Caudal Fins
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
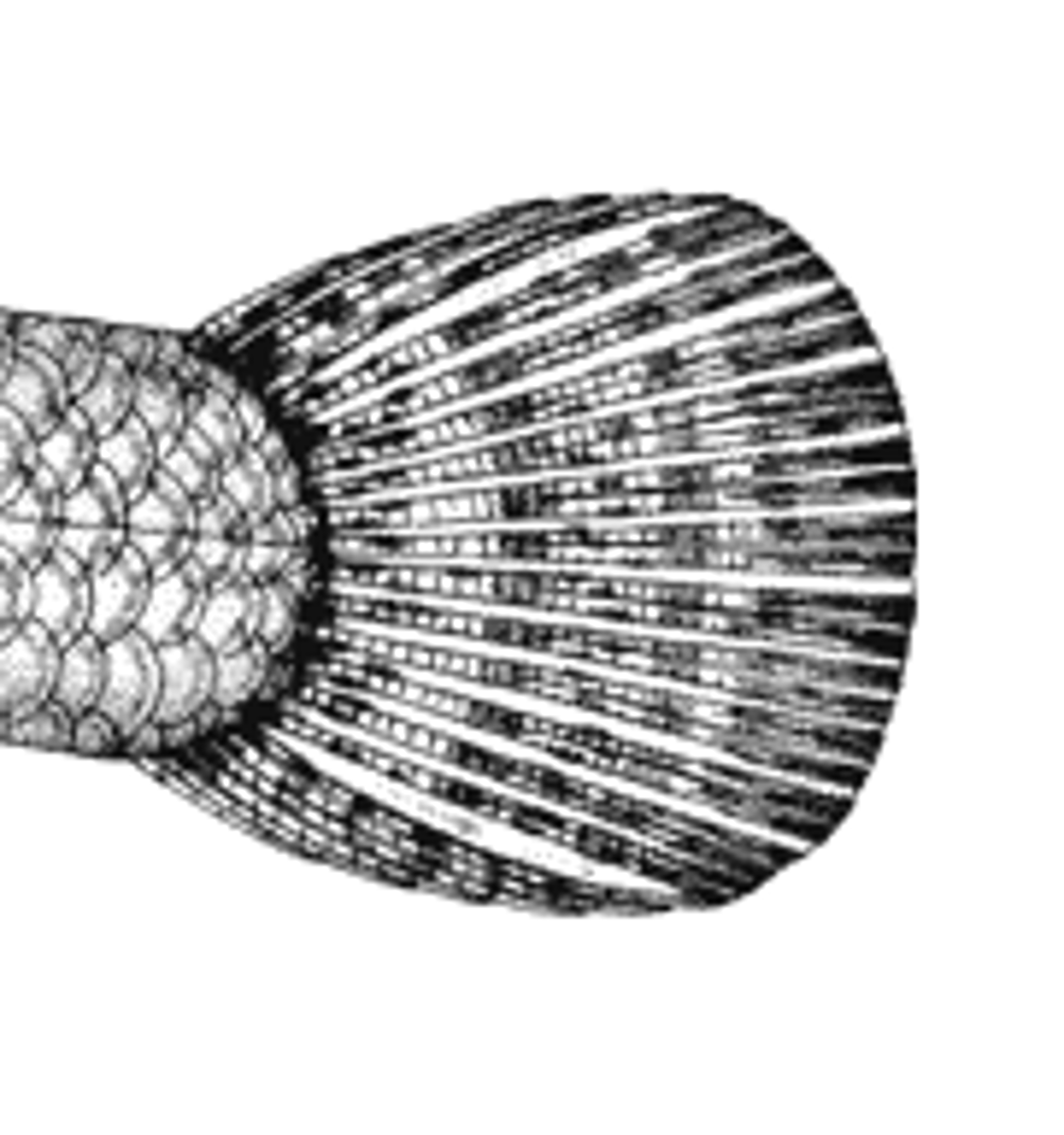
Homocercal fin
symmetrical caudal fin where the upper and lower lobes are roughly equal in size
- vertebral column ending near the middle of the caudal base rather than extending into the fin
