40) pancreas
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
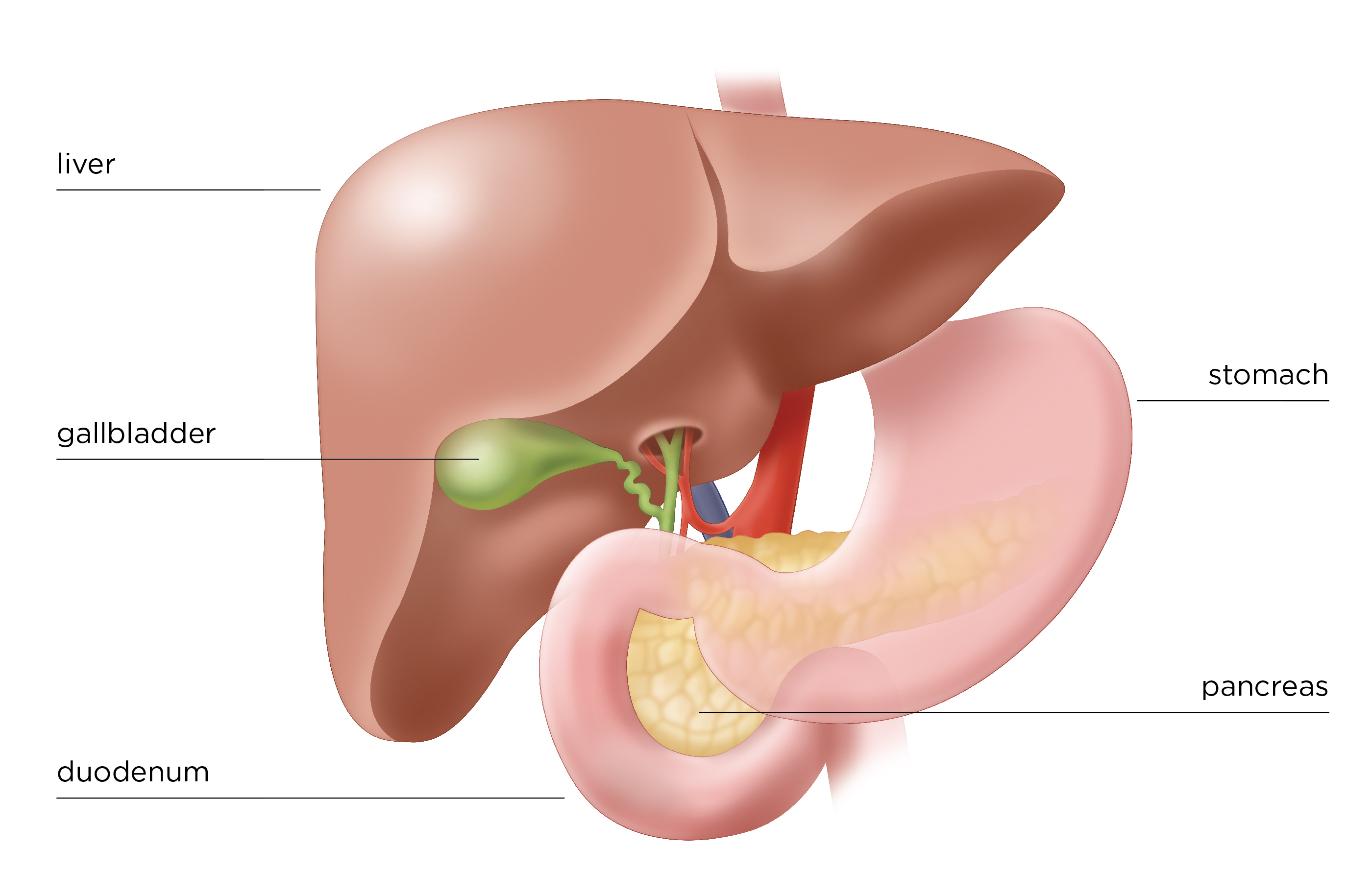
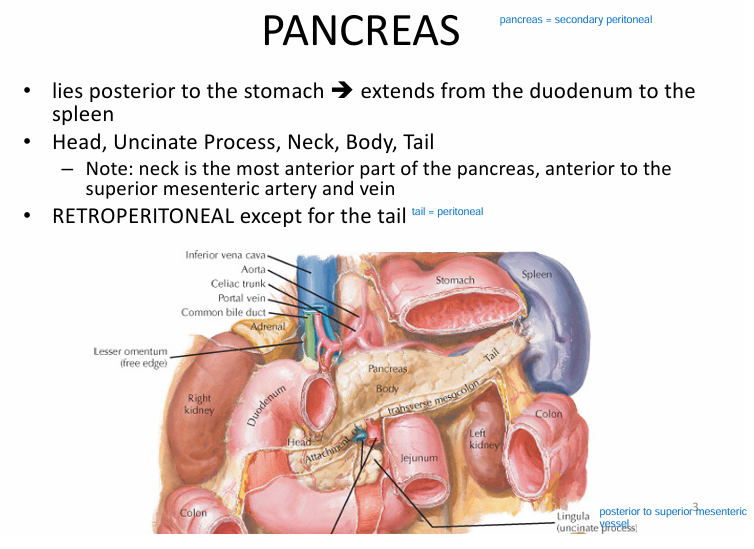
General info on pancreas:
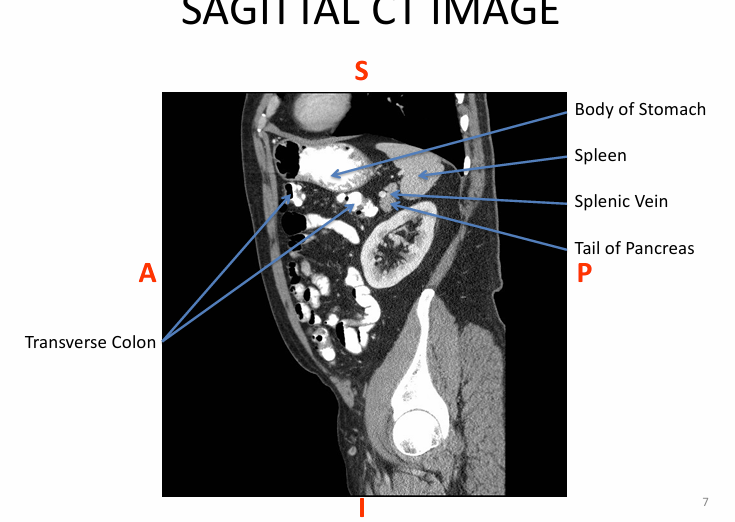
-posterior to stomach
-neck of pancreas is ANTERIOR to superior mesenteric artery/vein
-tail = peritoneal
-everything else = retroperitoneal
-linguila (uncinate process) = posterior to superior mesenteric artery
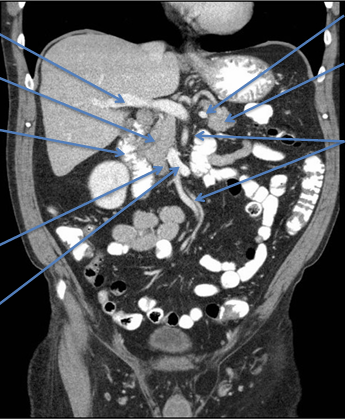
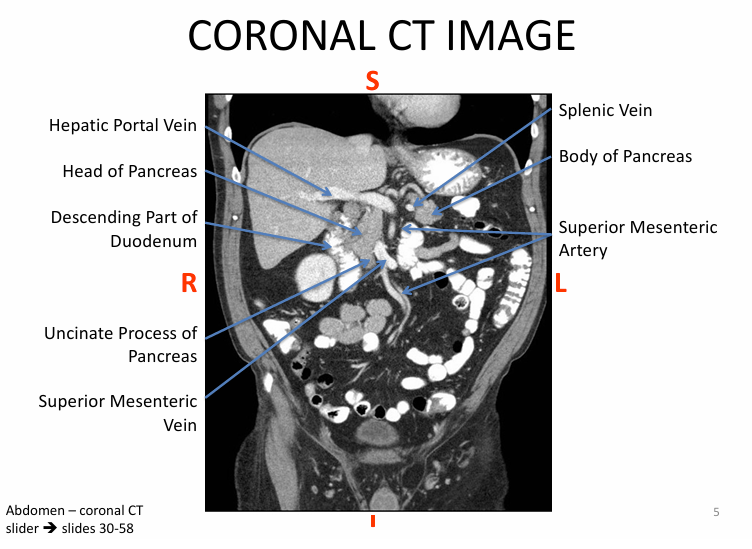
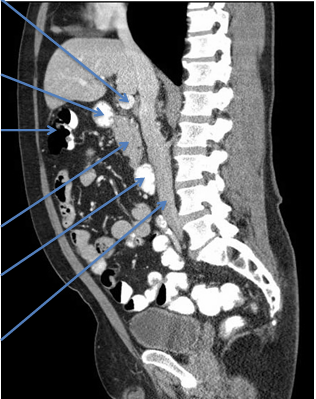
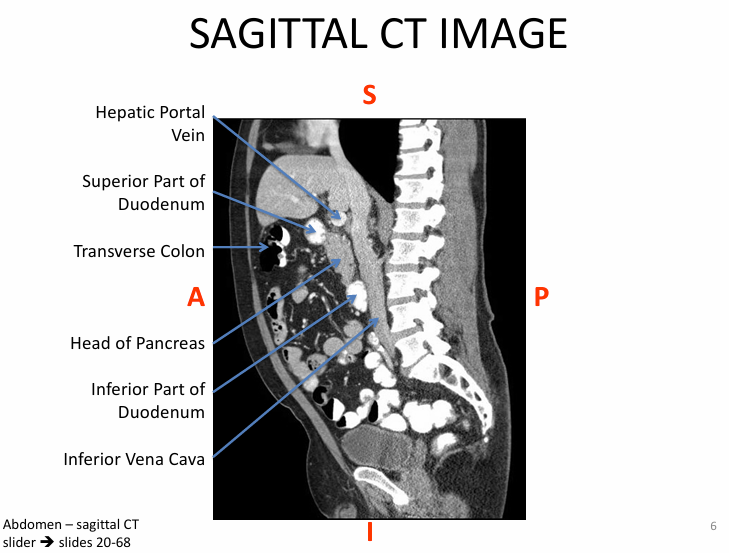
Function of pancreas
