Topic 2 AQA A Level
1/103
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
104 Terms
Name the process by which prokaryotic cells divide./1
Binary fission
What is a homologous pair of chromosomes?/1
(Two chromosomes that) carry the same genes;
Give two ways in which the arrangement of prokaryotic DNA is different from the arrangement of the human DNA/2
(Prokaryotic DNA) is 1. Circular (as opposed to linear); 2. Not associated with proteins/histones 3. Only one molecule/piece of DNA OR present as plasmids
Explain the advantages of lipid droplet and micelle formation in the digestion and absorption of lipids/3
1. Droplets increase surface areas (for lipase / enzyme action);
2. (So) faster hydrolysis / digestion (of triglycerides / lipids);
3. Micelles carry fatty acids and glycerol / monoglycerides to / through membrane / to (intestinal epithelial) cell;
Suggest and explain two ways the cell-surface membranes of the cells lining the intestine may be adapted to allow rapid transport of nutrients./2
1. Membrane folded so increased / large surface area;
OR
Membrane has increased / large surface area for (fast) diffusion / facilitated diffusion / active transport / co-transport;
2. Large number of protein channels / carriers (in membrane) for facilitated diffusion;
3. Large number of protein carriers (in membrane) for active transport;
4. Large number of protein (channels / carriers in membrane) for co-transport;
Describe how phagocytosis of a virus leads to presentation of its antigens./3
1. Phagosome / vesicle fuses with lysosome;
2. (Virus) destroyed by lysozymes / hydrolytic enzymes;
3. Peptides / antigen (from virus) are displayed on the cell membrane;
Describe how presentation of a virus antigen leads to the secretion of an antibody against this virus antigen./3
1. Helper T cell / TH cell binds to the antigen (on the antigen-presenting cell / phagocyte);
2. This helper T / TH cell stimulates a specific B cell;
3. B cell clones
OR
B cell divides by mitosis;
4. (Forms) plasma cells that release antibodie
When a nerve impulse arrives at a synapse, it causes the release of neurotransmitter from vesicles in the presynaptic knob. Describe how./3
1. (Nerve impulse / depolarisation of membrane) causes Ca 2+ channel (proteins) to open;
2. Ca 2+ enter by (facilitated) diffusion;
3. Causes (synaptic) vesicles to fuse with (presynaptic) membrane;
Name two structures present in plant cells that are not present in animal cells./1
1. Chloroplasts / plastids
2. Cell wall
3. Cell vacuole
4. Starch grains / amyloplasts
A biologist prepared a sample of organelles from an organ Explain why the solution the biologist used was ice-cold, buffered and the same water potential as the organ tissue/3
1. Ice-cold - Slows / stops enzyme activity to prevent digestion of organelles / mitochondria;
2. Buffered - Maintains pH so that enzymes / proteins are not denatured;
3. Same water potential - Prevents osmosis so no lysis / shrinkage of organelles / mitochondria / C;
In ultracentrifugation name the organelle that made up most of the first pellet from liver tissue after centrifuging at a low speed/1
Nucleus
The second centrifuge tube was spun at a higher speed to obtain the next sample of organelles from liver tissue. Explain why /1
Mitochondria / organelle less dense than nucleus / organelle in first pellet;
Compare and contrast the processes by which water and inorganic ions enter cells/3
1. Comparison: both move down concentration gradient;
2. Comparison: both move through (protein) channels in membrane;
Accept aquaporins (for water) and ion channels
3. Contrast: ions can move against a concentration gradient by active transport
DNA and RNA can be found in bacteria. Give two ways in which the nucleotides in DNA are different from the nucleotides in RNA./2
1. DNA contains thymine and RNA contains uracil;
2. DNA contains deoxyribose and RNA contains ribose.
The cell-surface membrane can be seen with a transmission electron microscope but not with an optical microscope. Explain why /1
Electron microscope has higher resolution (than optical microscope).
Describe how substances move across cell-surface membranes by facilitated diffusion./3
1. Carrier / channel protein;
2. (Protein) specific / complementary to substance;
3. Substance moves down concentration gradient;
Name two structures in a eukaryotic cell that cannot be identified using an optical microscope./1
Mitochondrion / ribosome / endoplasmic reticulum / lysosome / cell-surface membrane.
