Osmosis Experiment in BIO 202 Lab
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What is cell transport?
The movement of substances into and out of cells, which can occur with or without the use of energy.
What is the difference between active transport and passive transport?
Active transport requires energy (ATP) to move substances against the concentration gradient, while passive transport occurs without energy as substances move down the concentration gradient.
What is Brownian motion?
The constant, random motion of molecules that helps drive passive transport.
What is diffusion?
The random movement of solute molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, considered a passive form of transportation.
What is osmosis?
A special type of diffusion where the solvent (usually water) moves through a selectively permeable membrane from a region of higher solvent potential to a region of lower solvent potential.
What happens in a hypertonic solution with respect to a cell?
A hypertonic solution contains more solute than the cell, causing water to move out of the cell.
What is an isotonic solution?
An isotonic solution has the same concentration of solutes as the cell, resulting in no net movement of water.
What occurs in a hypotonic solution with respect to a cell?
A hypotonic solution contains fewer solutes than the cell, leading to an influx of water into the cell, which can cause cell lysis.
What is the purpose of the lab described in the notes?
To observe the physical effects of osmosis using dialysis tubing to simulate the movement of water into and out of human body cells.
What is dialysis tubing and its significance in the experiment?
Dialysis tubing is a semi-permeable membrane used to simulate cell membranes, allowing only small molecules like water to pass.
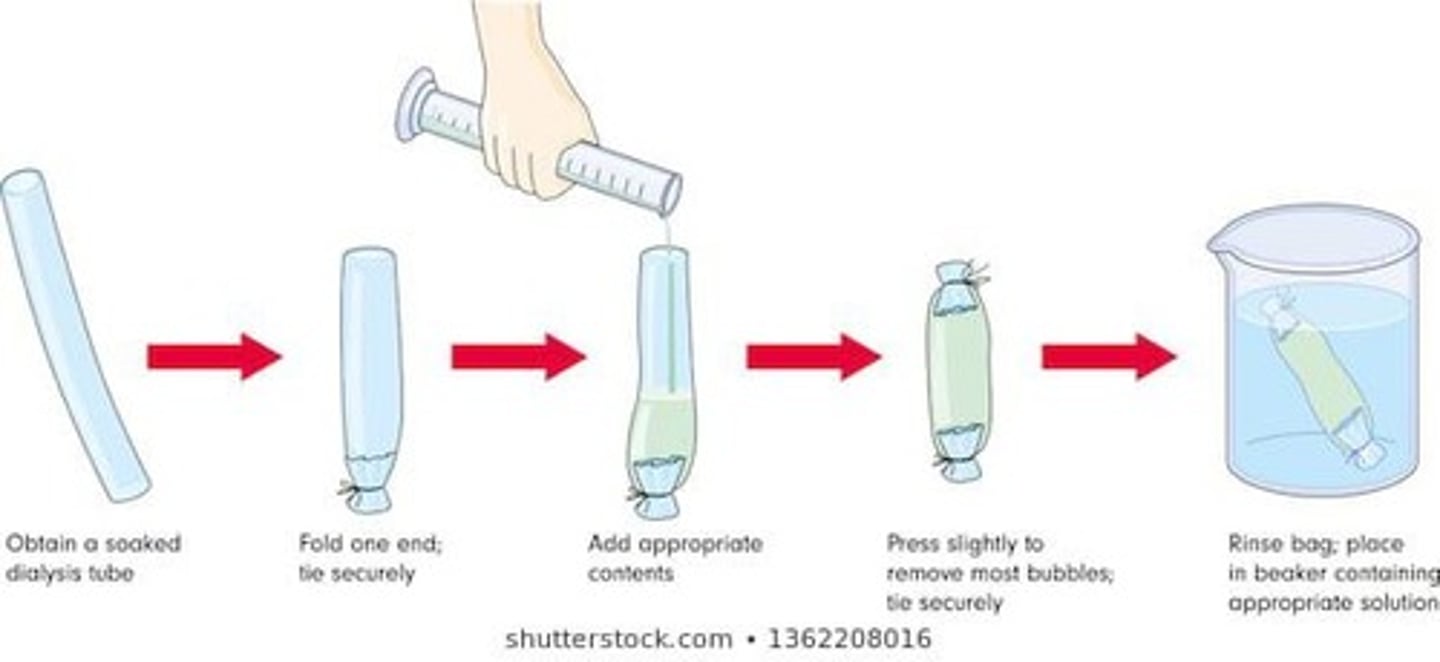
What solute was used in the osmosis experiment?
Sucrose was used as the solute in the experiment.
What was the independent variable in the osmosis experiment?
The sucrose concentration of the solutions.
What was the dependent variable in the osmosis experiment?
The mass of the dialysis tubes.
How does mass change indicate movement of water in the experiment?
Change in mass reflects the net movement of water into or out of the dialysis tubing.
What does a small mass change in Tube B indicate about its solution?
It indicates that Tube B was in an isotonic solution, as there was no significant net water movement.
What happens to red blood cells in a hypotonic solution?
Water enters the blood cells, causing them to swell and potentially burst.
Why is drinking seawater harmful?
Seawater is hypertonic compared to body cells, drawing water out of cells and leading to dehydration.
What is the significance of the concentration gradient in osmosis?
The concentration gradient drives the movement of water, with water moving from areas of lower solute concentration to higher solute concentration.
What is the role of a selectively permeable membrane in osmosis?
It allows certain molecules (like water) to pass while restricting others, facilitating the process of osmosis.
How does the rate of change in mass vary over time in dialysis tubes?
The rate of change slows down as the experiment proceeds due to the concentration gradient decreasing as equilibrium is approached.
What is the effect of sucrose concentration on water movement in dialysis tubing?
Higher sucrose concentration outside the tubing leads to water moving out of the tubing, while lower concentration leads to water moving in.
What is the relationship between solute concentration and osmotic pressure?
Higher solute concentration increases osmotic pressure, driving water movement towards the area of higher solute concentration.
What is the significance of the term 'net water movement'?
It refers to the overall direction of water movement, considering both the inflow and outflow of water.
What is the expected outcome of placing a cell in a hypertonic solution?
The cell will lose water, leading to shrinkage.
What is the expected outcome of placing a cell in a hypotonic solution?
The cell will gain water, potentially leading to swelling and bursting.