The Heart and Fetal Circulation
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
major components of the cardio system
heart, blood vessels, blood
functino of the cardio system
transportation of nutrients and oxygen, waste products, and horomones
what cavity is the heart in
middle mediastinum
what are veins
carry blood to heart
what are arteries
carry blood away from heart
what is the purpose of auricles on the outside of heart
increase holding capacity of atria
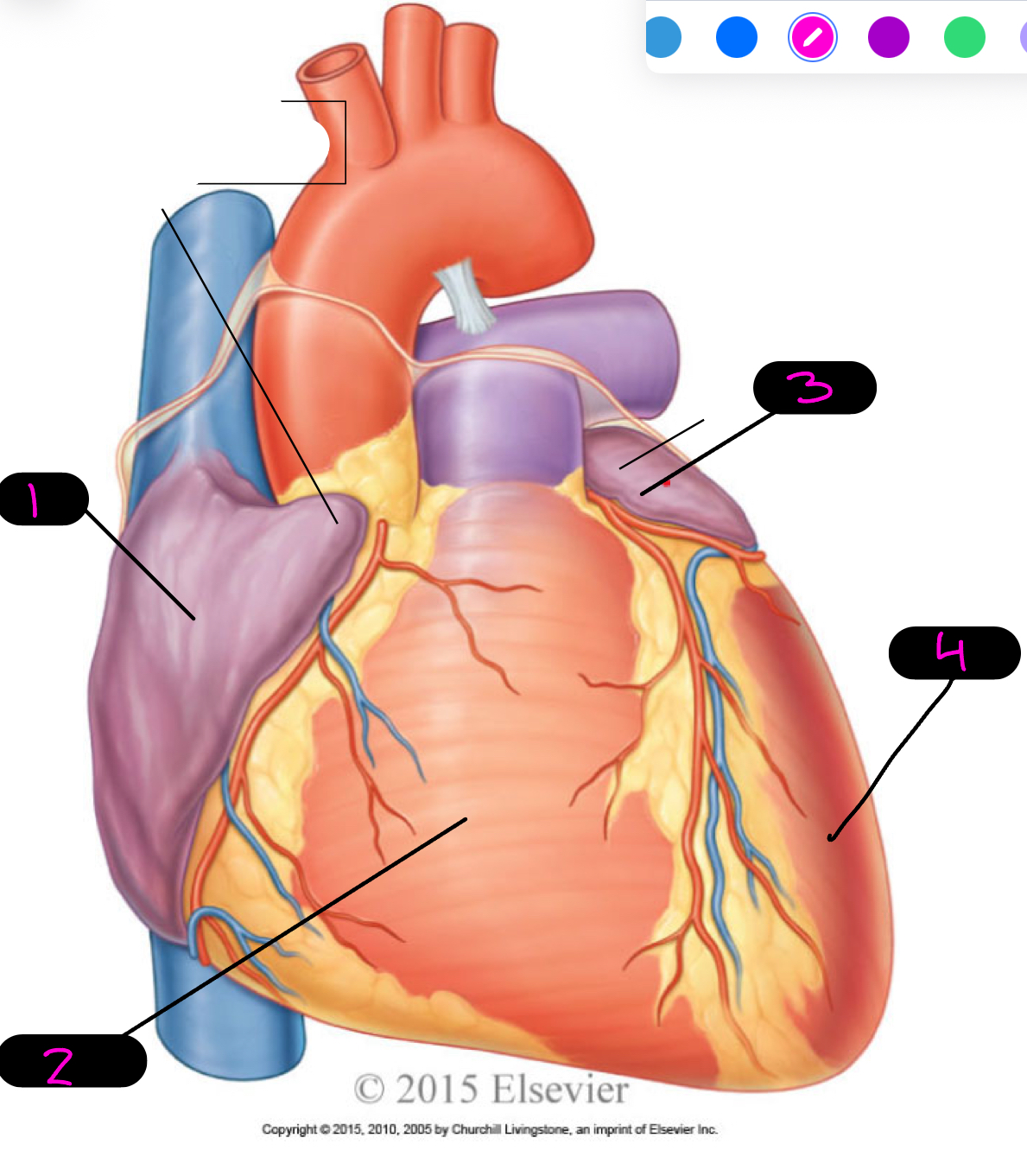
1
right atrium

2
right ventricle

3
left atrium
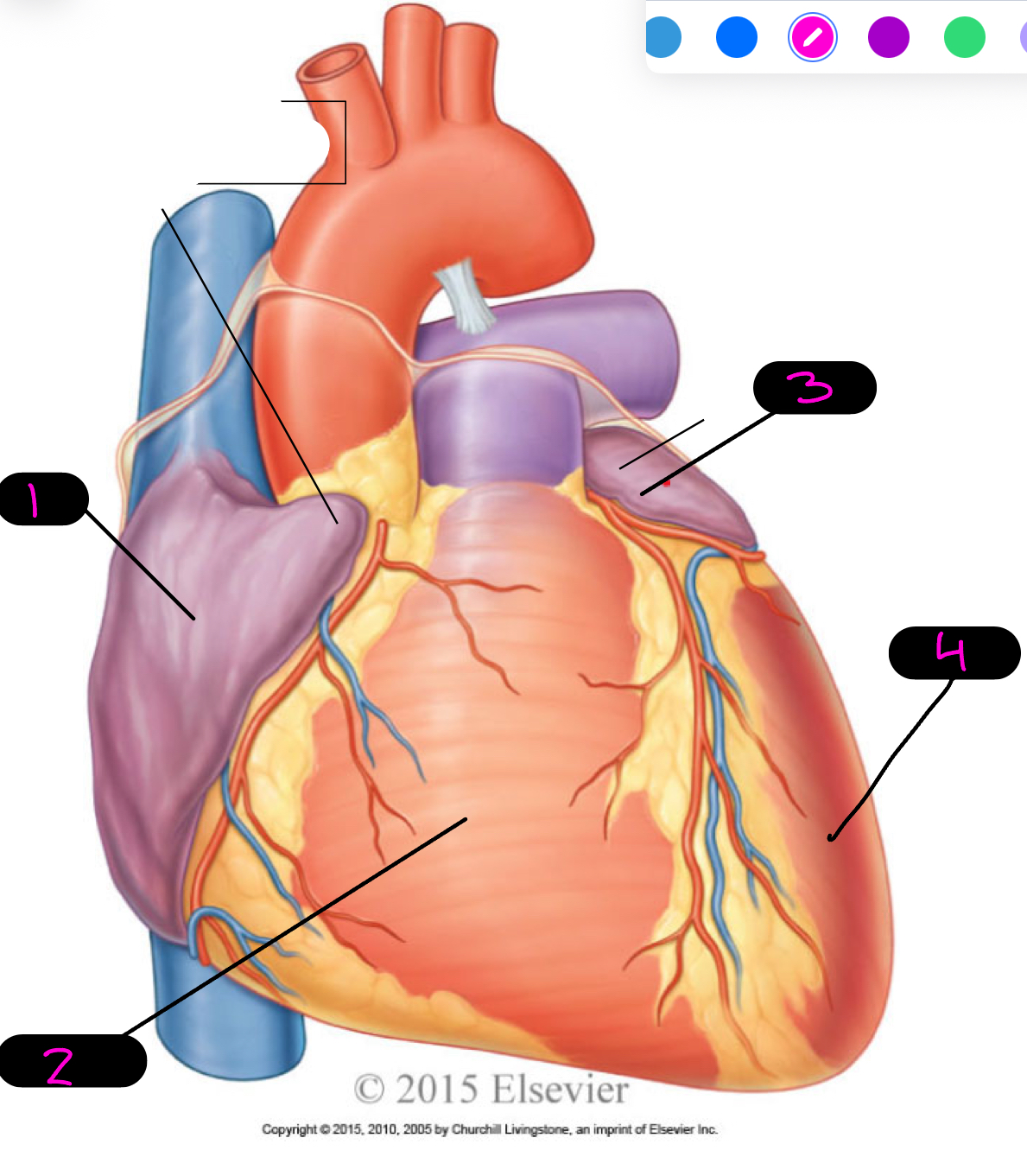
4
left ventricle
what are the great vessels of the heart
superior vena cava, inferior vena cava, pulmonary veins, pulmonary trunk/arteries, aorta

1
SVC
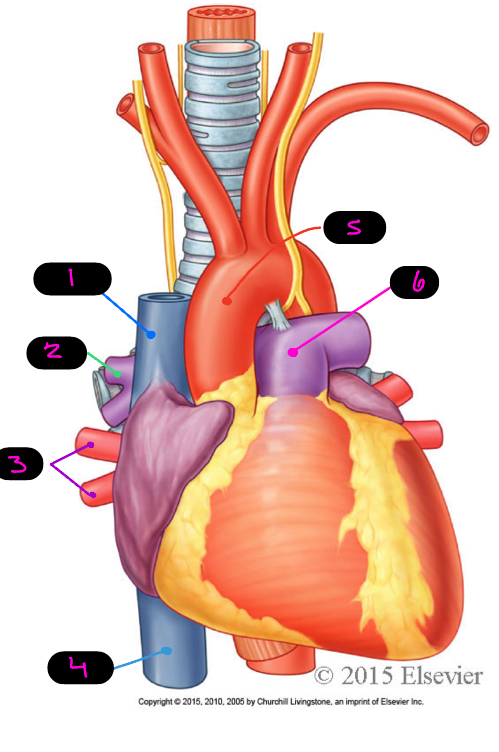
2
pulmonary arteries
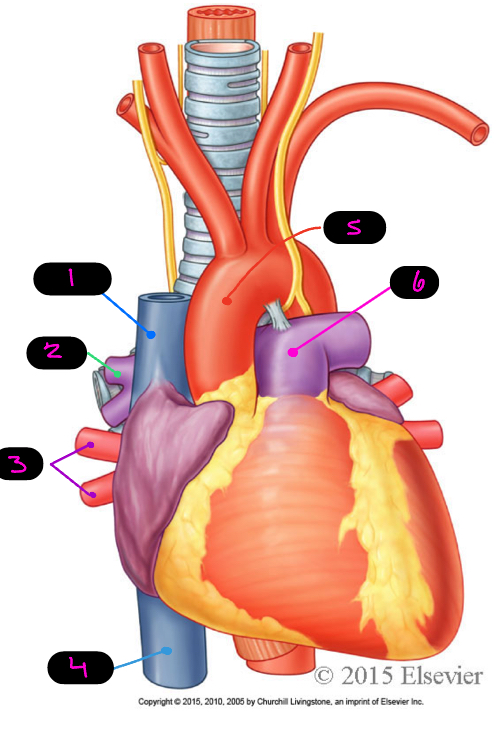
3
pulmonary veins
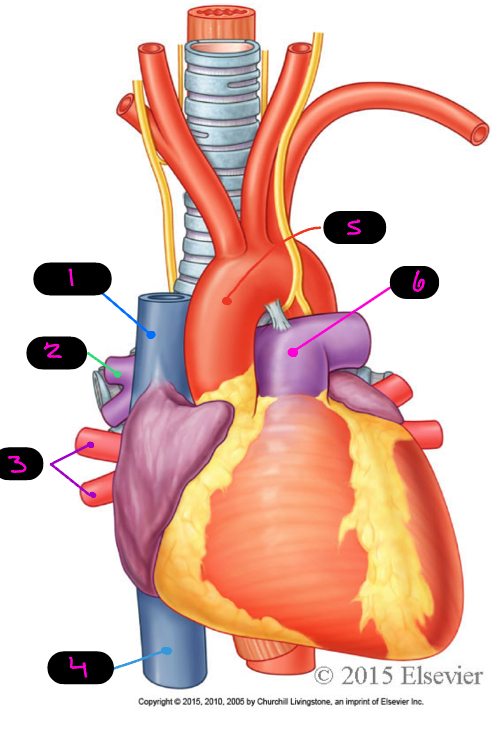
4
IVC
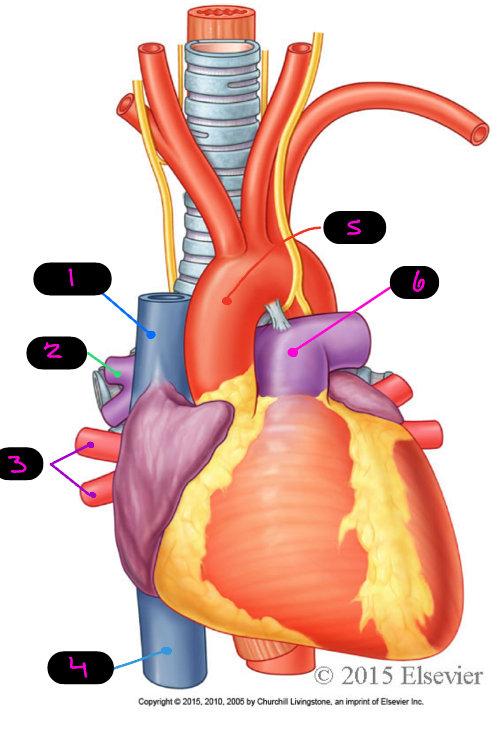
5
aorta
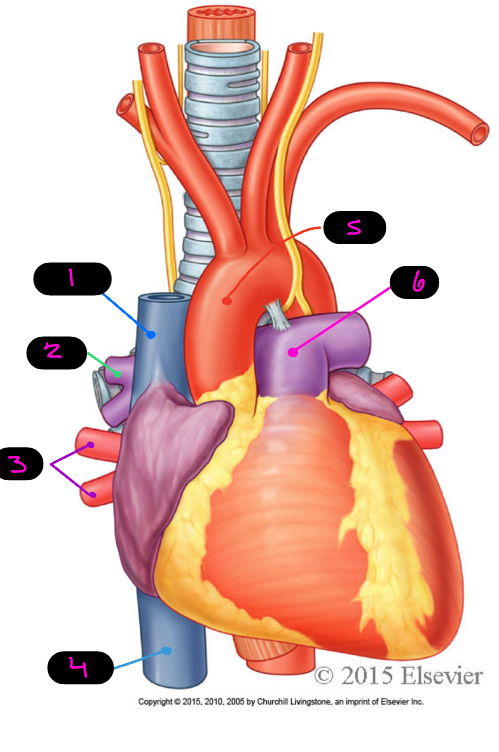
6
pulmonary trunk
where does the SVC return blood from
thoracic wall, upper limb, head and neck
where does the IVC return blood from
abdomen, pelvis, and lower limbs
what does the right atrium receive deoxy blood from
SVC, IVC, coronary sinus
what does the pulmonary trunk bifurcate into
right and left pulmonary arteries
what does the left atrium receive blood from
4 pulmonary veins
2 right and 2 left
how is backflow prevented in chambers
valves
what are the valves of the heart
tricuspid, bicuspid/mitral, pulmonary semilunar, aortic semilunar
what valve prevents backflow between right atrium and right ventricle
tricuspid valve
what valve prevents backflow between left atrium and left ventricle
bicuspid/mitral valve
what prevents backflow between right ventricle and pulmonary trunk
pulmonary semilunar valve
what prevents backflow between the left ventricle and the aorta
aortic semilunar valve

