Cheat Sheet 1: Biochemistry
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
Atoms
Single unit made up of neutrons, protons, and electrons
Ionic Bonds
Transfer of e- from one atom to another atom of very different electronegativity
Hydrolysis
Uses water to break polymers into monomers
Dehydration Reaction
Links monomers to form polymers, forming H2O in the process
Covalent Bonds
Sharing of e- between atoms of similar electronegativities
Molecule
Groups of 2+ atoms held together by chemical bonds due to electron interactions
Nonpolar
Equal e- sharing
Polar
Unequal e- sharing, forms dipole
Macromolecules
Large molecules (polymers) formed from the bonding of smaller molecules (monomers)
Hydrogen Bonds
Weak bond between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom (F, O, or N)
Monomer (Amino acid)
Building block of proteins
Monomer (Monosaccharide)
Building block of carbohydrates
Monomer (Nucleotide)
Building block of nucleic acids
Polymer (Peptide)
Chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
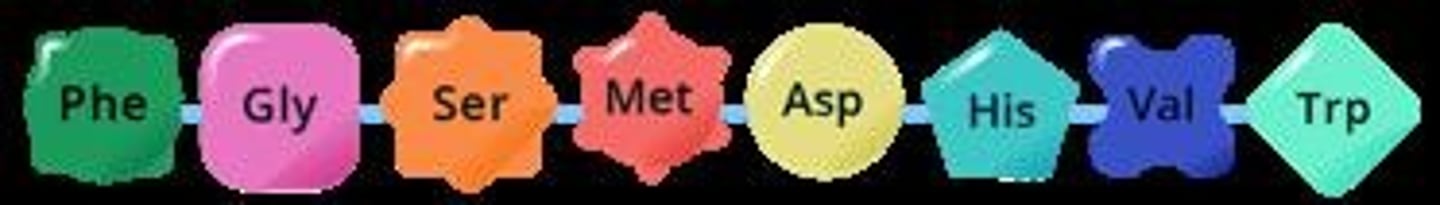
Polymer (Polysaccharide)
Chain of monosaccharides linked by glycosidic bonds
Polymer (Nucleic acid)
Chain of nucleotides linked by phosphodiester bonds
Polymer (Hydrocarbon chain)
Chain of hydrocarbons linked by covalent carbon-carbon bonds
Function of Lipids
Store energy
Function of Nucleic Acids
Encode, express, and store genetic info
Function of Proteins
Structure, transport, defense, storage, enzymes
Function of Lipids
