Serology Principles
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
humoral vs cell-mediated immunity
humoral= substances found in humors (body fluids) ie serum ie Ab, complement, antimicrobial peptides
cell-mediated = phagocyte activation, cytokines, T-cell activation
IgG
most prevalent in serum
longest half-life
opsonization of Ag, fixing complement (but IgG4 doesn’t fix complement!)
can cross placenta!
agglutination
IgM
pentamer → 10 binding sites
1st Ab to be produced
predominant in primary Ab response
complement fixation, agglutination, neutralize toxin, primary Ab in neonates
IgA
monomer in serum BUT dimer in secretion
passive immunity from mom -> newborn
can activate complement via alternate pw
IgD
part of B-cell Ag recognition unit
no protective fxn
IgE
important for parasitic infns
attaches to basophils & tissue mast cells
allergic hypersensitivity rxns
direct action or neutralization
Ab may bind directly to foreign bacteria, virus, poison, or enzymes to remove them from circulation
agglutination/aggregation
all Ab have at least 2 binding sites to attach to foreign organisms to remove from circulation
aggregated organisms are less free to move & can be engulfed more readily by macrophages = less mobile
opsonization
opsonin=prepare for eating
macrophages/PMNs recognize IgG1 and IgG3
lysis (complement activation)
refers to series of 9 serum protein that are normal present → mediate inflammation
complement activation → lysis of animal cells & Gram neg bacteria
inflammation
IgE stimulates an inflammatory response which is an important host defense
it is only w prolonged or extensive inflammation that the destructive effects outweigh benefits
enzyme linked immunosorbent assay: non-competitive
if reactive → +
ELISA: competitive
add unlabeled (unmarked) Ab to test Ag → add labeled Ab → if color changed → neg bc that means not enough binding sites for unlabeled so labeled will bind to Ag
chemiluminescent assay
measures light emission
precipitation assays
prozone vs postzone
can get zone of equivalence (optimum precipitation) = lattice formations
prozone: xs Ab present
postzone: xs Ag is present
—> both lead to false NEG (bc doesn’t lattice correctly?)
3 ways to measure precipitation
turbidimetry
nephlelometry
immunodiffusion (visually)
rocket electrophoresis
antisera incorporated into agar → Ag added to wells → electric current to drive Ag
Ag ppt when concentration is equal to that of antisera in agar
height of rocket = conc of Ag in well → compare unknowns to standards
countercurrent electrophoresis
pH of Ab soln to Ag of interest & unknown Ag are adjusted so have opposite charges → placed in wells in agar + current → ppt line at equivalence point = Ag from pathogen
→ when provider needs rapid dx → replaced w latex agglut or lateral flow assays
immunoelectrophoresis
used to see components of serum for abnormalities
Ag are separated by current
plate developed by placing Ab into trough cut in agar b/t 2 wells → ppt lines form as arcs in agar
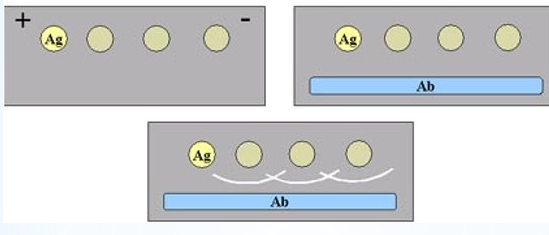
passive immunodiffusion
line of ppt on agar plate from Ab & Ag w/o electric current
radial immunodiffusion
Ab incorp into agar
wells cut out of agar → filled w pt serum
Ab diffuses out & makes ppt bands
Ouchertorlony
double diffusion bands
fluorescent Ab: direct vs indirect?
