Molecular Genetics - Quiz #2
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
41 Terms
What is the process by which proteins are made from DNA?
Proteins are made through transcription and translation of DNA into RNA, which is then used to build proteins.
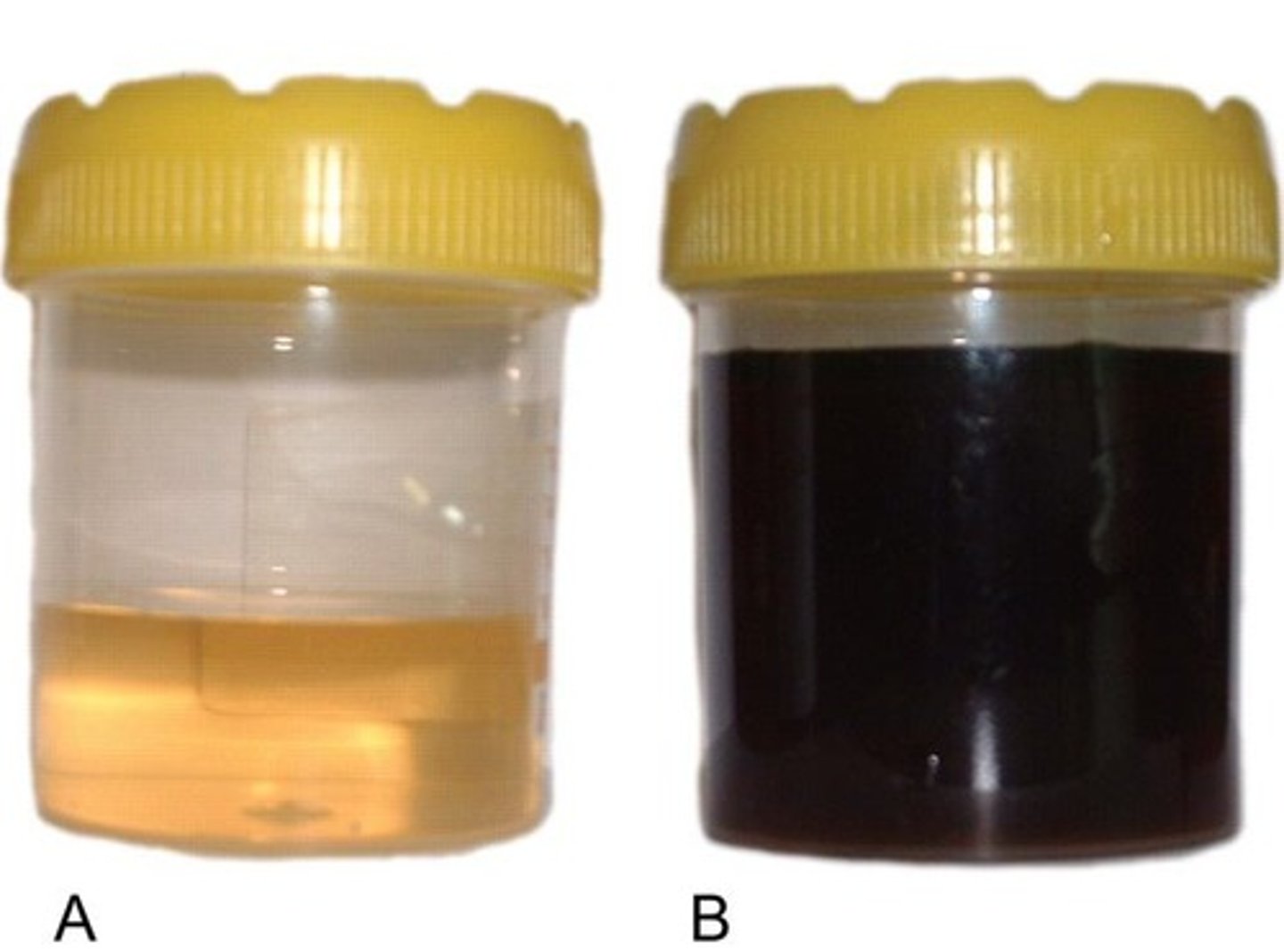
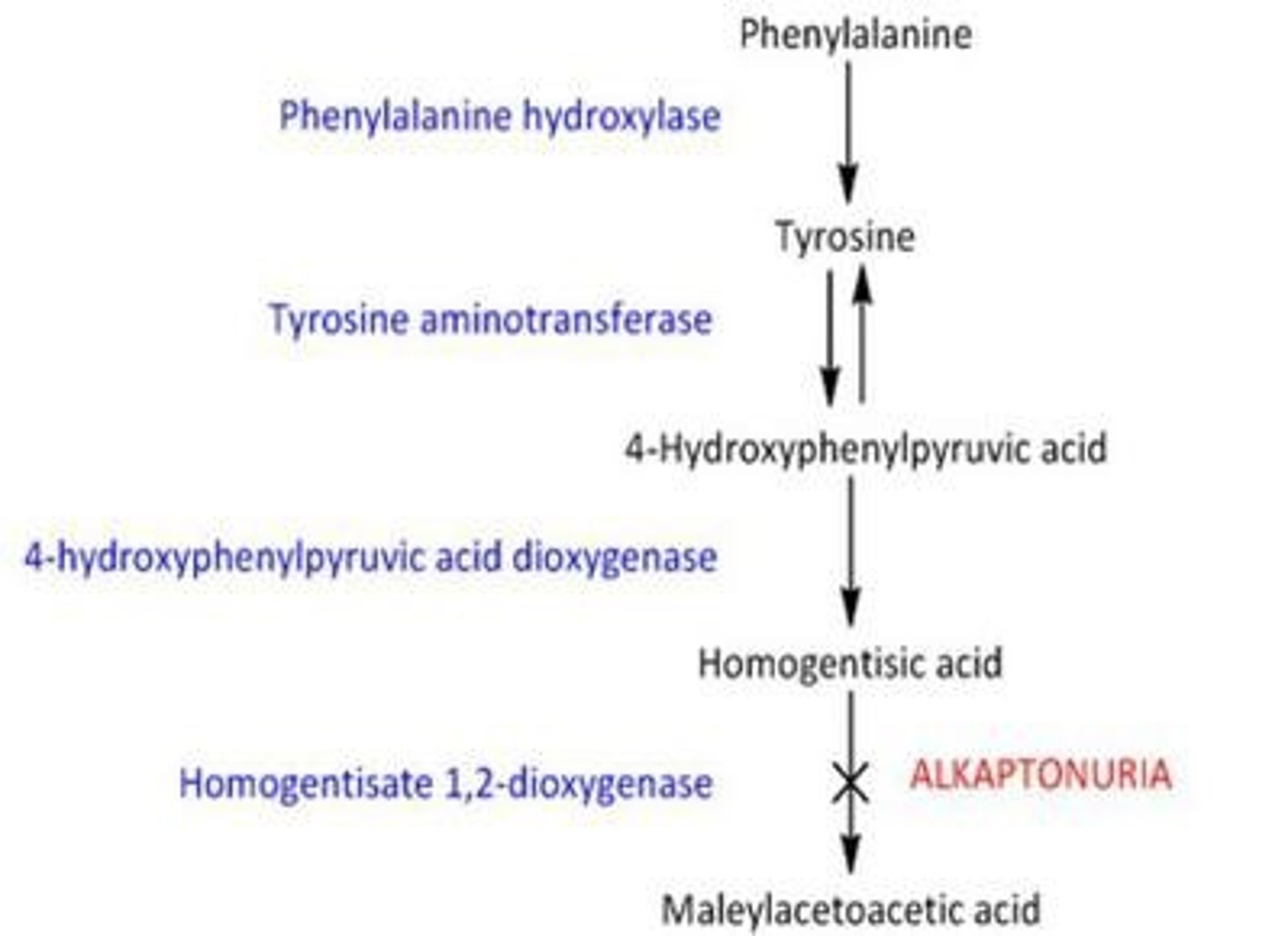
Who began early research into the importance of genes and what condition did he study?
