AP Macroeconomics Unit 2 Review
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Gross Domestic Product (GDP)
The market value of all the final goods and services produced within a country in a given time period.
Final Good or Service
A good or service that is produced for its final user and not as a component of another good or service.
Intermediate Good or Service
A good or service that is produced by one firm, bought by another firm, and used as a component of a final good or service.
Consumption Expenditure
The expenditure by households on consumption goods and services.
Investment
The purchase of new capital goods (tools, instruments, machines, buildings, and other constructions) and additions to inventories.
Government Expenditure on Goods and Services
The expenditure by all levels of government on goods and services.
Net Exports of Goods and Services
The value of exports of goods and services minus the value of imports of goods and services.
Total Expenditure Formula
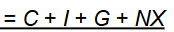
Real GDP
The value of the final goods and services produced in a given year expressed in the prices of the base year.
Nominal GDP
The value of the final goods and services produced in a given year expressed in the prices of that same year.
GDP Deflator Formula
An average of current prices expressed as a percentage of base-year prices.
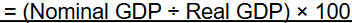
Real GDP Per Person (Capita) Formula
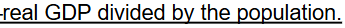
Business Cycle
A periodic irregular up and down movement of total production and other measure of economic activity.
Working-age Population
Total number of people aged 16 years and over who are not in a jail, hospital, or some other form of institutional care or in the U.S. Armed Forces.
Labor Force
The number of people employed plus the number unemployed.
Unemployment Rate Formula
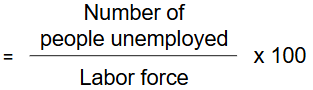
Labor Force Participation Rate Formula
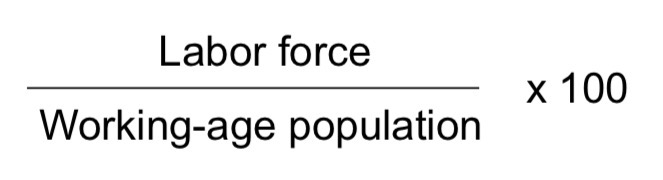
Discouraged Worker
A person who does not have a job, is available to work, but has not made efforts to find a job within the previous four weeks.
Frictional Unemployment
The unemployment that arises from normal labor turnover—from people entering and leaving the labor force and from the ongoing creation and destruction of jobs.
Structural Unemployment
The unemployment that arises when changes in technology or international competition change the skills needed to perform jobs or change the locations of jobs.
Seasonal Unemployment
The unemployment that arises because of seasonal weather patterns.
Cyclical Unemployment
The fluctuating unemployment over the business cycle that increases during a recession and decreases during an expansion.
Full Employment
When there is no cyclical unemployment or, equivalently, when all the unemployment is frictional, structural, or seasonal.
Natural Unemployment Rate
The unemployment rate when the economy is at full employment.
Potential GDP
The level of real GDP that the economy would produce when there is no cyclical unemployment (at full employment).
Consumer Price Index (CPI) Definition
A measure of the average of the prices paid by urban consumers for a fixed market basket of consumer goods and services.
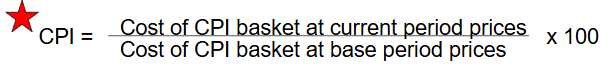
Inflation Rate Formula

Cost of Living Index Definition + Formula
A measure of changes in the amount of money that people would need to spend to achieve a given standard of living.

New Goods Bias
New goods do a better job than the old goods that they replace, but cost more.
The arrival of new goods puts an upward bias into the CPI and its measure of the inflation rate.
Quality Change Bias
Better cars and televisions cost more than the versions they replace.
A price rise that is a payment for improved quality is not inflation but might get measured as inflation.
Commodity Substitution Bias
If the price of beef rises faster than the price of chicken, people buy more chicken and less beef.
The CPI basket doesn’t change to allow for the effects of substitution between goods.
Outlet Substitution Bias
If prices rise more rapidly, people use discount stores more frequently.
The CPI basket doesn’t change to allow for the effects of outlet substitution.
Real Interest Rate Formula
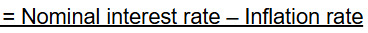
Disinflation
A decrease in the rate of inflation (a slowdown).
Deflation
A general decline in prices for goods and services.
Menu Cost
Result from a firm having to change prices.
Shoe Leather Costs
Refer to the cost of time and effort that people end up spending to counteract the effects of inflation.
Loss of Purchasing Power
Occurs because inflation causes the value of the individual dollar to decrease over time.
Wealth Redistribution
Lenders are hurt by unanticipated inflation; borrowers benefit.