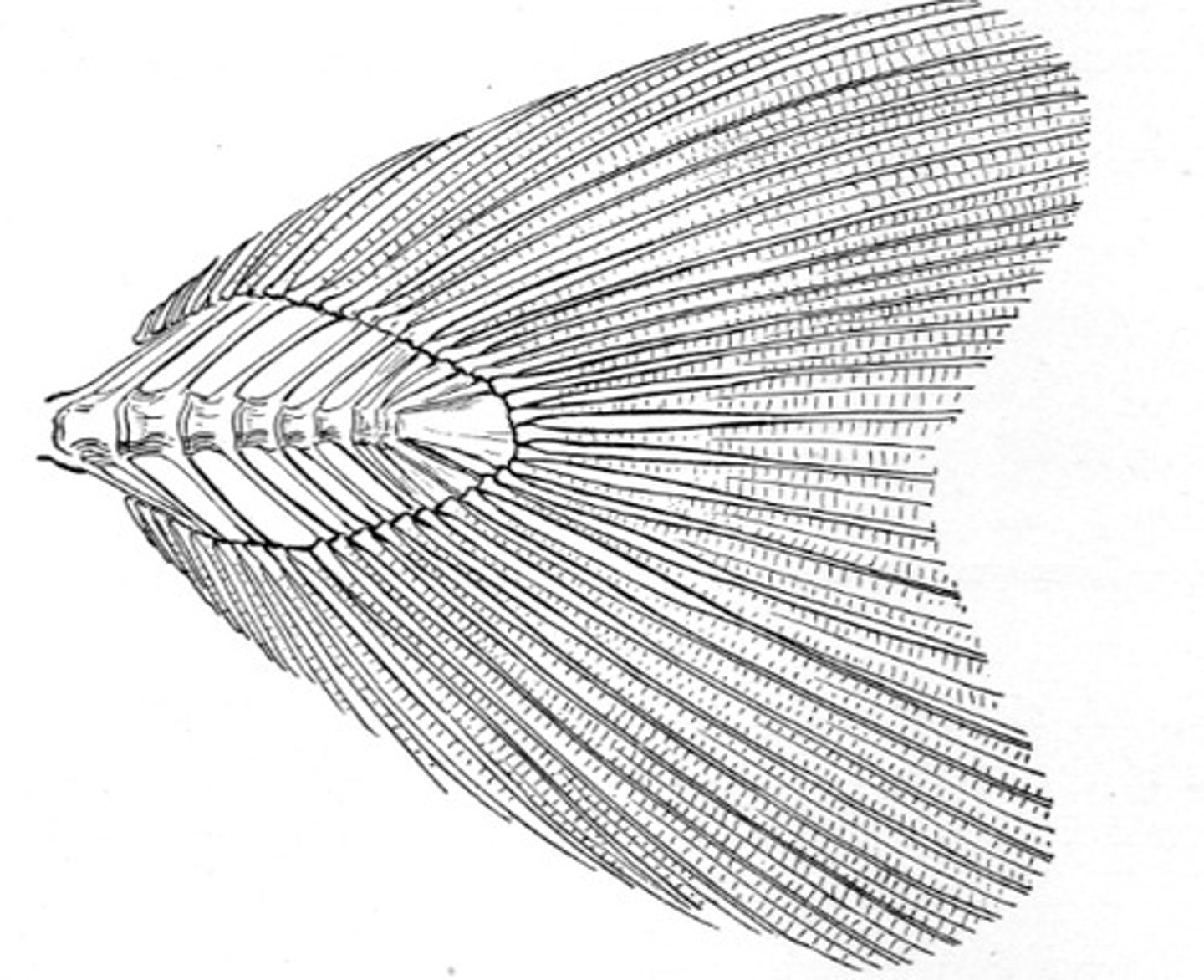
Lunate caudal fin
Crescent shaped forked tail for fast swimming pelagic fishes
-Homocercal
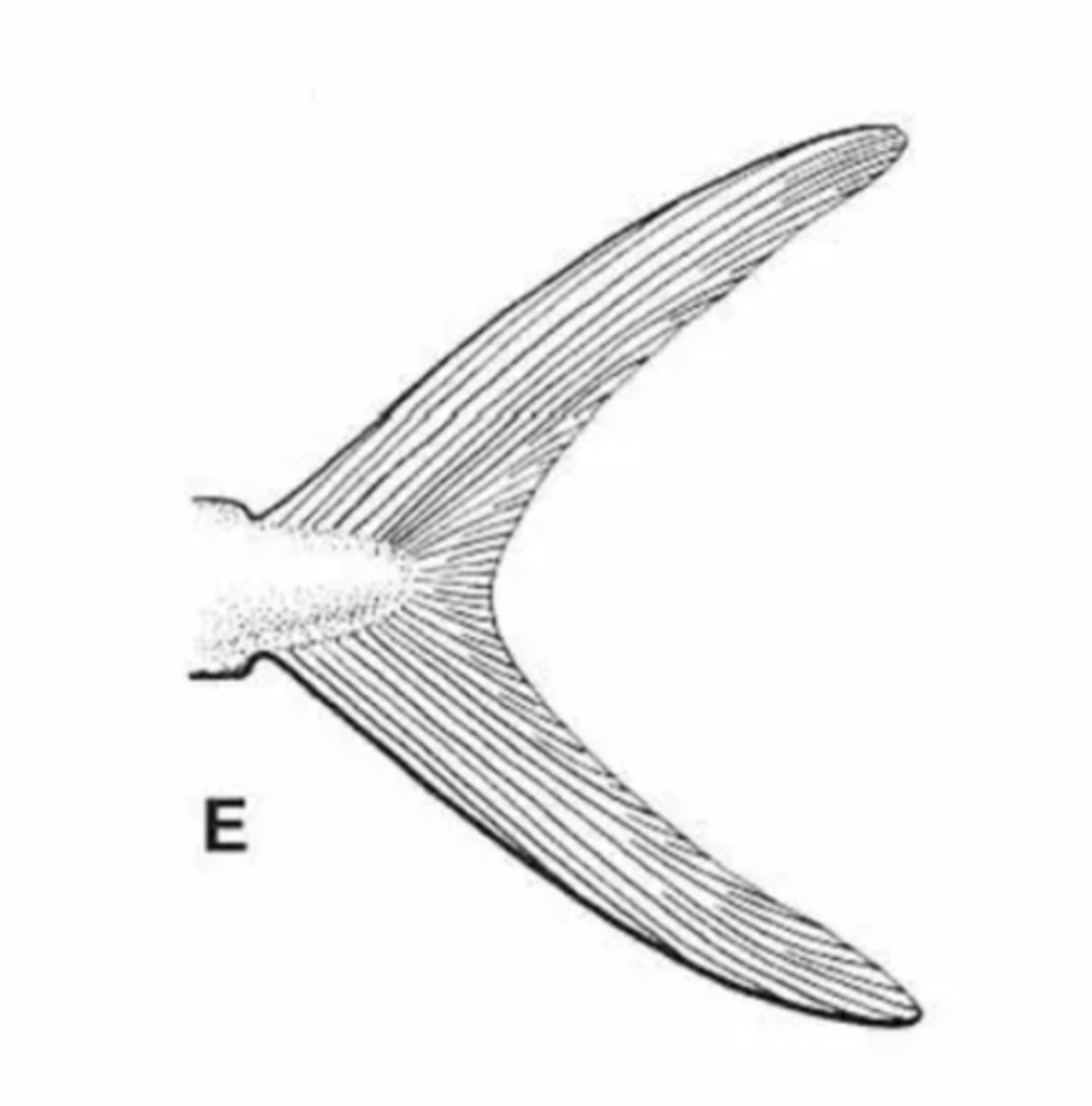
Forked caudal fin
V-shaped fin in many pelagic fishes that need sustained swimming