Describe how you could use cell fractionation to isolate chloroplasts from leaf tissue./3
1. How to break open cells and remove debris;
2. Solution is cold / isotonic / buffered;
3. Second pellet is chloroplast.
Which of the following features are present in a bacterium RNA, Cell wall, Enzyme molecules, capsid /2
RNA, Enzyme molecule, cell wall
Which of the following features are present in an HIV particle: RNA, Cell wall, Enzyme molecules, capsid /2
RNA, Enzyme molecule, capsid
Describe how the complementary strand of DNA is made/3.
1. (Complementary) nucleotides/bases pair
OR
A to T and C to G;
2. DNA polymerase;
3. Nucleotides join together (to form new strand)/phosphodiester bonds form;
Contrast the structures of DNA and mRNA molecules to give three differences./3
Contrast requires both parts of the statement
1. DNA double stranded/double helix and mRNA single-stranded;
2. DNA (very) long and RNA short;
3. Thymine/T in DNA and uracil/U in RNA;
4. Deoxyribose in DNA and ribose in RNA;
5. DNA has base pairing and mRNA doesn't/ DNA has hydrogen bonding and mRNA doesn't;
6. DNA has introns/non-coding sequences and mRNA doesn't
Human papilloma virus (HPV) is the main cause of cervical cancer. A vaccine has been developed to protect girls and women from HPV. Describe how giving this vaccine leads to production of antibody against HPV./4
1. Vaccine/it contains antigen (from HPV);
Term ‛antigen' may be first mentioned with point 2
2. Displayed on antigen-presenting cells;
e.g. macrophage/phagocyte/B cells
3. Specific helper T cell (detects antigen and) stimulates specific B cell;
4. B cell divides/goes through mitosis/forms clone to give plasma cells;
5. B cell/plasma cell produces antibody;
Some scientists support the theory that mitochondria are organelles that evolved from prokaryotic cells. Give one piece of evidence that supports the theory that mitochondria evolved from prokaryotic cells./1
Circular DNA / smaller/70S ribosomes / no introns / no histones/proteins associated with DNA;
What is the advantage to cells of having mitochondria?/2
1. Able to respire aerobically;
2. So make (more) ATP/ release (more) energy;
Give two ways in which pathogens can cause disease./2
1. (Releases) toxins;
2. Kills cells / tissues.
Putting bee honey on a cut kills bacteria. Honey contains a high concentration of sugar. Use your knowledge of water potential to suggest how putting honey on a cut kills bacteria/3.
1. Water potential in (bacterial) cells higher (than in honey) / water potential in honey lower (than in bacterial cells);
2. Water leaves bacteria / cells by osmosis;
3. (Loss of water) stops (metabolic) reactions
The events that take place during interphase and mitosis lead to the production of two genetically identical cells. Explain how/4
1. DNA replicated;
Reject: DNA replication in the wrong stage
2. (Involving) specific / accurate / complementary base-pairing;
3. (Ref to) two identical / sister chromatids;
4. Each chromatid / moves / is separated to (opposite) poles / ends of cell.
A student cut thin sections of tissue at different distances from the tip of a root. She stained the sections and viewed them with an optical microscope. The student cut thin sections of tissue to view with an optical microscope.
Explain why it was important that the sections were thin./2
1. To allow (more) light through;
Accept: transparent
2. A single / few layer(s) of cells to be viewed.
Some cancer cells have a receptor protein in their cell-surface membrane that binds to a hormone called growth factor. This stimulates the cancer cells to divide. Scientists have produced a monoclonal antibody that stops this stimulation. Use your knowledge of monoclonal antibodies to suggest how this antibody stops the growth of a tumour/3
