The Cell
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Cell Theory
Foundational concept applying to all living organisms.
States that all living things are made of cells, cells are the basic unit of life, and all cells arise from preexisting cells.
Fluid Mosaic Model
Location: Plasma membrane of all cells.
Function: Describes the membrane as a dynamic structure with a fluid lipid bilayer in which proteins float and move.
Process:
Membrane transport (passive & active)
Cell signaling
Membrane protein movement and restructuring

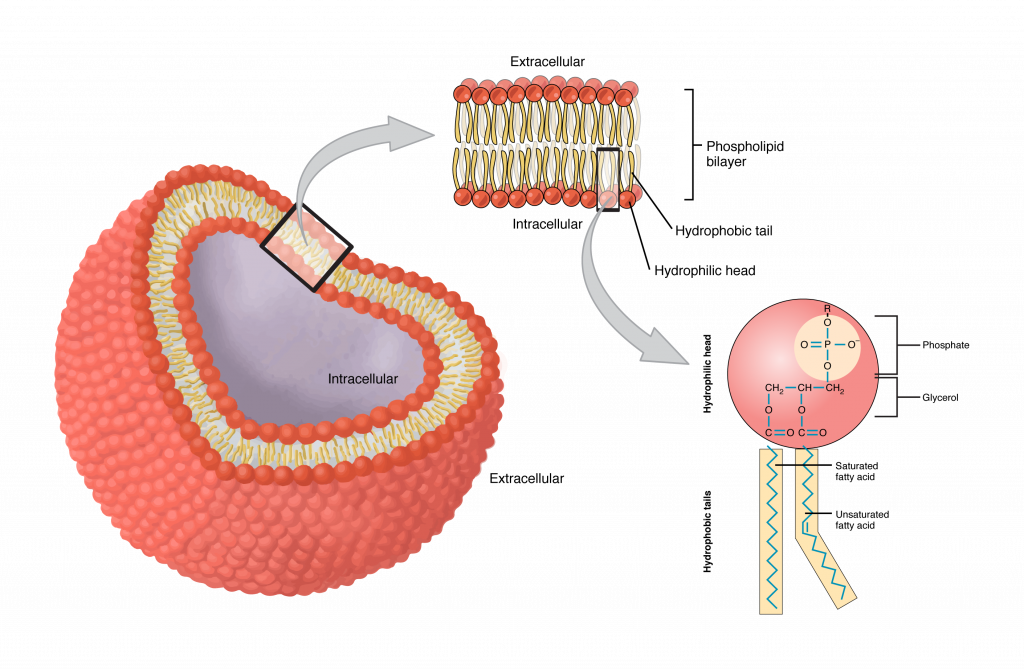
Phospholipids
Location: Major component of the plasma membrane.
Function: Form a bilayer with hydrophilic heads (outward) and hydrophobic tails (inward) that serves as a barrier to water-soluble substances.
Process:
Self-assembly into bilayers in water due to amphipathic nature.
Lateral movement within the membrane for fluidity and flexibility.
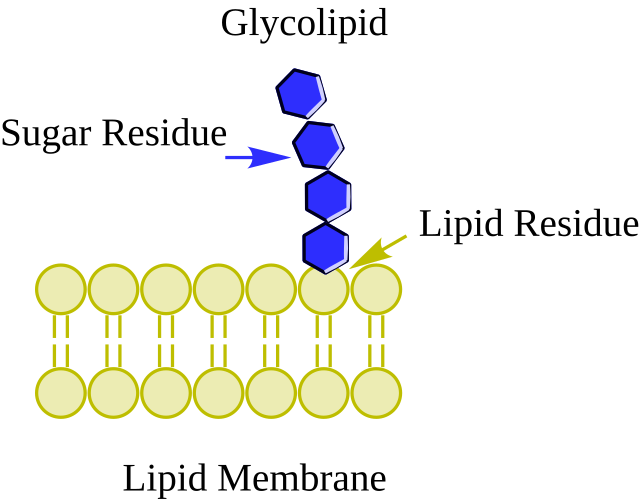
Glycolipids
Location: Outer layer of the plasma membrane.
Function: Provide energy and serve as recognition sites for cell interactions (e.g., immune response).
Process:
Cell-cell communication
Formation of the glycocalyx, a carbohydrate-rich area for signaling and protection.