-Homocercal
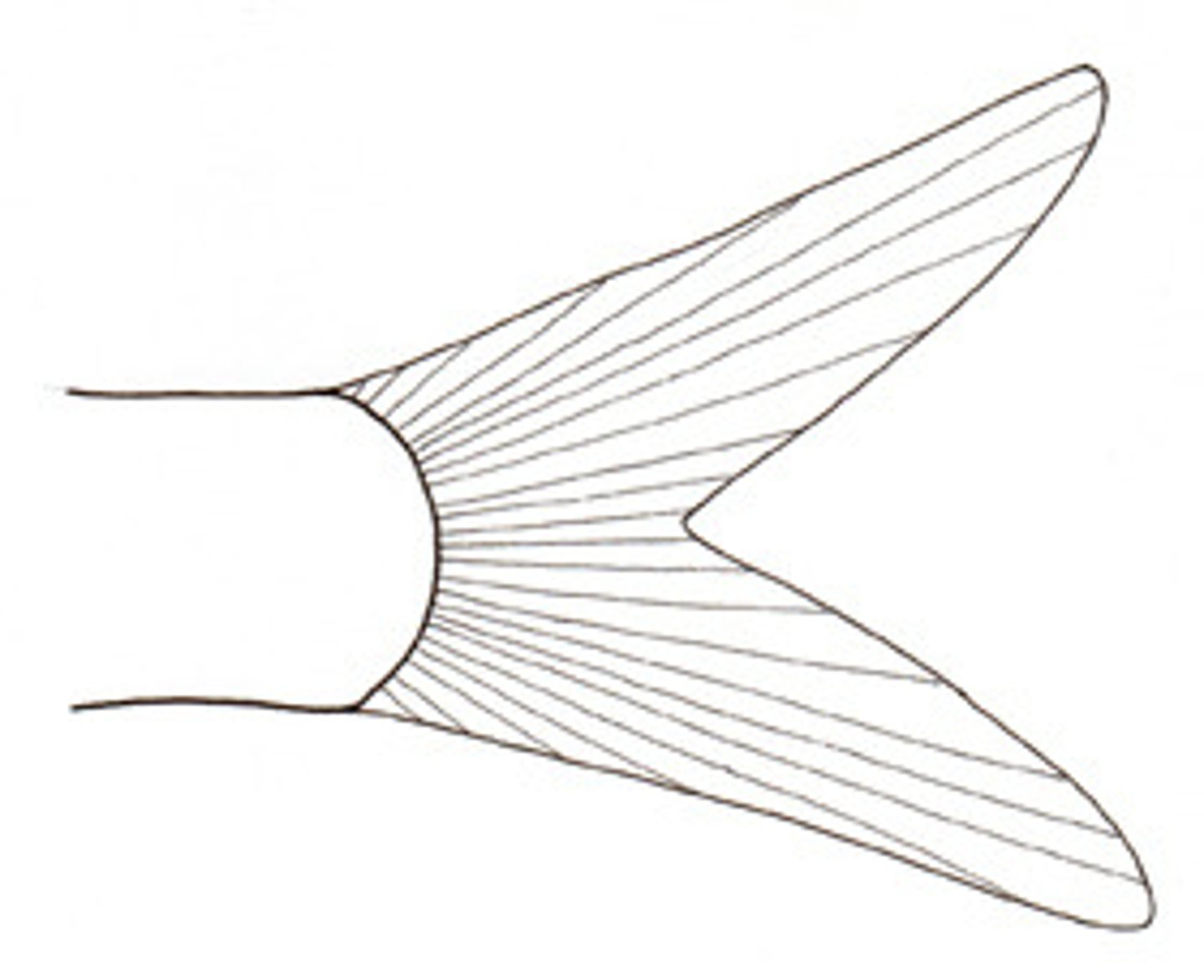
Emarginate caudal fin
slight inward curve
-Homocercal
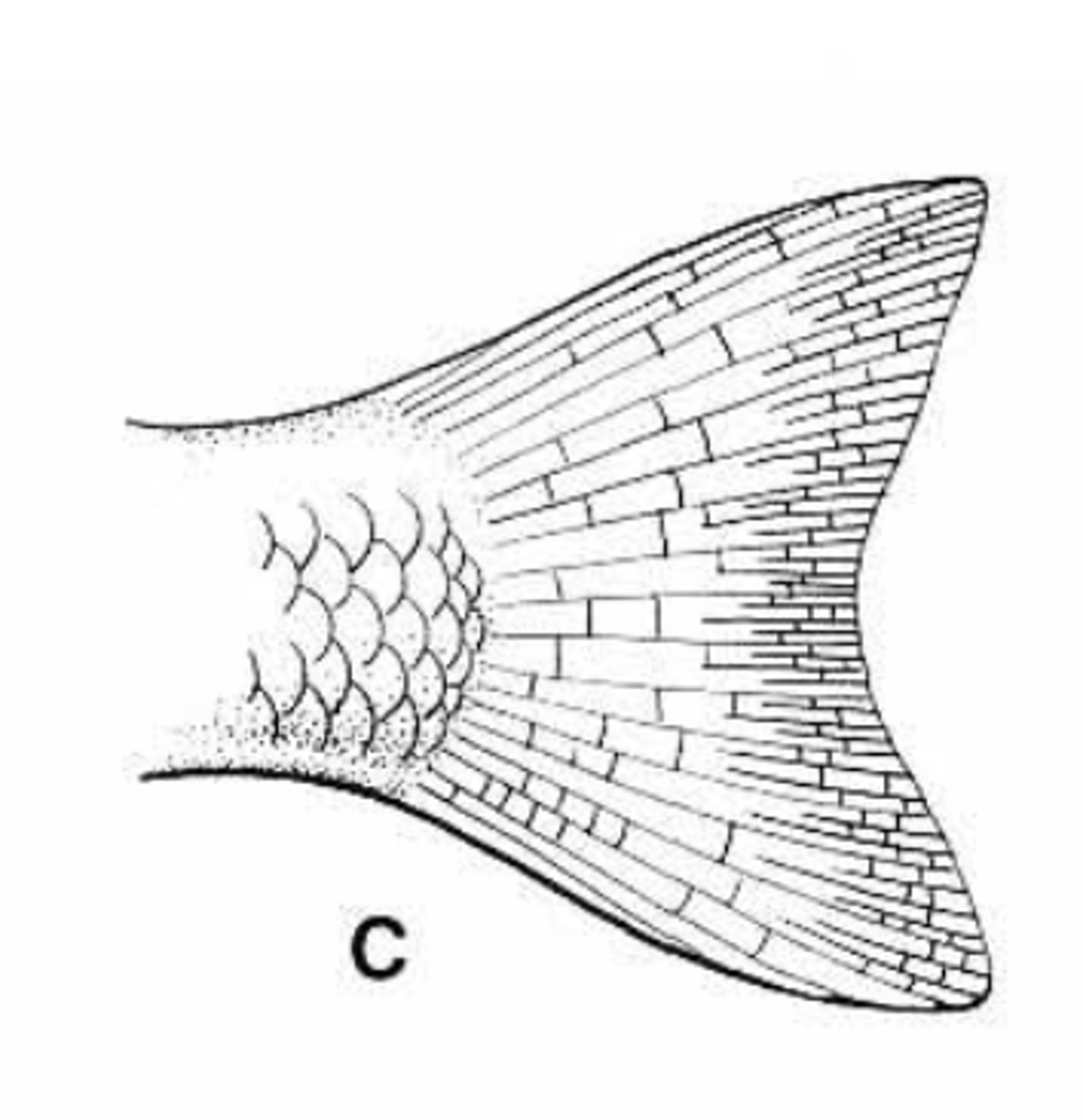
Truncate
mostly straight/ cubed off
-Homocercal
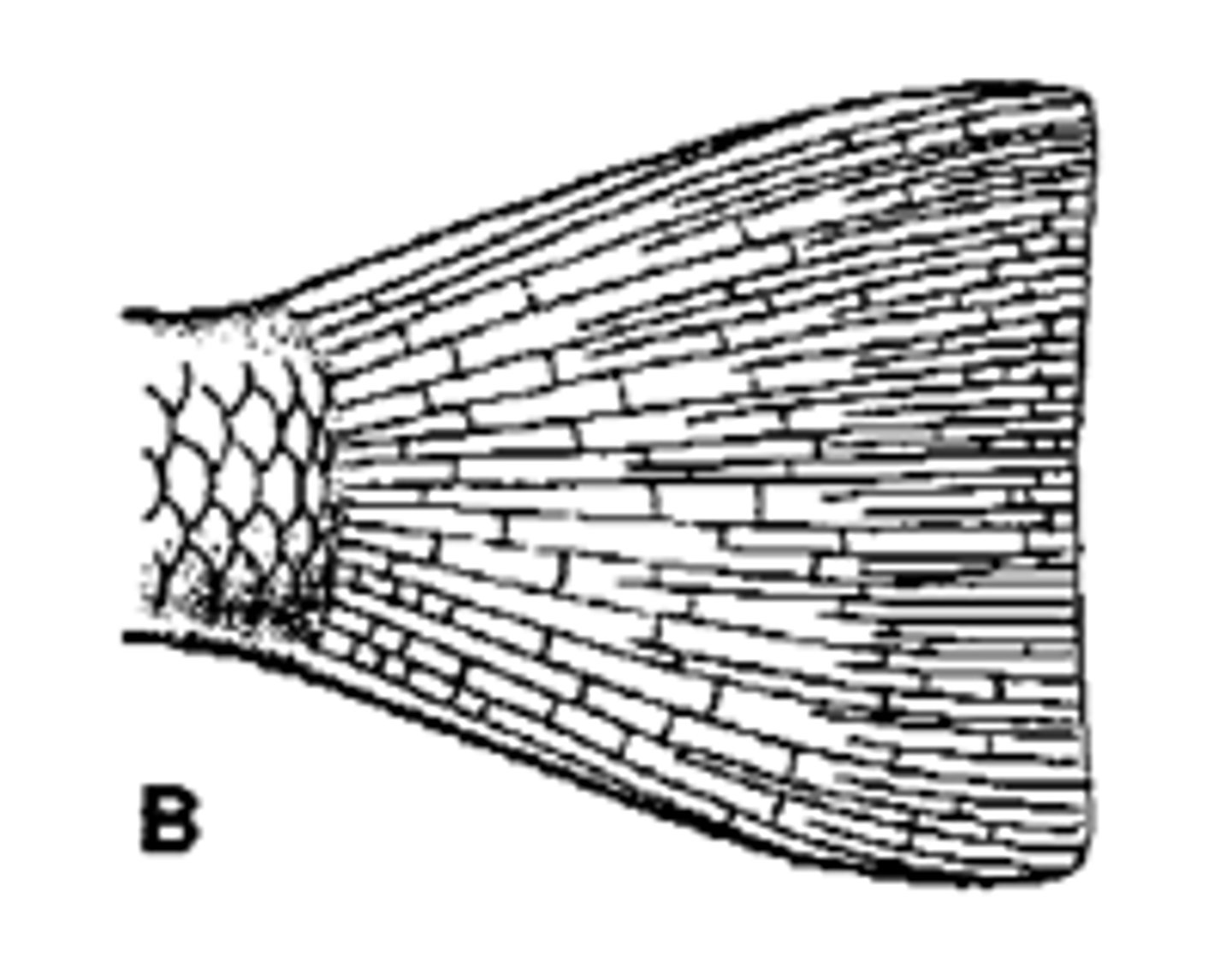
Rounded caudal fin