1. Antibody has specific tertiary structure / binding site / variable region
2. Complementary shape to receptor protein
3. Prevents growth factor binding to receptor.
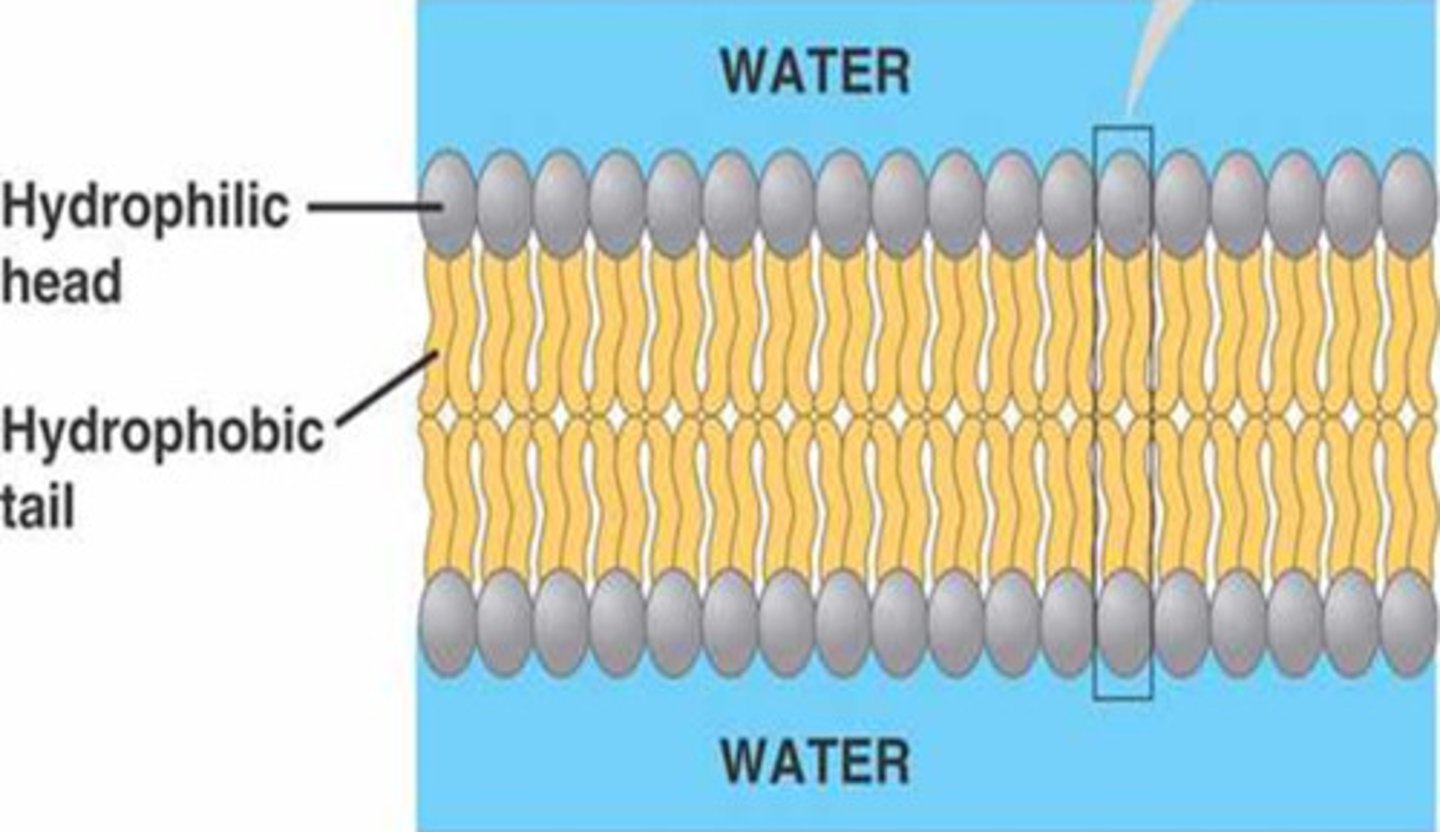
Describe how phospholipids are arranged in a plasma membrane./2
1. . Bilayer;
2. Hydrophobic / fatty acid / lipid (tails) to inside;
3. Polar / phosphate group / hydrophilic (head) to outside
Describe how the RER is involved in the production of enzymes./2
1. Rough endoplasmic reticulum has ribosomes
2. To make protein
Describe how the Golgi apparatus is involved in the secretion of enzymes./1
Any one of:
- Golgi apparatus modifies protein
- packages / put into Golgi vesicles
- transport to cell surface
Describe how bacteria are destroyed by phagocytes./3
1. Phagocyte engulfs to form vacuole / phagosome
2. Lysosome empties contents into vacuole / phagosome
3. Releasing enzymes that hydrolyse bacteria
Give two structures a bacterial cell may have that a white blood cell does not have./2
Two suitable structures;;
Examples,
1. Cell wall;
2. Capsule / slime layer;
3. Circular DNA;
4. Naked DNA / DNA without histones;
5. Flagellum;
6. Plasmid;
7. Pilus;
8. 70s / smaller ribosomes;
9. Mesosome;
Describe the role of the centromere in mitosis./2
1. Holds chromatids together;
2. Attaches (chromatids) to spindle;
3. (Allows) chromatids to be separated / move to (opposite) poles / (centromere) divides / splits at metaphase / anaphase;
Homologous chromosomes carry the same genes but they are not genetically identical.Explain why./1
(Homologous chromosomes) carry different alleles;
Other than independent segregation, give one way in which meiosis allows the production of genetically different cells./1
Crossing over / alleles exchanged between chromosomes or chromatids / chiasmata formation / genetic recombination;
What is the function of the mitochondrion / 1
Aerobic respiration