direct fluor Ab → looking for Ag
indirect fluor Ab: Ab from rabbit + anti-rabbit labeled Ig → looks for Ab
IFA principle
slide w Ag
Ab pt sample
Ab+Ag complex
incubate 30 min & rinse
add conjugate w/fluorescent tag, incubate, rinse
read w fluorescent microscope
western blot
proteins
used as confirmation for HIV Ab/Ag = gold standard
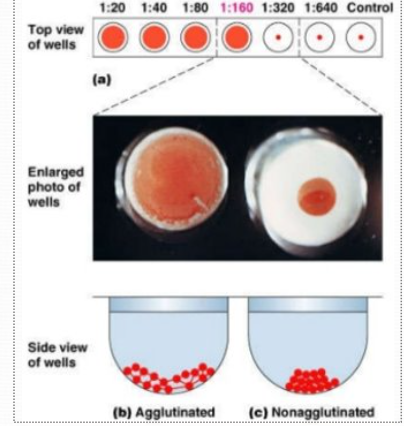
agglutination
sensitization = initial binding
lattice formation = enhance lattice formation via low ionic strength saline, inc viscosity, agitation, temp, pH
direct agglut = natural Ag-Ab
passive/indirect agglut= latex particles Ag
prozone vs postzone
prozone = xs Ab
postzone = xs Ag
acute hepatitis panel includes
HAV IgM
HBV core IgM
HBSAG
HCV IgG
Diasorin Liaison XL runs
MMR
Varicella IgG
CMV IgG & IgM
HSV1/2 IgG
EBV panel
Quantiferon TB Gold plus
syphilus (Trepsure)
Syphilis work up
screen w/EIA test for IgG and IgM
rapid plasma reagin (RPR) - non treponemal test - can be false +
Treponema pallidum - Particle Agglutination (TP-PA) (Treponemal test)
RPR = rapid plasma reagin
antibody in pt = reagin=anti-cardiolipin (Ab to tissue lipids)
Ab produced as the body responds to lipid material released from damaged cell → can have false +
Ag - cardiolipin w/choline chloride, cholesterol, lecithin; charcoal added for macro viewing
50 uL serum + 1 drop of Ag
calibrated needle (20 gauge)
100 RPM at 8 min
Ag made fresh daily
microscopic flocculation 100x
VDRL: venereal disease research laboratory
performed on CSF or serum
Ag-cardiolipin, cholesterol, and lecithin
50 uL + 1 drop Ag
calibrated needle: 22 gauge, CSF
180 RPM rotation at 8 min
Ag made fresh daily
microscopic flocculation 100x (like agglutination)
Treponema pallidum particle agglutination
tanned sheep rbc coated w Nichols strain of T. pallidum
pt sera incubated w sensitized & unsensitized gelatin particles
pt sera w specific Ab will bind w Ag → smooth mat of agglutinated particles
compact button results from the absence of specific Ab
agglutination in w both cells results from non-specific Ab
titers =
the last positive dilution
lateral flow assay (LFA)
Cryptococcus neoformans/gattii
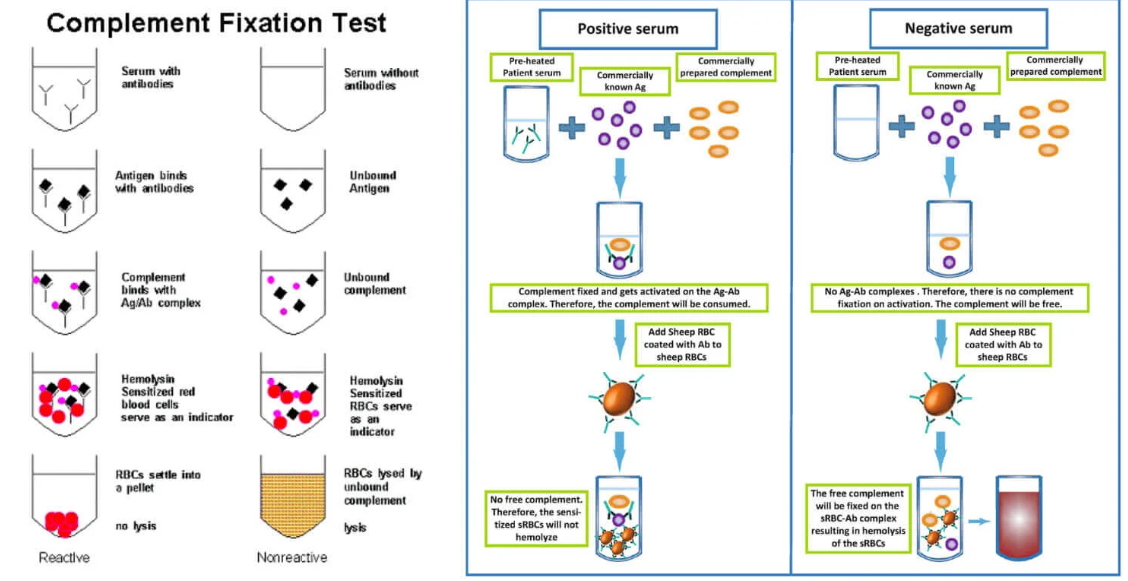
complement fixation
Ag mixed w/ test serum to be assayed for Ab
standard amount of complement is added to bind to any Ag-Ab complexes
sensitized erythrocytes are added
amount of rbc lysis is determined
no lysis = reactive (no complement available to lyse the cells)
lysis = non reactive (complement is free to lyse the cells)