1
pulmonary semilunar

2
right AV, tricuspid
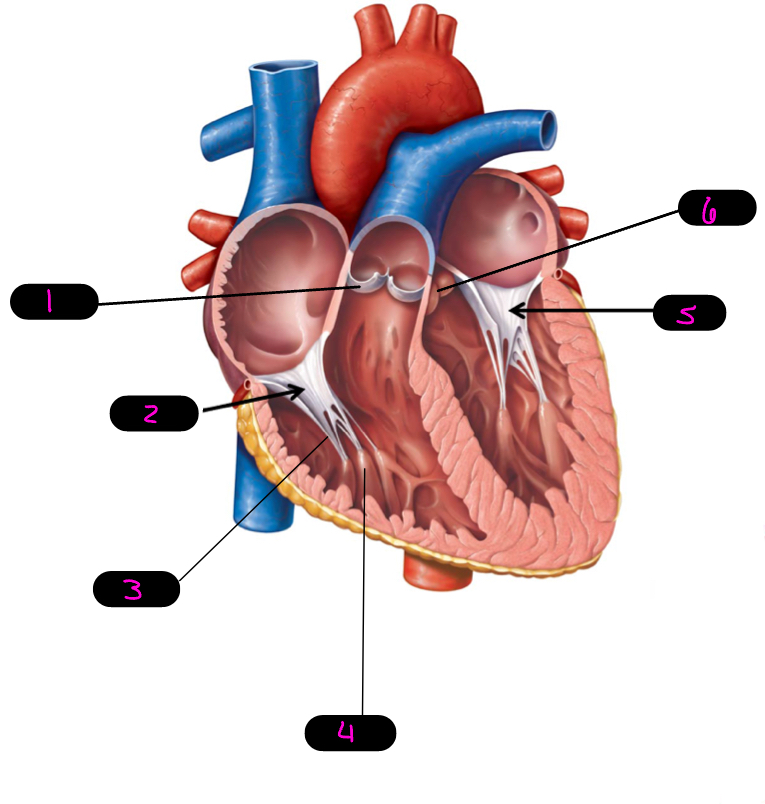
3
chordae tendineae
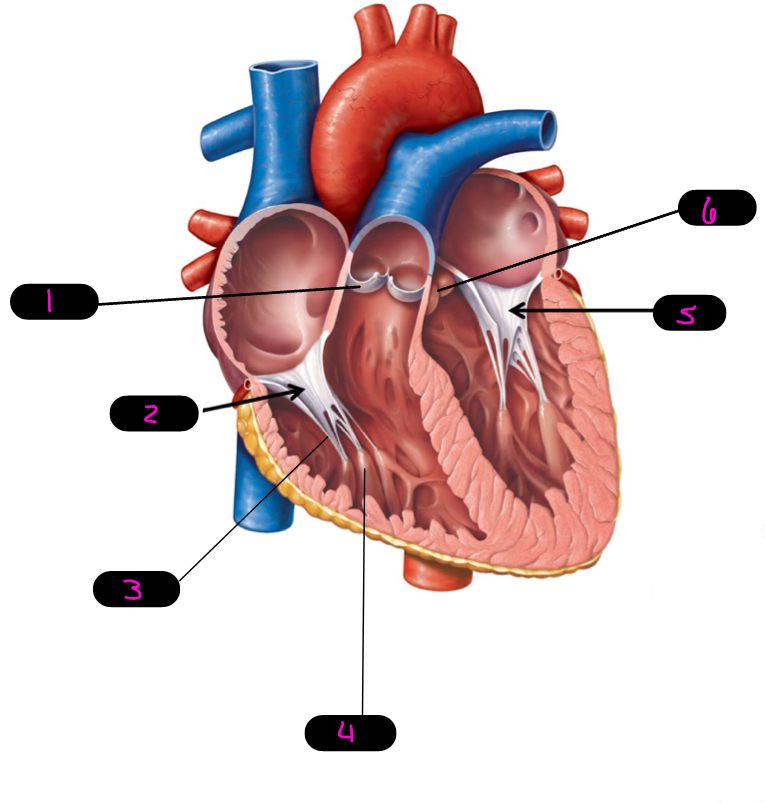
4
papillary muscle

5
left AV/bicuspid/mitral
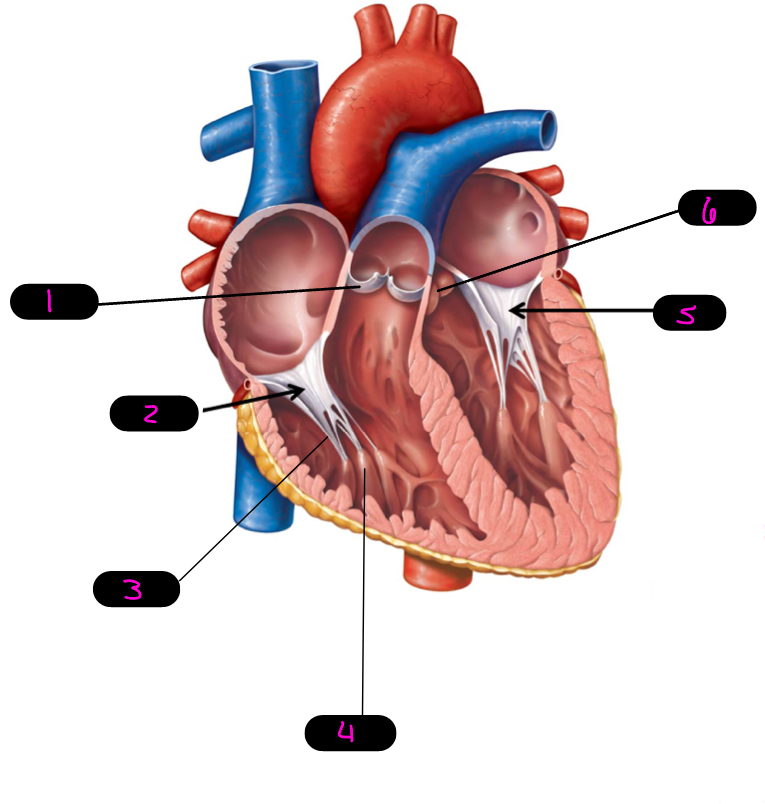
6
aortic semilunar
what is it called when ventricles contract to pump blood out of heart
systole
what closes in systole
tri and bi valvles
what sound is systole
S1 “lub”
what is it called when the ventricles relav and blood fills them
diastole
what is closed in diastole
pulmonary and aortic valves
what sound is diastole
S2, “dub”
what are the layers of heart (superficial to deep)
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
is the RV or LV thicker
LV - has to pump to whole body
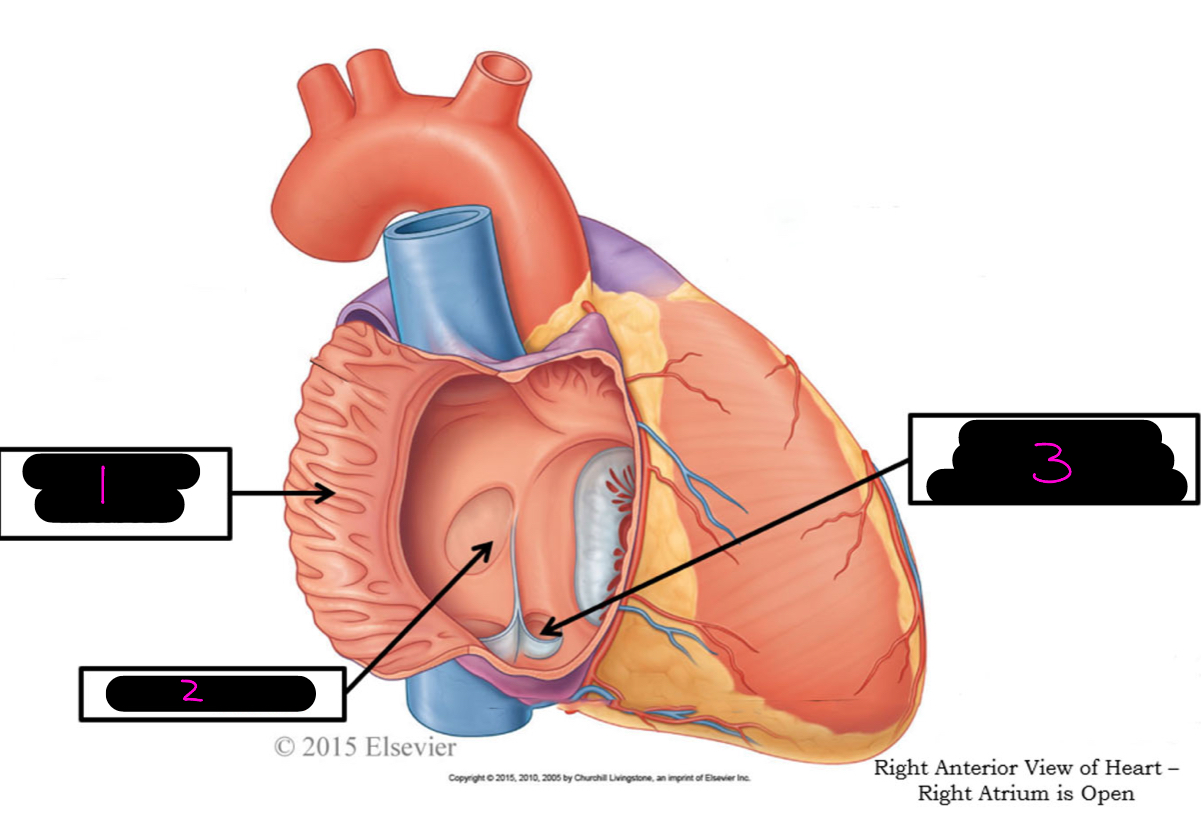
1
pectineate muscle
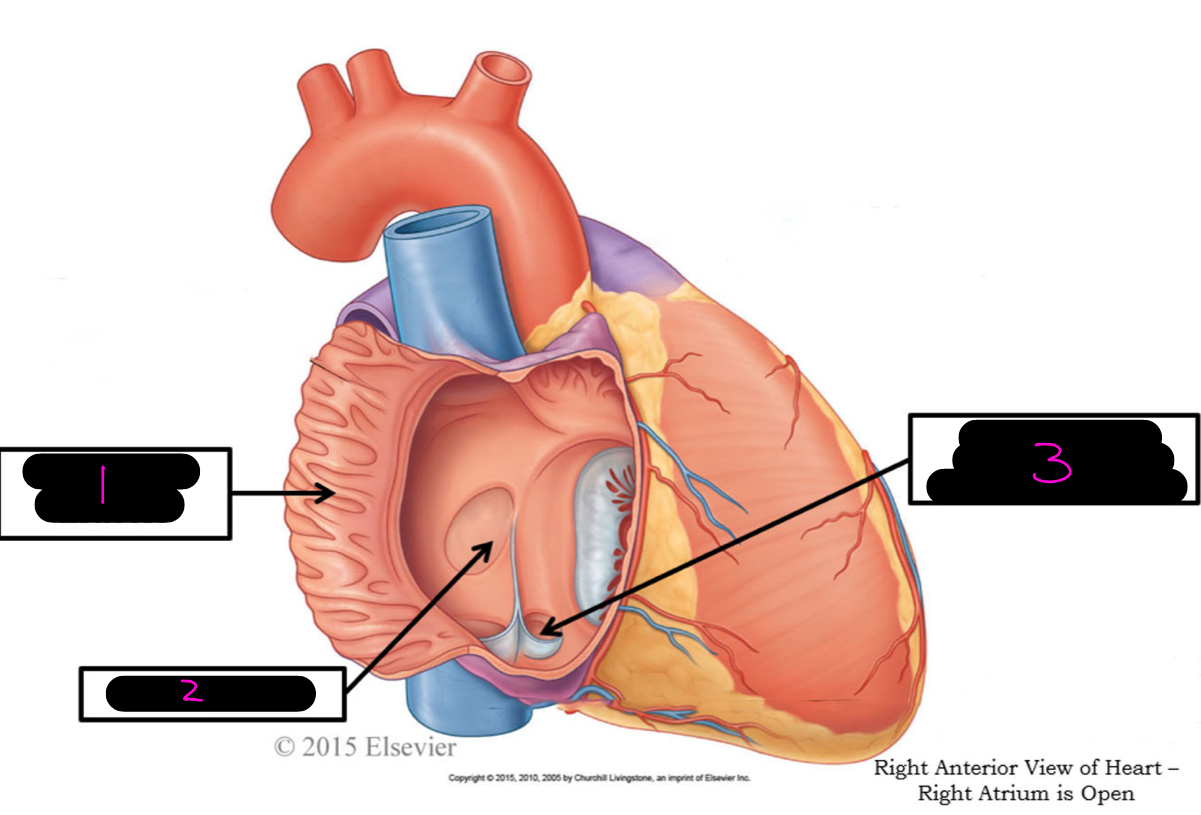
2
fossa ovalis
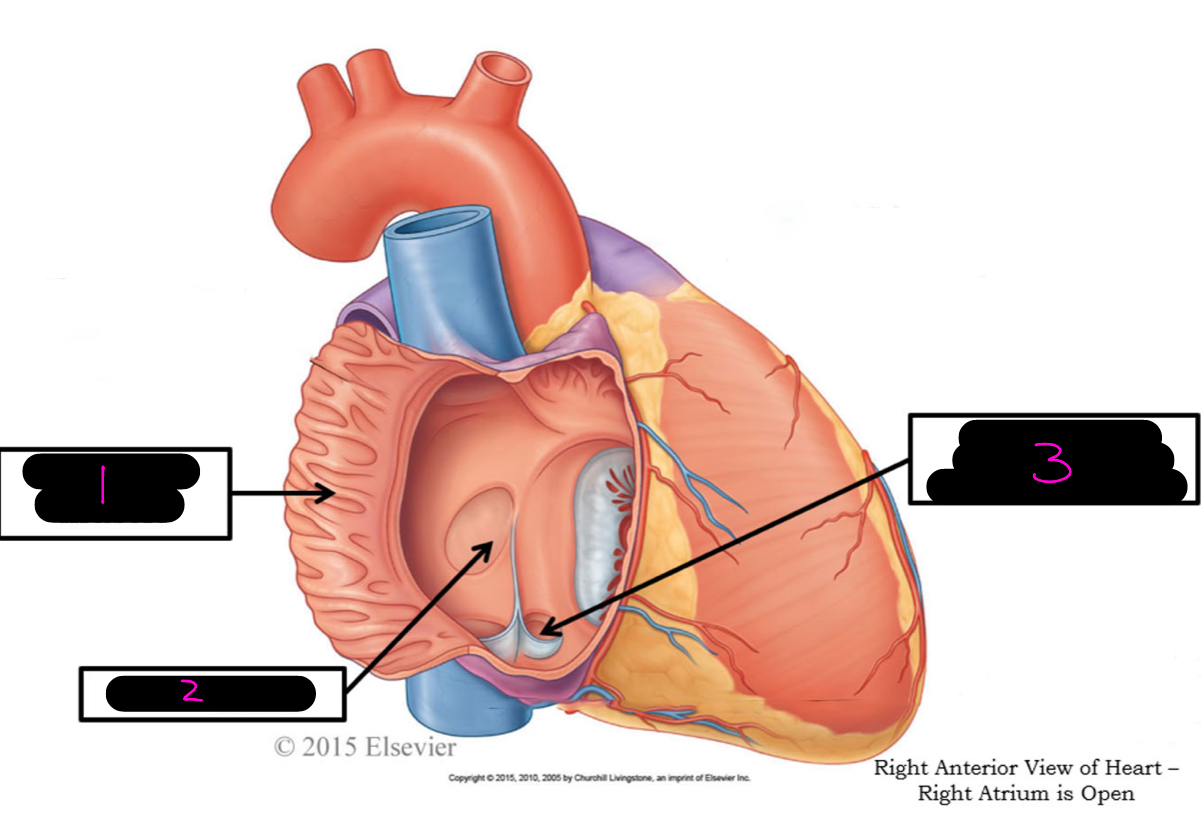
3
opening of coronary sinus
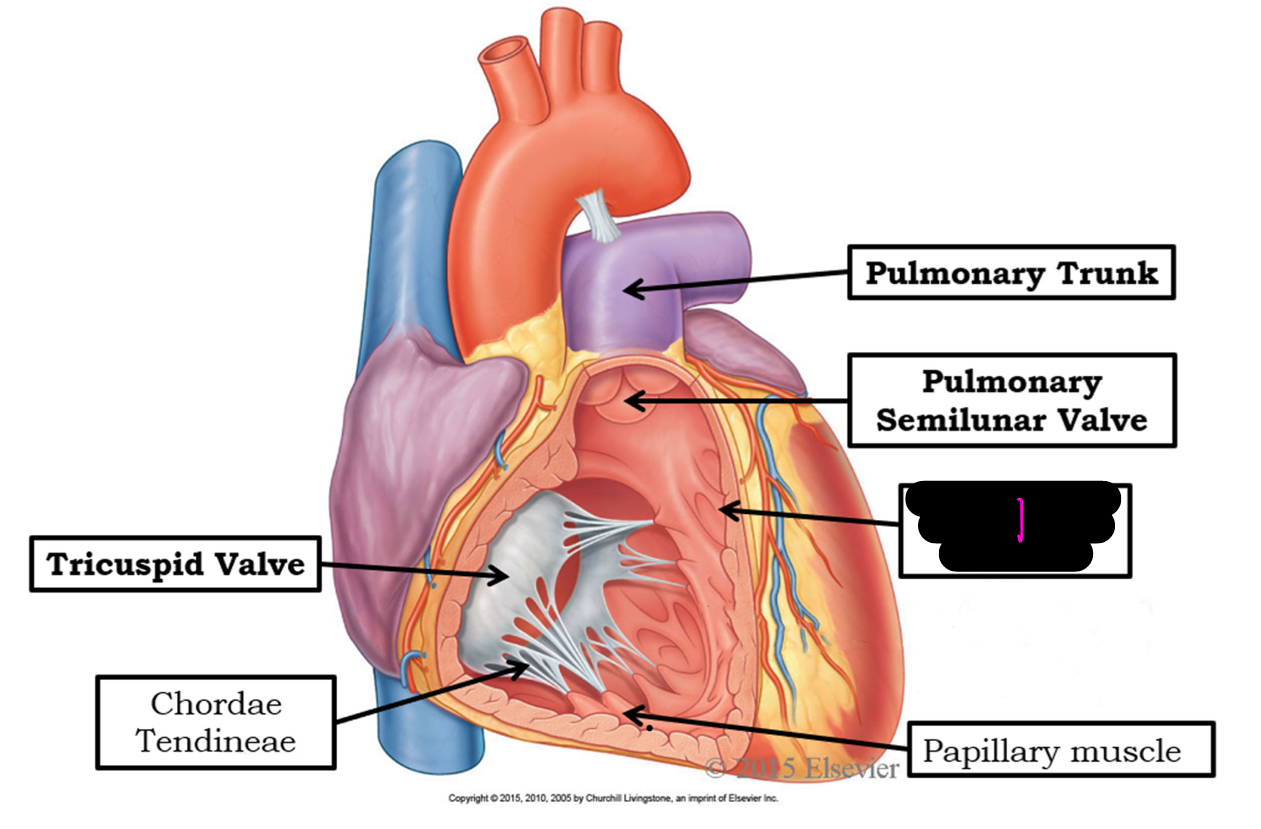
1
trabeculae carneae
what is trabeculae carnea
rib of muscle that is in RV and LV that attachtes to papillary muscles
when is main blood flow into the coronary circulation
diastole (when heart is relaxed)
why can blood not flow into myocardium in systole
contraction of myocardium compresses coronary arteries and the entrances of the coronary circulation are blocked becasue the aortic semilunar is open