Scientists use this antibody to detect an antigen on the bacterium that causes stomach ulcers. Explain why the antibody will only detect this antigen./3
1. Antibody / variable region has specific amino acid sequence
2. The tertiary structure of the binding site is complementary to these antigens;
3. Forms complex between antigen and antibody;
Describe the function of a chloroplast./2
1. Absorbs light
Light dependent reaction = marking point 1.
2. For photosynthesis
3. Produces carbohydrates /lipids / proteins
Describe what happens during anaphase that results in the production of two genetically identical cells./2
1. Sister chromatids
2. To opposite poles
In prophase of mitosis, the chromosomes become visible. Describe what happens in metaphase/2
Spindle formed centromere / chromatids attaches to spindle
Chromatids line up / move to middle / equator of cell
In prophase of mitosis, the chromosomes become visible. Describe what happens in anaphase/2
Centromere splits / chromatids separate / pulled apart
To opposite poles of centrioles
Cells lining the human intestine complete the cell cycle in a short time. Explain the advantage of these cells completing the cell cycle in a short time./2
1. Replace cells quickly 2. Divide rapidly
Give one advantage of using a TEM rather than a SEM./1
Higher resolution / higher maximum magnification
OR Allows internal structures within cells to be seen
Give one advantage of using a SEM rather than a TEM./1
Any one of
1. Thin sections do not need to be prepared
shows surface of specimen
2. can have 3-D images
3. Can be used on thick(er) specimens
A group of scientists homogenised liver tissue before carrying out cell fractionation to isolate mitochondria. Explain why they a) homogenised the tissue b) filtered the resulting suspension c) kept the suspension ice cold during the process d) used isotonic solution during the process.
