - certain circumstances where its bad and good.
How does personality shape the way your well being is impacted by social media?
- Neuroticism = increase vulnerability to the effects of negative online interactions and content
- N amplifies the effects of stress on mood which can be extrapolated to social media effects. (Suls & Martin)
How does C associate with social media?
High conscientiousness is associated with cautious self-presentation and information sharing online (Liu & Campbell)
- protective factor for excessive/disordered SM use
What personality traits are protective factors against cyberbullying
Agreeableness and Conscientiousness (Xu et al 2024) - less likely to engage in cyberbullying behaviour.
Which personality trait can be a risk factor for excessive/disordered SM use
Extraversion (Sindermann et al 2020)
How can we use personality insighst to enhance wellbeing?
- target wellbeing interventions at trait expression (mindfulness for high N)
- personality development programmes (resilience training for those Low C or high N
- promoting pos lifestyle habits that align with individuals personality traits.
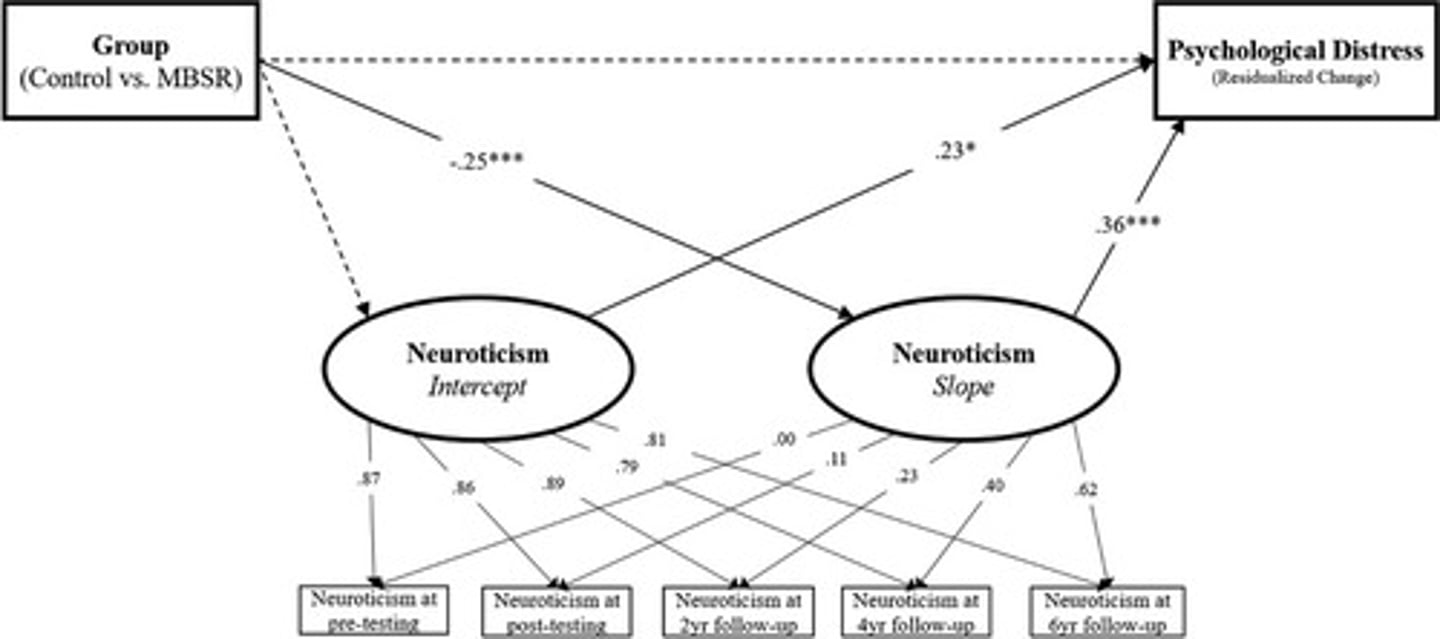
What did Hanley et al (2019) find on mindfulness as an invention?
The intervetion reduced psychological distress up to 6 years after intervention
- expression of N trait seemed to decline over period (stress reduction) achieved by changing the personalities of the people.
What strategies did Martens et al (2022) target to improve psychological well being?
- self-control
- self-reflection
- self-esteem
- emotional self regulation
1072 adolescents (M =12 y/o)
How did the interventions improve psychological well being? Martens et al (2022)
increased resilience, reduced aggression
Which personalty traits were the benefits of the intervention more pronounces in? (Marten et al 2022)
Adolescents high in Neuroticism
What healthy lifestyle habits are best for those high In openness? (aligns activities to increase wellbeing)
Creative activities (art based interventions targeting self expression)
What healthy lifestyle habits are best for those high In Conscientiousness? (aligns activities to increase wellbeing)
Goal-based and structured activities such as setting fitness milestones
What healthy lifestyle habits are best for those high In Extraversion? (aligns activities to increase wellbeing)
Exercise that involves social interactions such as group sports and clubs (rub clubs)
What healthy lifestyle habits are best for those high In Agreeableness? (aligns activities to increase wellbeing)
Team-based or cooperative activities such as gardening groups, neighbourhood clean up drives/
What healthy lifestyle habits are best for those high In Neuroticism? (aligns activities to increase wellbeing)
Activities that reduce anxiety and promote resilience (solo yoga/walking)