BPH
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
pharmachieve
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
BPH
non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate
can cause urinary symptoms identical to prostate cancer
not cancer —> cant spread to other parts of body
common in older men
cause elevated PSA (prostate specific antigen)
prostate enlargement depends on DHT
Type II 5 alpha reductase metabolizes circulating testosterone into DHT —> binds to androgen receptors = BPH
3 components:
Mechanical obstruction by enlarged prostate
Dynamic obstruction caused by tone of prostatic smooth muscle
the reaction of the bladder to the obstruction
diagnostic evaluation:
PSA = prostate specific antigen = tells about prostate size and predicts risk of BPH progression
clinical presentation
urinary frequency - need to urinate frequently
urinary urgency - sudden, urgent need to urinate
hesitancy - difficulty initiating
incomplete bladder emptying - feeling of persistent residual urine
straining - need strain or push to initiate and maintain urination
decreased force of stream - loss of force of urinary stream
dribbling - loss of small amounts of urine
Storage related symptoms = FUN
Frequency
Urgency
Nocturia
Voiding related symptoms
Hesitancy
incomplete bladder emptying
straining
decrease force of stream
dribbling
risk factors
Aging —> not common <40
Family hx (close male relative)
Medications = mimic or exacerbate symptoms
antihistamines
diuretics
African descent males
Lifestyle
obesity increases risk
Comorbidities
diabetes and heart disease can increase risk
drug causes
Antihistamines
prevent bladder muscle from contracting
Decongestants
tighten muscles in prostate and bladder neck = more difficult for urine to leave bladder
Diuretics
increased urine production
Opiates
impaired bladder contractility
TCAs
anticholinergic effects
goals of therapy
provide relief or resolution of lower urinary tract symptoms (LUTS)
decrease risk of progression of BPH
prevent complications from bladder outlet obstruction
early diagnosis of prostate cancer
reduce risk of surgical intervention
non pharm
Watchful waiting
periodic visits to physician —> no treatment
Lifestyle changes
fluid restriction
avoid irritative beverages (caffeine or alcohol)
avoidance and/or monitoring of some medications (diuretics, decongestants, antihistamines, antidepressants)
elevate legs before resting if existing pedal edema
timed voiding (bladder retraining)
pelvic floor exercises
treat constipation
Surgery
treatment options
alpha blockers = FAST!
5-alpha reductase inhibitors = decrease prostate size but SLOW
PDE5 inhibitors = QUICK (ED)
antimuscarinics = can use with alpha blockers
Beta 3 Adrenergic agonists
Desmopressin = nocturia
algorithm
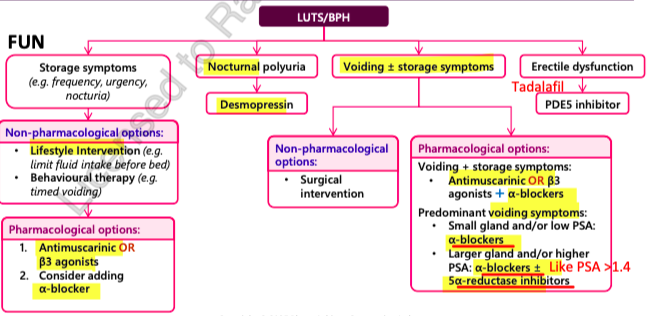
alpha blockers
Selective = SAT (when your on an airplane, the seat your selected, you SAT ahead of time)
Silodosin
Alfuzosin
Tamsulosin
Nonselective = DT —> need dose titration bc it can cause decrease in BP
Doxazosin
Terazosin
tips:
work FAST! but does NOT decrease risk of progression (little impact on prostate growth)
effects in 1 week but can take up to 6 weeks for full effect
all equally effective
interactions:
Antihypertensives (increased hypotension) —> for Non selective b/c increases risk of hypotension
CYP3A4 inhibitors
s/e:
Dizziness, hypotension (esp with Doxazosin and Terazosin)
HA
Asthenia (abnormal weakness)
Nasal congestion
Hypotension
Tamsulosin = floppy iris syndrome (only issue if having cataract surgery), retrograde ejaculation
Silodosin = retrograde ejaculation
avoid CrCl<30
give w food
use selective ones to reduce risk of hypotension