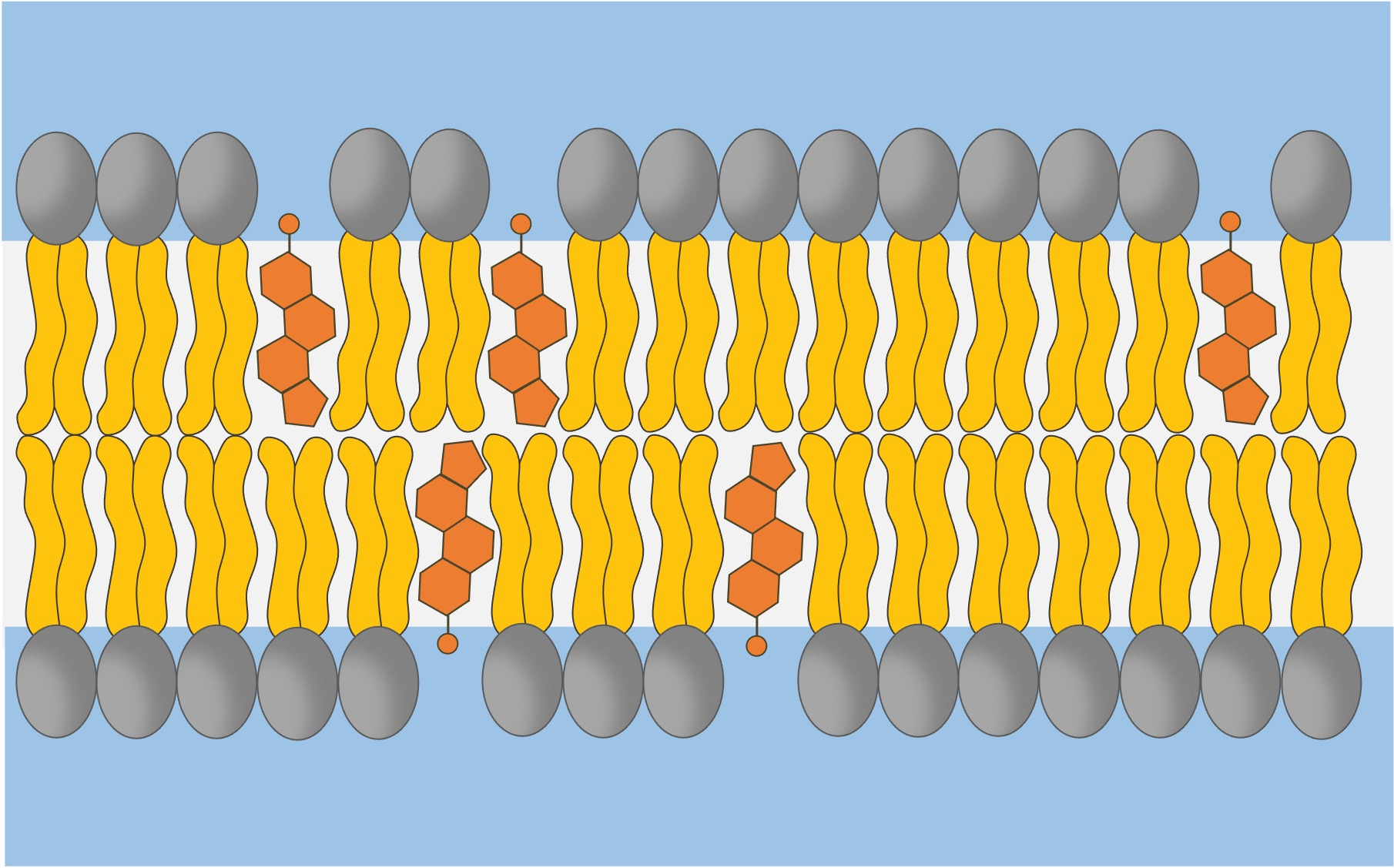
Cholesterol
Location: Embedded within the phospholipid bilayer.
Function: Stabilizes membrane fluidity and integrity, especially with temperature changes.
Process:
Buffers membrane fluidity by stabilizing phospholipids.
Reduces membrane permeability to small water-soluble molecules.
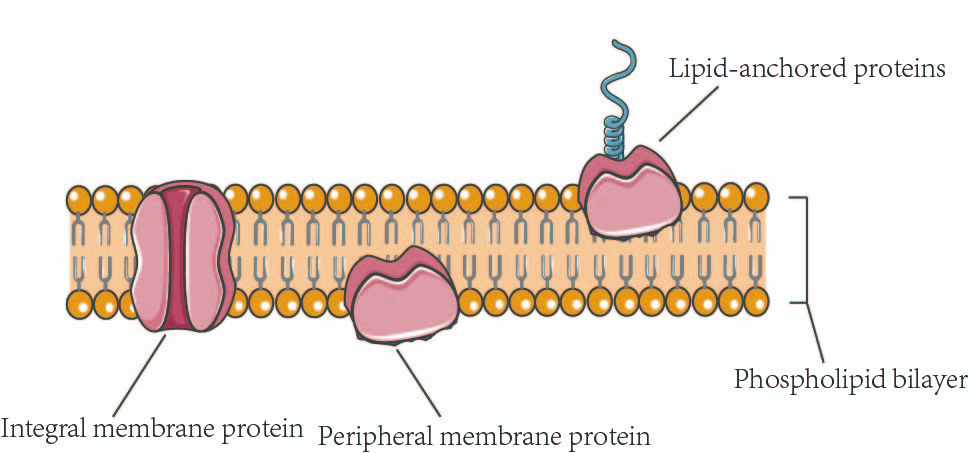
Membrane Proteins
Location: Embedded in or attached to the plasma membrane.