Archibald Garrod studied alkaptonuria, a condition where urine turns black on contact with air.
What hypothesis explains the link between genes and proteins?
The One Gene-One Polypeptide Hypothesis states that each gene codes for a specific polypeptide.
What is the Central Dogma of molecular genetics?
The Central Dogma states that genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins.
What is transcription in the context of protein synthesis?
Transcription is the process of copying information from DNA into RNA.
What is the role of messenger RNA (mRNA)?
mRNA carries the genetic information from DNA to ribosomes for protein synthesis.
What is the function of transfer RNA (tRNA)?
tRNA binds to specific amino acids and transfers them to the ribosome to build proteins.
What is ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and its role?
rRNA is a component of ribosomes that facilitates the binding of mRNA and tRNA during protein synthesis.
What enzyme is responsible for creating RNA during transcription?
RNA Polymerase reads the DNA template and synthesizes a complementary RNA strand.
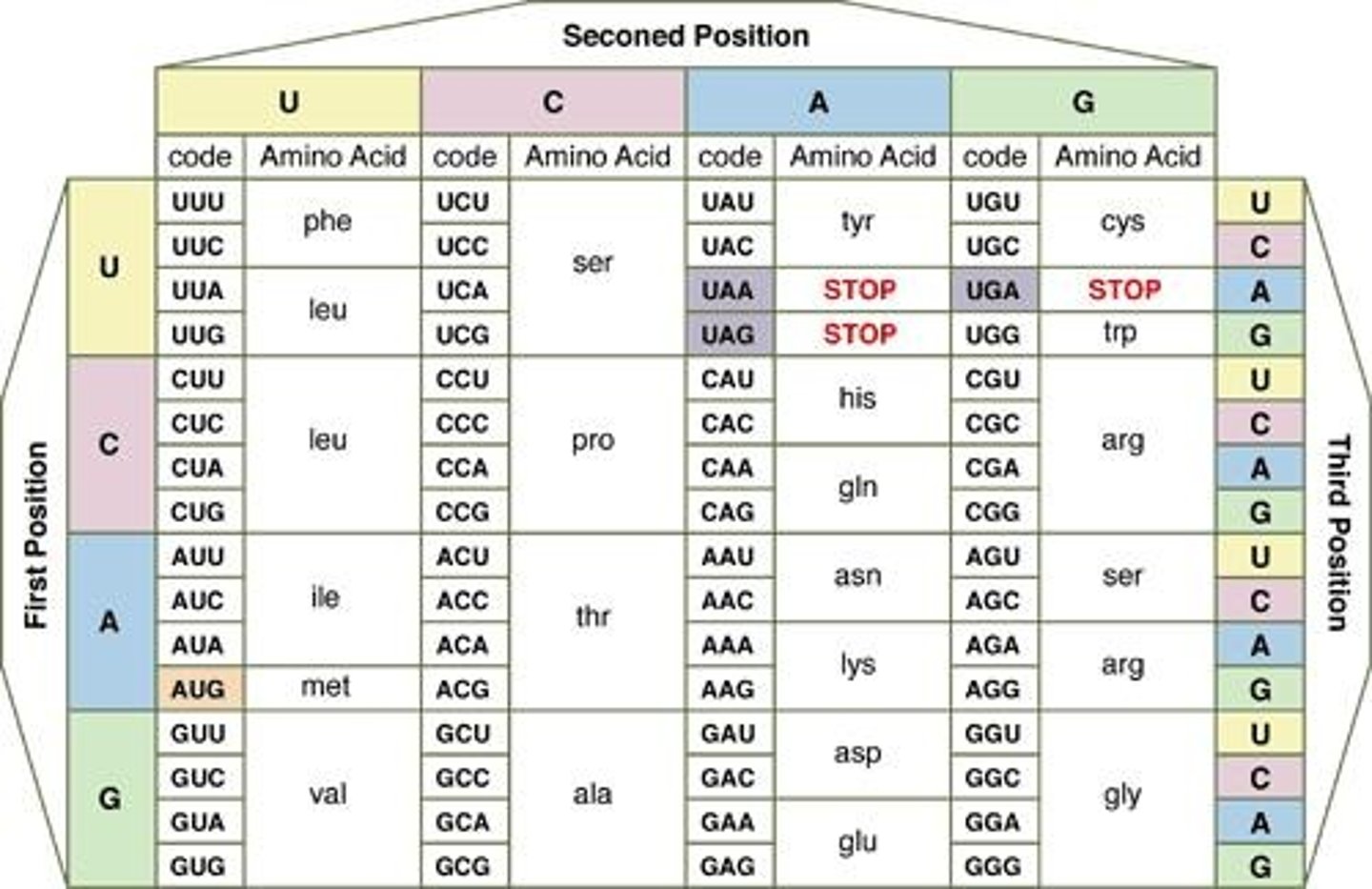
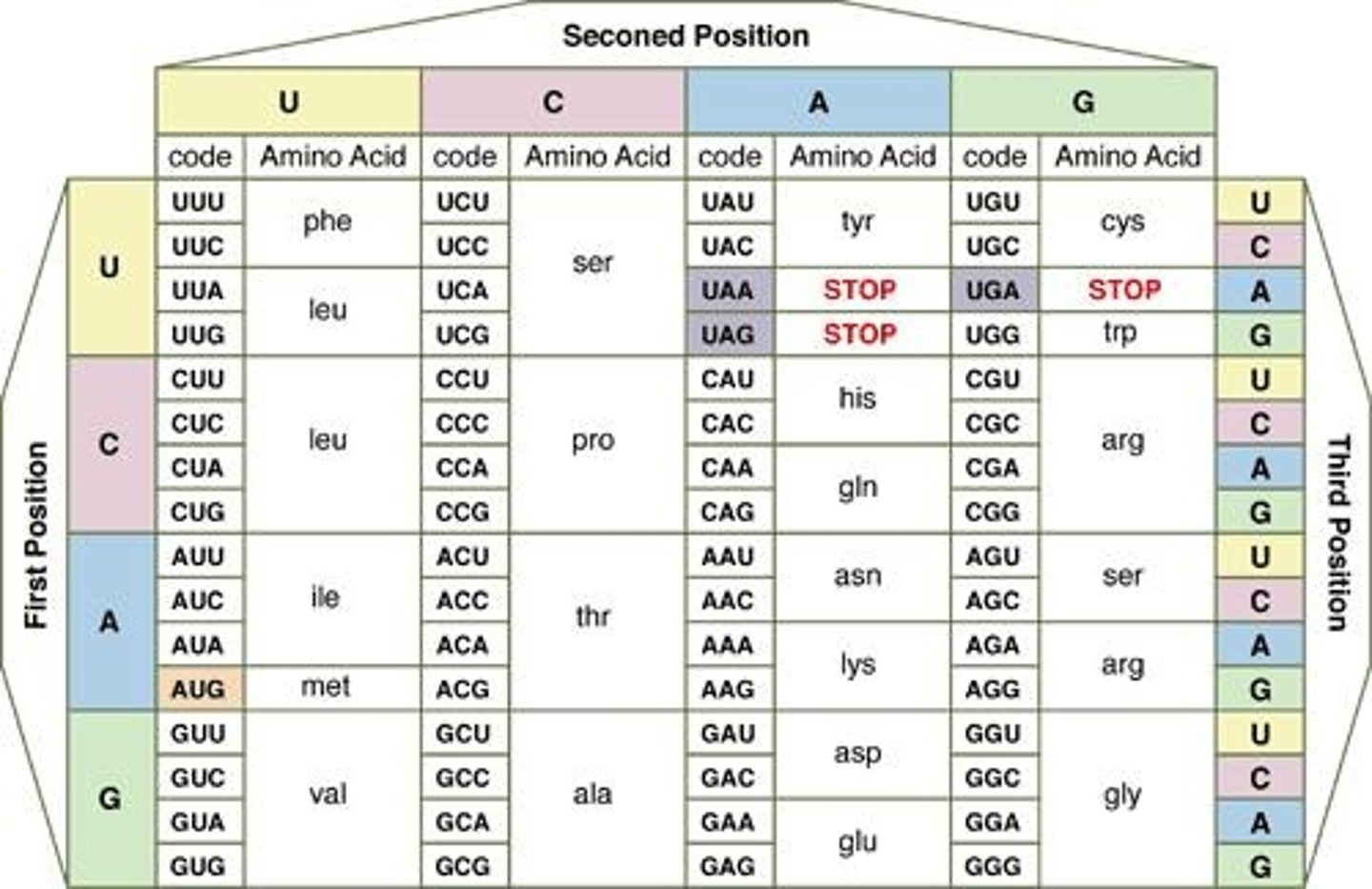
What is a codon?
A codon is a sequence of three nucleotides in RNA that codes for a specific amino acid.
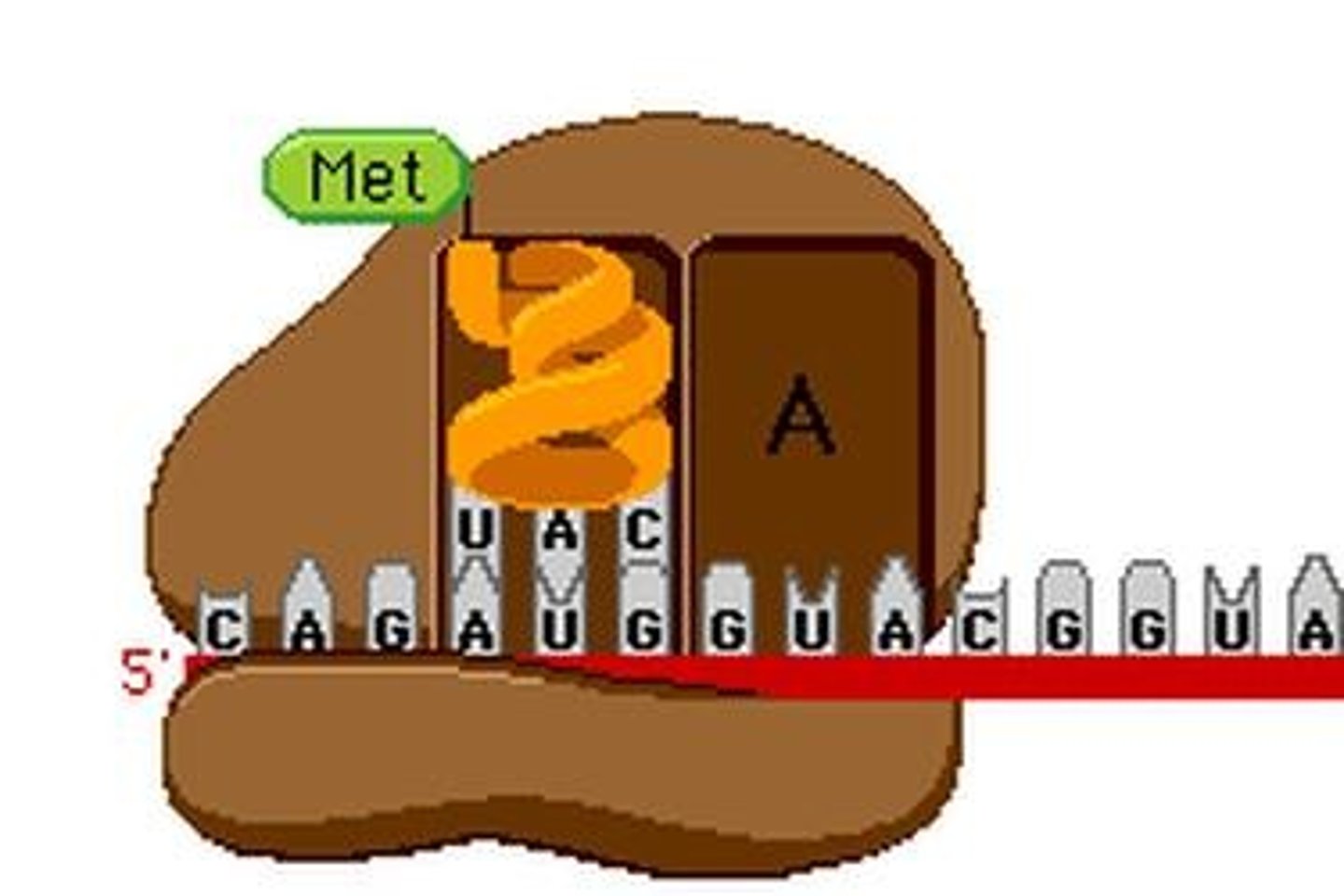
What is the significance of the start codon?
