Quiz 9- Securing IoT
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcard set on lectures 22 and 23.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
True
True or False: In Zigbee, every network must have only one coordinator
Coordinator
Responsible for forming the network, including selecting channel, allow child nodes to connect.
Plays a routing role to relay messages from one node to another, as well as send/receive data
Router
A node with a routing capability and is also able to send/receive data.
Also allows other nodes to join the network through it
A network may have many of these
False; never
True or False: A router needs to go to sleep when not in use.
End Device
A node which is only capable of sending and receiving data
Cannot have child nodes connects to it
A network can have many of these
True
True or False: An end device has no routing capability and cannot relay messages
End Device
Which Zigbee node can have a sleep schedule where the parent node will buffer if the child is sleeping.
coordinator; routers
In Zigbee, a network consists of a single ____, and multiple of ____ and/or end devices.
True
True or False: In Zigbee, each node, except the coordinator, is associated with a either router or the coordinator (it’s parent).
False; can have multiple children
True or False: In Zigbee, a parent may only have one child.
Zigbee
An end device can only communicate directly with its own parent
Each router and the coordinator can communicate directly with any other router/coordinator within radio range
True
True or False: A router can be both a child and a parent
False; cannot
True or False: End devices can be parents
Reason why router and end devices are split
Routers need to maintain information about
Its children
Its own parent
all peer routers with which the node has direct radio communication
End device only needs to know its parent
Pre-configured network
Done by manufacturer. Typically cannot be modified or extended.
Self-configured network
System that is easily installed and configured by the end-user. Can modify or extend by the user.
Custom network
System adapted for specific application, designed and installed by designer using custom devices.
Data eavesdropped by adversary
Name a confidentiality threat in Zigbee
Adversary injects data into network
Name an integrity threat in Zigbee
Adversary delayed data being sent to coordinator
Name an availability threat in Zigbee
Pros of Zigbee
Designed to support battery operated devices (end devices)
Flexible location of nodes, since not tied to power supply
Easy modification of network by adding, removing, re-positioning nodes
E.g. lighting system for a building
Other vulnerabilities of Zigbee
Flexible location of nodes means that adversary can compromise a node and attempt to re-program a node or extract secrets
Adversary can attempt to add malicious nodes to the network
Network structure makes disruption easier to pull off
Access control list (Protection method in Zigbee)
Only allow pre-defined “good” nodes to join network
Frame counters (Protection method in Zigbee)
Ensures freshness, checking rejects any such repeated messages to prevent replay attacks on the network
MAC address
This is a 64-bit address, allocated by the IEEE, which uniquely identifies the device - no two devices in the world can have the same IEEE address.
Network Address
This is a 16-bit address identifies the node within the network and is local to that network
Two nodes in separate networks may have the same _____ address.
Randomly assigned by parent when joining network
Used by Zigbee to identify nodes. Higher level applications may choose to use MAC
(Step 1) Coordinator creating network
Set Extended PID and its own network address (always 0x0000)
Select radio channel
Set PAN ID of network. Scan to hear what is nearby, and randomly generate a value
(Step 2) Joining a network
Search for network by scanning channels. May have multiple networks. Application will determine which network to join
Select parent. Node may hear multiple parent candidate in network. Pick parent closest to coordinator
Send join message to parent, if parent accepts, parent assign network address to node (Parent checks with trust center to determine whether node is permitted device)
Obtain PAN ID, Extended PAN ID, and network address
A coordinator or router can be configured to only allow joins for new nodes for a certain time period
Network Key
Common to all nodes in a network. Randomly generated by coordinator
Used to encrypt/decrypt maintenance data. Sometimes used to encrypt/decrypt user data
Link Key
Used to secure communications between two nodes
Generated and assigned by coordinator
Can use together with network key
Trust Center
A single entity known as the ____ ____ is responsible for authenticating new devices wanting to join, as well as distribute security credentials. Trust center is typically also the coordinator
Encrypt network key with link key when a node joins the network.
How do we get the network key into a node?
Deassociation Attack
Adversary decouples a node from its neighbor, parent, child, AP, etc.