1) Endocrine (1%)
-pancreatic ISLET of langerhans
-glucose homeostasis
(insulin, glucagon) → directly into blood
—
2) Exocrine (99%)
-pancreatic ACNI
-secrete zymogens (enzymes for digestion)
-secrete bicarbonate
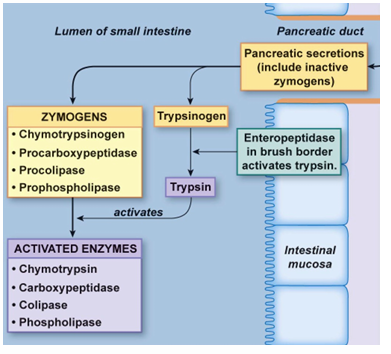
How are pancreatic enzymes secreted?
CCK (cholecystokin)
(enteroendocrine cells - part of duodenum)
or
Parasympathetic stimulation
(via vagus nerve)
→ zymogen (inactive pancreatic enzymes) release from ACINAR cells
→ ex. TRYPSINOGEN
→ in contact w/ brush border enzyme (ENTEROPEPTIDASE)
→ converts trypsinogen to trypsin
→ trypsin activates other zymogens
—
drains into main pancreatic duct
→ joins w/ common bile duct
→ empties into 2nd part of DD
How is bicarbonate secreted?
enteroendocrine cells of duodenum → release SECRETIN
→ pancreatic duct cells release bicarbonate
What is the FUNCTION of bicarbonate?
1) protect duodenal wall (raise pH)
2) inactivates pepsin (from stomach)
3) provide optimal pH for activated pancreatic enzymes
(enzymes operate @ higher pH)
Discuss the delivery of pancreatic juice.
1) pancreatic duct
1) common bile duct
2) hepato-pancreatic ampulla (convergence of 1))
3) hepatopancreatic sphincter
- Mm of bile + pancreatic juice into SI