The start codon (AUG) initiates translation and codes for the amino acid methionine.
What are stop codons and their function?
Stop codons (UAA, UAG, UGA) signal the termination of protein synthesis.
What is the genetic code?
The genetic code is the relationship between nucleotide sequences and the amino acids they encode.
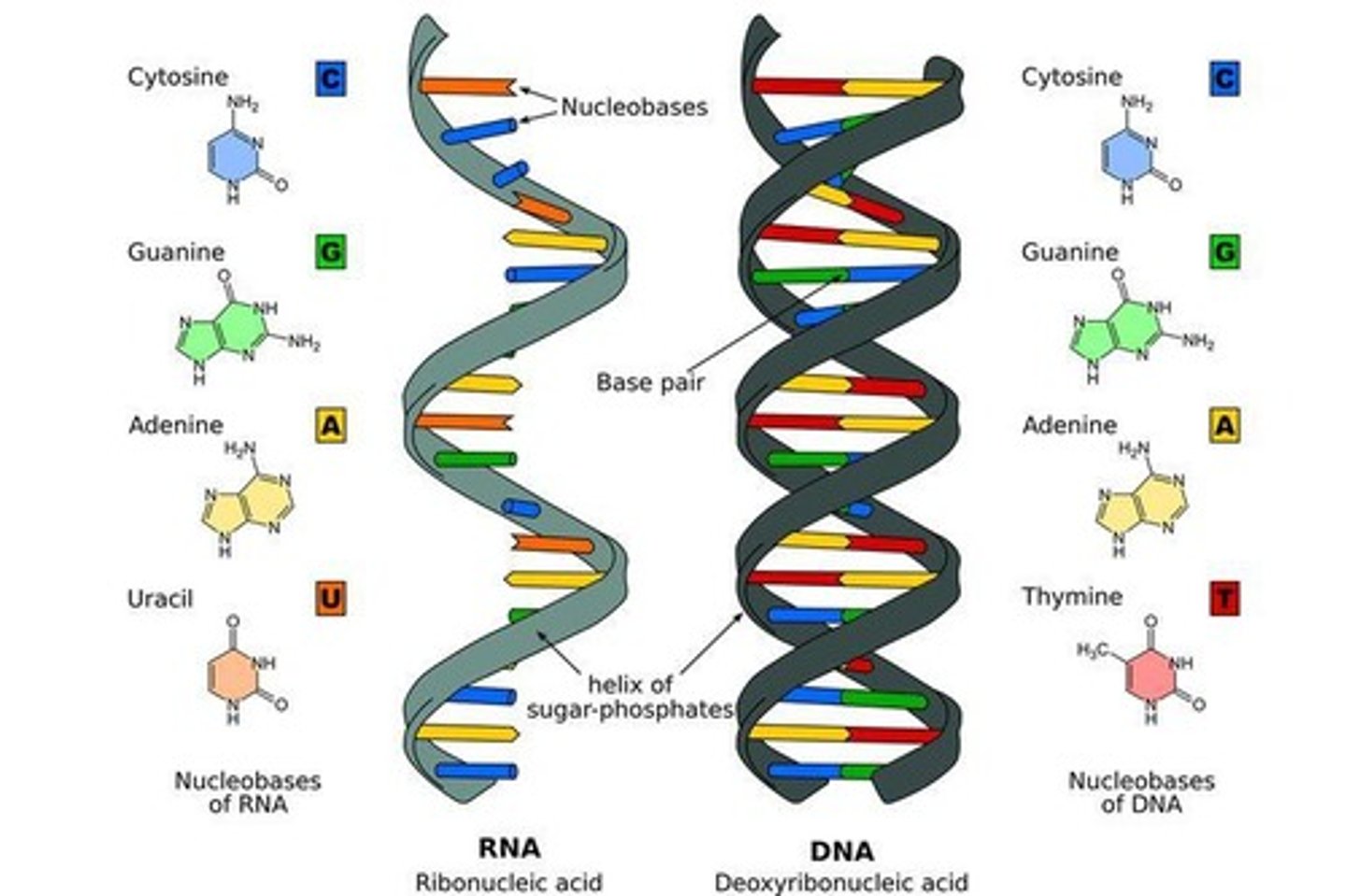
How does RNA differ from DNA in terms of structure?
RNA is single-stranded, contains ribose sugar, and uses uracil (U) instead of thymine (T).
What is pre-mRNA?
Pre-mRNA is the initial RNA strand that must be modified before becoming mature mRNA.
What happens during the folding of proteins?
Folding is the process where an amino acid chain assumes its functional three-dimensional shape.
What does it mean that the genetic code is universal?
The same codons specify the same amino acids across all living organisms, indicating a common evolutionary origin.
What is the role of the ribosome in protein synthesis?
Ribosomes facilitate the translation of mRNA into a polypeptide chain by coordinating tRNA and mRNA.
What is the purpose of the genetic code's redundancy?
The redundancy allows for multiple codons to code for the same amino acid, providing a buffer against mutations.
What is the relationship between amino acids and proteins?
Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, linked together in specific sequences to form polypeptides.
What is the primary function of ribosomal RNA (rRNA)?
To make up ribosomes and facilitate the binding of mRNA and tRNA during translation.