circular/ smooth edged to allow for short quick bursts
-Homocercal
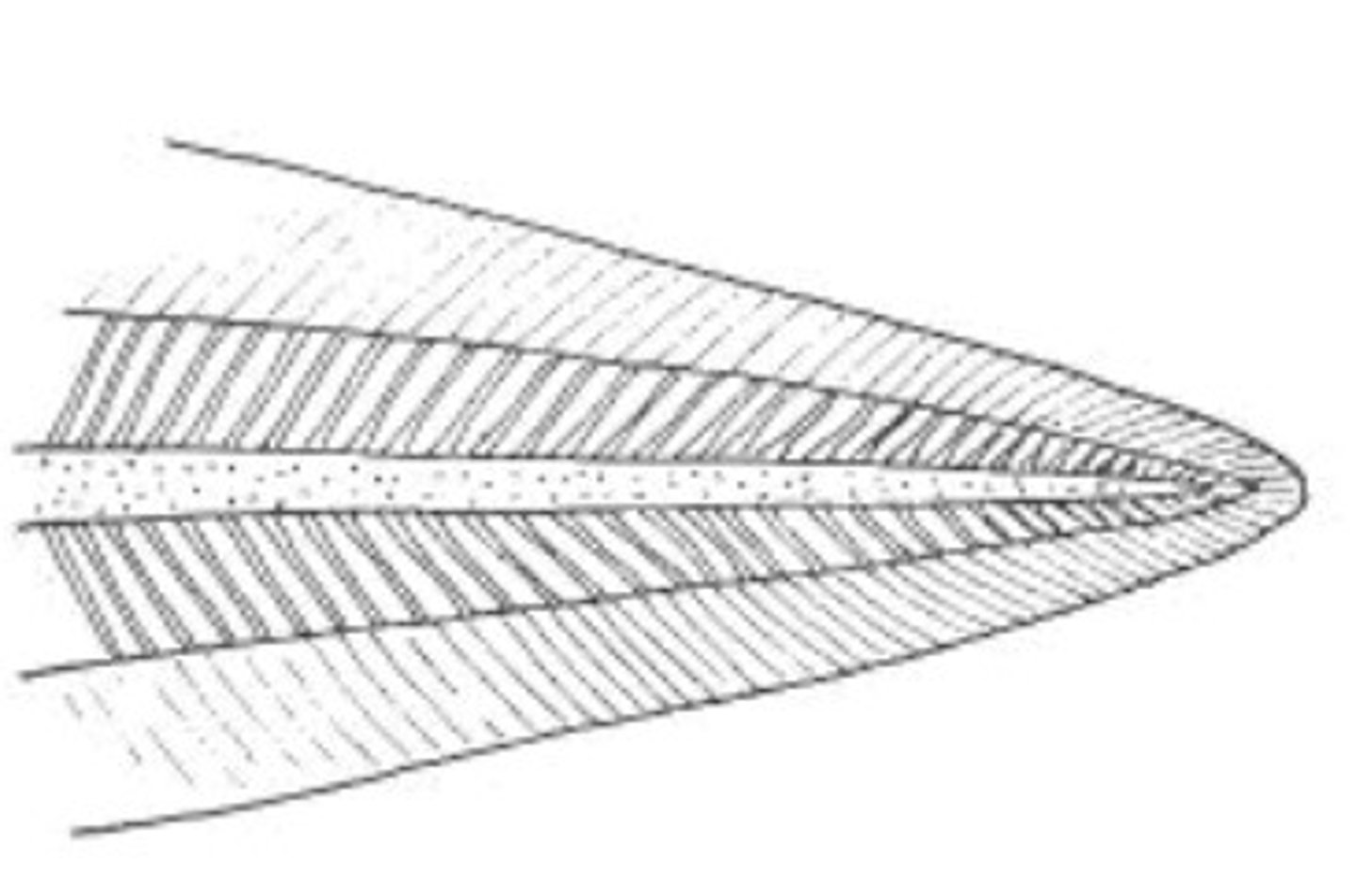
Protocercal
primitive undifferentiated; rays extend around end of notochord; found in lampreys, and most larvae
heterocercal fin
tail fin with unequal lobes in which the vertebral column turns upward into the larger lobe