1
right coronary artery
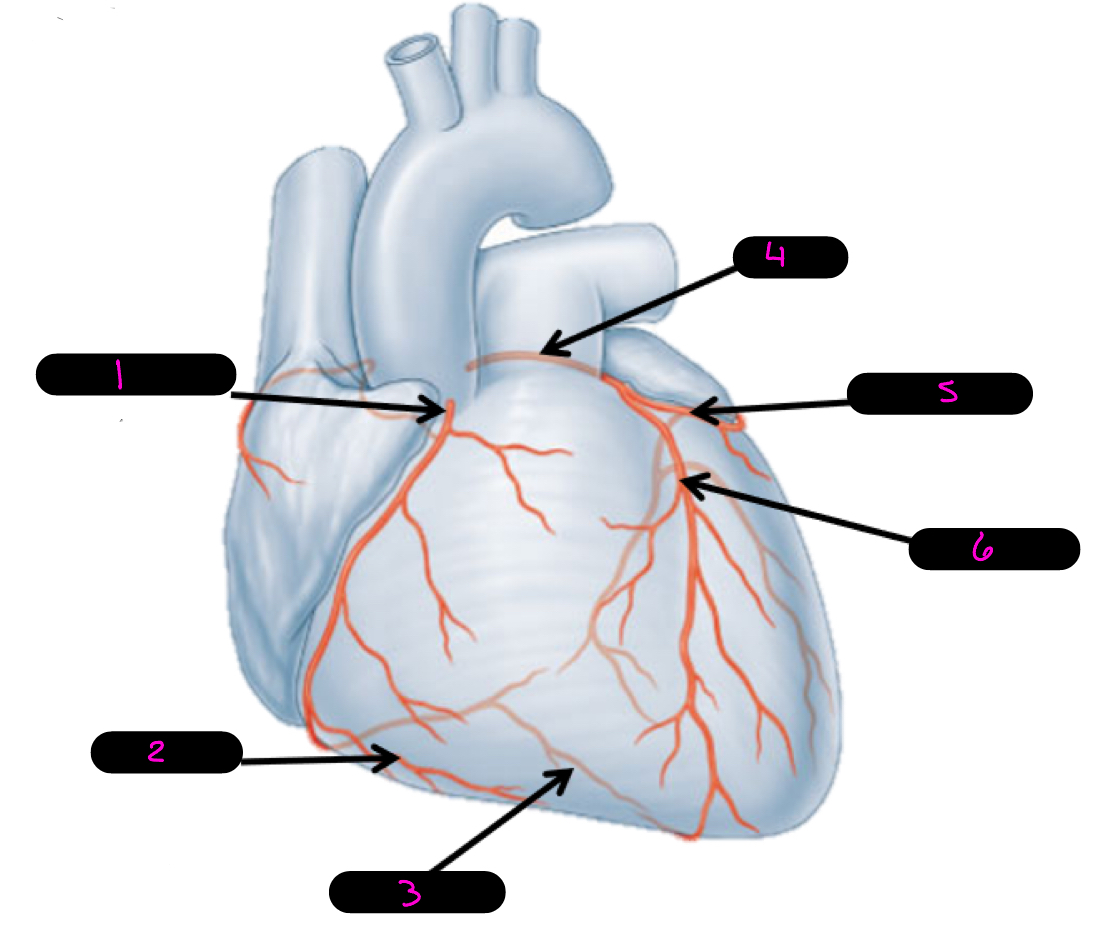
2
right marginal artery
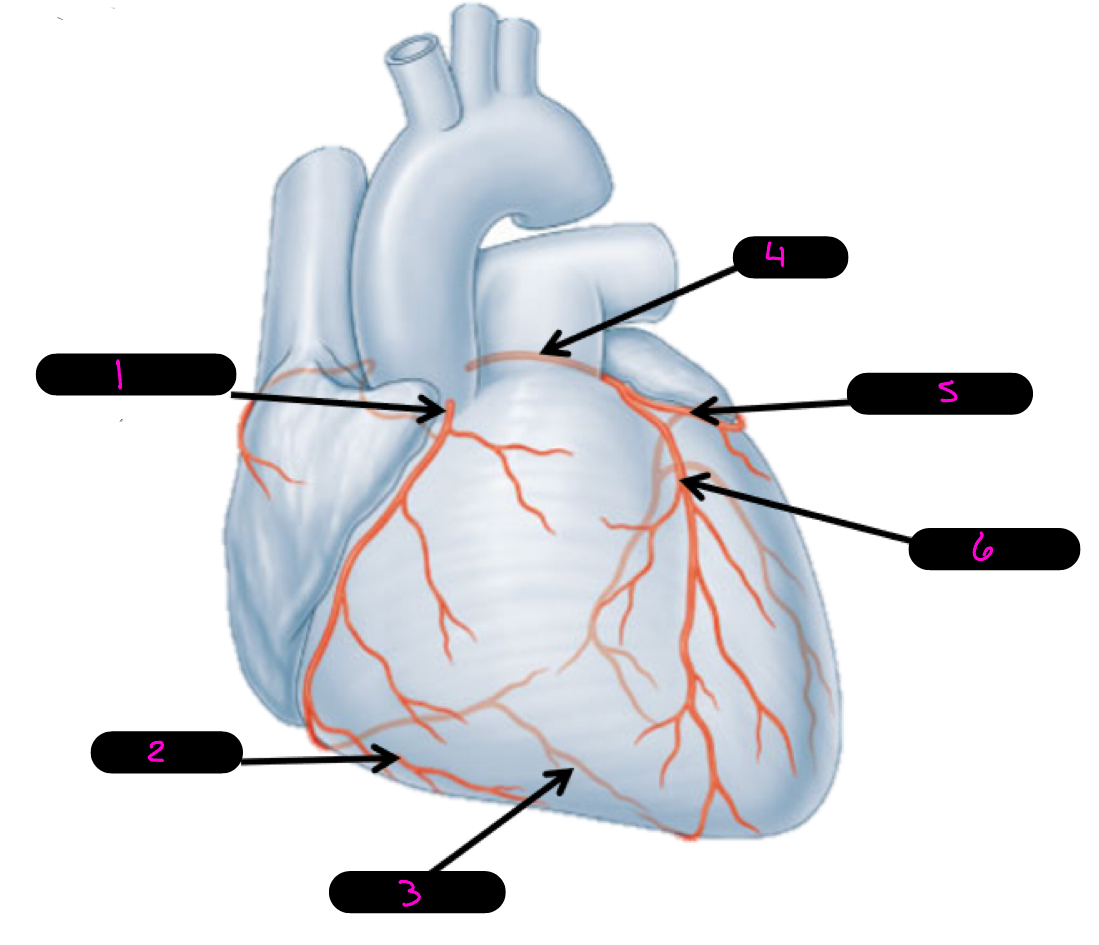
3
posterior interventricular artery
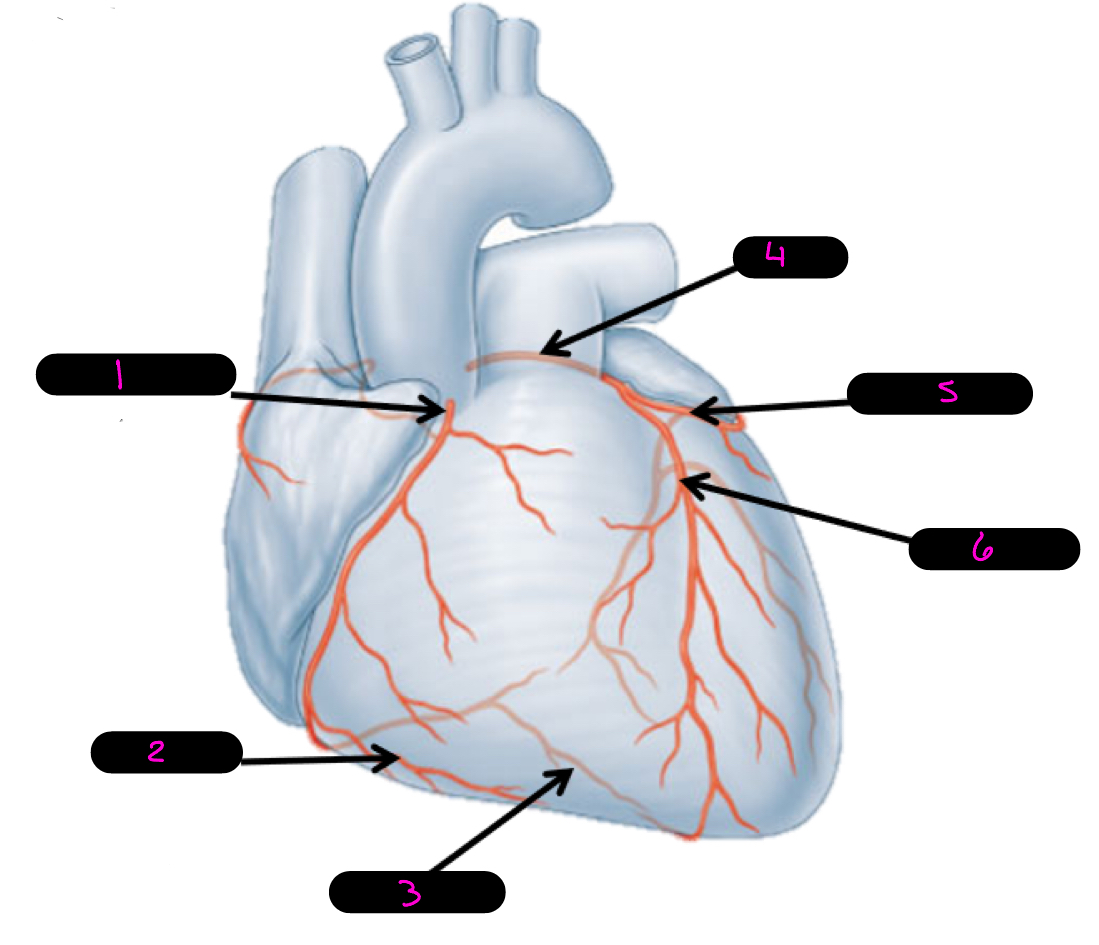
4
left coronary artery
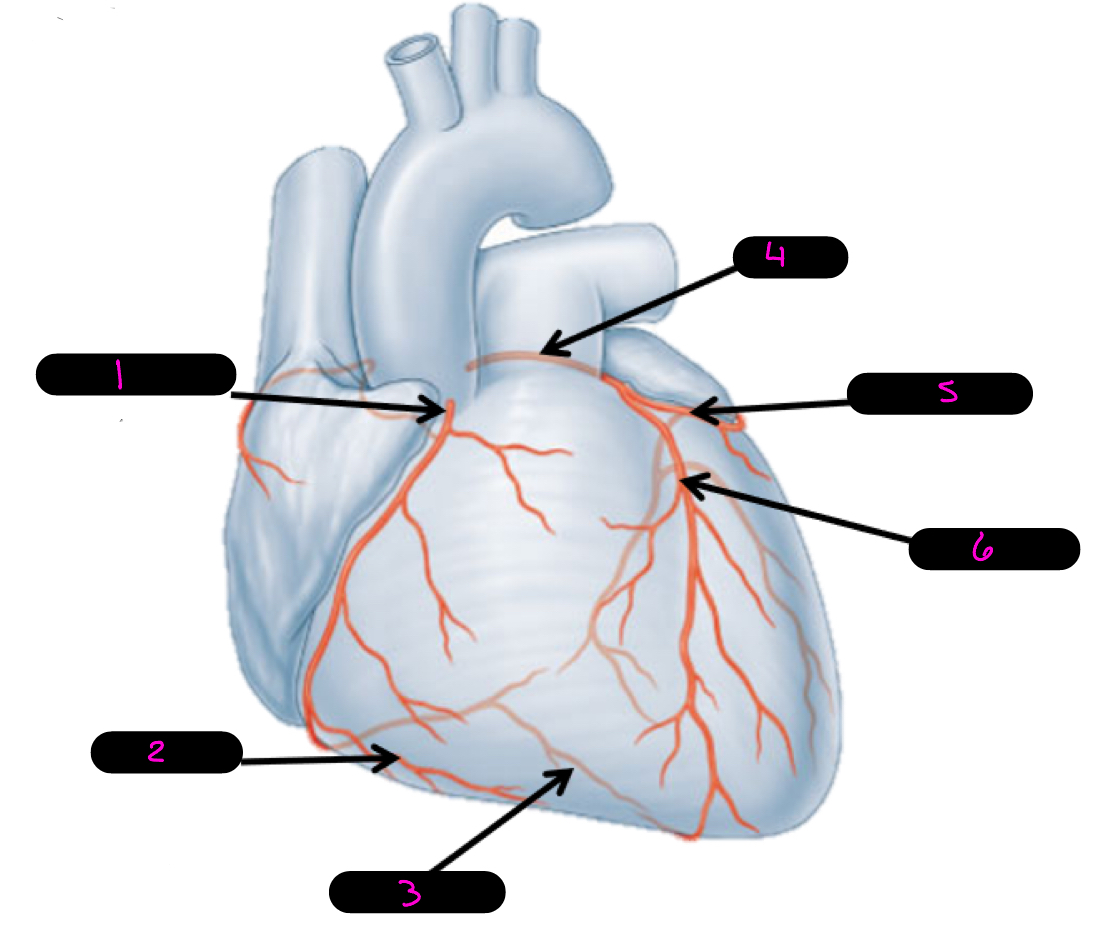
5
circumflex artery
