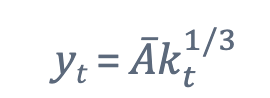Chapter 5: The Solow Growth Model
1/15
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ECON
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What is the solows growth model?
the Solows Growth model is a model that extends the production model by allowing capital to accumulate over time.
in this model capital is no longer fixed and it changes with savings and depreciation
in short this model shows how capital accumulation can be an engine of long term growth
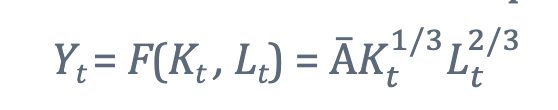
What aspect of the formula is solows differnet in compared to the previous model?
whats different is that variables change over time, so we add a “t” subscript
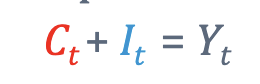
what is this formula? and its variables?
This formula shows that output can be used for consumption or investments( all outputs must be consumed today or invested for the future)
Ct: = consumption
It = investments
These variables are called resource constrants
we also assume ther is no imports or exports.
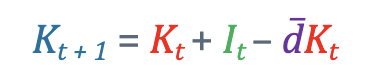
What is this formula? and its variables
This is capital accumulation and it shows use that goods invested for the future determines how the capital stock evolves.
Kt+1= next years capital
Kt = this years Capital
It = this years investments
đ = depreciation rate (usually 7-10% per year)
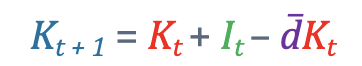
whats the intuition of the Capital accumulation formula?
Capital tmr = what we keep from today + new investments - what wears out
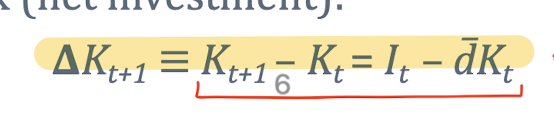
whats the intuition of the change in capital stock formula?(looking at I)
if we increase It this yr, the change in Kt-1 will go up. the oppoiste will happen if we dont invest.

What is the capital accumulation formula?
Kt+1= next years capital
Kt = this years Capital
It = this years investments
đ = depreciation rate (usually 7-10% per year)
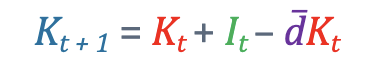
What is the change in capital stock formula?
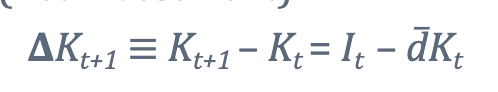
What is the Labour force, model set up?
It the amount of labour in the economy that is given exogenously at a constant level
we hold labour fixed for now so we can focus on capital accumulation
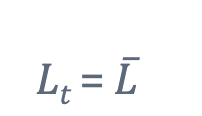
What are the variables in model setup: investment
It = investment for period t
Yt = Output for period t
s-bar = the fraction of output invested
It = s-(bar)Yt
St = total savings → St = It = s(-bar)Yt
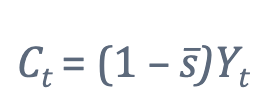
what does this formula say?
This formula tells us that consumption is the share of output not invested. basically ts ask where our investment came from

whats happening here? (context gross national savings rate by county)
Canada: we can see 1/5 of total income is saved for canada
US: 18% of total income is saved, most likley due to the spending and materialistic culture
China: Really high ravings rate bevcause chinas culture they do not spend much and rather put it in saving
Greece: o the lower side and it is due to its debt crisis
Lebanon: it has a -6% rating, meaning they are dis saving. they save less then they borrow from other countries
What may be a reason for why people save?
interest rate increases
education, healthcare so they dont have to save for emergency pension system
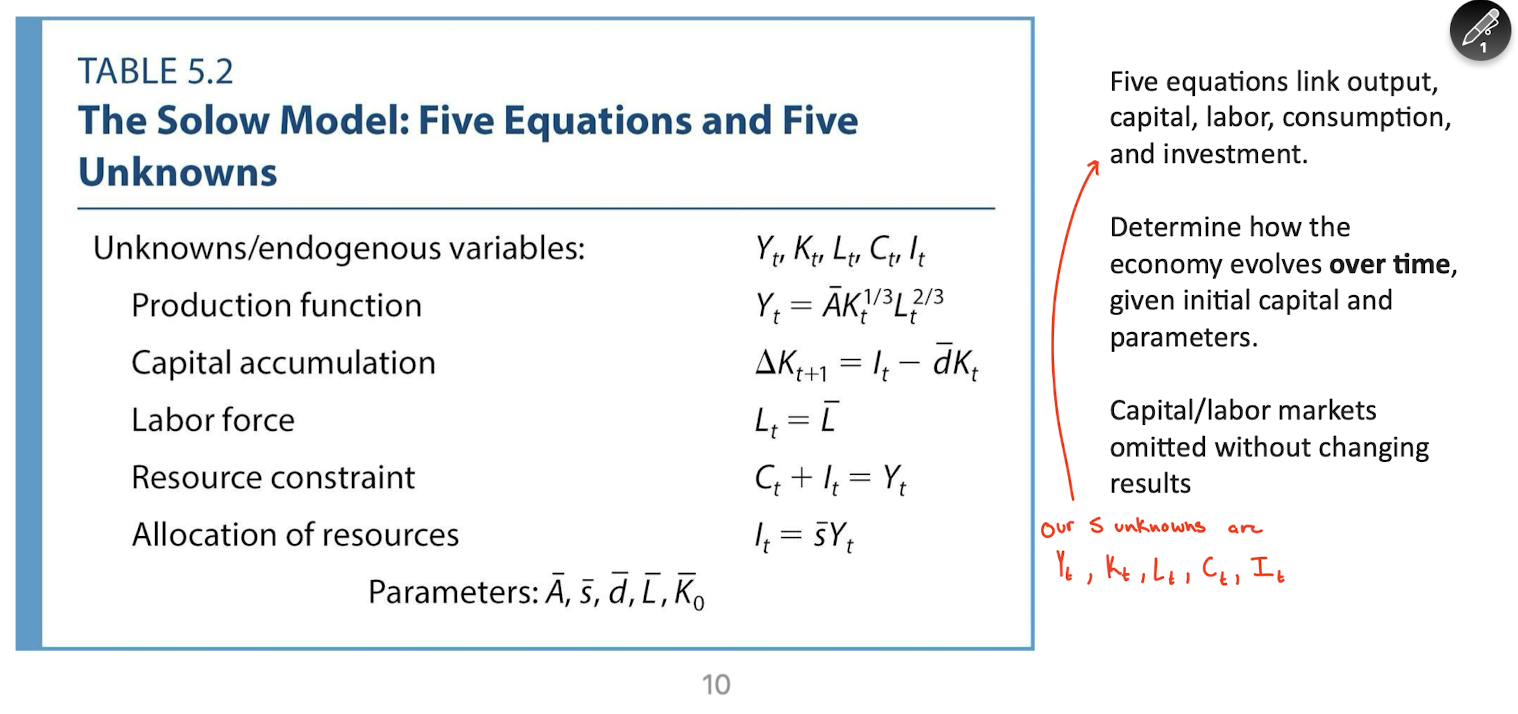
Important slide you can skip

Define solows model variables in per capiat terms…