Function: Transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell recognition, intercellular joining, and attachment to cytoskeleton.
Process:
Facilitated diffusion and active transport
Signal transduction cascades
Enzymatic catalysis
Cell Junctions
Location: Between adjacent cells in tissues.
Function: Connect cells together and regulate communication, transport, and adhesion.
Process:
Formation of tissue barriers
Signal propagation in coordinated cells (e.g., muscle tissues)
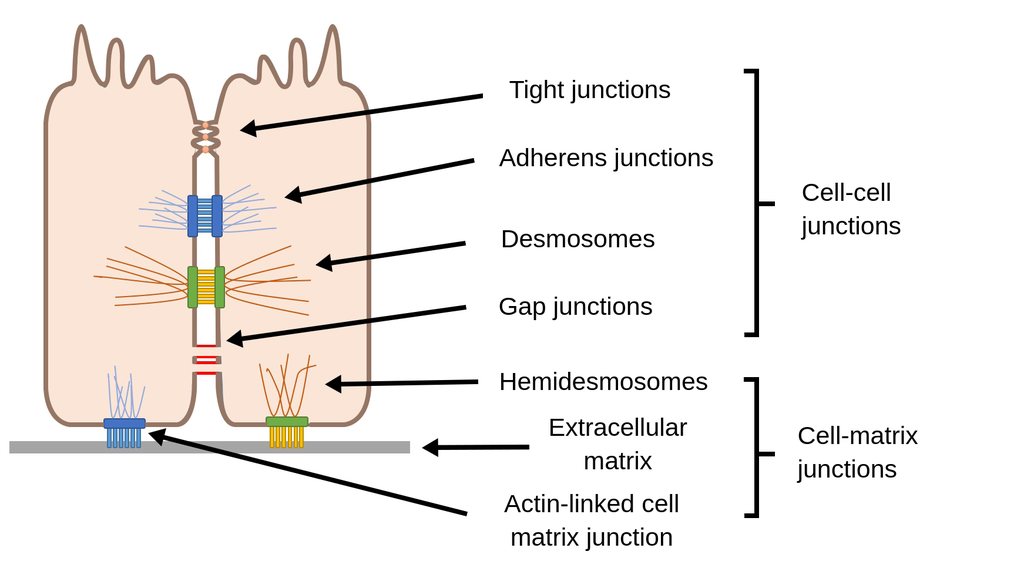
Tight Junctions
Location: Epithelial cells (e.g., intestines, blood-brain barrier).
Function: Seal spaces between cells to prevent leakage of molecules.
Process:
Sealing of intercellular space
Regulation of paracellular transport
Desmosomes
Location: Skin and cardiac muscle cells.
Function: Provide strong adhesion to resist mechanical stress.
Process:
Cadherin proteins link cytoskeletons of adjacent cells
Withstand shearing forces (e.g., in skin)
Gap Junctions
Location: Heart, smooth muscle, and some neurons.
Function: Allow direct communication and passage of ions/small molecules between cells.
Process:
Connexons (protein channels) align to form communication pathways
Electrical coupling in heart and coordinated contractions
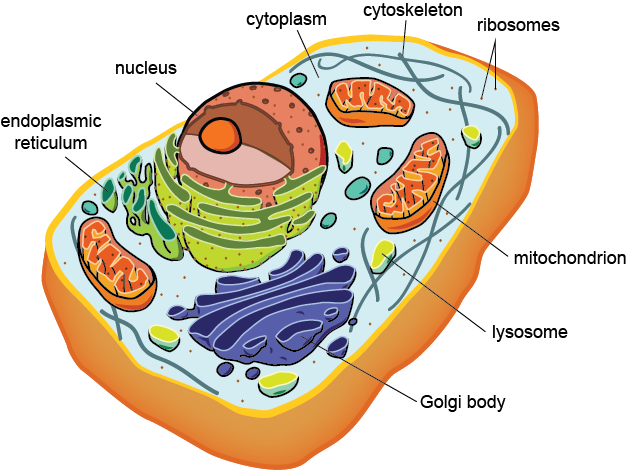
Organelles
Location: Cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells.
