Chapter 3: Individual Differences and Emotions
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Individual Differences (ID)
The many attributes, such as traits and behavior, that describe each of us as a person (big part of what give us our unique identities, essential in the application of OB)
Intelligence
Represents an individual’s capacity for constructive thinking, reasoning, and problem solving (viewed as IQ, but it can be much more complex than that)
Practical Intelligence
The ability to solve everyday problems by utilizing knowledge gained from experience to purposefully adapt to, shape, and select environments
Personality
The combination of relatively stable physical, behavioral, and mental characteristics that gives individuals their unique identities
Big Five Personality Dimensions
Extroversion, Agreeableness, Conscientiousness, Emotional Stability, and Openness to experience
Extroversion
Outgoing, talkative, sociable, assertive
Agreeableness
Trusting, good-natured, cooperative, softhearted
Conscientiousness
Dependable, responsible, achievement-oriented, persistent
Emotional Stability
Relaxed, secure, unworried
Openness to Experience
Intellectual, Imaginative, curious, broad-minded
Proactive Personality
Is an attribute of someone “relatively unconstrained by situational forces and who effects environmental change”
Proactive People
Identify opportunities and act on them, show initiative, take action, and persevere until meaningful change occurs
The Dark Triad
Narcissism, psychopathy, and machiavellianism
Narcissists
Characterized as having a grandiose sense of self-importance, requiring or even demanding excessive admiration, having a sense of entitlement lacking empathy, and tending to be exploitative, manipulative, and arrogant
Psychopaths
Can be aggressive and lack concern for others, guilt, or remorse when their own actions do others harm
Machiavellians
Believe the ends justify the means, often maintain emotional distance, and are manipulative
Personality and Performance
Personality characteristics are likely to have the greatest influence and effect on performance when you are working in situations that are unstructured and with few rules
Conscientiousness Performance
Strongest and most positive effects on performance across jobs, industries, and levels
Show strong sense of purpose, obligation, and persistence
Extroversion Performance
