1. anaerobic respiration
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
7 Terms
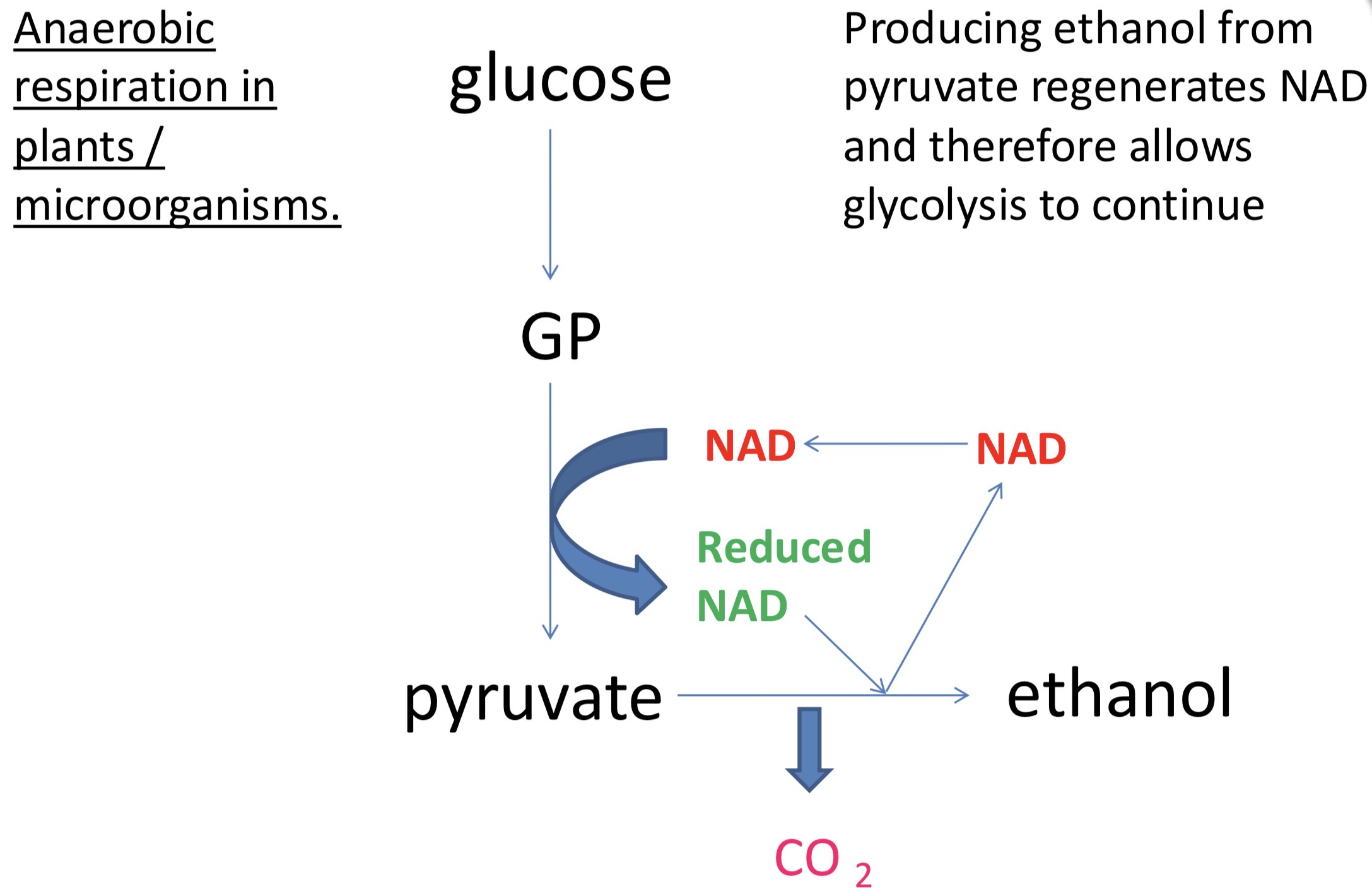
ALTERNATIVES FOR PYRUVATE
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION-1
reduced NAD is used to convert pyruvate into lactate (rather than entering the ETC)
pyruvate is reduced and reduced NAD is oxidised
lactate lowers pH of blood, which affects CNS
so muscle contractions are affected and muscles become fatigued
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION- 2
after exercise, lactate needs to be oxidised back into pyruvate