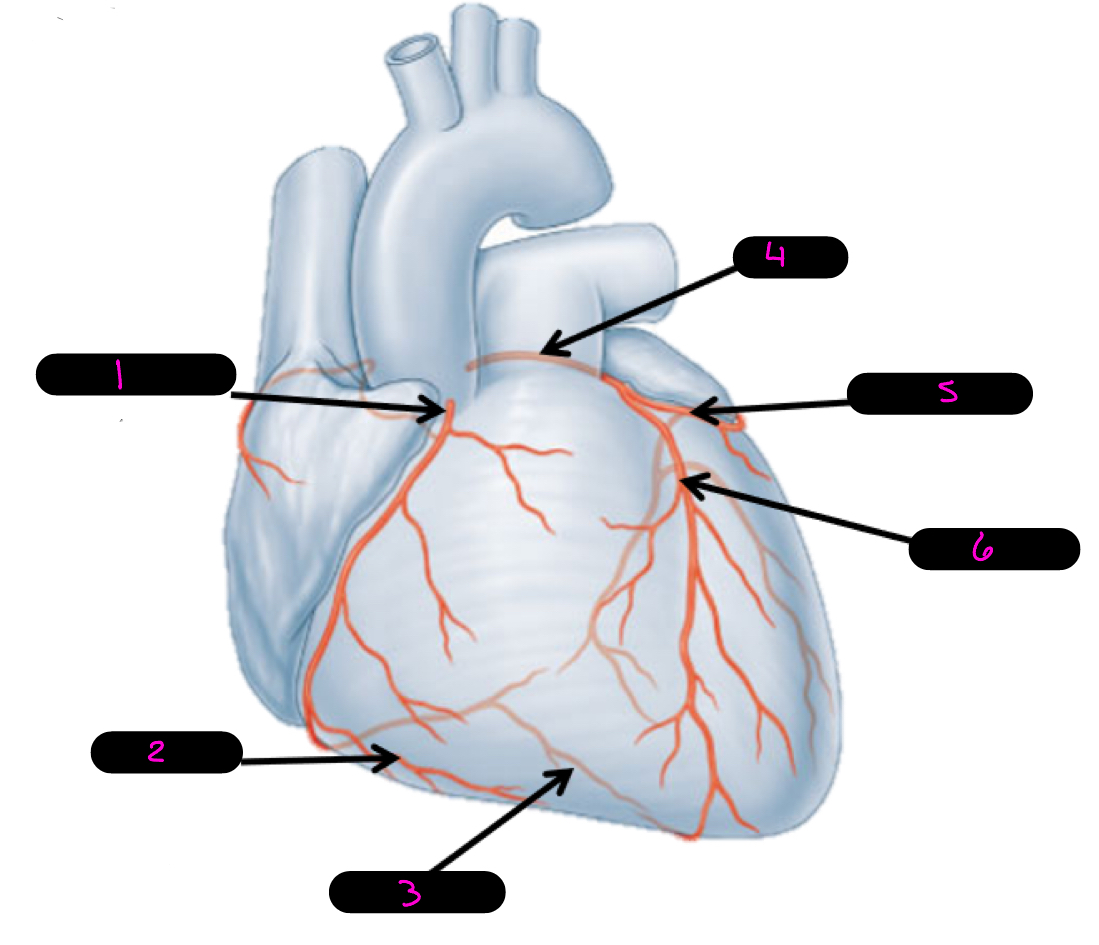
6
anterior interventricular artery
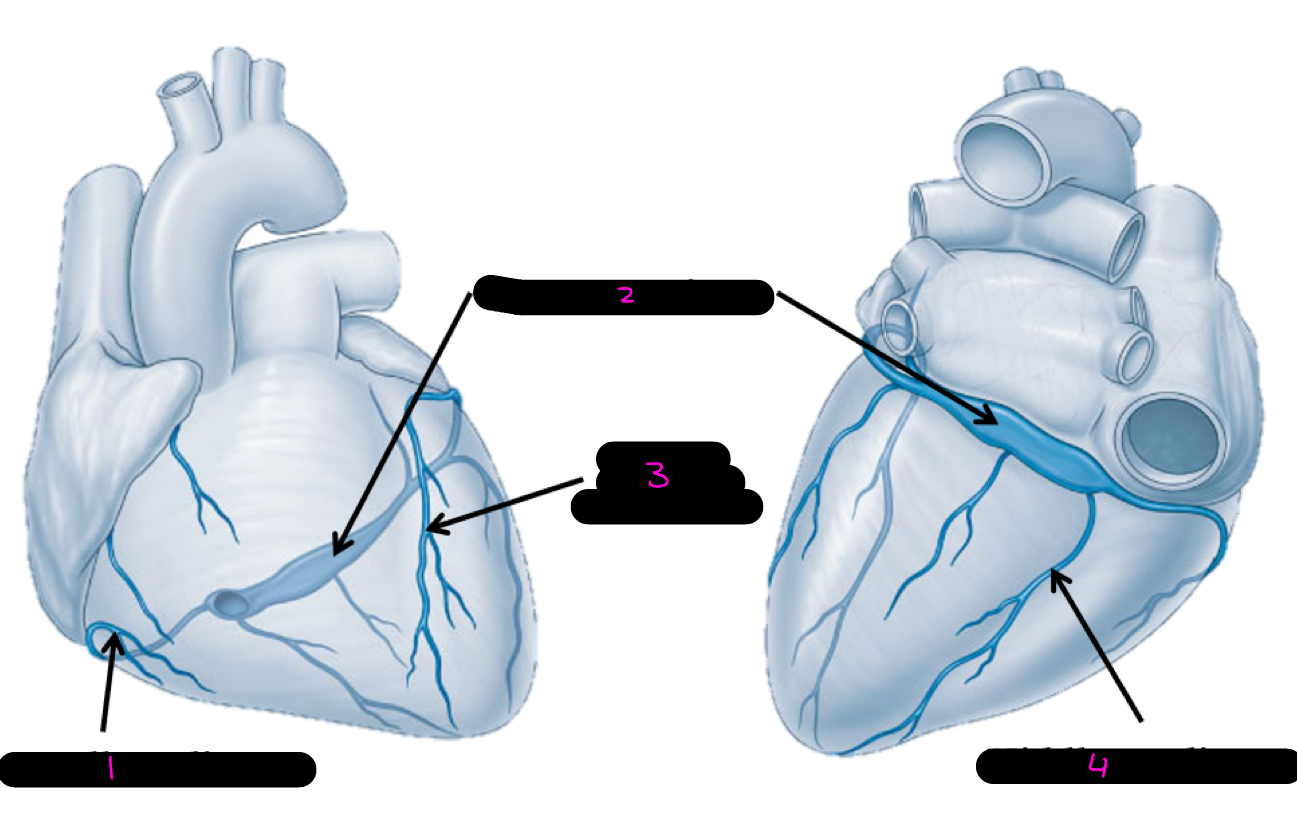
1
small cardiac vein
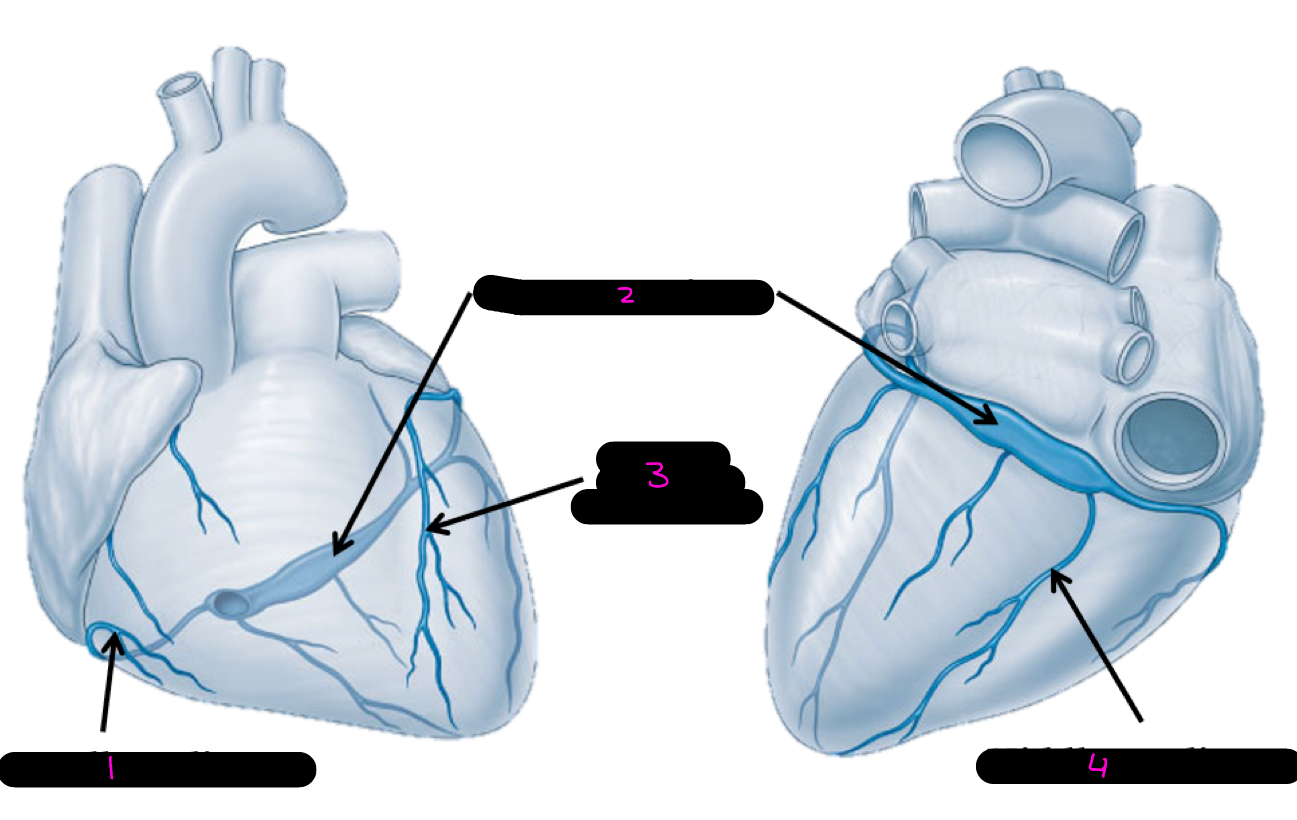
2
coronary sinus
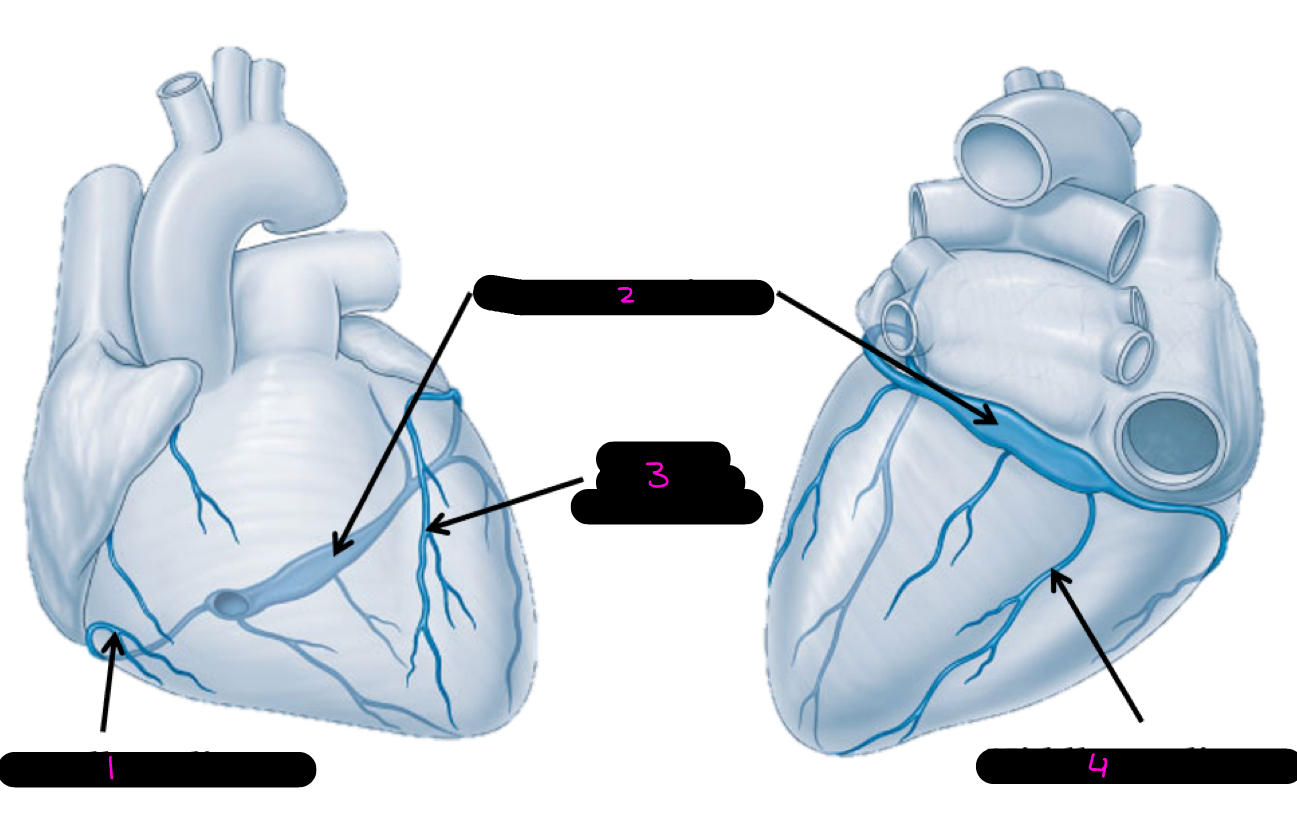
3
great cardiac vein
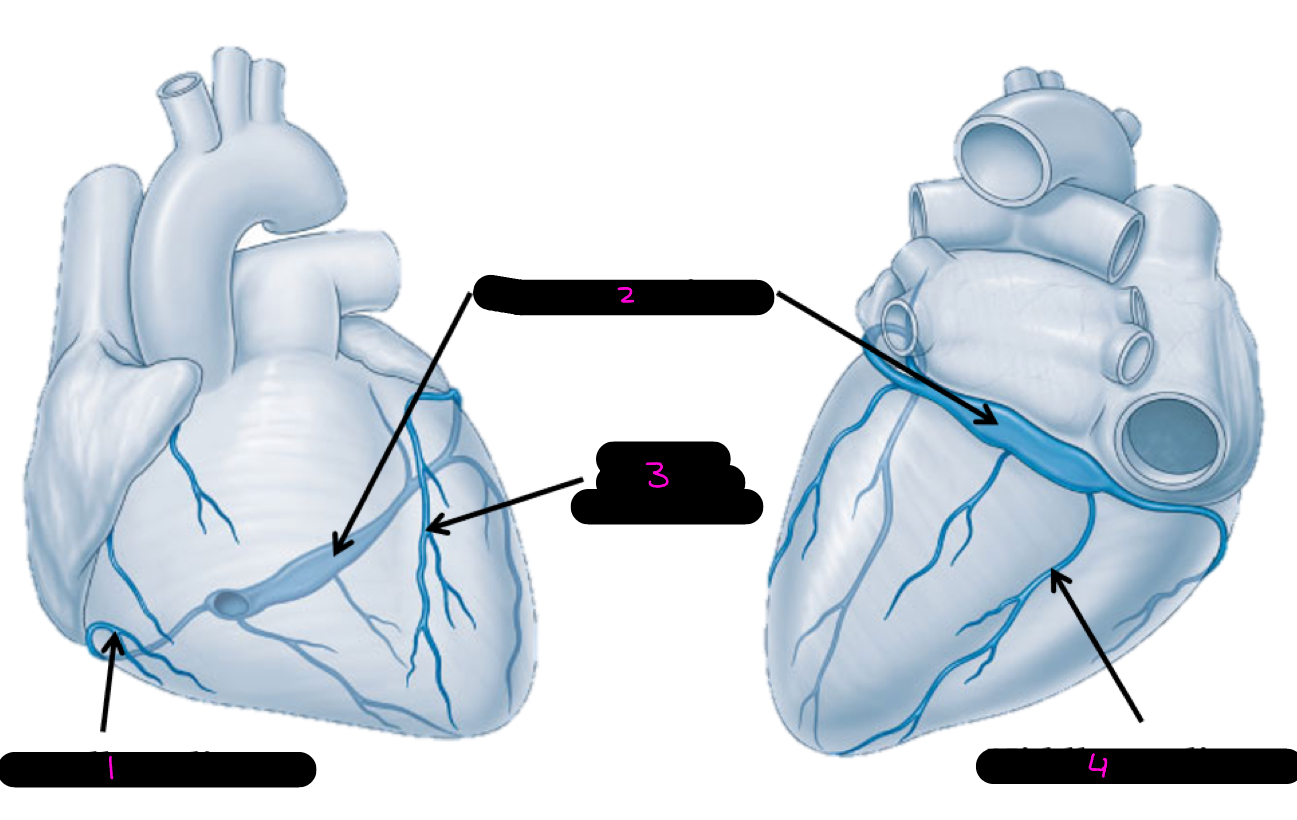
4
middle cardiac vein