Beneficial if the job involves interpersonal interaction
Stronger predictor of job performance than agreeableness
Agreeableness Performance
Likely to fit and excel in jobs requiring interpersonal interaction, such as customer service
More likely to stay at their jobs, be kind and get along with others, and thus have positive relationships and experiences at work
Openness Preformance
Linked with higher levels of creativity compared with other traits
May be more likely to quit/ seek and find new jobs, even if they’re satisfied with their current jobs
Come as a “double—edged Sword” for employers
Emotional Stability Performance
Associated with higher job satisfaction and well-being
Difficult to find a downside to this in the workplace
Employees High on Neuroticism
Have opposite experiences.
higher levels of burnout
Core Self-Evaluations (CSEs)
Represent four narrow and positive individual traits:
Generalized self-efficacy
Self-esteem
Locus of Control
Emotional Stability
Self-Efficacy
A person’s belief about his or her chances of successfully accomplishing a specific task (“I can do that”)
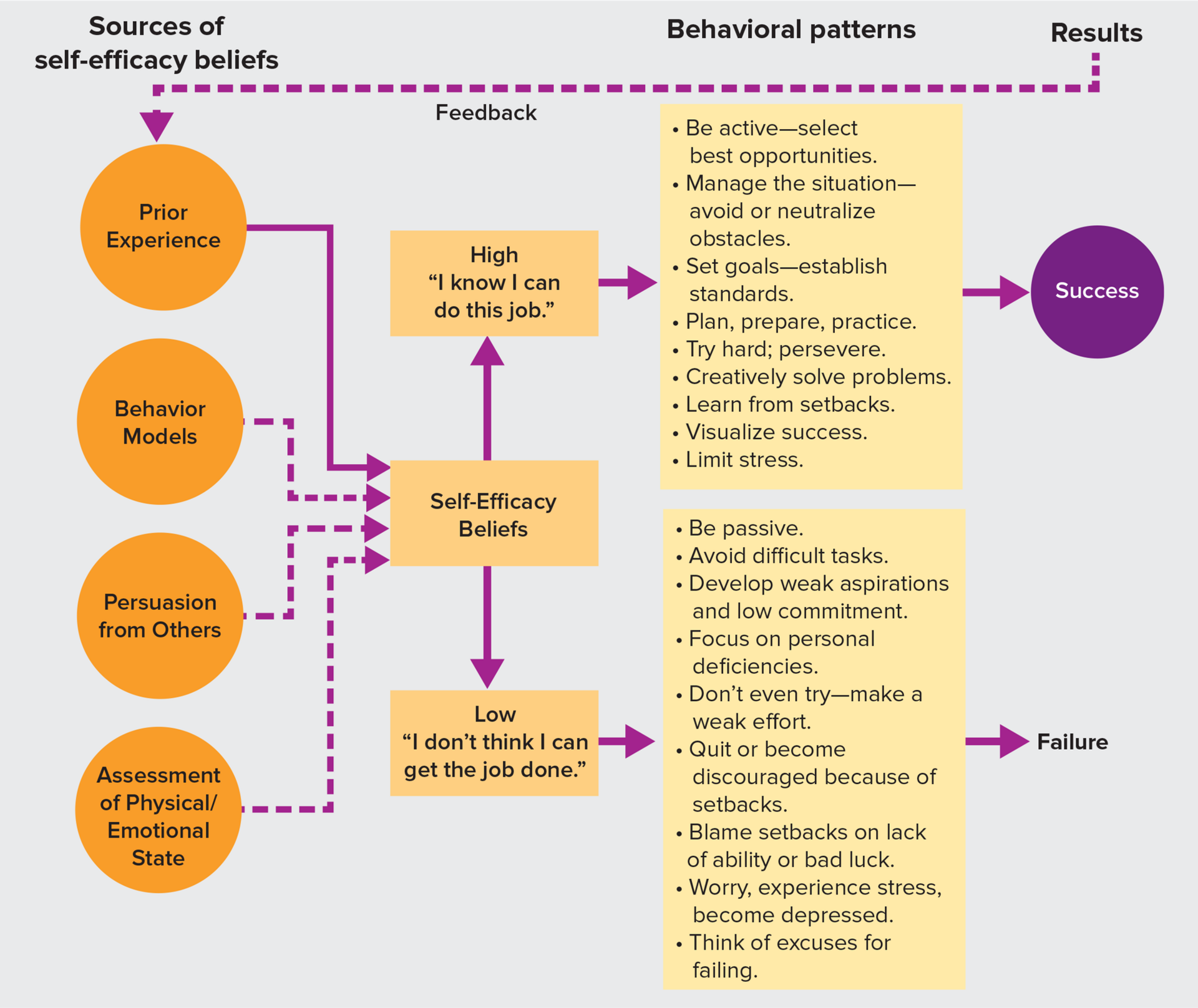
Self-efficacy can be developed by…
Helpful nudges from parents, role models, and mentors
Self-esteem
Your general belief about your self-worth
Locus of Control
A relatively stable personality characteristic that describes how much personal responsibility we take for our behavior and its consequences
Interpersonal Locus of Control
People who believe they control the events and consequences that affect their lives
External Locus of Control
Those who believe their performance is the product of circumstances beyond their immediate control
Emotional Stability
Individuals with high levels of this tend to be relaxed, secure, unworried, and less likely to experience negative emotions under pressure (low levels are prone to anxiety and tend to view the world negatively)
Emotional Intelligence (EQ/EI)
The ability to monitor your own emotions and those of others, to discriminate among them, and to use this information to guide your thinking and actions
Four Key Components of EQ/EI
Self-awareness
Self-management
Social awareness
Relationship management
Emotions
Complex, relatively brief responses aimed at a particular target, such as a person, information, experience, or event (also change psychological and/or physiological states)