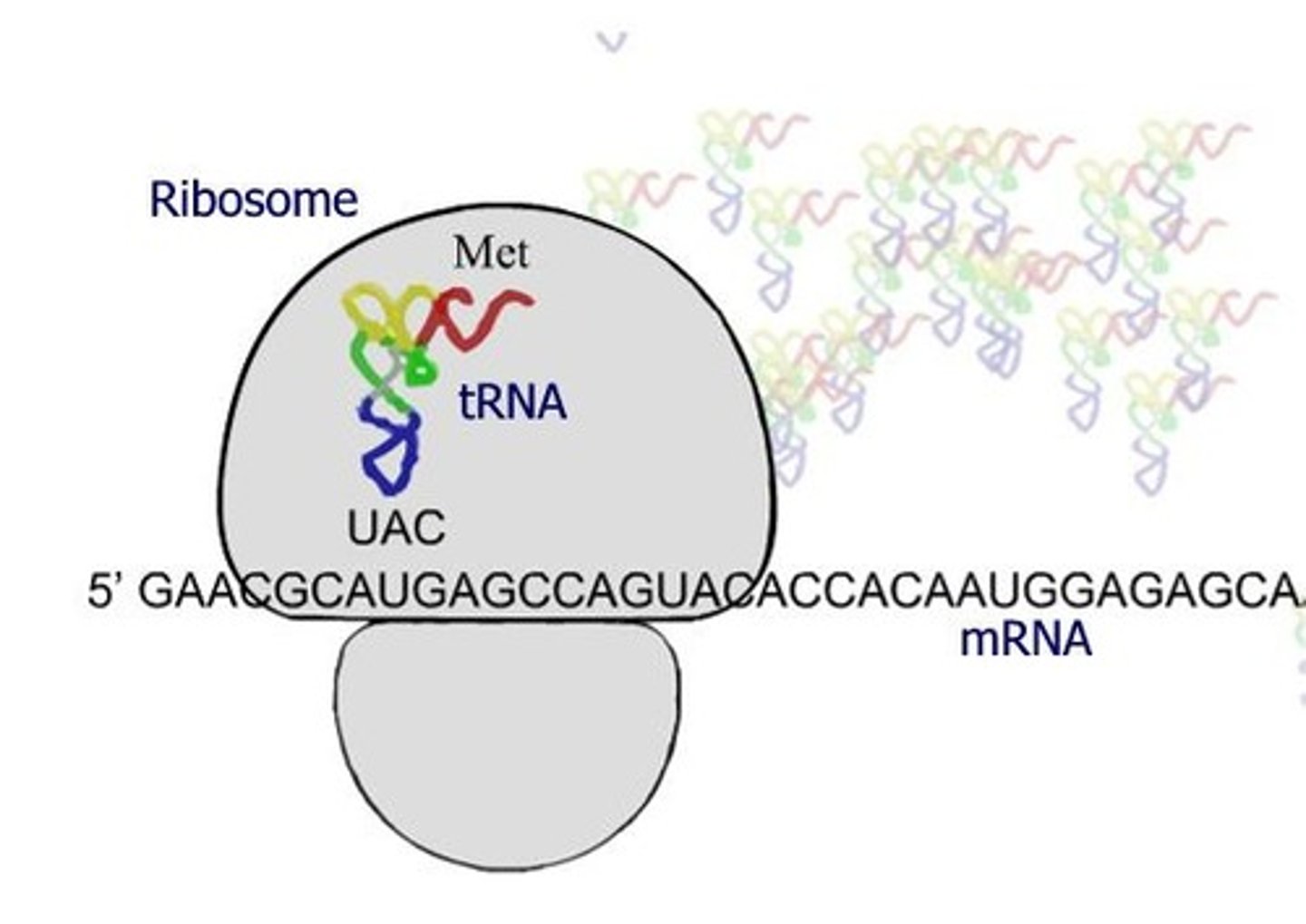
What are the three main steps of protein synthesis?
Initiation, Elongation, and Termination.
What is the role of the initiator codon in protein synthesis?
The initiator codon (AUG) signals the start of translation and codes for the amino acid methionine.
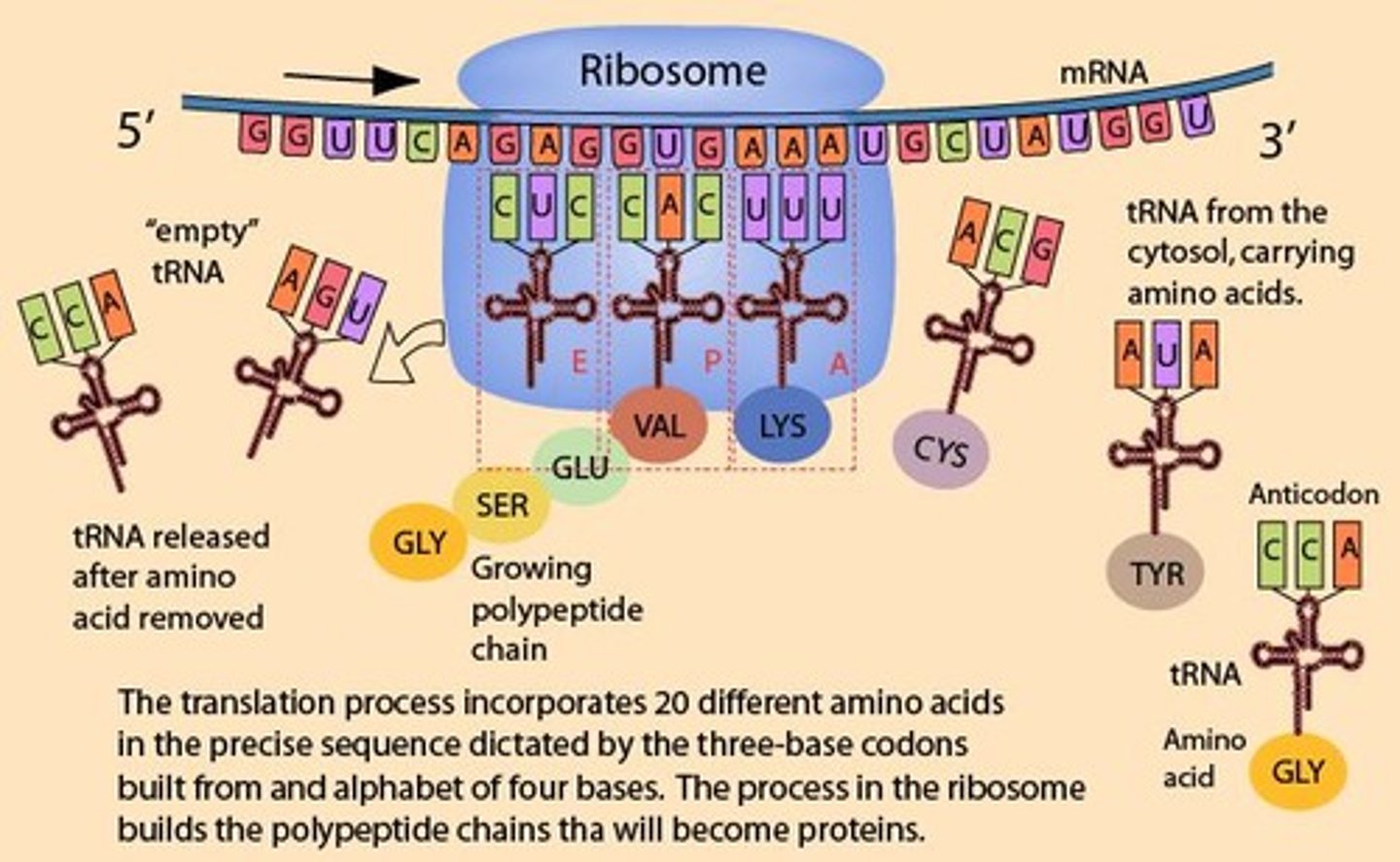
What is the function of the A, P, and E sites in the ribosome?
A Site: binds aminoacyl tRNA; P Site: forms peptide bonds; E Site: prepares tRNA for exit.