IgG and IgM interpretations
G+/M+ = recent infn
G+/M- = past infn
G-/M+ = acute infn or false pos IgM
Herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1)
generally assoc’d w oral, ocular, pharyngeal lesions ie cold sores, watery blisters, keratitis
HSV-2
accounts for 2/3 of genital/anal infns; oral can occur
recurrent genital herpes
HSV-1 and 2 latency
virus remains latent indefinitely → reactivation via different factors → cutaneous outbreaks
HSV 1 and 2 lab ID
viral culture
direct Ag test by immunofluor
ELISA
cytology - Tzank Smear
real time PCR - DiaSorin
Herpes ELISA tesets
microtiter plates coated w/ recombinant glycoprotein 1 Ag/glycoprotein 2 Ag
proxidase-conjugated antihuman IgG (HSV1/HSV2)
…
read optical densities
Varicella-Zoster virus (HHV-3)
chickenpox (primary)
most freq in children
starts w rash → maculopapules, vesicles, scabs → highly contagious until scab falls off
Zosters or Shingles
occurs in adults w painful eruption of vesicular lesions w inflammation of dorsal root or cranial nerve sensory ganglia
Varicella-Zoster virus pathology
transmits via direct contact, resp secretions, airborne
complication: neonatal varicella → VZV infn in early pregnancy may result into congenital Varicella syndrome
VSV lab ID
culture: shell vial - mouse monoclonal Ab specific for VZV glycoprotein conjugated to FITC
direct immunofluor
cytology
PCR
ELISA
Epstein-Barr Virus (HHV-4)
aka “kissing disease”/infectious mononucleosis
Ab secretion due to inf mono = EBV specific Ab, heterophile Ab, auto-Ab
EBV assoc’d Ab
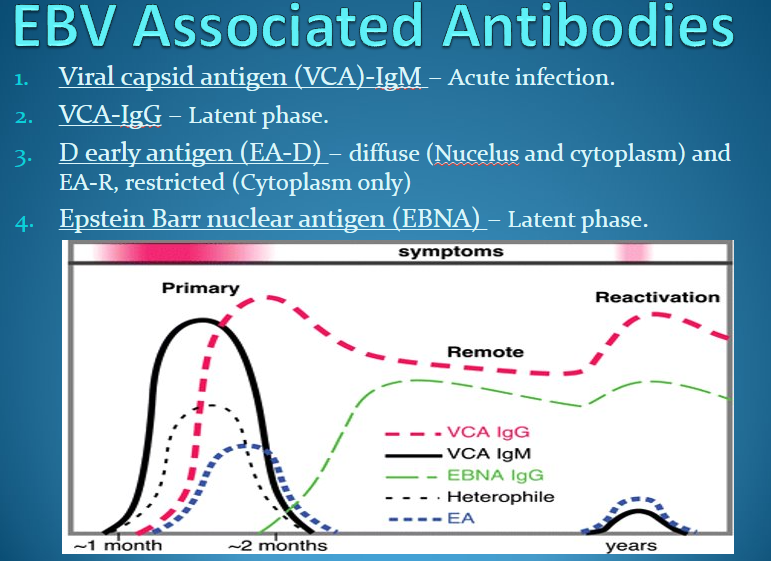
heterophile Ab =
= Ab that are capable of reacting w similar Ag from 2 or more unrelated species
detected using “monospot test”
in IM formed due to Ag on inf’d cells
Forssman: formed after exposure to certain bacteria (Salmonella, Shigella, Strep pneumo)
serum sickness: formed in resp to injections of horse serum (in some vaccines)
auto Ab
auto anti-i, common cold agglutinin
uhhhhh
heterophile Ab’s
inf mono Ab → absorbed by beef rbcs
Forssman Ab → ““ guinea pig rbcs
serum sickness by both beef & guinea pig (rxn to protein in antiserum of non-animal source)
rapid latex test “monospot” : purified bovine rbc extract as Ag
Paul-Bunnel test: used to titer pt’s serum (EBV-mono)

CMV IgM and IgG
in newborns → IgM Ab is dx significant for congenital infn bc IgM does not cross placenta
IgG persists for life (can cross placenta)
CMV lab ID
shell vial
FITC
…