-Chondrichthyes and primitive bony fishes (sturgeons - Acipenseridae)
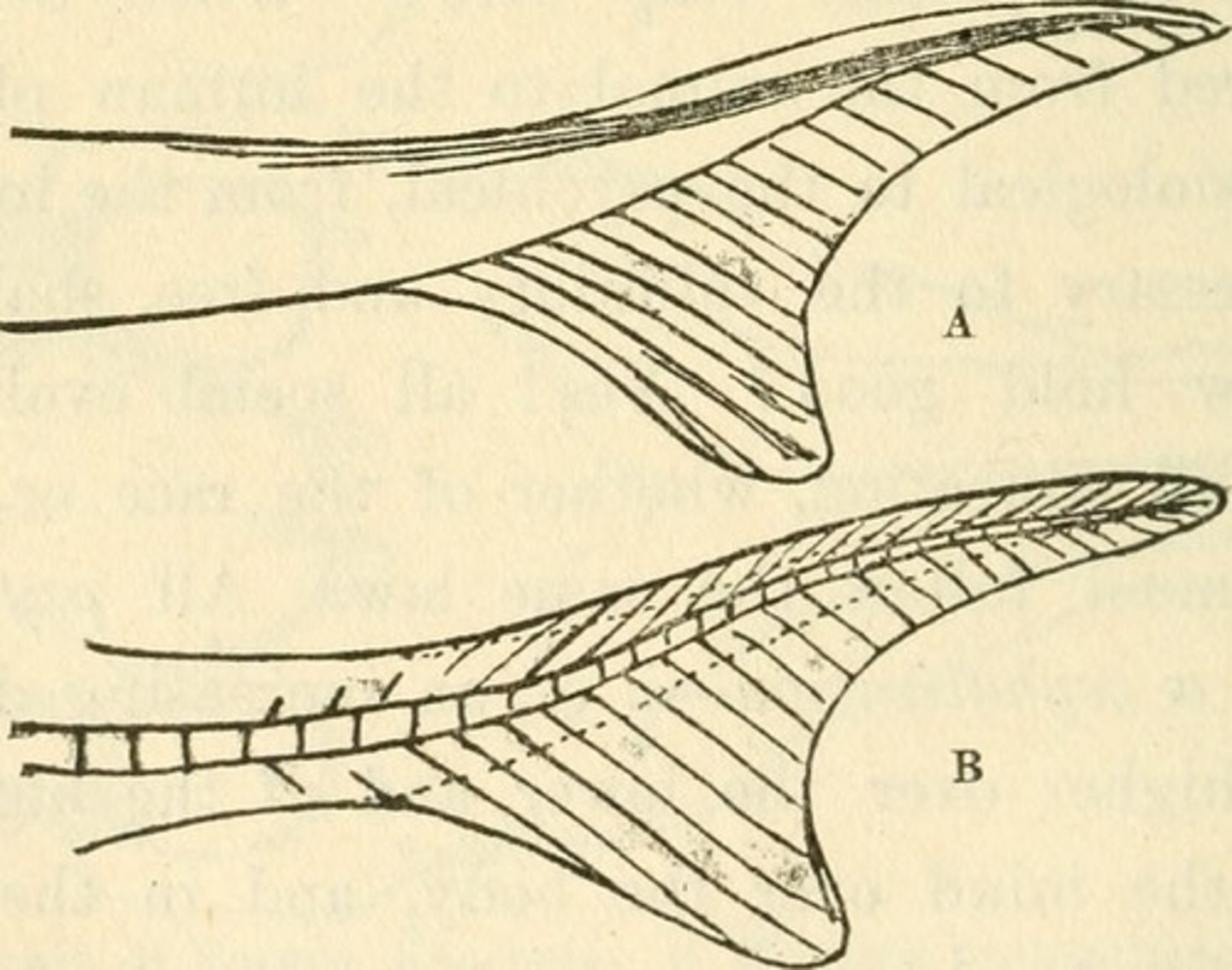
Abbreviated heterocercal
vertebral column turns upward into the caudal fin, but only partially extends into it, creating a tail that is more