Fluency Mid-Term Test - Part One: Basics of Stuttering
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What is stuttering
Stuttering is a speech disorder that typically emerges in early childhood, it is characterised by frequent repetitions of sounds and monosyllabic words, sound prolongation and interruptions in the forward flow of speech which are blocks. Stuttering is often accompanied by physical muscle tension and struggle.
What impacts does stuttering have?
Stuttering can impact a child’s academic, emotional and social abilities and their later vocational potential and achievements. People who stutter are often paid less than people who do not stutter
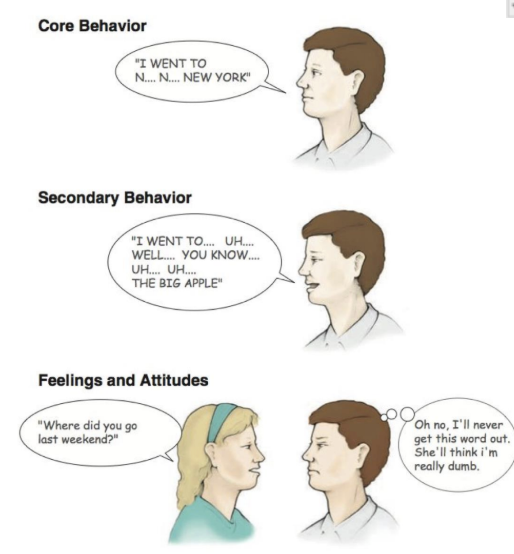
Components of stuttering
Core behaviours = basic speech behaviours
Secondary behaviours = physical concomitants
Feelings & attitudes = emotional characteristics
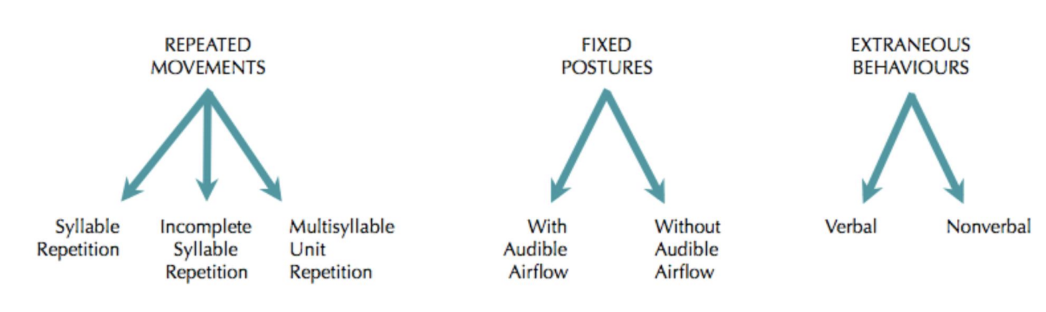
Types of speech disfluency
part-word repetitions (sound or syllables)
single-syllable whole-word repetitions
multi-syllable word repetitions
phrase repetitions
prolonged sounds
blocks & broken words - pauses
tense pause - when a block occurs in between words
interjections - can be used as a secondary behaviour - to delay saying the word
revisions & incomplete utterances
Stuttering-like / stuttered disfluencies
part-word repetition
single-syllable word repetition
dysrhythmic phonation
sound prolongations
blocks
broken words
Speech behaviours - Other disfluencies
phrase repetition
revision
Interjection
Speech behaviours of stuttering - Lidcombe Behavioural Data Language
Frequency of disfluencies
number of disfluencies per 100 words or syllables
most of speech in PWS is fluent
~ 10% (on average) is stuttered
large fluctuations depending on day or situation
The one constant about stuttering is that it changes!
People who stutter find that they often don’t stutter when whispering, when talking to a baby or when talking to a pet as they don’t see this as a pressurised environment, pressure makes stuttering worse
Duration of disfluencies
from beginning to end of disfluent event
repetitions: number of extra iterations of speech segment - /k/ /k/ /k/ cat - only three /k/ sounds are counted because these are the sounds that were additional to the word
longer than 0.5 sec more likely to be judged as stuttered
overall mean of 1 sec, but can be much longer
Secondary behaviours = physical concomitants
Tense body movements
most frequently in head & neck
other body parts possible - sometimes people clench their fist or tap their foot or clench their toes in their shoe
may be covert
Assumption that behaviours develop as techniques to get out of stuttering
however, also been observed in children
Secondary behaviours
head jerks
squinting
eye closing
facial grimaces
tongue protrusion
pressured lips
jaw wide open
jaw closed tightly
clenching hands
arm movements
raising shoulders
irregular inhalation
Feelings & attitudes = emotional characteristics
Complex emotions develop
fear, anxiety, panic, frustration, shame, humiliation, anger, …
can occur prior, during & after stuttering
can lead to avoidance behaviours
saying own name
certain speech sounds
speech situations
Different Behaviours of Stuttering
Factors that influence stuttering
Repeated readings of a passage
Adaptation effect
reading passage 5 times – stuttering frequency on average decreases by half, stuttering will reduce each time that they read it - can anticipate what sounds will be tricky, motor planning rehearsal
Consistency effect
stuttering tends to occur on same words during repeated readings
Adjacency effect
when stuttered words are removed from a passage, stuttering tends to occur near removed ones during repeated reading
Auditory feedback and how it influences stuttering
Auditory feedback
Delayed Auditory Feedback – DAF
creates slow & unusual speech
can reduce or eliminate stuttering
can induce disfluencies in NFS
Altered Auditory Feedback – AAF
change pitch up- or downwards
Masking
noise presented though earphones eliminates feedback
reduces or eliminates stuttering
fluency-inducing conditions
change in customary speech / acting
singing
whispering
rhythmic speech
reduced speech rate / slow / prolonged speech
chorus reading
Shadowing
Loci of stuttering - Language factors
first word of utterance
>90% initial word consonants
consonants > vowels
content words > function words
can be function words > content words in children
stressed > unstressed syllables
increased utterance length
difficult sounds? – individual factor
Age at onset of stuttering
range 1.5 - 5 years
mean of 33 months
possible but much less probably for stuttering to begin in older children, teens & adults
24-36 months: 56% of onsets
18-42 months: 84% of onsets
Gender (biological sex) of stuttering
Overall
3 males to 1 female
Childhood (near onset)
2 males to 1 female
Adulthood
4 males to 1 female
Incidence & prevalence of stuttering
Prevalence
number of all cases currently identified
even if they did not begin recently
Lifetime incidence
number of all cases ever exhibited a disorder
currently or in the past
even if they recovered
Prevalence of stuttering in school
Subgroup mean of preschool kids who stutter = 3.46%
Subgroup mean of school kids who stutter = 0.83%
Lifetime percent of people who stutter = 0.72%
incidence of stuttering studies
varies from 3.2% - 17.7%
=> 5% lifetime incidence
Incidence & prevalence of stuttering in New Zealand
speech recordings at 2;0 years of age
2/42 children stuttered
5% prevalence
speech recordings at 3;6 years of age
1/42 children stuttered
2.4% prevalence
Incidence & prevalence of stuttering Estimates for New Zealand
overall population
5,200,000
NZ stuttering incidence (5%)
260,000
NZ stuttering prevalence (0.7%)
36,400