pyruvate can then enter Krebs cycle and be respired aerobically to produce CO2, H2O and lots of ATP
O2 is needed to oxidise lactate so you continue to breathe deeply for some time after exercise
DIFF BETWEEN O2 DEMAND AND O2 AVAILABLE- GRAPH
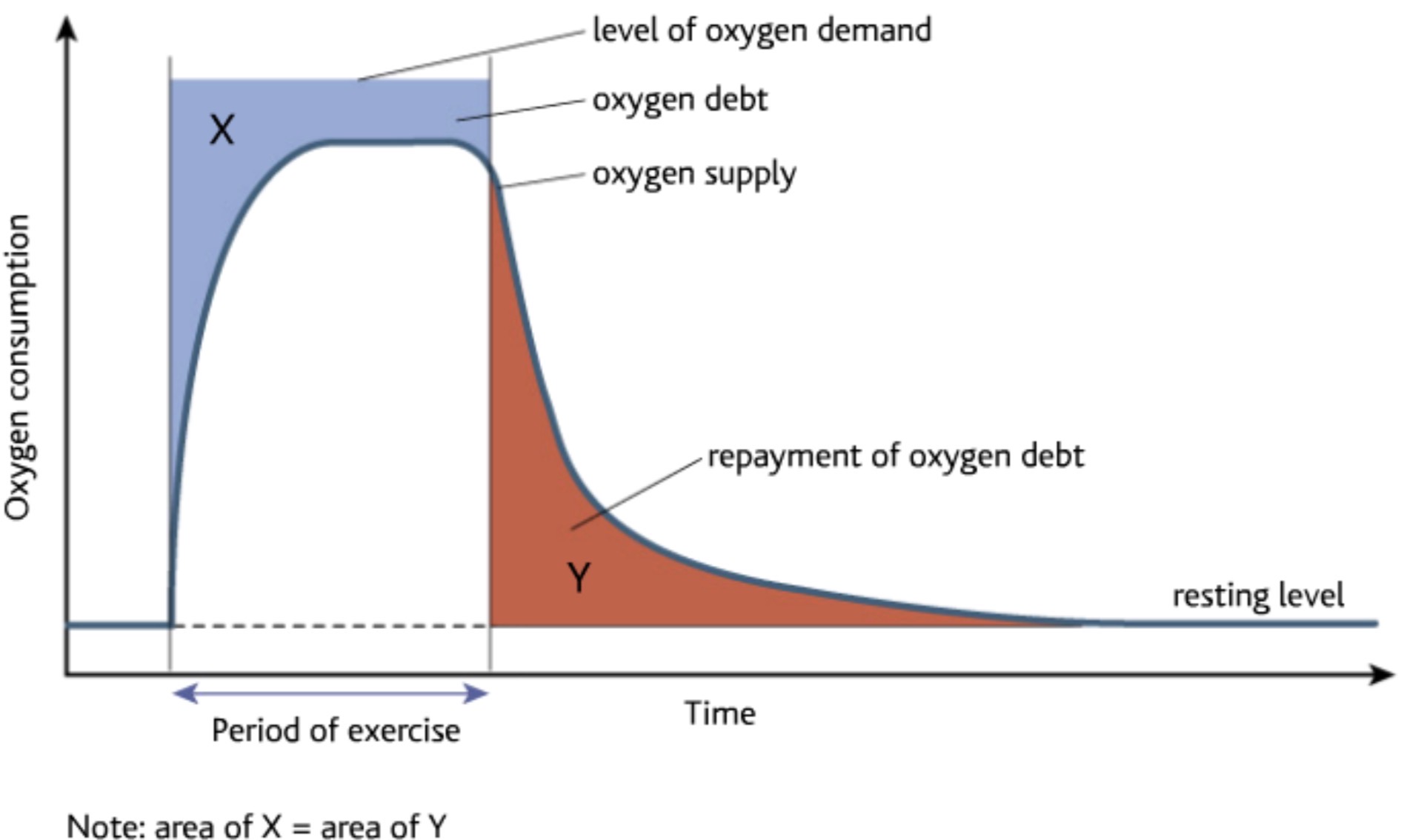
EPOC
after strenuous exercise, we continue to breathe deeply to get as much O2 into body- to provide O2 to oxidise lactic acid that has built up during anaerobic resp- known as EPOC (excess post-exercise oxygen consumption)
but scientists realised that we take in more O2 after exercising than is needed to oxidise lactic acid– so must be using this O2 for other things
EPOC- USE FOR EXCESS O2
