Cardiovascular System Notes
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
The heart is two ___________
pumps
There are 2 __________ of the cardiovascular system
circulatory sections
_____________- heart pumps blood to lungs
Pulmonary
_____________- heart pumps blood to body
Systemic
Size: About the size of your __________ (9×14cm)
fist
Heart Coverings: __________- a double- walled sac around the heart composed of 2 layers
Pericardium
A superficial __________
fibrous pericardium
A deep two-layer _________
serous pericardium
Serous Pericardium: The _________ lines that internal surface of the fibrous pericardium
parietal layer
The _________ (epicardium) lines the surface of the heart
parietal layer
Heart Covering: Fluid between these layer ________
protects heart, reduces friction
Pericardium protects and _____ the heart. Prevents _____
anchors; overfilling
Heart Wall: Epicardium - _________________
Outer layer - reduces friction
Heart Wall: Myocardium ________________
Cardiac Muscle
Heart Wall: Endocardium - __________________
thin inner lining within the heart chambers
Valves: _____ Atrioventricular (AV) Valves
2
_________- between RA and RV
Triscupid
_________- (mitral) b/w LA and LV
Bicuspid
Valves: ______ Semilunar (SL Valves (cusps)
2
________ - between RV and Pulmonary Artery
Pulmonary valve
______- between LV and Aorta
Aortic valve
AV Valves connected to the walls of the ventricles by ____________. Helps them open and shut with each contraction.
Chordae Tendinae
Heart Sounds: ___________ of heart valves give the characteristic "_______" sounds.
Opening and closing; Lub Dub
Stethoscope-
instrument used to listen to heart sounds
AV Valves Close -
Lub
SL Valves Close -
Dub
Cardiac Conduction System: ____________________________________________________________________
Group of specialized cardiac muscle cells that cause the heart to contract.
Cardiac Conduction System: SA (sinoatrial) node: _______________________
anatomical pacemaker
Cardiac Conduction System: SA (sinoatrial) node: starts the sequence by causing the _______________________ to contract
atrial muscles
Cardiac Conduction System: Bundle of His: Bundle of cardiac muscle fibers that _______________________________
conducts the electrical impulses that regulate the heartbeat
Cardiac Conduction System: Bundle of His: Also called __________________________
atrioventricular bundle
Cardiac Conduction System: Purkinje fibers: carry the contraction impulse from both the left and right bundle branch to the _______________________
myocardium of the ventricles
Cardiac Cycle- One complete _____________
heartbeat
Systole- ____________________the relaxation of a chamber
the contraction of a heart chamber
pumps blood from the chambers into the arteries.
Diastole- ____________________
the relaxation of a chamber
relaxes and allows the chambers to fill with blood
Cardiac Cycle is regulated by ______________
medulla oblongata
Parasympathetic - ____________
slow heart rate
Sympathetic - _____________
increase heart rate because of increased oxygen demand
Cardiac Output = ______________
Stroke Volume x Heart Rate
the amount of ______ pumped by each ______ in one ______. Normally 4 to 8 L/min.
blood; ventricle; minute
Heart Rate =
number of beats per minute
Stroke Volume =
the amount of blood pumped by the left ventricle with each heart beat
Cardiac Output Example: A patient has a heart rate of 75 beats/min. Her stroke volume is 70 ml/beat. What is her cardiac output?
CO = (75 beats/min) x (70 ml/beat)
CO = 5250 ml/min or 5.25 L/min
Blood Pressure (BP): Force per unit area exerted on the wall of a blood vessel by its contained blood
Express in _________________
millimeters of mercury (mm Hg)
Blood Pressure (BP): Recorded as Systolic Pressure/Diastolic pressure:
Average: 120/80-140/90 mm Hg
Too low: hypotension
Too high: hypertension
Maintaining Blood Pressure: The main factors influencing blood pressure are:
Cardiac output (CO)
Peripheral resistance (PR)
Blood volume
Maintaining Blood Pressure: Blood pressure =
CO x PR
Maintaining Blood Pressure: Blood pressure varies directly ________________
with CO, PR, and blood volume
Blood flows in the same direction as the decreasing pressure gradient: __________________
arteries to capillaries to veins.
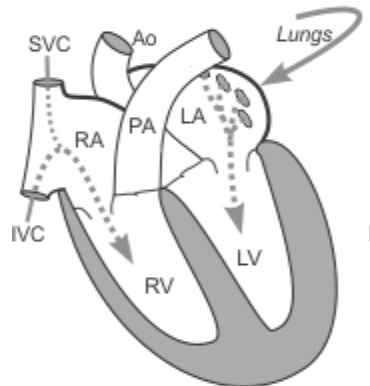
Diastole
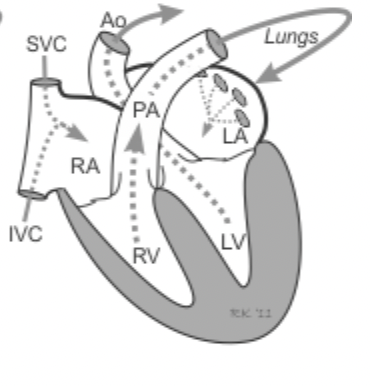
Systole