symmetrical than a truly heterocercal tail
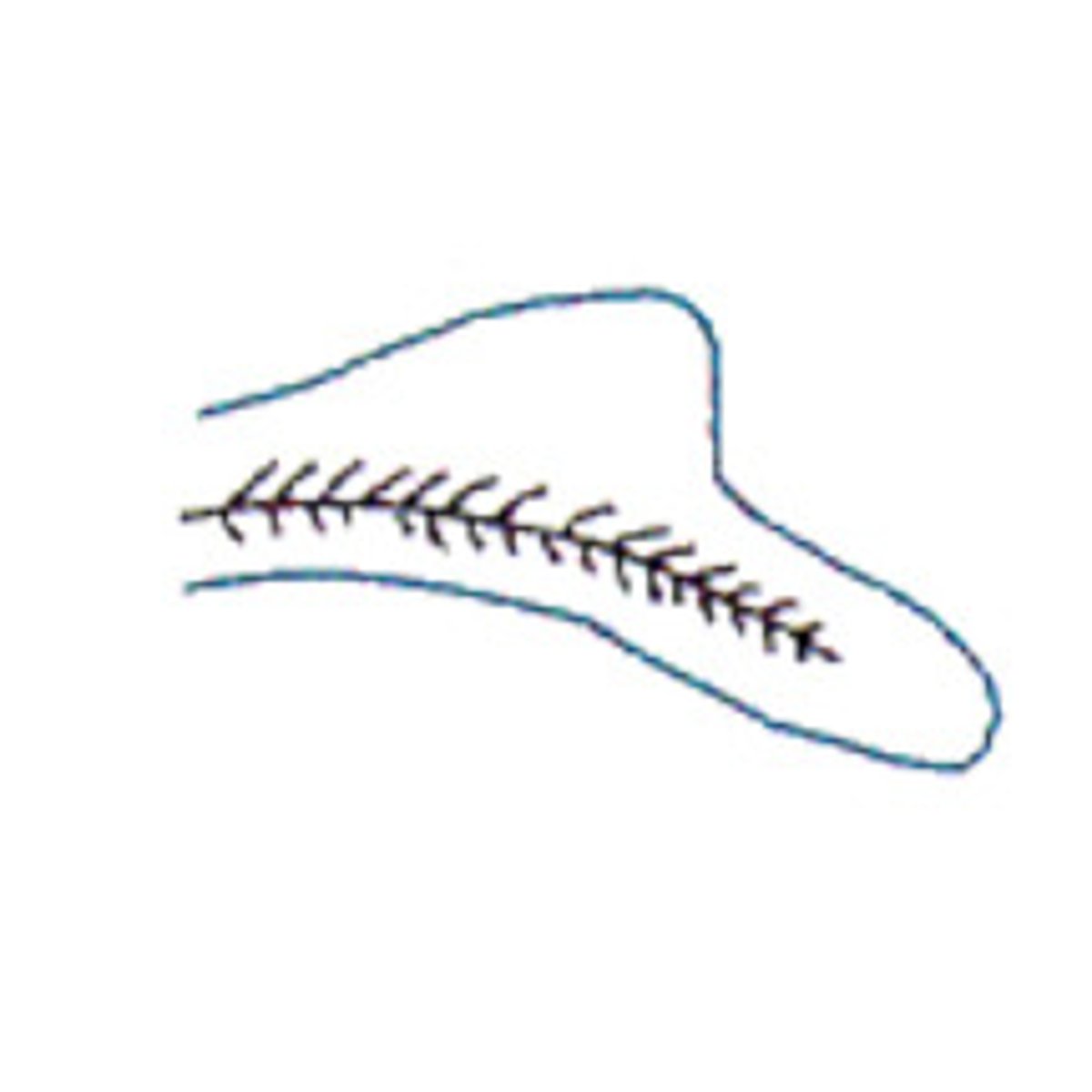
Hypocercal
Caudal fin with lower lobe being larger than upper lobe
-eg flying fish

diphycercal caudal fin (leptocercal)
tail similar to the protocercal, but secondarily derived; vertebral column