1
base of aorta

2
right coronary artery
3
left coronary artery
4
right marginal artery
5
posterior interventricular artery
6
anterior interventricular artery

7
circumflex artery

8
small cardiac vein
9
middle cardiac vein

10
great cardiac vein

11
coronary sinus
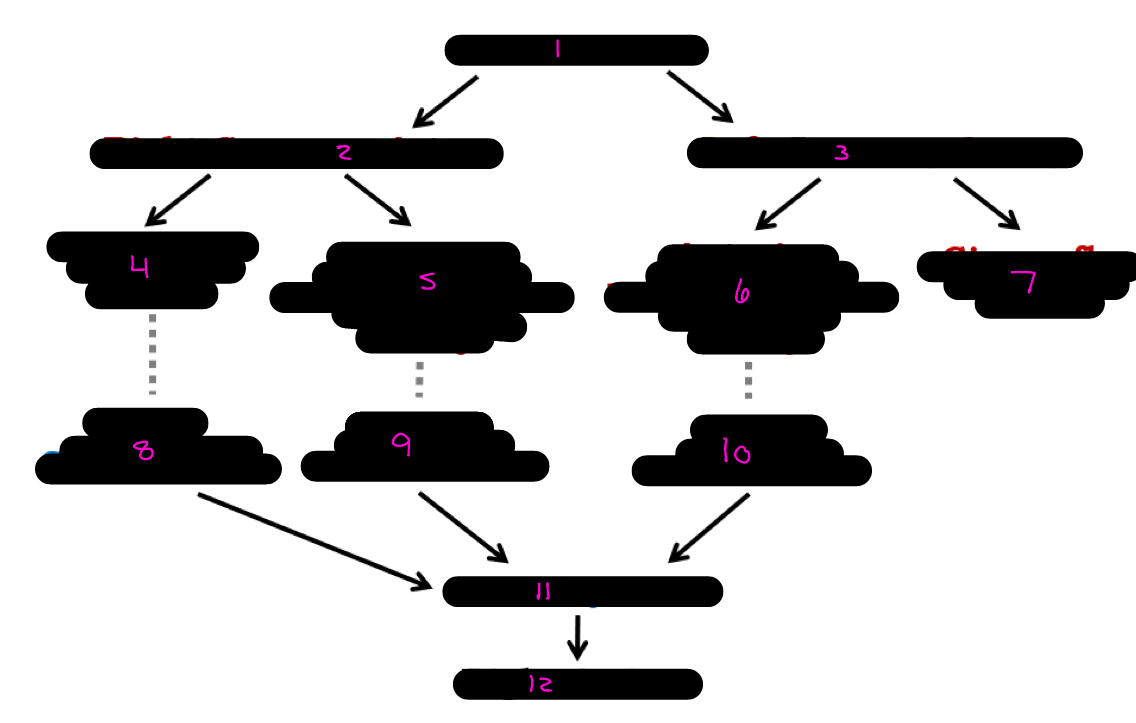
12
right atrium
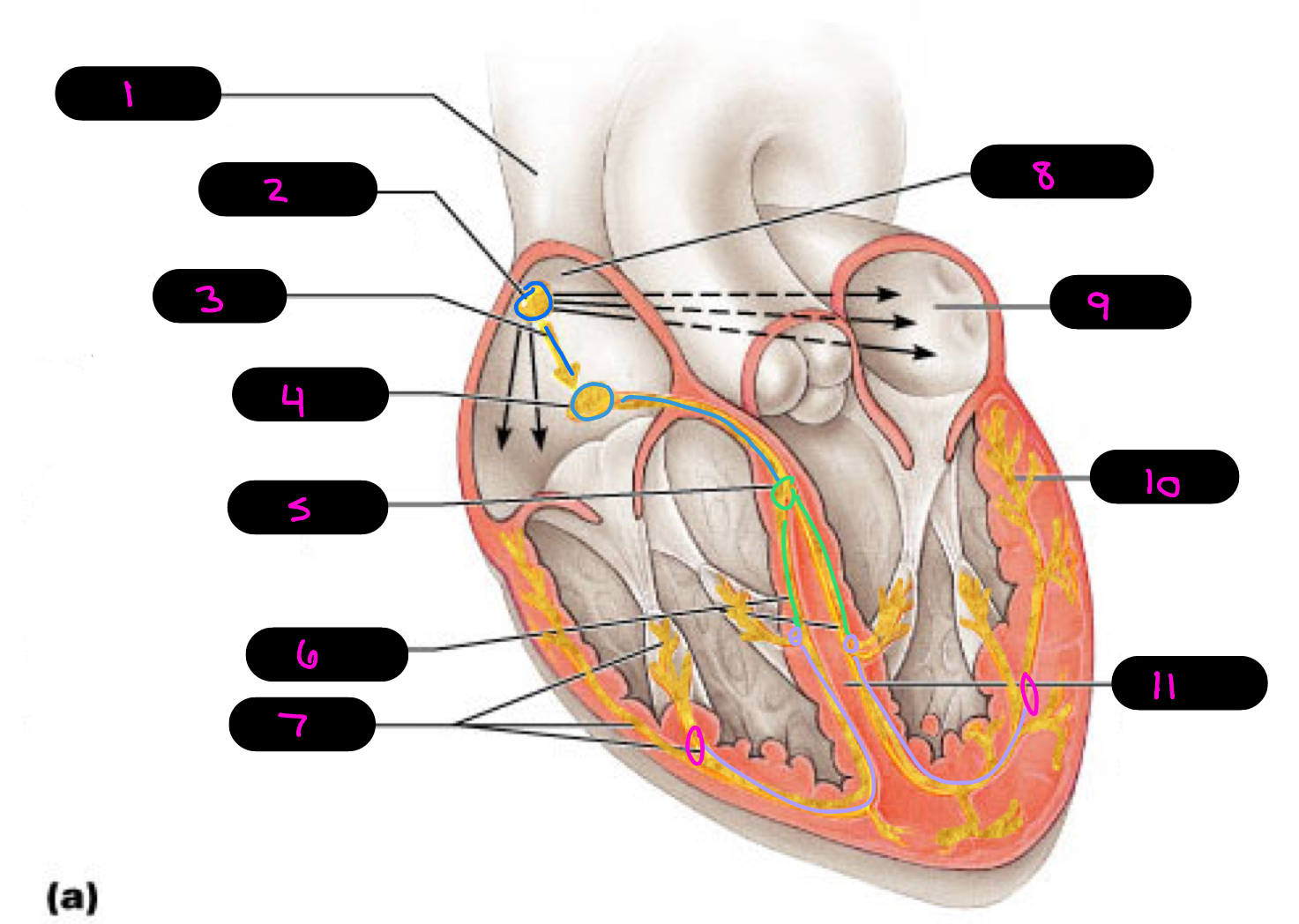