a) Breaks open cells releasing organelles
B) Removes cell debris / complete cells / tissue; (C) Reduces / prevents enzyme activity; d) Prevents osmosis / no (net) movement of water / water does not enter organelle / water does not leave organelle; So organelle / named organelle is not damaged / does not burst / does not shrivel;
What is an HPV antigen?/2
Protein / glycoprotein / glycolipid / polysaccharide;
Causes immune response / antibody production;
Accept: B / T cell production
A vaccine can be used to produce immunity to HPV. Describe how memory cells are important in this process./3
Memory cells produced / remain / stored (from previous infection
(When individual) comes into contact with virus / antigen (again);
Rapid / secondary / greater response / many or more antibodies produced;
Destroys virus / antigen before it can cause harm / symptoms / cancer;
There are large numbers of mitochondria in an epithelial cell from the small intestine. Explain how these organelles help the cell to absorb the products of digestion./2
(Site of aerobic) respiration / ATP production / energy release;
Active transport / transport against the concentration gradient;
Name the process in which cells become adapted for different functions./1
Differentiation / specialisation
Give two ways in which pathogens can cause disease when they enter the body of their host./2
Damage / destruction of cells / tissues;
Production of toxins;
Vaccines provide protection against disease. What is a vaccine?/2
"Contains antigen / proteins / dead / weakened microorganism / pathogen / virus / bacteria;
Stimulates production of antibodies / plasma cells / memory cells
What is a tissue?/1
(Group of) similar / identical cells / cells with a common origin;
A student cut a thin section of tissue from a potato and examined it with an optical microscope. The student cut a thin section of the tissue. Explain why it was important that the section was thin./2
"Need a single layer of cells / only a few cells thick / not too many layers / detail obscured by cells underneath;
Light must be able to pass through
Phagocytes and lysosomes are involved in destroying microorganisms. Describe how./3
Phagocytes engulf pathogens / microorganisms;
Enclosed in a vacuole / vesicle / phagosome;
Lysosomes have enzymes;
That digest / hydrolyse molecules / proteins / lipids / microorganism;
Penicillin is an antibiotic. It prevents the formation of bacterial cell walls. As a result, bacterial cells that have been treated with penicillin swell and burst as water enters. i) Explain how water enters a bacterial cell. (2) ii) Explain why penicillin has no effect on plants cells (1)
water potential lower / more negative in cell;
(water enters by) osmosis;
ii) plant cell wall made of a different substance / cellulose / penicillin does not affect cellulose;
Describe how B-lymphocytes respond when they are stimulated by antigens./4
divide by mitosis / form clones;
produce plasma cells;
(plasma cells) make antibodies;
(plasma cells) produce memory cells;
What is an antigen?/2
molecule / part of molecule / protein / glycoprotein / named molecule;
that stimulates an immune response / eq;
Describe how B-lymphocytes respond when they are stimulated by antigens./4
divide by mitosis / form clones; produce plasma cells; (plasma cells) make antibodies; (plasma cells) produce memory cells;
In which phase of the cell cycle does DNA replication take place?/1
Interphase / S-phase;
Describe the role of the spindle during mitosis./2
Attachment of centromeres / chromosomes / chromatids; Separation of centromeres / chromatids / chromosomes;
Meiosis also occurs during the life cycle of organisms. What is the importance of meiosis?/2
"Halves chromosome number / haploid;
Diploid / full number restored at fertilisation
What is vaccination?/2
Divide by mitosis / form clones; produce plasma cells; (plasma cells) make antibodies; (plasma cells) produce memory cells;
Give two processes which occur during interphase that enable cell division to occur./2
Increase in volume of cell / volume of cytoplasm / increase in mass / cell bigger; increase in number of organelles; synthesis of protein / named protein; DNA replication / increase / chromosomes copied; ATP synthesis / respiration;"
Explain how the shape of a red blood cell allows it to take up a large amount of oxygen in a short time./2
Large surface area to volume ratio;
For diffusion;
OR
Flat / thin;
So oxygen can reach all haemoglobin / centre rapidly / short pathway;
What is the biological importance of reducing the chromosome number when the cell divides by meiosis?/2