minimize s/e of doxazosin and terazosin by taking at bedtime
renal: Silodoson
CrCl 30-50 = reduce dose
CrCl <30 = AVOID
Silodosin and Alfuzosin = take with food
provide symptomatic relief
used in patients awaiting surgery/ unwilling for surgery
rare: allergic reaction to tamsulosin in patients with sulfa allergy
5 alpha reductase inhibitors
Finasteride, Dutasteride
REDUCE PROSTATE SIZE! = decrease risk of progression = decrease risk of surgical intervention (most effective if prostate is large; prostate vol >30ml)
use if large prostate (>30ml) and higher PSA (>1.4ng/ml)
Dutasteride = higher efficacy @ reducing DHT @ 6 months
SLOW!! takes 6-12 months for symptomatic relief
decrease PSA by 50%
lifelong therapy —> if stop, prostate will re-grow
interactions:
CYP3A4 inhibitors (dutasteride only) = Clarithromycin, itraconazole, fluconazole, verapamil, amiodarone
S/E: low risk
Impotence
sexual dysfunction
decreased libido
decreased semen quantity at ejaculation
gynecomastia (rare)
risk of suicidal ideation (rare; finasteride)
use in patients awaiting surgery/ unwilling for surgery
compliance is important for effective decrease
hazardous drug handling consideration!
tadalafil
PDE5 inhibitor —> used DAILY
Quick onset!
used for daily management of erectile dysfunction and BPH
s/e:
dyspepsia
HA
nasal congestion
back pain
flushing
visual disturbances
permanent vision or hearing loss (rare)
interactions:
Alpha blockers = decrease in BP
nitrate based meds = FATAL hypotension
CrCl < 30 = avoid once daily dosing
AVOID NITRATES!!!! decrease in BP!!
can take w or w/o food
antimuscarinics
Fesoterodine, Oxybutynin, Solifenacin, Tolterodine
QUICK onset!
symptomatic relief of overactive bladder (helpful for storage sx) = FUN sx
s/e:
Dry mouth
drowsiness
constipation
small risk of urinary retention —> use with caution if residual urine vol >250 cc
interactions:
TCA’s
Anticholinergics
used in combo with alpha blockers!
oxybutynin = most anticholinergic
Tolteridone = doesnt cross BBB = good in elderly
DO NOT USE IN UNCONTROLLED NARROW ANGLE GLAUCOMA!
mirabegron ER
Beta 3 adrenergic agonist
symptomatic relief of overactive bladder
s/e:
Hypertension —> AVOID IN UNCONTROLLED HTN
Nsopharyngitis
UTI
Tachycardia
interactions:
moderate inhibitor of CYP2D6 (substrates = Fluoxetine, Paroxetine, Venlafaxine, Mirtazapine, Codeine)
weak inhibitor of PgP
well tolerated
can be used in combo with antimuscarinics
should not be chewed or crushed
desmopressin
used in nocturnal polyuria = decreases # nocturnal voids and increases hrs of undisturbed sleep
QUICK ONSET —> 1 hr
s/e:
Hyponatremia
Xerostomia (dry mouth)
HA
Dizziness
Abdominal pain
interactions:
Loop diuretics
corticosteroids
any hyponatremia associated agents
Na levels must be taken at baseline in all men, then 7 days and then 30 days after starting
Sodium levels should be taken with dose increases and periodically during treatment
combination therapy
Alpha blockers (silodosin, alfuzosin, tamsulosin, doxazosin, terazosin) + 5-Alpha reductase inhibitors (dutasteride and finasteride)
appropriate and effective in patients with LUTS associated with prostate enlargement (>30 ml)
rapid relief by alpha blocker and sustained relief of symptoms from 5-alpha reductase inhibitors (by decreasing PSA, prostate volume, altering disease progression and preventing need for surgery)
cons:
additive side effects
increased associated with new cardiac failure (high risk for non-selective alpha blockers)
most improvement in LUTS = improves symptoms and flow rate vs either agent alone
if successfully treated, can discontinue alpha blocker after 6-12 months
if sx re-occur: can restart alpha blocker
monitoring