1
superior vena cava
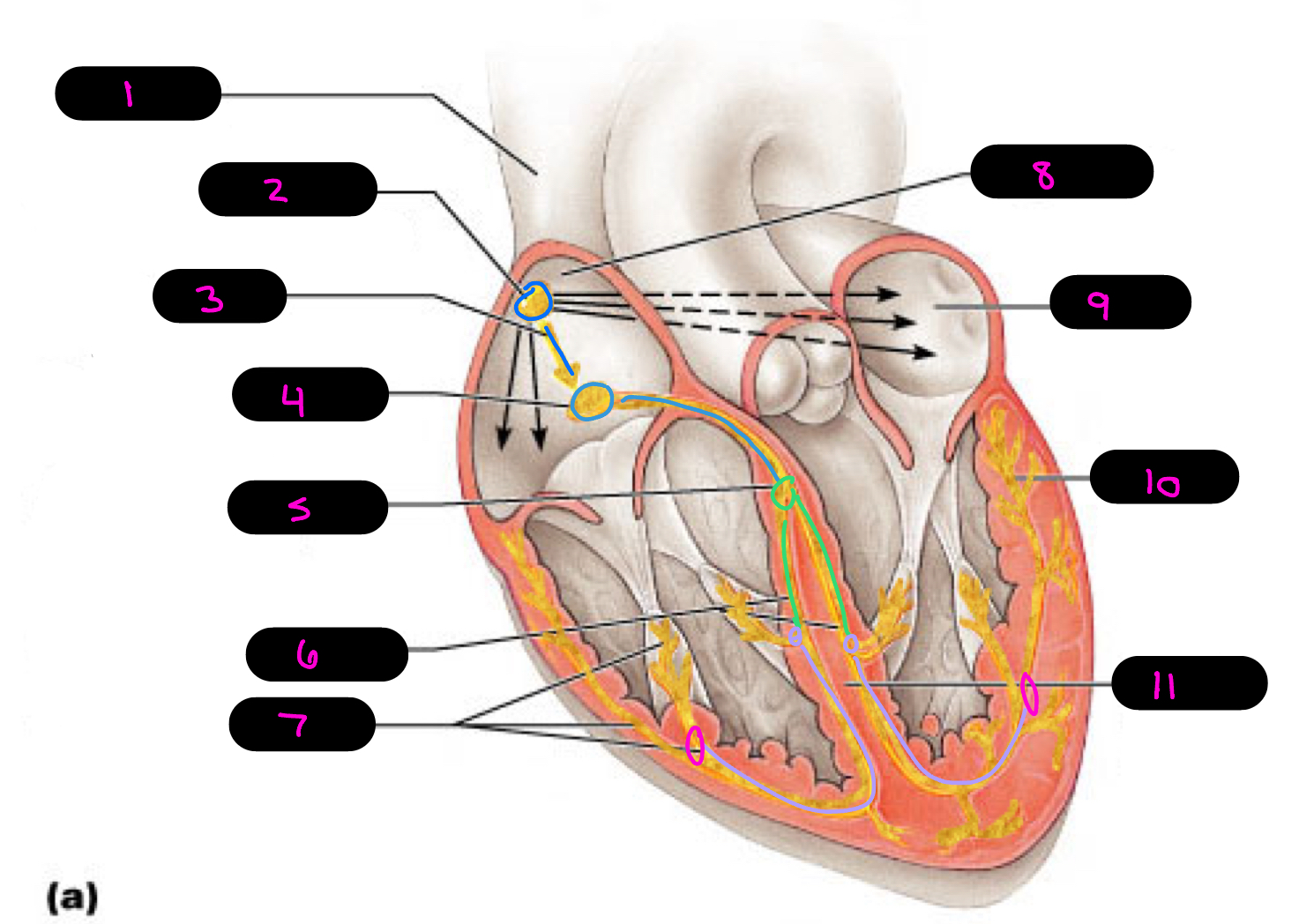
2
sinoatrial (SA) node (pacemaker)
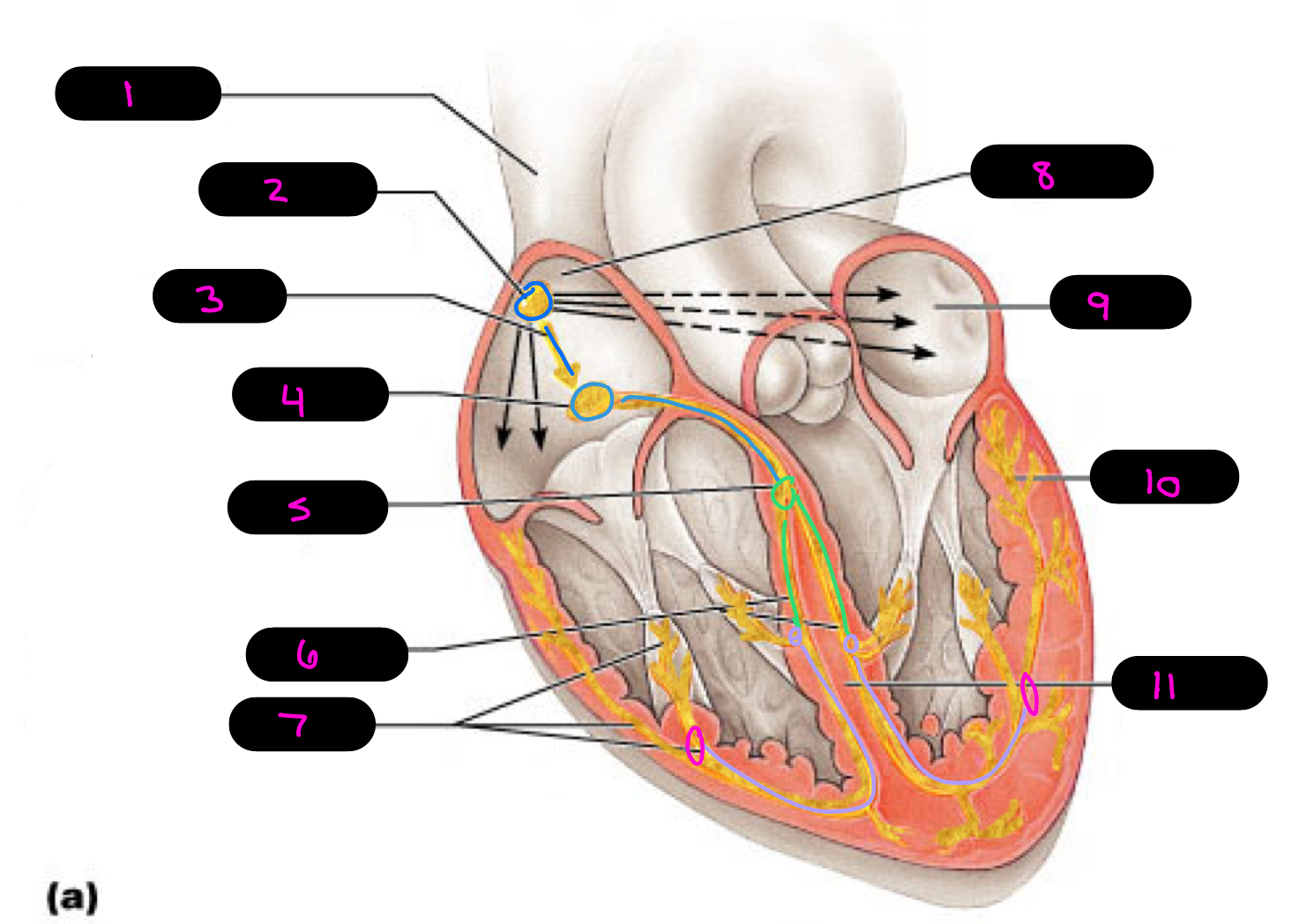
3
internodal pathway
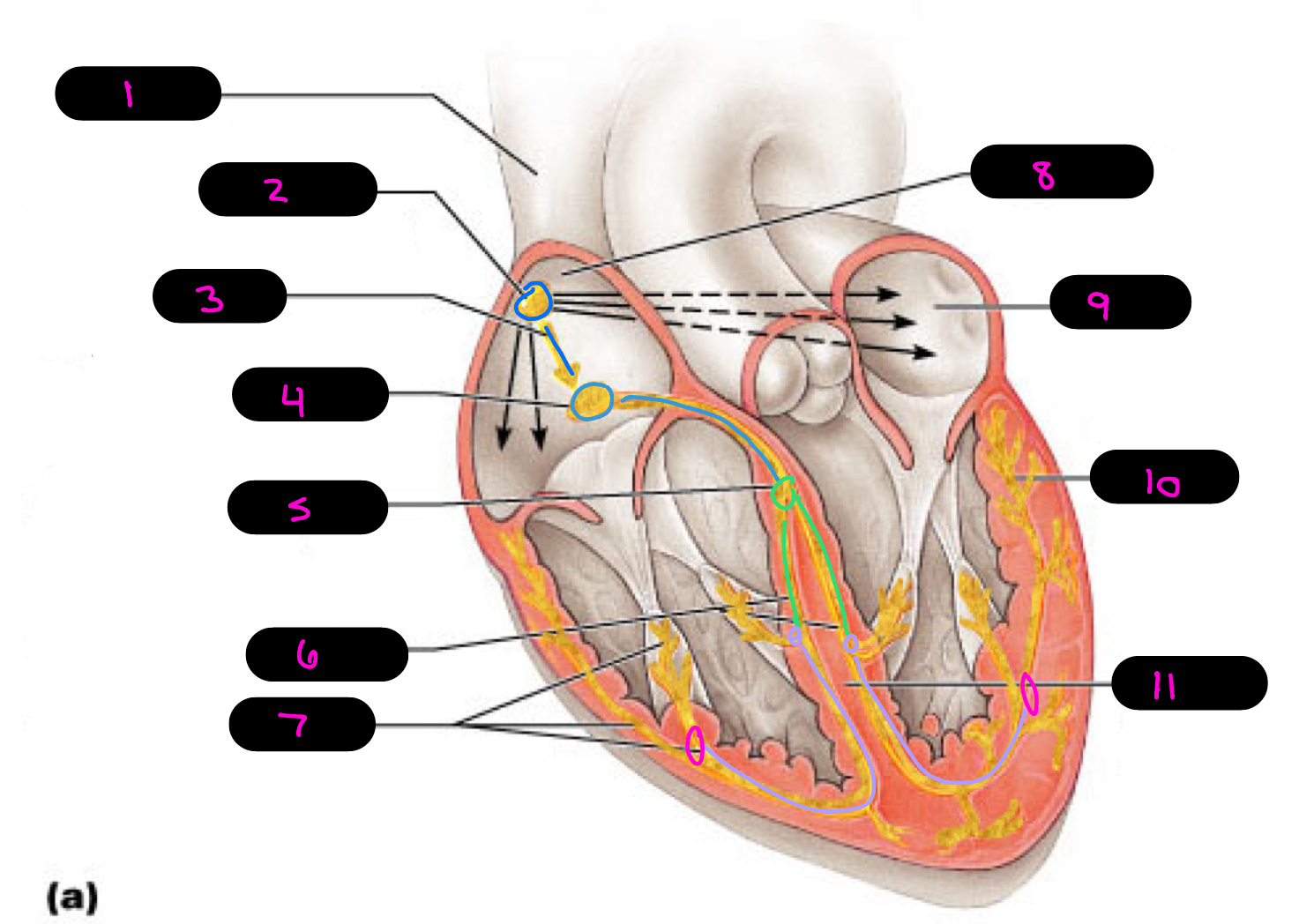
4
atrioventricular (AV) node
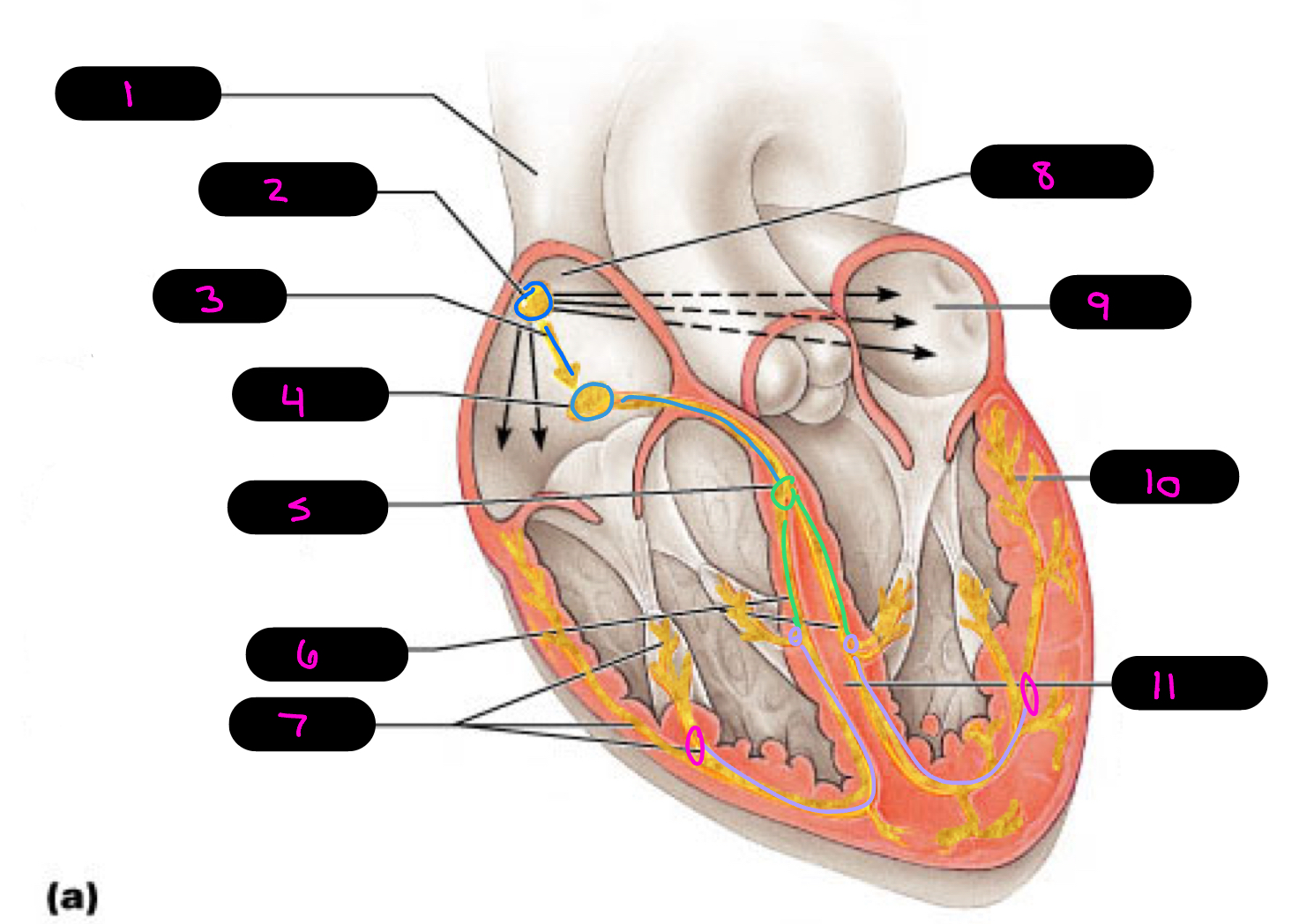
5
atrioventricular bundle of His
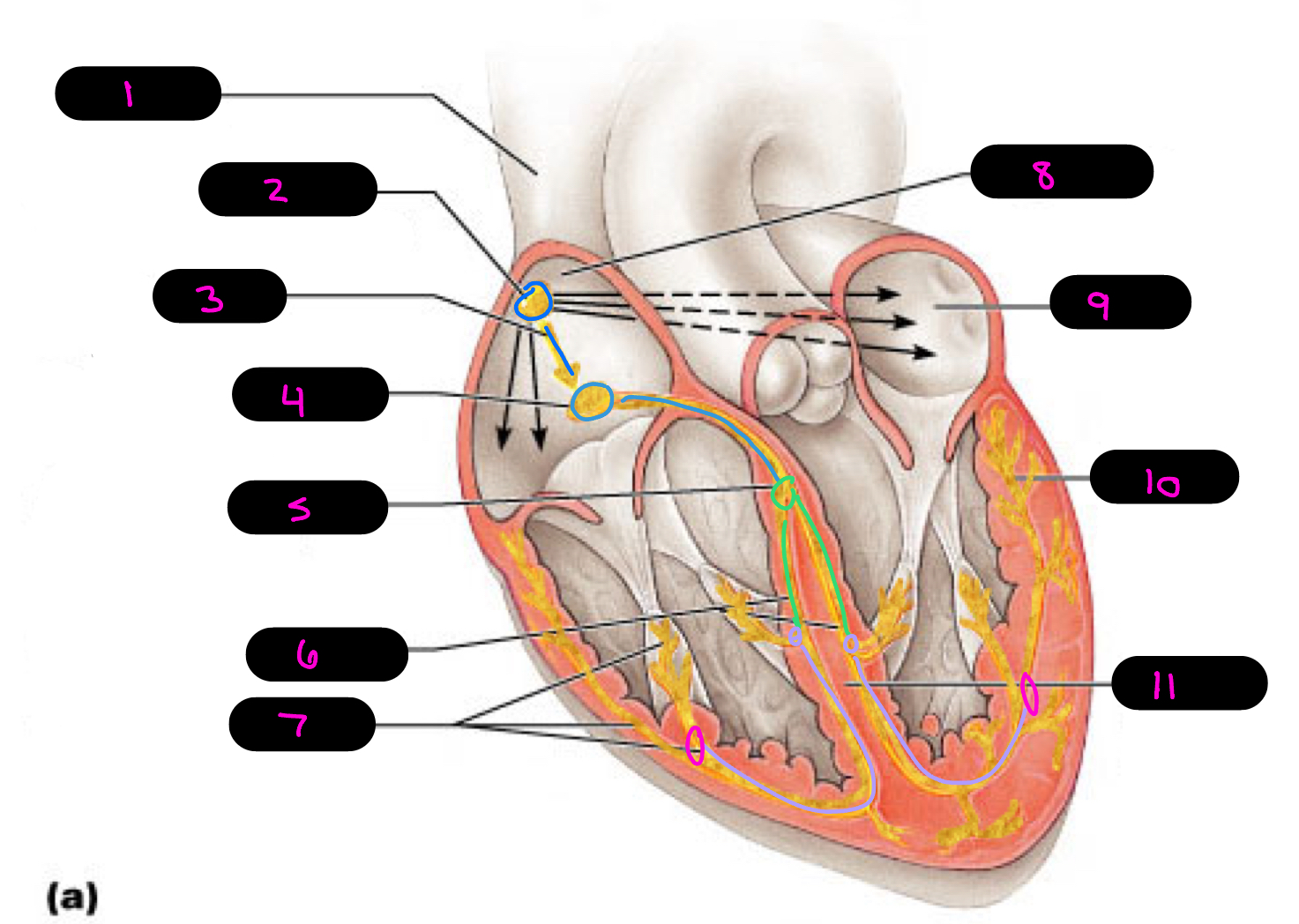
6
bundle branches