Function: Specialized compartments performing distinct functions essential for cell survival and function.
Process: Each organelle carries out distinct cellular functions essential for survival and homeostasis.
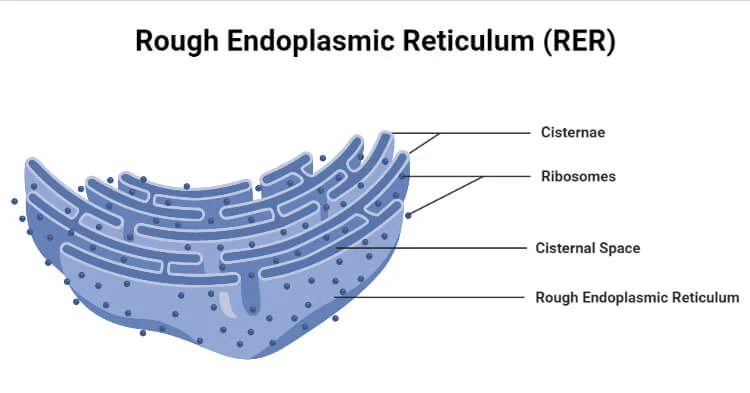
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER)
Location: Near the nucleus, studded with ribosomes.
Function: Synthesizes proteins for secretion or membrane use. Process:
Translation of proteins on bound ribosomes
Protein folding and transport to Golgi
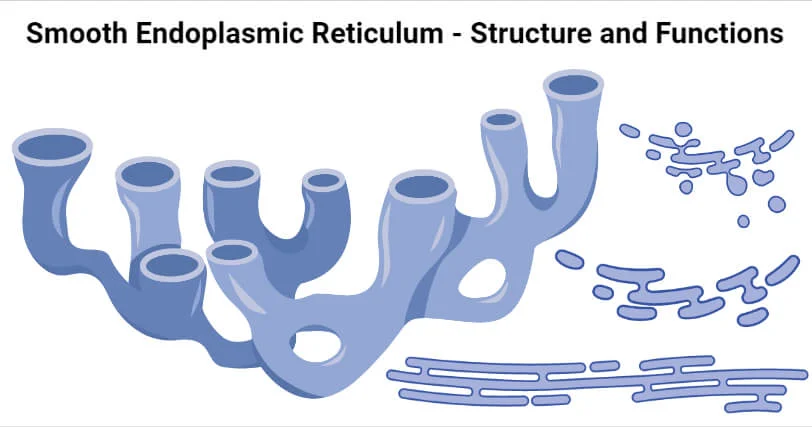
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER)
Location: Throughout the cytoplasm, no ribosomes.