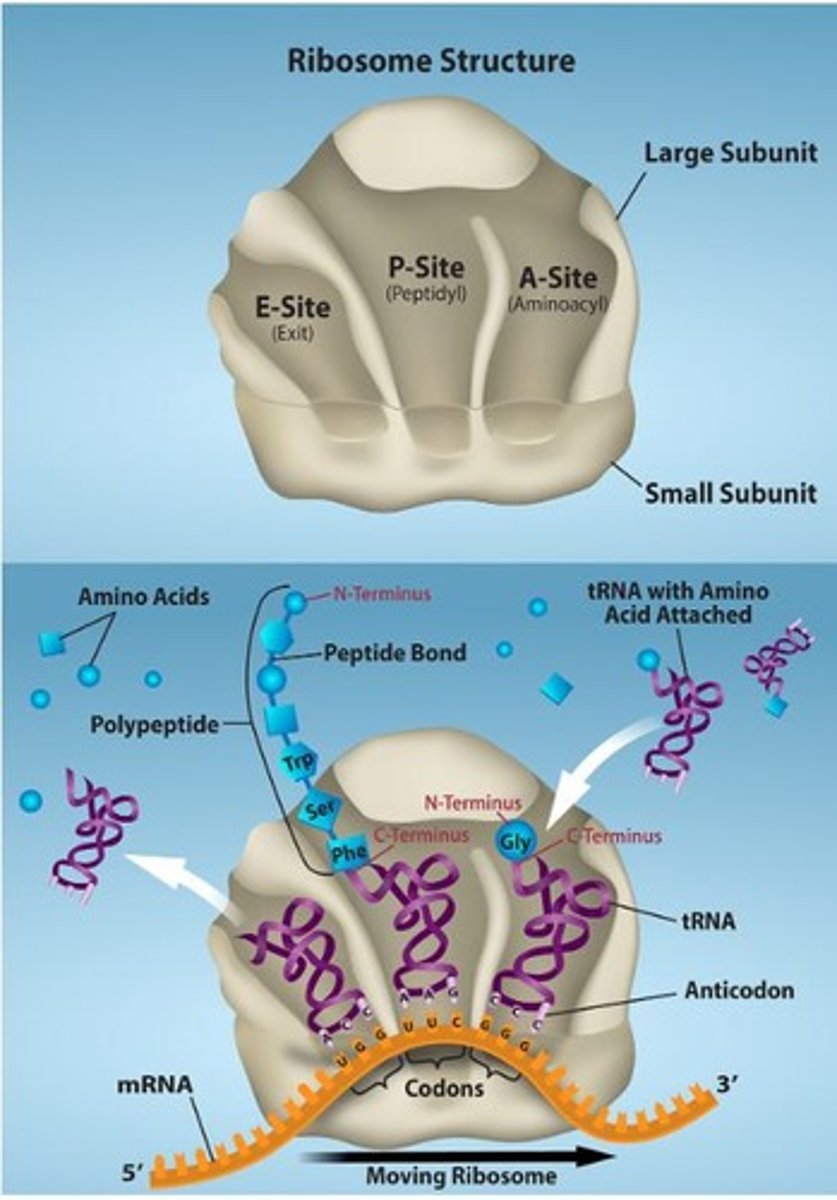
What occurs during the elongation phase of translation?
Ribosomes move along mRNA, reading codons and bringing in corresponding tRNA with amino acids.
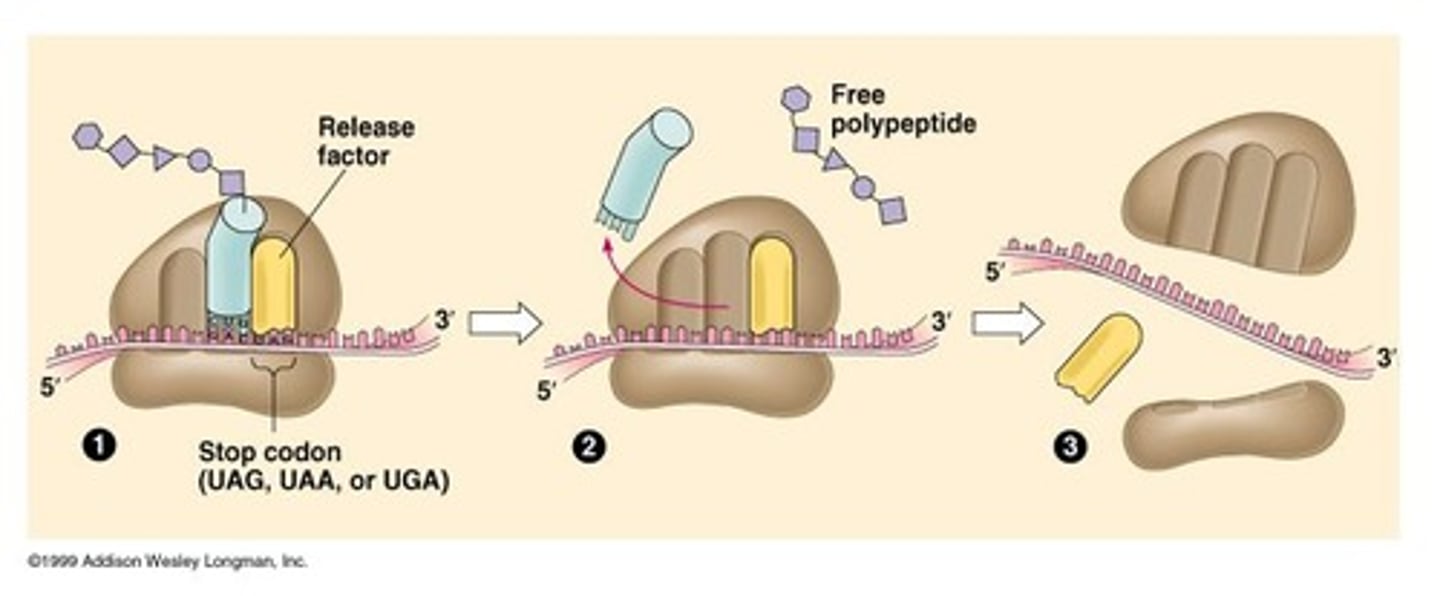
What triggers the termination of translation?
A stop codon in the mRNA causes the release factors to disassociate the translation complex.
What is the purpose of post-transcriptional modifications in RNA?
To prepare the RNA for translation by adding a 5' cap and a poly-A tail, and removing introns.
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
RNA polymerase binds to the promoter and synthesizes RNA by adding nucleotides in the 5' to 3' direction.