7
purkinje fibers
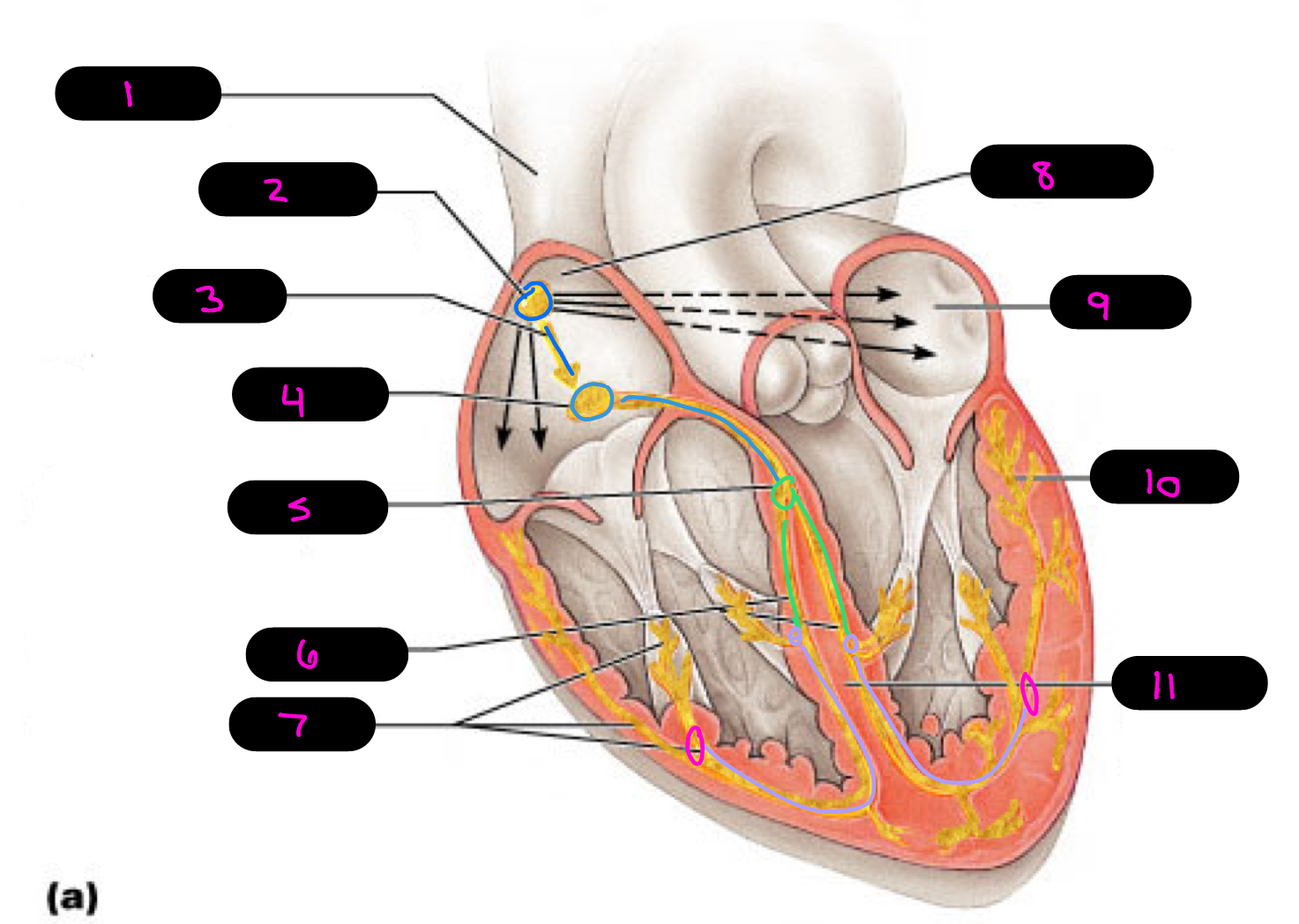
8
right atrium
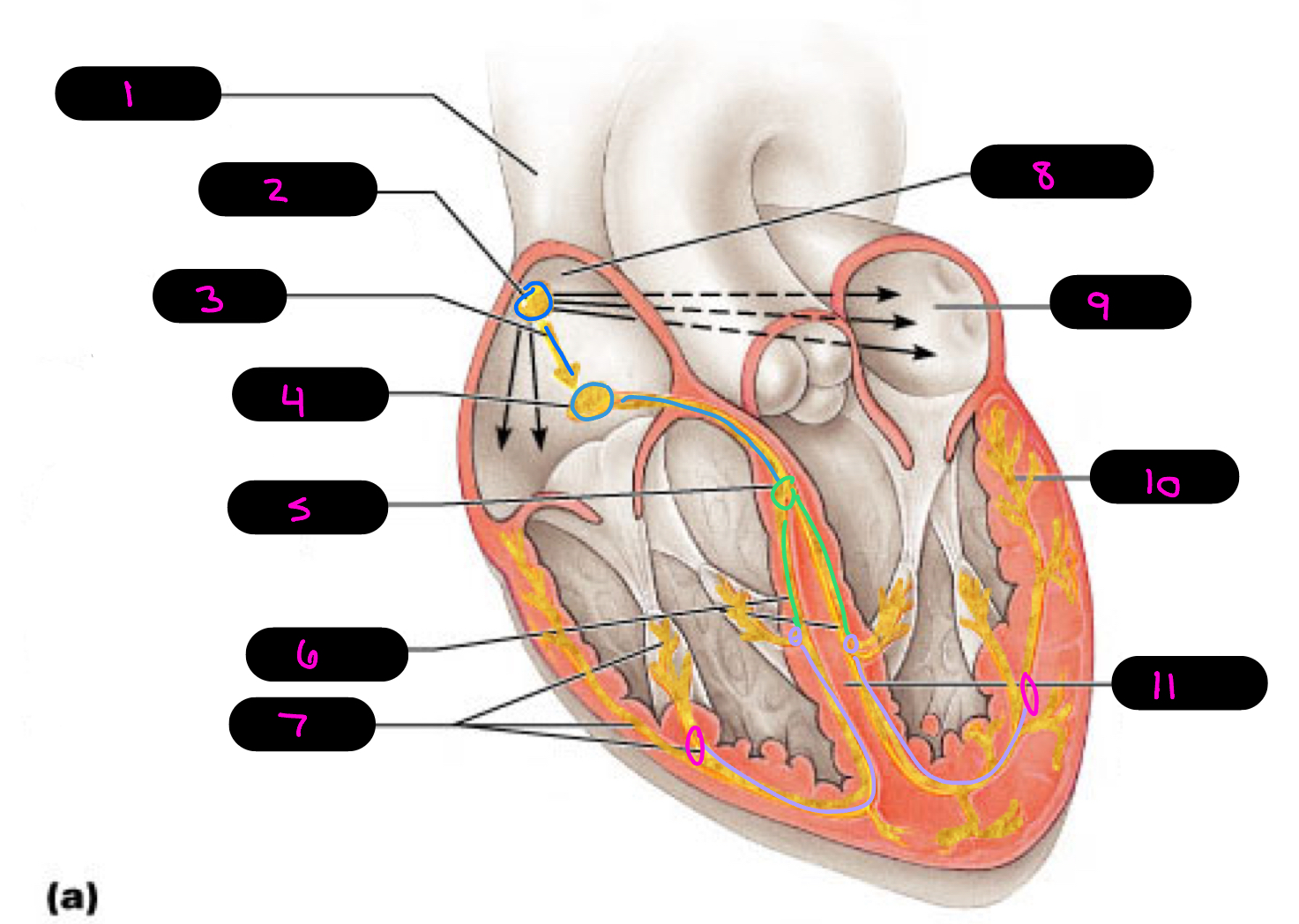
9
left atrium