Can be done by jamming signal temporarily (e.g. disrupt heartbeat messages)
Common behavior is to re-associate (or re-initialize) then associate with malicious node
Pre-installed key approach
A common link key is pre-installed into every node at time of manufacture, i.e. every node has the same key
If a key is leaked, every device still shared the same key so all is compromised
But.. makes it easy for any node you buy to talk to the coordinator
However: traffic is encrypted using the network key. So a leaked link key is used only to inform a node of the network key at joining.
Install code approach
Get rid of common key for all devices
Each device has an “install code” programmed at the factory (should be randomly generator and not tired to any other credentials like MAC address and should never be put directly on the product)
When user buys node, will input this install code into the coordinator
Ideal is that a node will use this install code to generate a link key. Same for coordinator.
Other security protection
Use OOB to initiate nodes (Use NFC, barcode, or QR code to transmit initialization parameters)
Vendor specific implementation
Not always applicable nor desirable (DoS attack by launching deassociation attack)
Touchlink Protocol
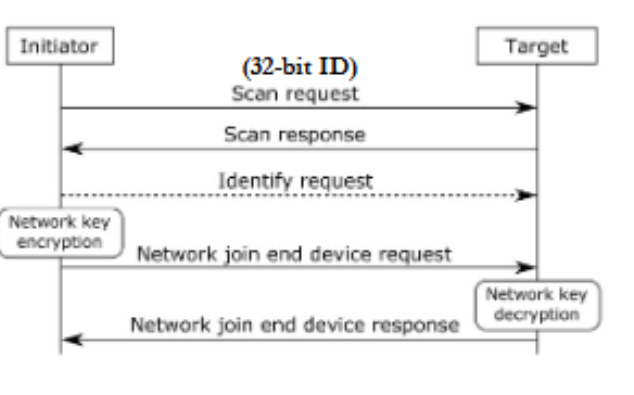
Touchlink Protocol
When lightbulb receives a scan request, will check the RSSI (received signal strength indicator)
If RSSI value is higher than some threshold, continue, else ignore
RSSI value higher than threshold implies that the initiator device is close by
Using proximity as a security mechanism (Zigbee range is hundreds of meters, but Touchlink limits it to something smaller (vendor specific))
Forces the adversary to be physically near
Reset-to-factory request (Zigbee light link)
A device receiving this message with valid transaction ID will cause the device to rest to factory new state, deleting all network and key info.
Join network request (Zigbee light link)
Used to instruct device to join new initiator network
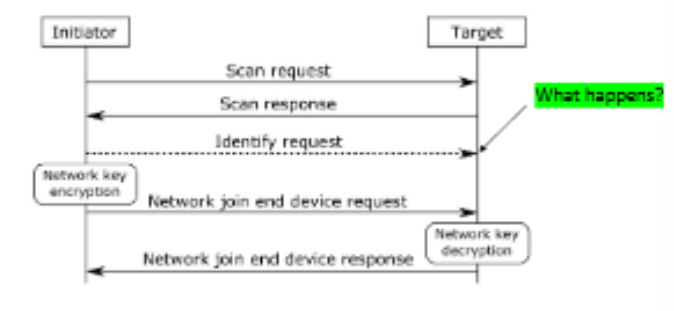
Identify request attack
Lights will blink to identify themselves
During this period, bulb unresponsive to other commands, including turning bulb off
The identify request is not encrypted, Just need transaction ID and duration
Adversary sends this message and set duration to max, 0xFFFE (~18 hrs)
Factory reset attack
Reset the configuration of a ZigBee device to the factory-new state
Done by sending reset to factory new request
Another form of DoS attack
Discretionary Access Control
Owner of the object controls access.
You can share a file on onedrive with others by specifying their emails. You can control whether they can view, edit, and download
Mandatory A/C
System implements control based on security policies and labels. E.g. top secret, secret, confidential, etc..
Role-based A/C
Access based on roles in an organization. E.g. finance, accounting, TA, professor, etc.
Attribute-based A/C
Access based on attributes and policies. E.g. doc can only be read if user is in accounting department and during business hours from on-campus network.