PCR = useful in i-compromised pt (bc don’t have Ab → false NEG)
ELISA = determine pt’s immune status
why is fungal serology important?
bc fungi grows slow → can rapid detect Ag
titer of 1:32 or a 4-fold or greater rise in titer are significant in making dx
Coccidiomycosis tube precipitin (TP)
detects IgM
POS as early as 1-3 weeks
rarely in CSF (IgM can’t cross BBB)
highly specific
disappears w/in 4-6 mo’s → little prognostic value
Cocci complement fixation
detects IgG in serum, pleural fluid, peritoneal fld, joint fluid
serum titer 1:2-1:4 = presumptive early infn
> 1:16 = disseminated infn
CSF titer 1:2 = meningitis
cross-reactivity w/ Histoplasma
immunodiffusion
m/c method for screening Ab
single bands = chronic infn
2 or more bands = dissemination or active dz
Aspergillosis
opportunistic pathogen: A. fumigatus, flavus, niger, terreus
lab dx: immunodiffusion, ELISA, skin test
Blastomycosis
B. dermatitidis
broad based budding yeast
dx: immunodiffusion, ELISA, complement fixation
Candidiasis
Candida albicans & other Candida sp
opportunistic pathogen
Cryptococcosis
pigeons = chief vector
Histoplasmosis
tuberculate macroconidia
Histo immunodiffusion
qualititative test for serum, plasma, CSF, pleural fluid
Ag H&M proteins of histoplasmin
M band = early dz, inactive dz, or skin testing
H & M band = active progression of dz & chronic pulmonary dz
Histo complement fixation
titers of 1:64 or higher = presumptive Histo
yeast form = primary Histoplasmosis
mycelial form = chronic dz
x-reactivity occurs
Name the markers in AHP panel
HAV IgM
HBV core IgM
HBSAG
HCV IgG
What is the confirmatory test for reactive Hepatitis B surface antigen result?
neutralization?
What is confirmatory test for HIV infn (old gold standard)
Western blot
Name different methodologies used in serology.
complement fixation
immunodiffusion
lateral flow
What is the principle for EIA & what does ELISA stand for?
ELISA = enzyme linked immunosorbent assay
Name the tests used to test for H. pylori in the lab & name which one is the best test and why.
Name differences b/t VDRL & RPR in testing for syphilis (especially the Ag components).
Which agglutination tests are used at UCI and what do they test for?
Name the purpose of the IgM diluent.
Explain the principle of complement fixation & what the results mean if there is a button vs no button of rbcs.
button = no rbc’s lyse → Ab-Ag complex formed = POS
no button = rbc’s lysed bc complement protein didn’t bind to Ag-Ab complex → binds/lyse rbc = NEG