10
purkinje fibers
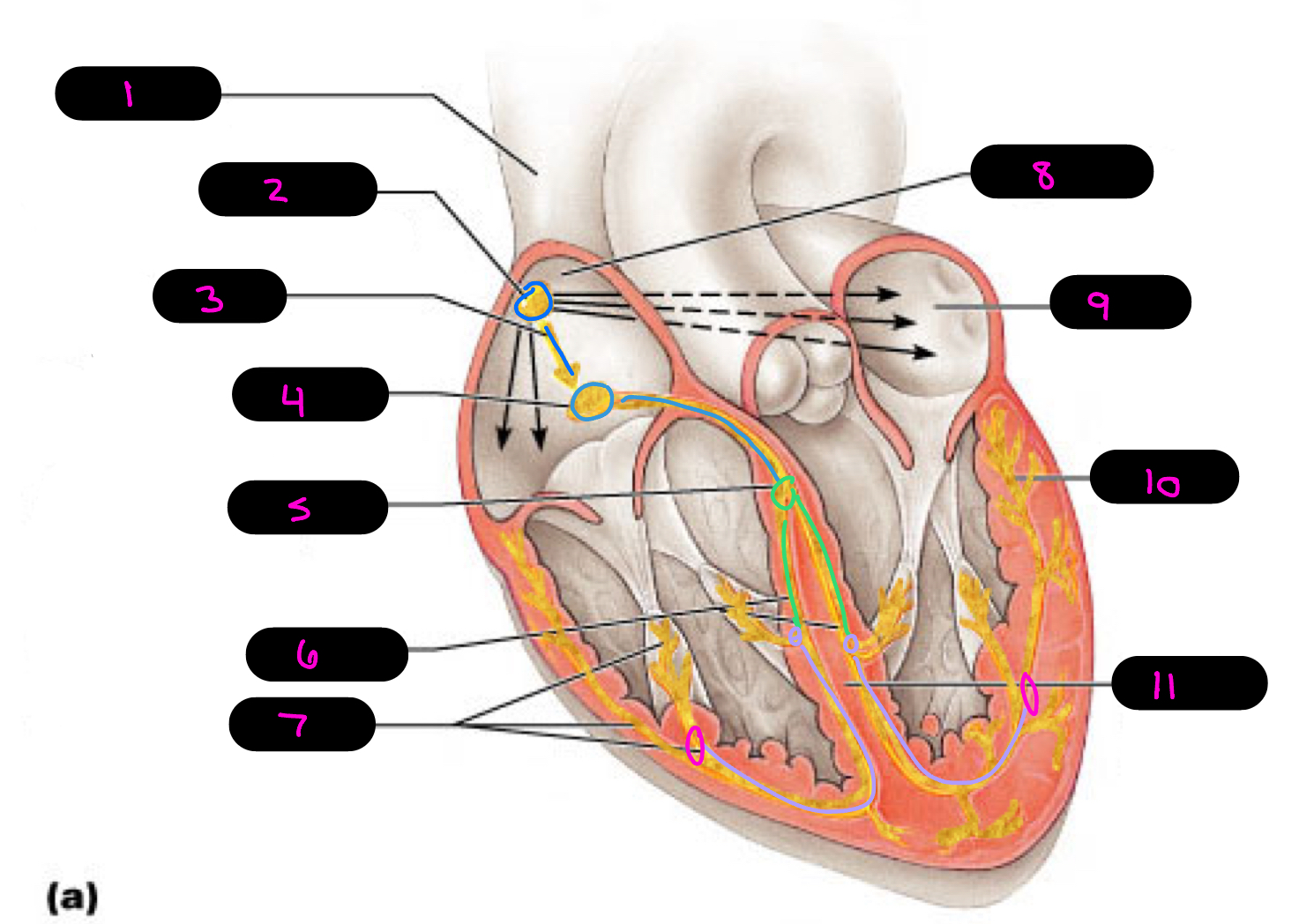
11
interventricular septum
what alters the intrinsic cardiac muscle contraction set by pace maker cells
para/sympathetic activation
fetal circulation facts:
non-functioning lungs, cannot provide own nutrients, cannot remove own waste, use mothers circulation to fulfill deficiencies
what provides the fetus with nutrients and maternal and fetal blood to communicate
placenta
how does the placenta communication occur
via umbilical vessels in umbilical cord, there is 1 umbilical vein, and 2 umbilical areries
what is the umbilical veins pathway
through primitive liver and carries oxygenated blood to the IVC
what does the umbilical vein regress to
ligamentum teres (round ligament of the liver)
what is a hole that shunts blood from the RA to the LA and bypass lungs in utero
foramen ovale
what does the foramen ovale become post utero
fossa ovalis
what is a utero thing that shunts blood that made it to the left pulmonary artery to the aorta
ductus arteriosus
what does the ductus arteriosis regress to
ligamentum arteriosum
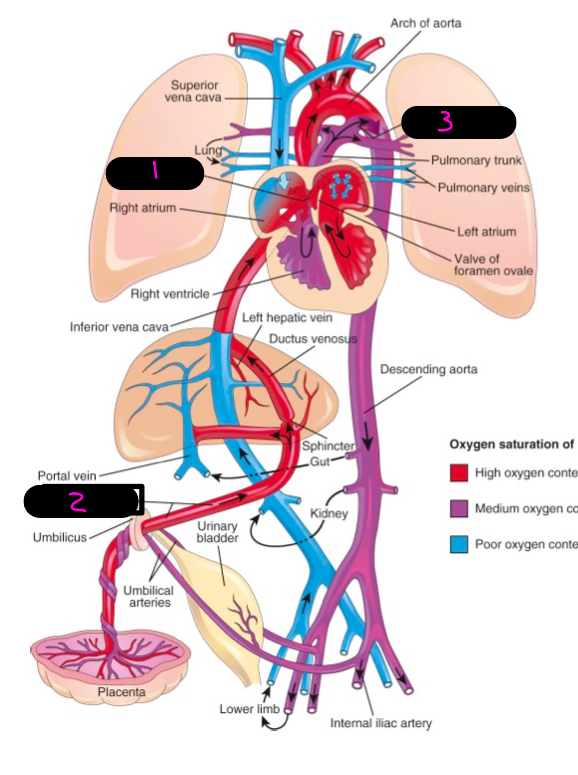
1
foramen ovale
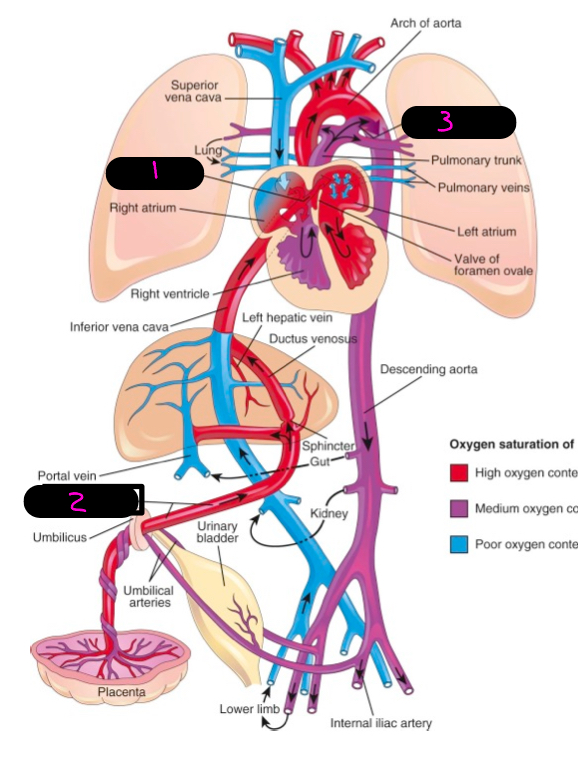
2
umbilical vein
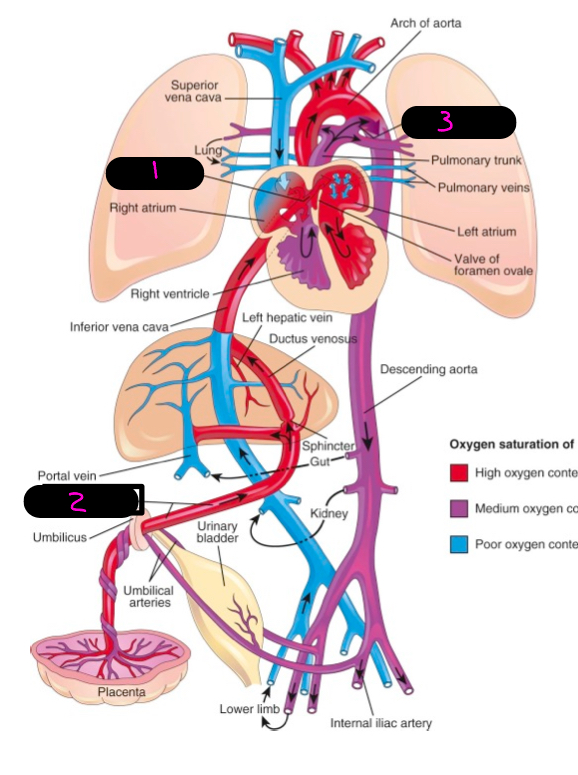
3
ductus arteriosis