Function: Synthesizes lipids, detoxifies drugs, stores calcium.
Process:
Lipid metabolism
Drug detoxification (especially in liver cells)
Calcium ion storage for signaling in muscle cells
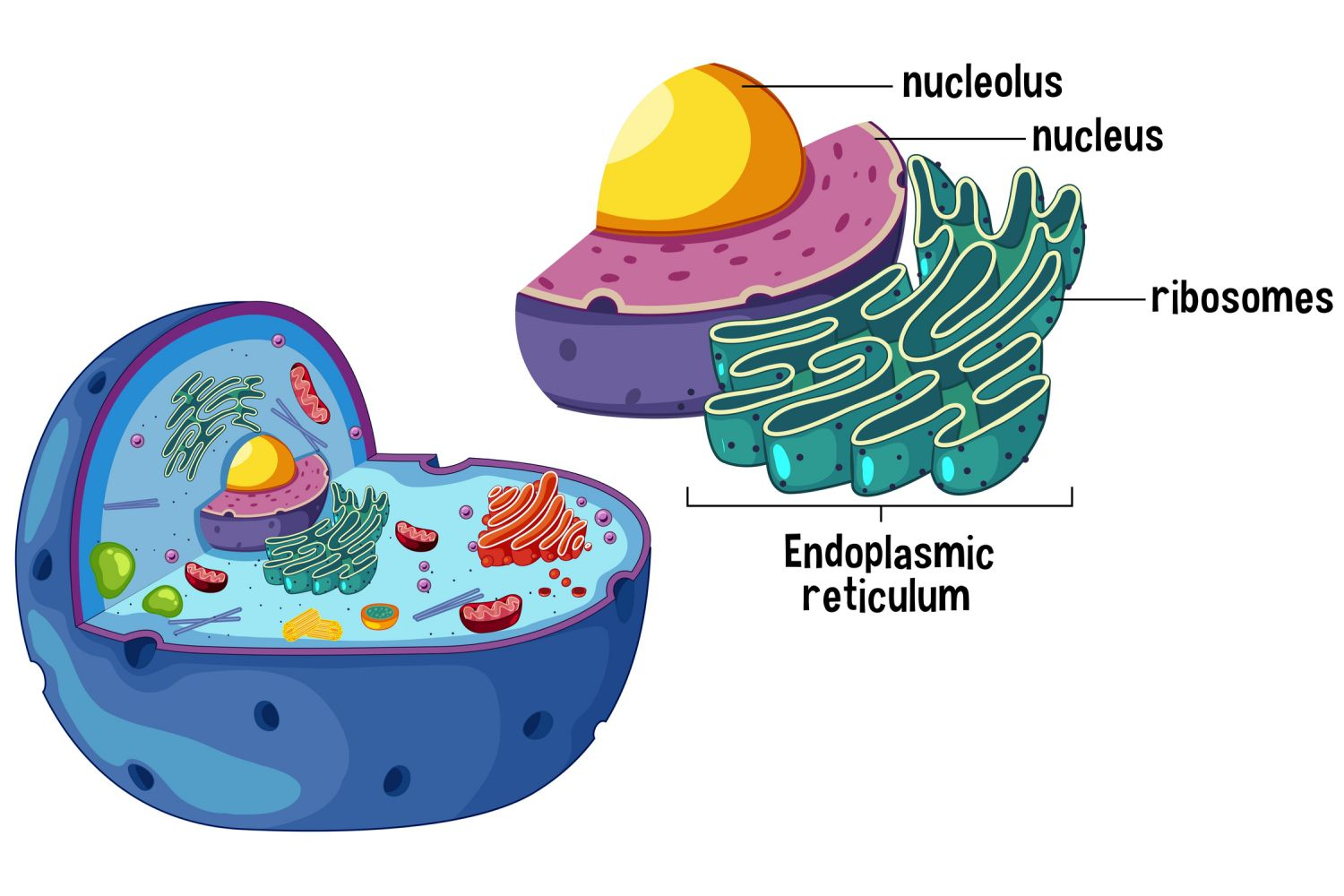
Ribosomes
Location: Free in cytoplasm or bound to RER.
Function: Site of protein synthesis (translate mRNA into polypeptides).
Process:
Translation (protein synthesis)
Polypeptide formation via tRNA and amino acid linkage
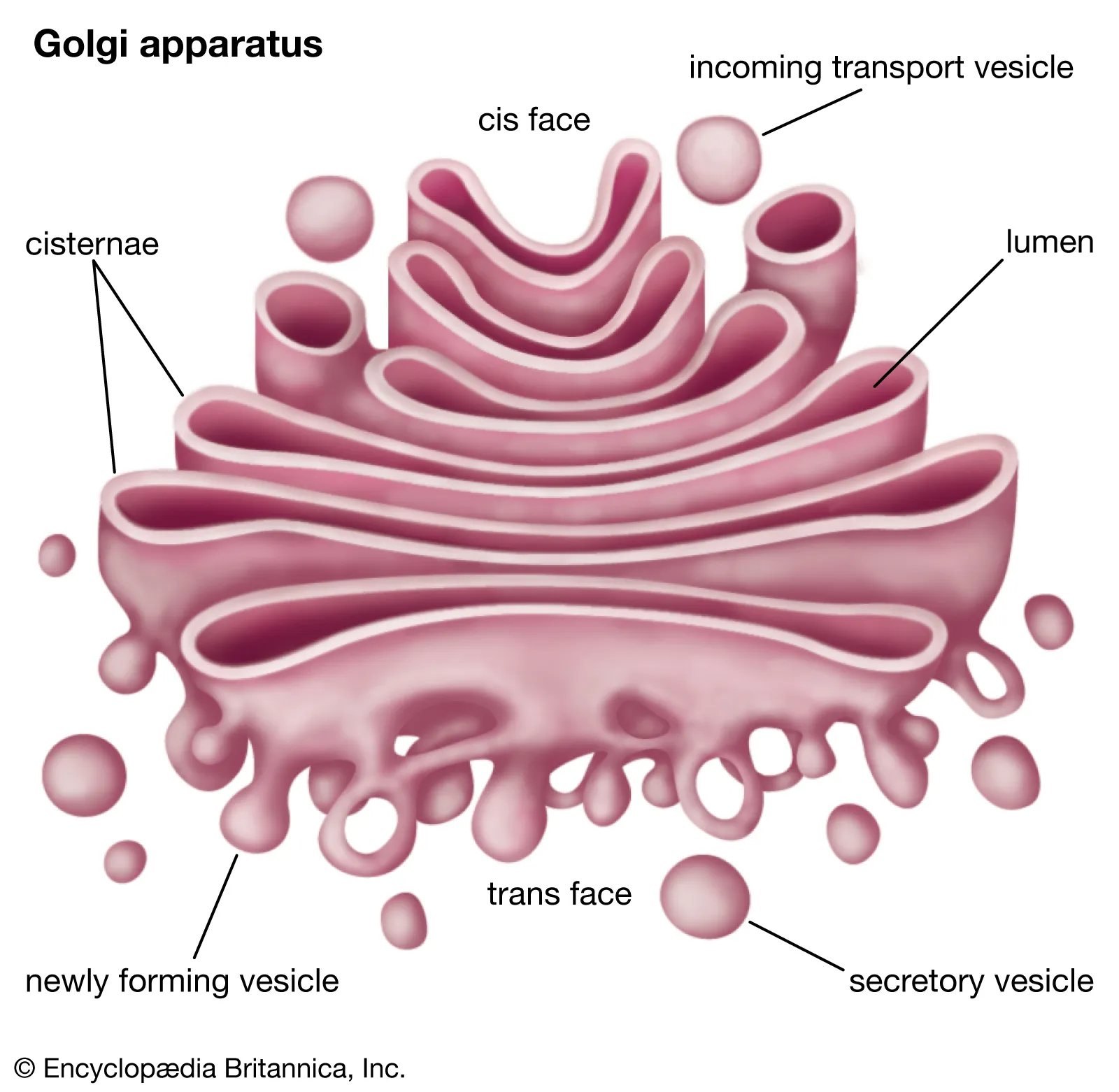
Golgi Apparatus
Location: Near ER and nucleus.
Function: Modifies, packages, and ships proteins and lipids via vesicles.
Process:
Vesicle transport from ER to Golgi