extends straight back to end of caudal fin, dividing into symmetrical parts (2 or 3 lobes); found in lungfishes (Dipnoi)

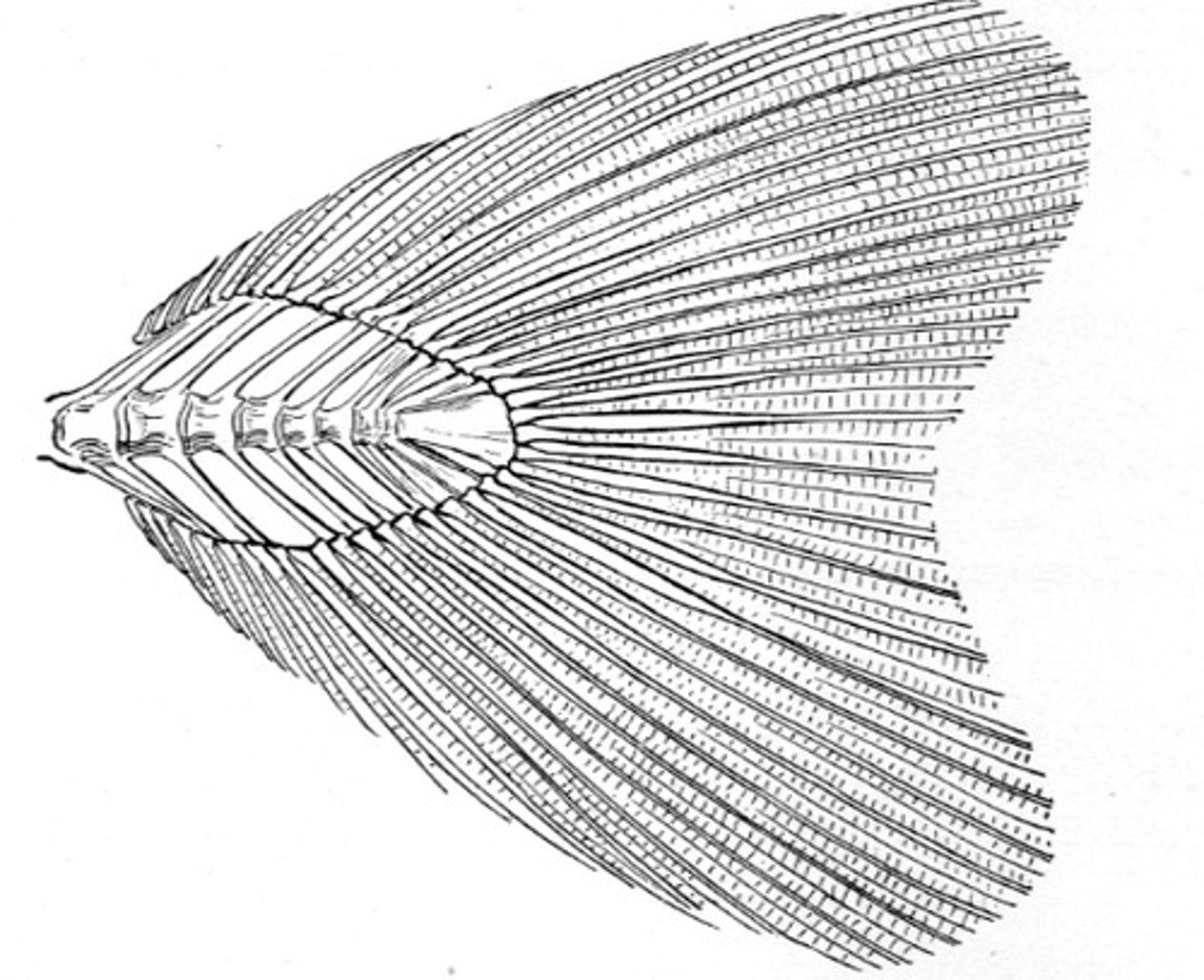
Isocercal
last vertebra modified as a flattened plate; found in cods
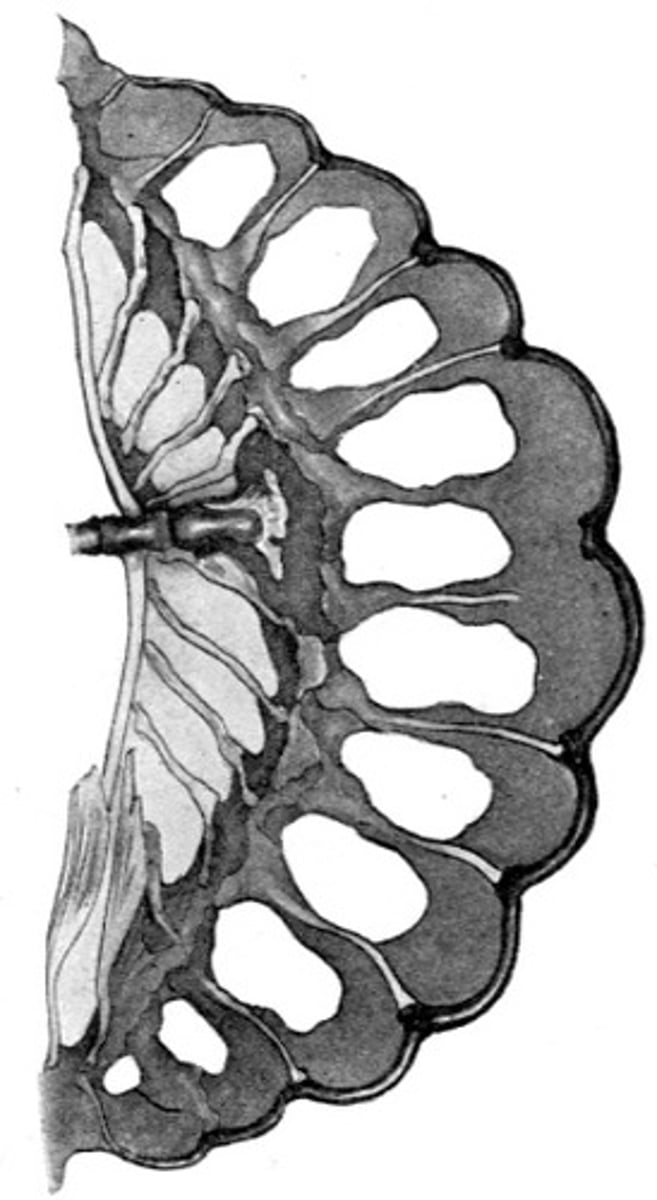