"Later fertilisation / cell fusion; (NOT just 'sexual reproduction')
Restoring diploid / original number / not doubling chromosome number;"
Contrast mitosis and meiosis / 4
Each sentence must contrast. Meiosis: Reduces the chromosome number; (Homologous) chromosomes associate in pairs; Crossing-over / chiasmata formation; Two / (nuclear stages) divisions / → 4 offspring cells; Genetically different product MITOSIS: Maintains the same chromosome number as in the parent nucleus; (Homologues) independent / do not pair
(IGNORE ref. separation; No crossing-over;; One / (nuclear stage) division / → 2 offspring cells; Genetically identical (product);
Give one process which occurs in the nucleus of a cell during interphase which is necessary before cell division can take place./1
replication / duplication / doubling of chromosomes /
replication of DNA / transcription of DNA;
Explain one advantage of cells lining the human gut dividing very frequently./1
to replace cells;
A student investigated the stages of mitosis in a garlic root. The root tip was placed on a microscope slide with a stain. A cover slip was placed on top and the root tip was firmly squashed.Explain why (i) a root tip was used; (ii) a stain was used; (iii) the root tip was firmly squashed. (3)
"i) where mitosis / division / growing / occurs ii) to distinguish chromosomes / chromosomes not visible without stain; iii) to let light through / thin layer;"
What is an antibody? /2
protein / immunoglobulin;
specific to antigen;
idea of 'fit' / complementary shape;
Describe how antibodies are produced in the body following a viral infection./6
1. virus contains antigen;
2. virus engulfed by phagocyte / macrophage;
3. presents antigen to B-cell;
4. memory cells / B-cell becomes activated;
5. (divides to) form clones;
6. by mitosis;
7. plasma cells produce antibodies;
8. antibodies specific to antigen;
9. correct reference to T-cells / cytokines;
An optical microscope cannot be used to see a plasma membrane. Explain why./2
Does not have the resolution / cannot distinguish between points this close together;
As light has longer wavelength;
Explain how the inner membrane is adapted to its function in mitochondria / 2
increased surface area;
for respiration / enzymes;
Describe how a sample consisting only of chloroplasts could be obtained from homogenised plant tissue./3
use of differential centrifugation / or description;
first / low-spin pellet discarded / spin at low speed to remove cell
wall material / cell debris;
supernatant re-spun at higher speed / until pellet with chloroplasts is found;
method of identifying chloroplasts e.g. microscopy;
Describe two functions of the fatty acid tails in the phospholipid bilayer / 2
two of the following:
form(water) impermeable barrier to water-soluble substances / selectively permeable / allows non-polar molecules to pass through;
allows cell to maintain different concentrations either side;
makes membranes self-sealing / able to fuse with other membranes / able to form vesicles / gives flexibility / fluidity;
Give one function of a glycoprotein/1
"(surface / extrinsic protein) for cell recognition / binding to hormones / identification"
Give one similarity in the way in which active transport and facilitated diffusion transport substances across the membrane./1
"involves carrier / transmembrane / transport proteins;
Give one way in which active transport differs from facilitated diffusion./1
"requires energy / requires use of ATP / moves substances / ions / molecules against a concentration gradient;"
Give two factors, other than cost, that should be considered when selecting an antibiotic to treat a bacterial disease./2
"side effects / allergic reactions / low toxicity to cells;
interaction with other drugs / effective in conditions of use / reasonably stable; should only act on the problem bacteria / narrow spectrum; how much resistance the bacteria have built up;"
An antigen in a vaccine leads to the production of antibodies. Describe the part played by B lymphocytes in this process./4
1 macrophages present antigens to B lymphocytes;
2 antigen binds to / is complementary to receptors on lymphocyte;
3 binds to a specific lymphocyte;
4 lymphocytes become competent / sensitised;
5 (B) lymphocytes reproduce by mitosis / (B) lymphocytes cloned;
6 plasma cells secrete antibodies;
Palisade cells are the main site of photosynthesis. Explain one way in which a palisade cell is adapted for photosynthesis./2
relevant adaptation;
and explanation for second mark; e.g.