Glycosylation and final folding of proteins
Shipping via vesicles to membrane or lysosomes
Lysosomes
Location: Cytoplasm.
Function: Contain digestive enzymes to break down waste, old organelles, and pathogens (cellular "clean-up").
Process:
Endocytosis and autophagy
Enzymatic hydrolysis of macromolecules
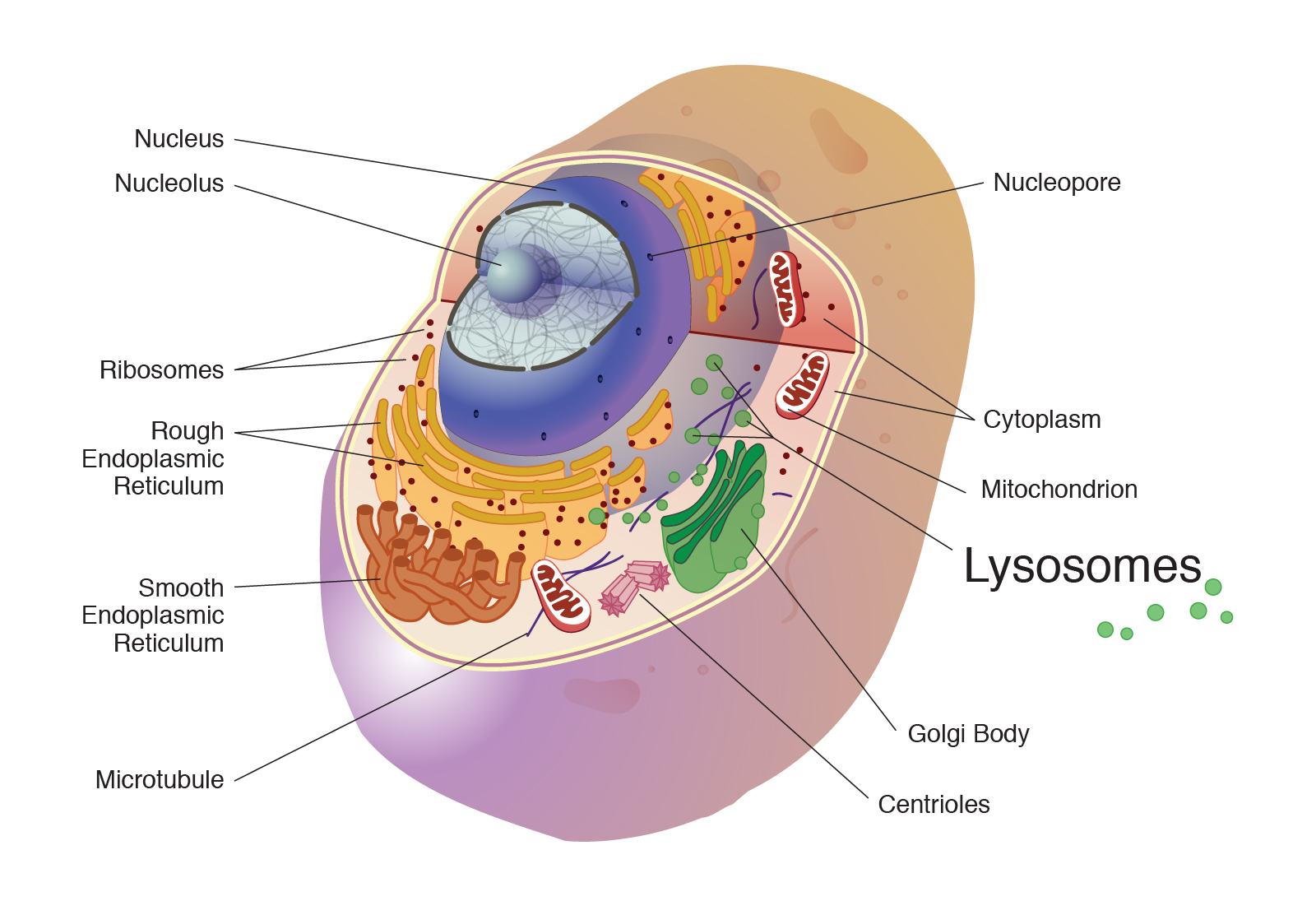
Peroxisomes
Location: Cytoplasm.
Function: Break down fatty acids and detoxify hydrogen peroxide and other harmful substances.
Beta-oxidation of long-chain fatty acids
Neutralization of hydrogen peroxide via catalase
Mitochondria
Location: Cytoplasm.
Function: Produce ATP via aerobic respiration; known as the cell's powerhouse.