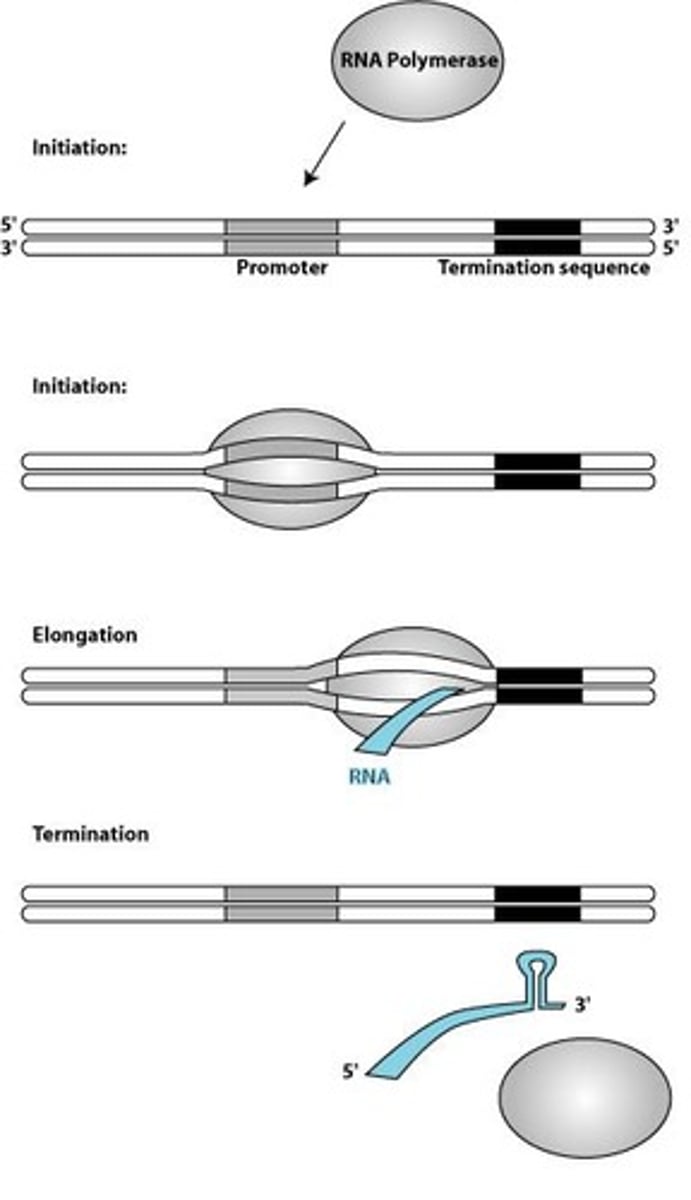
What is the significance of the TATA box in transcription?
It is part of the promoter that helps RNA polymerase bind to DNA and initiate transcription.
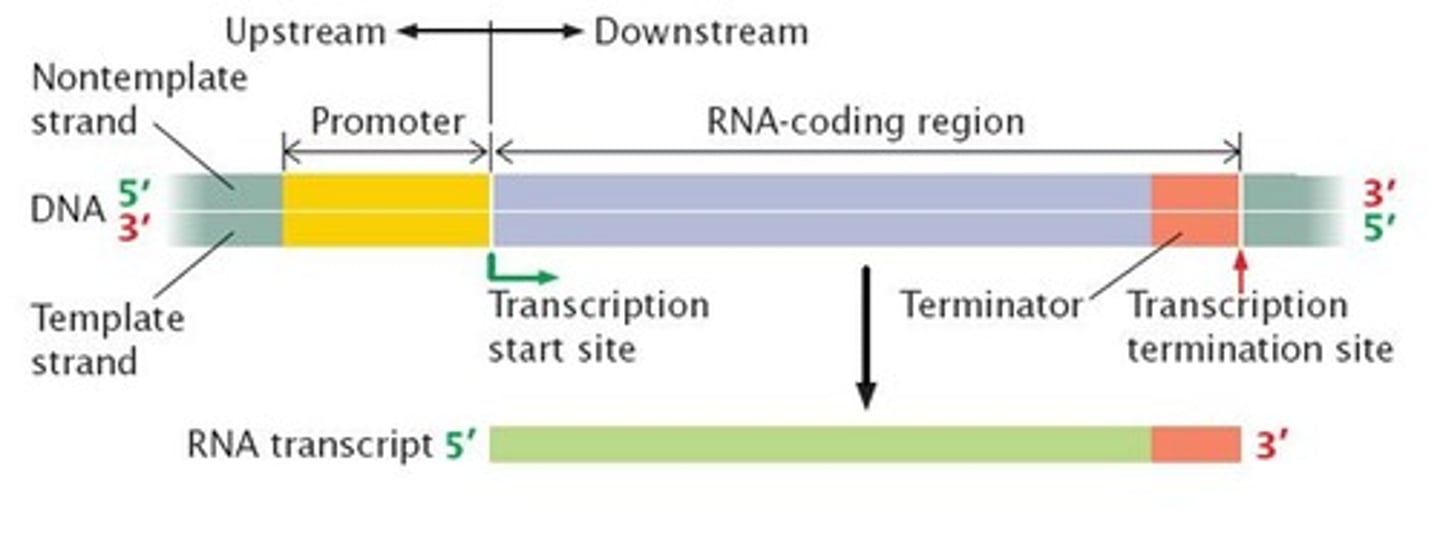
What are introns and exons in the context of RNA?
Introns are non-coding sequences that are removed, while exons are coding sequences that are spliced together.
What is alternative splicing?
A process that allows for the production of different mRNAs from a single pre-mRNA, leading to multiple proteins from one gene.