idea of many chloroplasts / lots of chlorophyll;
to trap or absorb light (energy);
elongated cells;
idea of maximum light absorption / light penetration;
chloroplasts move;
to trap or absorb light (energy);
range of pigments;
can absorb a range of wavelengths / colours / for max light absorption;
large S.A. or cell wall feature e.g. thin / permeable;
for (rapid) CO2 absorption;
Explain how three features of a plasma membrane adapt it for its functions./6
Feature and adaption; for example
1 phospholipid bilayer (as a barrier);
2 forms a barrier to water soluble / charged substances /
allows non-polar substances to pass
OR
maintains a different environment on each side / compartmentalisation;
3 bilayer is fluid;
4 can bend to take up different shapes for phagocytosis /
form vesicles / self repair;
5 channel proteins (through the bilayer) / intrinsic protein;
6 let water soluble / charged substances through / facilitated diffusion;
7 carrier proteins (through the bilayer);
8 allow facilitated diffusion / active transport;
9 surface proteins / extrinsic proteins, glycoproteins / glycolipids;
10 cell recognition / act as antigens / receptors;
11 cholesterol;
12 regulates fluidity / increases stability;
Small samples of plant tissue were placed in a cold, isotonic solution and then treated to break open the cells to release the organelles. The different organelles were then separated. Describe a technique that could be used to
(i) break open the cells; (ii) separate the organelles. / 2
(i) homogeniser / blender / pestle and mortar / description
e.g. grind with sand;
(ii) centrifuge / description e.g. spin at high speeds;
Explain why the structure of a membrane is described as fluid-mosaic./2
idea of molecules / named molecules moving = Fluid;
idea of both proteins and phospholipids = Mosaic;
Explain why meiosis is important in sexual reproduction, apart from producing gametes that are genetically different./2
produces haploid cells / chromosome number halved;
fertilisation maintains the diploid / chromosome number (in next generation);
Describe two events during interphase which prepare a cell for mitosis./2
"DNA replication; synthesis or proteins / build-up of energy stores / growth / increase in cytoplasm;
Changes to the protein coat of the influenza virus cause antigenic variability. Explain how antigenic variability has caused some people to become infected more than once with influenza viruses./2
memory B / T cells do not recognise (new antigens);
antibodies previously produced are not effective
as shape not complementary to new antigen;
Oxygen and water move through plasma membranes into cells. Describe two ways in which these movements are similar./2
passive / do not require energy / ATP;
movement down a concentration gradient / by diffusion;
go through phospholipid (bilayer) / not by protein / carriers;
The MMR vaccine contains attenuated microorganisms.
What is an attenuated microorganism?/2
Microorganism alive/active;
But does not cause symptoms of disease/Avirulent;
Name two structures found in a prokaryotic cell that are not found in a human cell./2
Cell wall;
smaller/70S ribosome(s)
Capsule/slime layer;
(Bacterial) flagellum;
Circular DNA/chromosome;
Plasmid;
Mesosome;
Describe how HIV is replicated after it has entered a human cell./4
Reverse transcriptase;
Accept integrase/description of action of
Enzyme uses (HIV) RNA to make DNA (copy);
DNA joined to (host) cell's DNA/chromosome;
DNA used to make HIV RNA (copies);
Accept (HIV) DNA replicated when (T) cell divides
And HIV capsid proteins/enzymes;
Made at (host) ribosomes;
Assembly of new virus particles;
Budding off from membrane (of host cell);
The destruction of T-cells by HIV leads to the death of an infected person. Explain how./2
"Not enough/no T-cells to activate B-cells/lead to antibody production/ activate immune system;
Describe two differences between active transport and facilitated diffusion./2
Active transport against / facilitated down with concentration gradient;
Accept answers in terms of water potentials
Active transport uses ATP/energy, /facilitated doesn't;
Reject along/across gradient
Active uses carrier (proteins), / facilitated (often) uses channel (proteins);
Explain why molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are able to diffuse across membranes./2
Lipid/fatty acid part of membrane is non-polar/hydrophobic;
Accept lipid/fatty acid bilayer
Oxygen and carbon dioxide small/ non-polar (molecules);
Oxygen/carbon dioxide can diffuse through/dissolve in/
get between molecules in this layer;
Down a concentration gradient;
What is the function of the RNA molecules in HIV virus?/1
Carries genetic information / to make DNA;
Describe how new viruses are produced after HIV has infected a T cell./3
DNA copy made (of viral RNA);
Inserted into host DNA / chromosomes;
(Uses viral DNA to) make viral proteins/particles;
Makes viral RNA;
(Host) cell makes new viruses;
"Budding off" / wrapped in cell membrane;
Accept reverse transcriptase makes DNA for 2 marks in correct context;
The structure of a plasma membrane is described as a fluid mosaic. Explain why./2
Fluid = molecules move around;
Mosaic = proteins floating among phospholipids/not just phospholipids/
other molecules in it/made of different sorts of molecules;