Insulation, energy storage, endocrine signaling, cell structure
Triglycerides
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
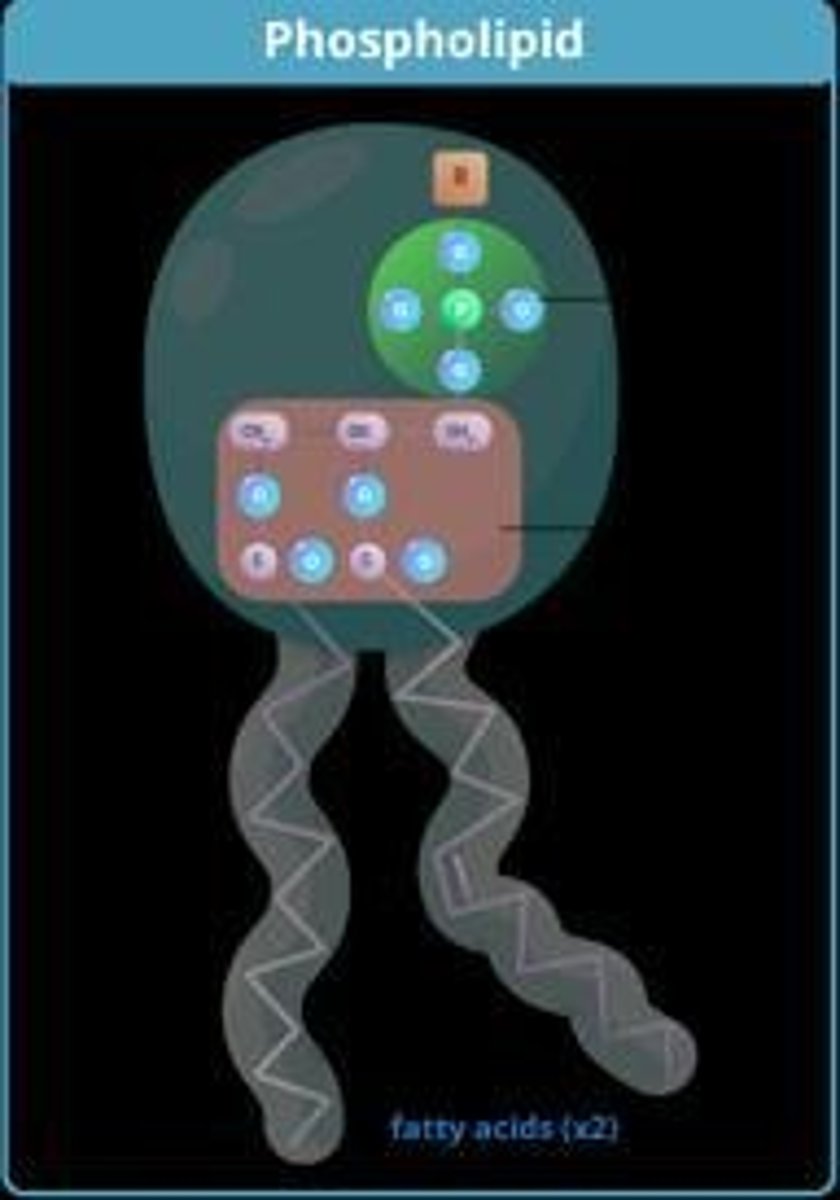
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids + phosphate group attached to glycerol backbone
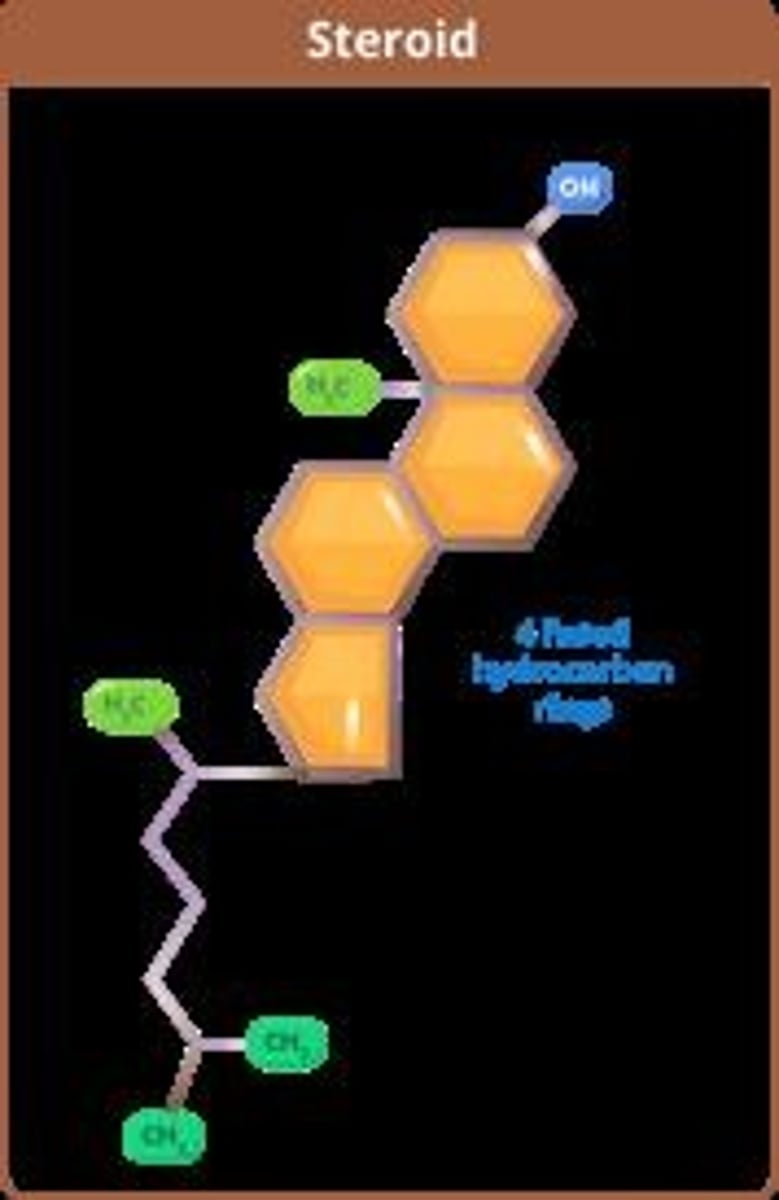
Steroids
Three 6-membered rings + one 5-membered ring
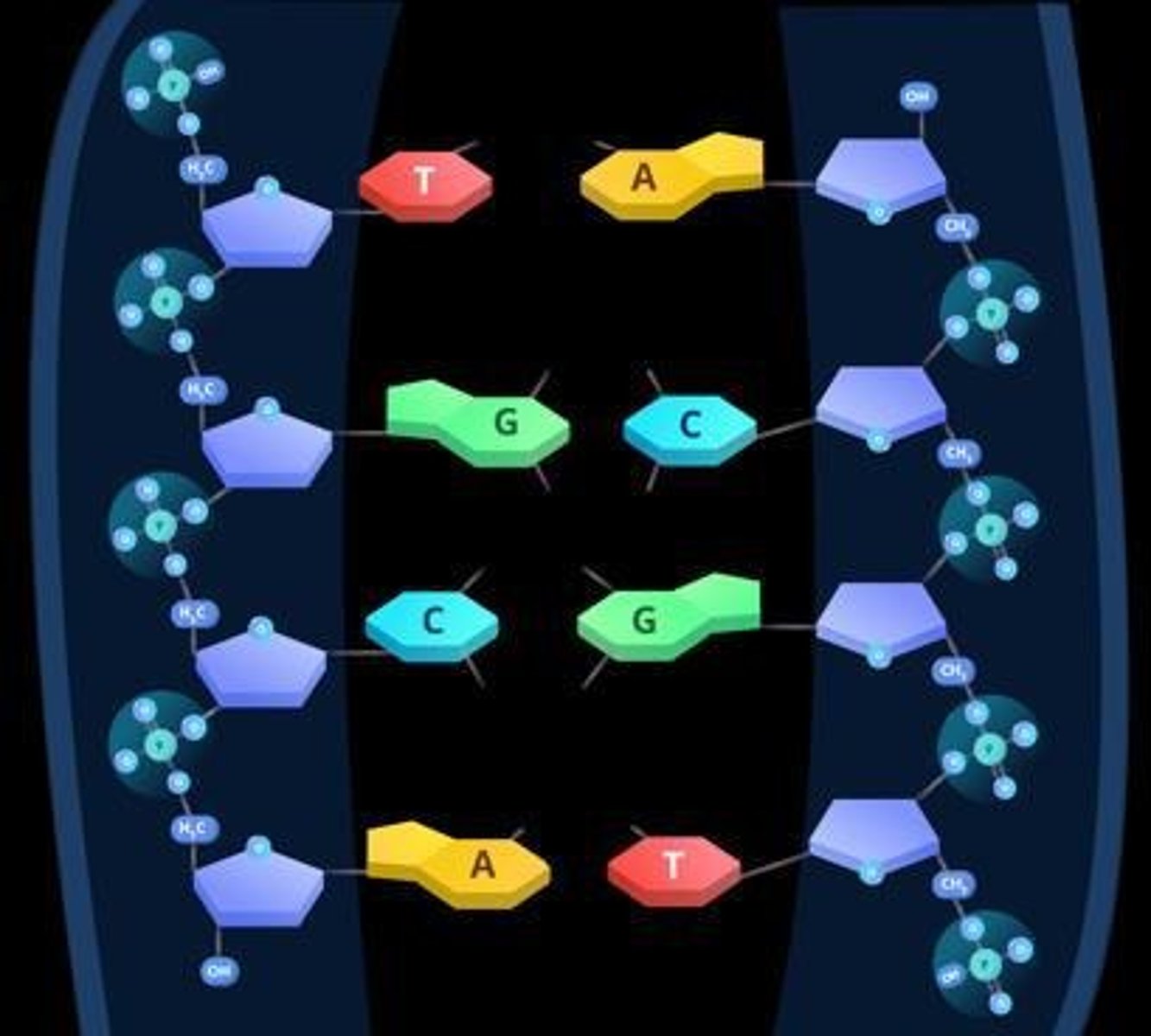
DNA Structure
Bases are A, T, C, G. Contains deoxyribose sugar and 2 complementary antiparallel (5' to 3') strands of double helix.
RNA Structure
Has bases A, U, C, and G, with a ribose sugar and is single stranded.
Chargaff's Rule
A & T, and G & C are always present in equal amounts (i.e., if DNA is 20% A, it is also 20% T).