oxidise lactate into pyruvate
convert pyruvate into glucose in a process called gluconeogenesis that happens in liver (glucose used to replenish glycogen stores)
restore ATP and phosphocreatine levels in muscle fibres
reoxygenate myoglobin in muscles
maintain increased rate of chemical reactions as a result of increased temps and adrenalin production
supply heart w/ the extra O2 it needs to maintain elevated heart rate
supply diaphragm and rib muscles w/ extra O2 needed to maintain rapid breathing rate
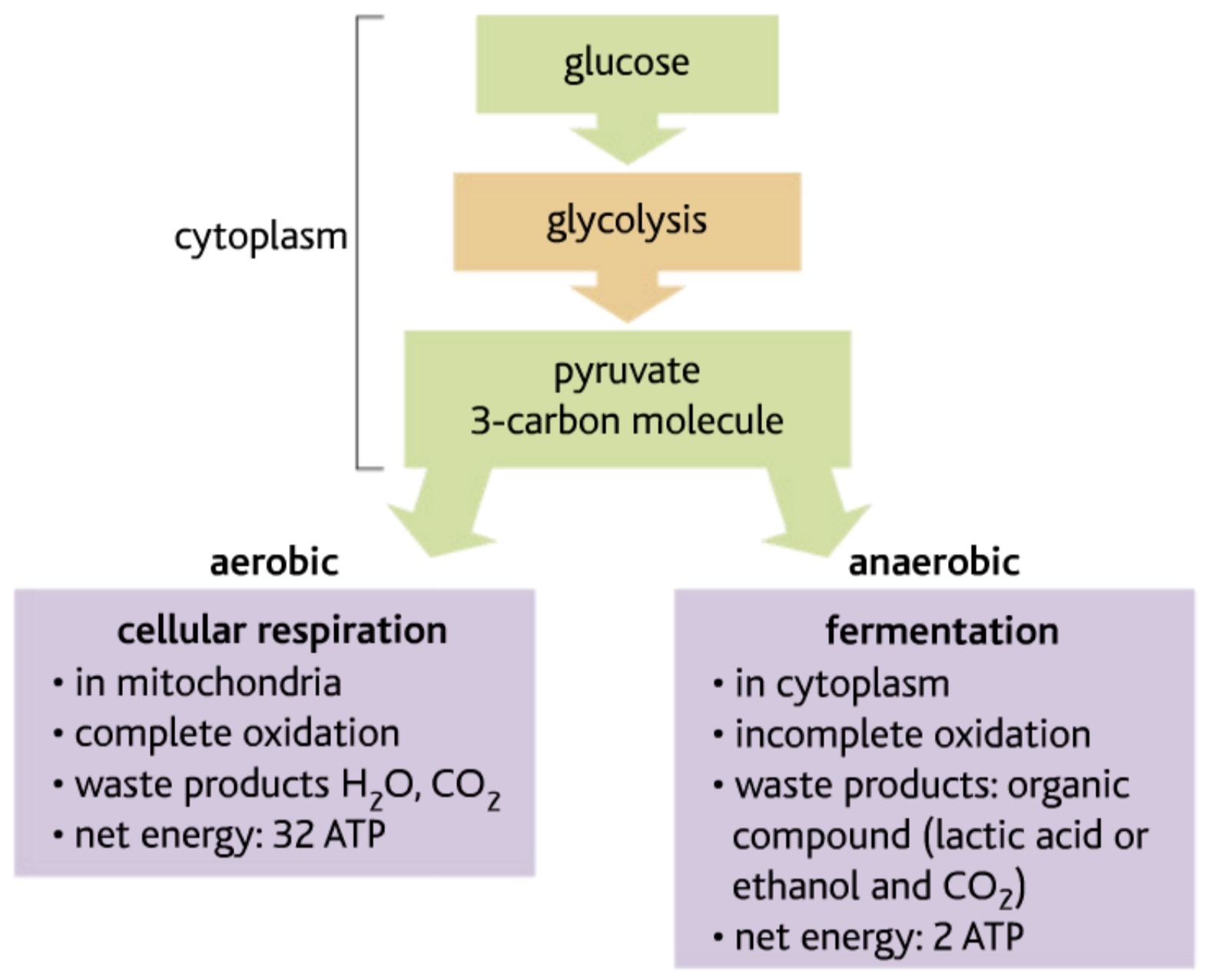
ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION- DIAGRAM