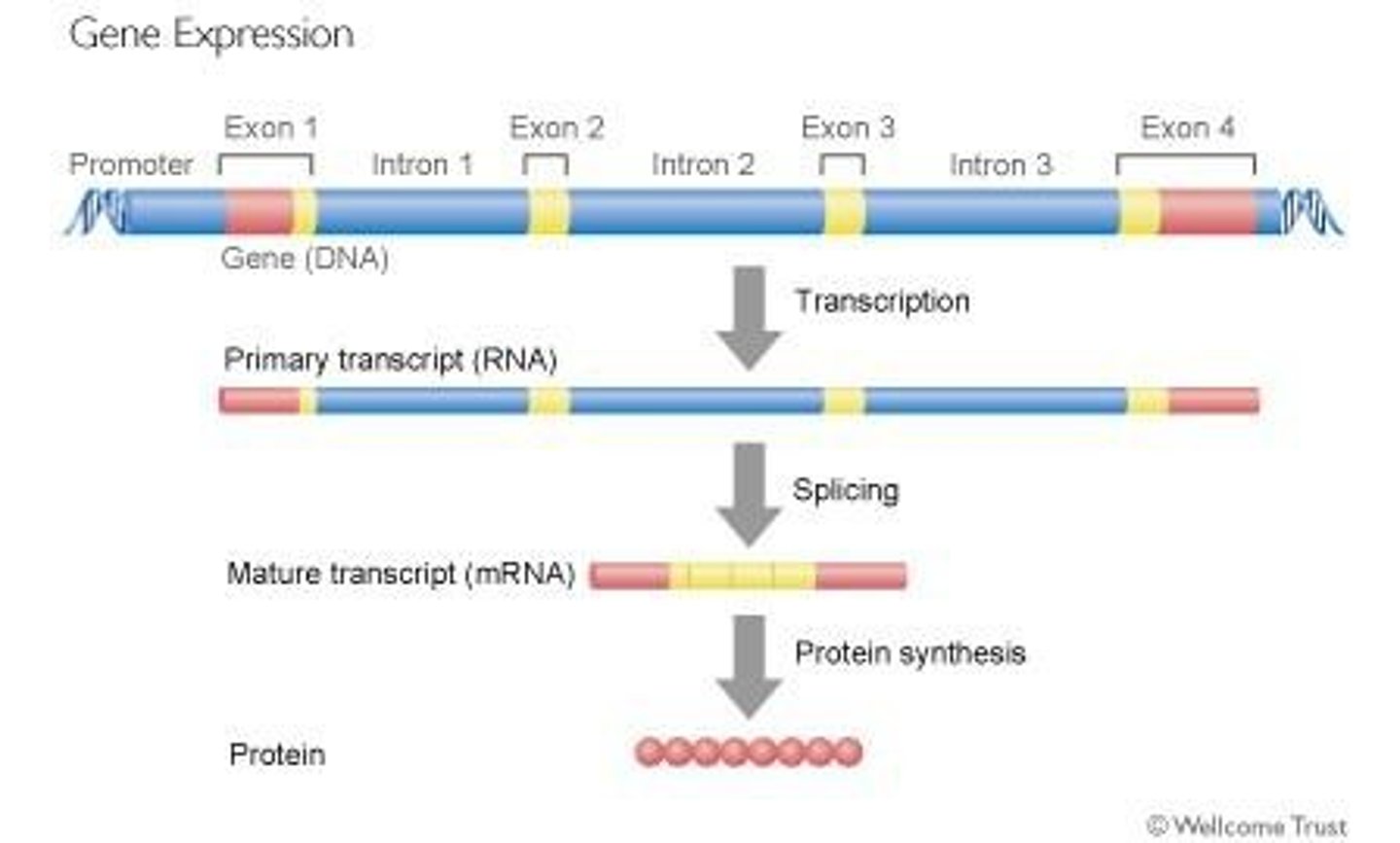
What is the function of spliceosomes?
Spliceosomes remove introns from RNA and join exons together.
What is the role of the 5' cap in mRNA?
It protects the mRNA from degradation and serves as a binding site for ribosomes during translation.
What is the poly-A tail and its function?
A chain of adenine nucleotides added to the 3' end of mRNA that protects it from enzymatic degradation.
What is the difference between the coding strand and the template strand of DNA?
The coding strand has the same sequence as the mRNA (except for T/U), while the template strand is used by RNA polymerase to synthesize RNA.
What is the reading frame in mRNA?
The way codons are arranged in groups of three nucleotides.
How does the ribosome know where to start translation?
It recognizes the 5' cap and the start codon (AUG) on the mRNA.
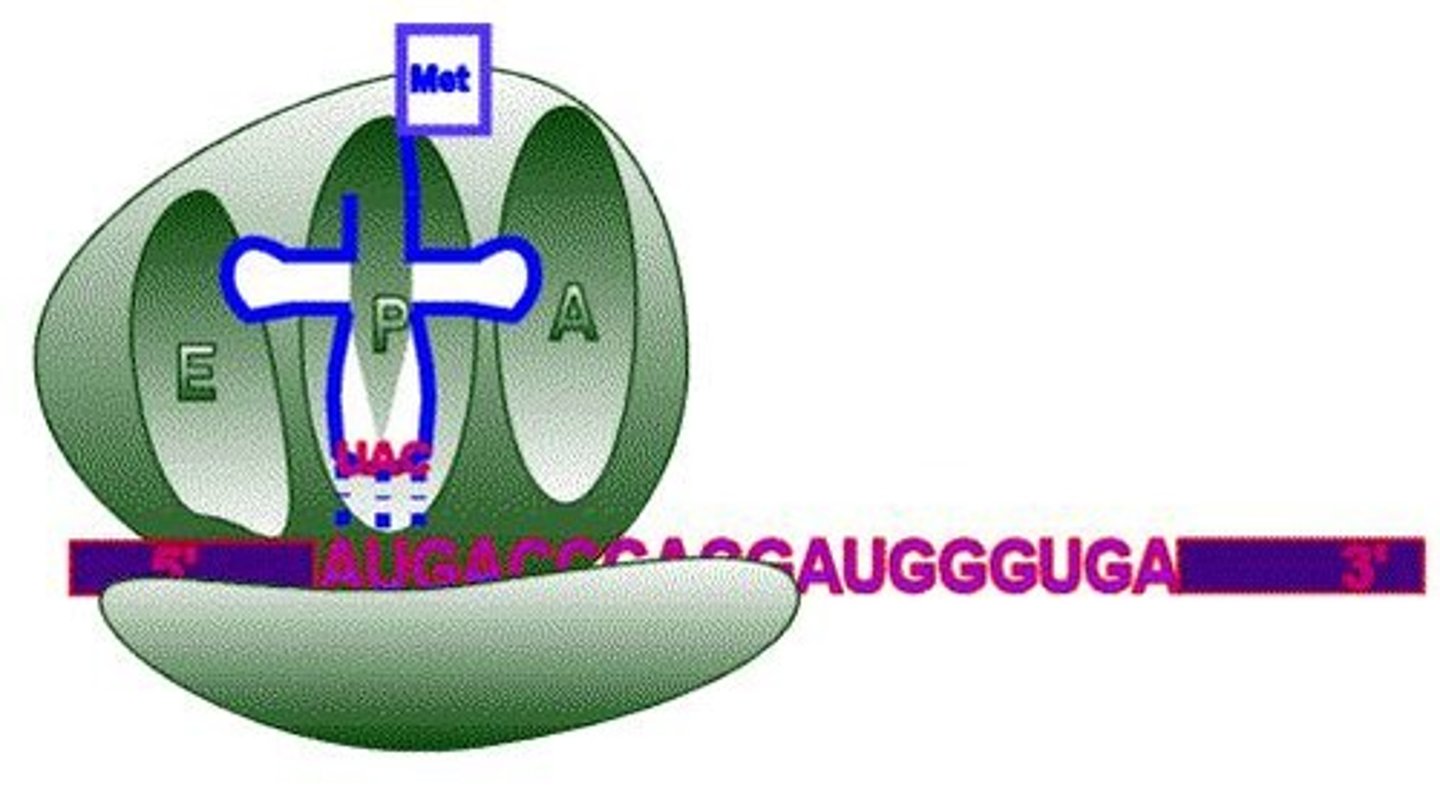
What happens to the ribosome during termination of translation?
It disassociates from the mRNA and releases the newly synthesized protein.
What is the significance of codons in mRNA?
Codons are sequences of three nucleotides that code for specific amino acids during protein synthesis.
What is the function of tRNA in translation?
tRNA carries specific amino acids to the ribosome and matches them to the corresponding codon on the mRNA.
What is the overall goal of translation?
To convert the mRNA code into a specific amino acid sequence to form a protein.