Process:
Cellular respiration:
Glycolysis (in cytoplasm)
Krebs cycle (in matrix)
Electron transport chain (on inner membrane)
Apoptosis regulation and calcium storage
Cytoskeleton
Location: Throughout the cytoplasm.
Function: Maintains cell shape, provides support, enables intracellular transport, and assists in cell movement.
Process:
Microfilaments (actin) support shape and cell movement.
Intermediate filaments provide mechanical stability.
Microtubules guide vesicle and organelle movement and form mitotic spindles.
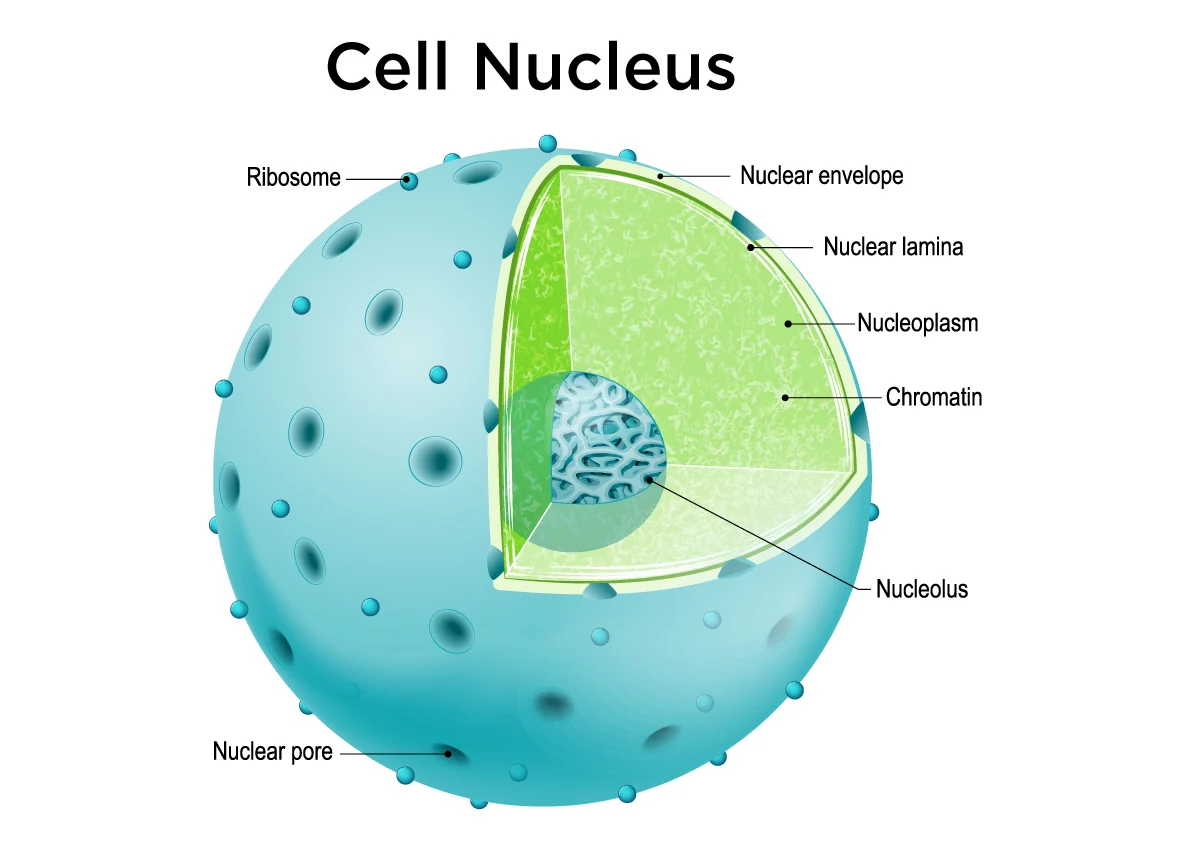
Nucleus
Location: Center of most eukaryotic cells.