Gephyrocercal
"bridge tail" no hypural plate
Dorsal and anal fins have grown around
posterior end of fish
-not true caudal fin
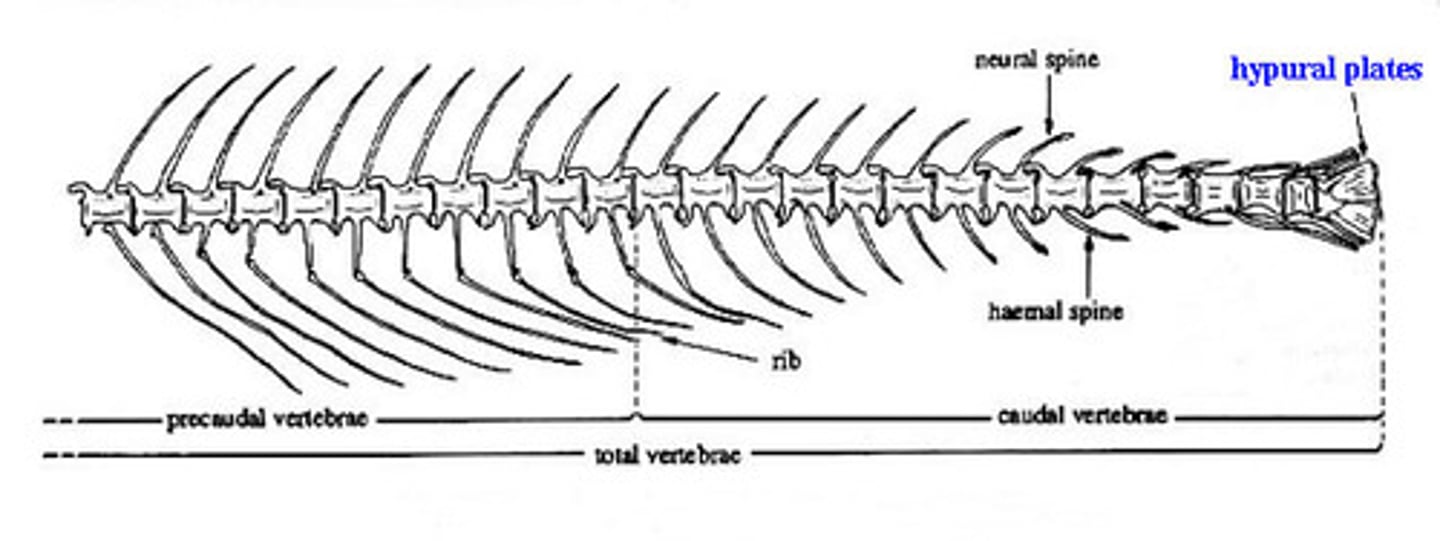
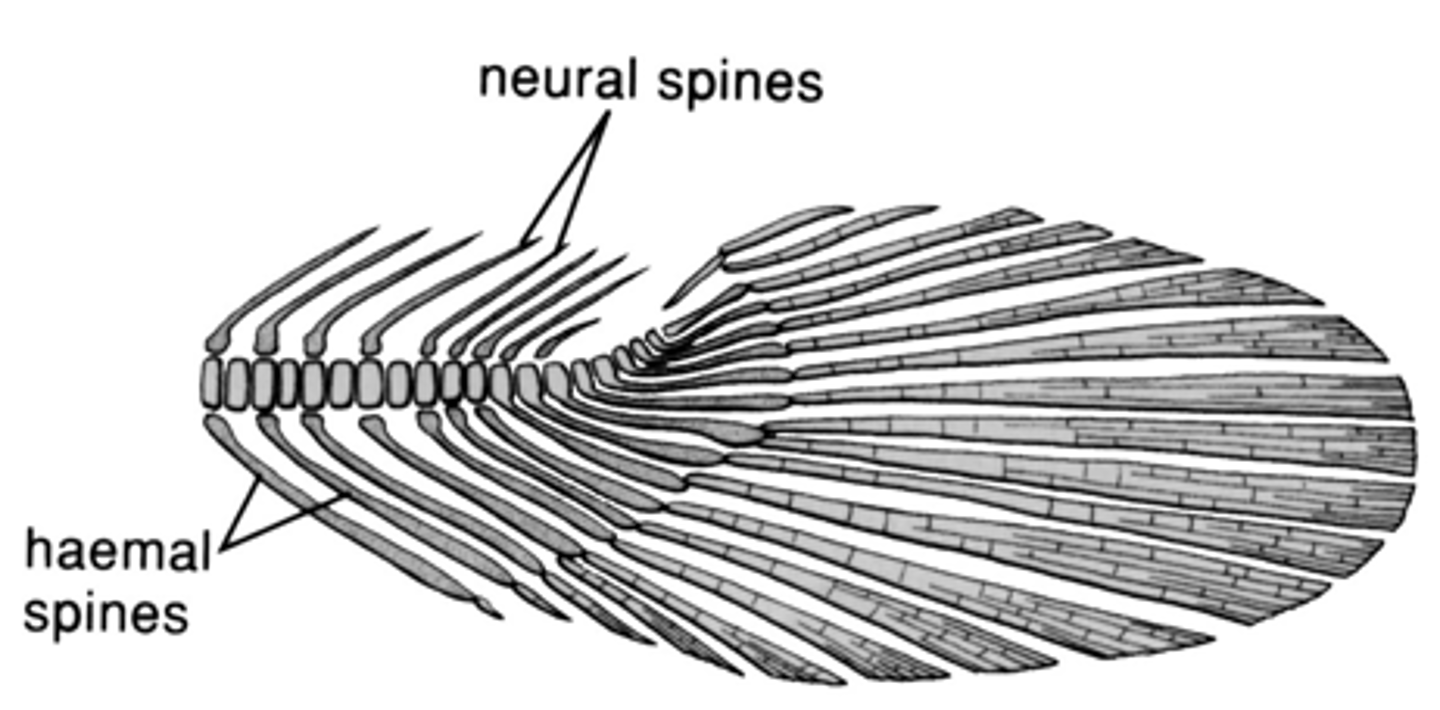
hypural plate
internal structure that marks the end of the vertebral column