Function: Stores genetic material (DNA); controls cell activities by regulating gene expression.
Processes:
Houses transcription (formation of RNA from DNA).
Coordinates cell growth, metabolism, and reproduction.
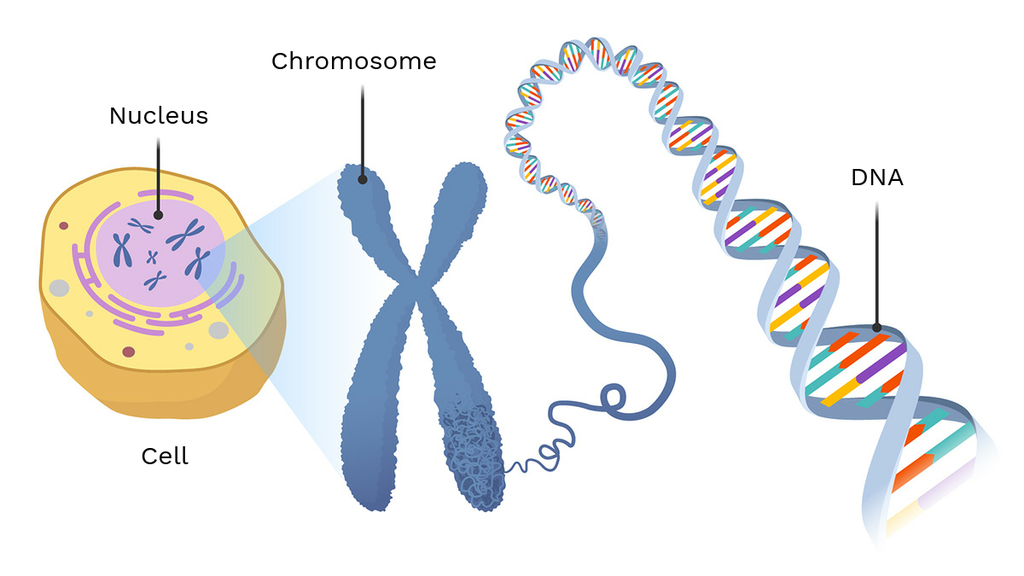
DNA
Location: Inside the nucleus (as chromatin/chromosomes).
Function: Carries genetic instructions for protein synthesis and inheritance.
Processes:
Replication (copies DNA before cell division).
Template for transcription in gene expression.
RNA and Protein Synthesis
Location: RNA is synthesized in the nucleus and functions in the cytoplasm.
Function: RNA transfers genetic instructions from DNA to ribosomes for protein production.
Processes:
mRNA: carries code from DNA.
tRNA: brings amino acids to ribosomes.
rRNA: part of ribosome structure.
Transcription
Location: Nucleus.
Function: Converts DNA instructions into messenger RNA (mRNA).
Process:
Initiation: RNA polymerase binds to DNA.
Elongation: mRNA strand is built.
Termination: mRNA detaches and exits nucleus.
Translation
Location: Ribosomes in cytoplasm or RER.
Function: Converts mRNA sequence into a chain of amino acids (polypeptide).
Process:
Initiation: mRNA binds to ribosome.
Elongation: tRNAs deliver amino acids, forming peptide bonds.
Termination: Stop codon halts process; protein released.
Protein Structure
Location: Synthesized in ribosomes, functions throughout the cell/body.
Function: Proteins are essential for structure, enzymes, signaling, and transport.
Levels of Structure:
Primary: Sequence of amino acids.
Secondary: Alpha helices and beta sheets (folded from hydrogen bonds).
Tertiary: 3D shape from interactions between R-groups.
Quaternary: Multiple polypeptides forming a functional protein (e.g., hemoglobin).