Water Balance and Membrane Physiology in Cells
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
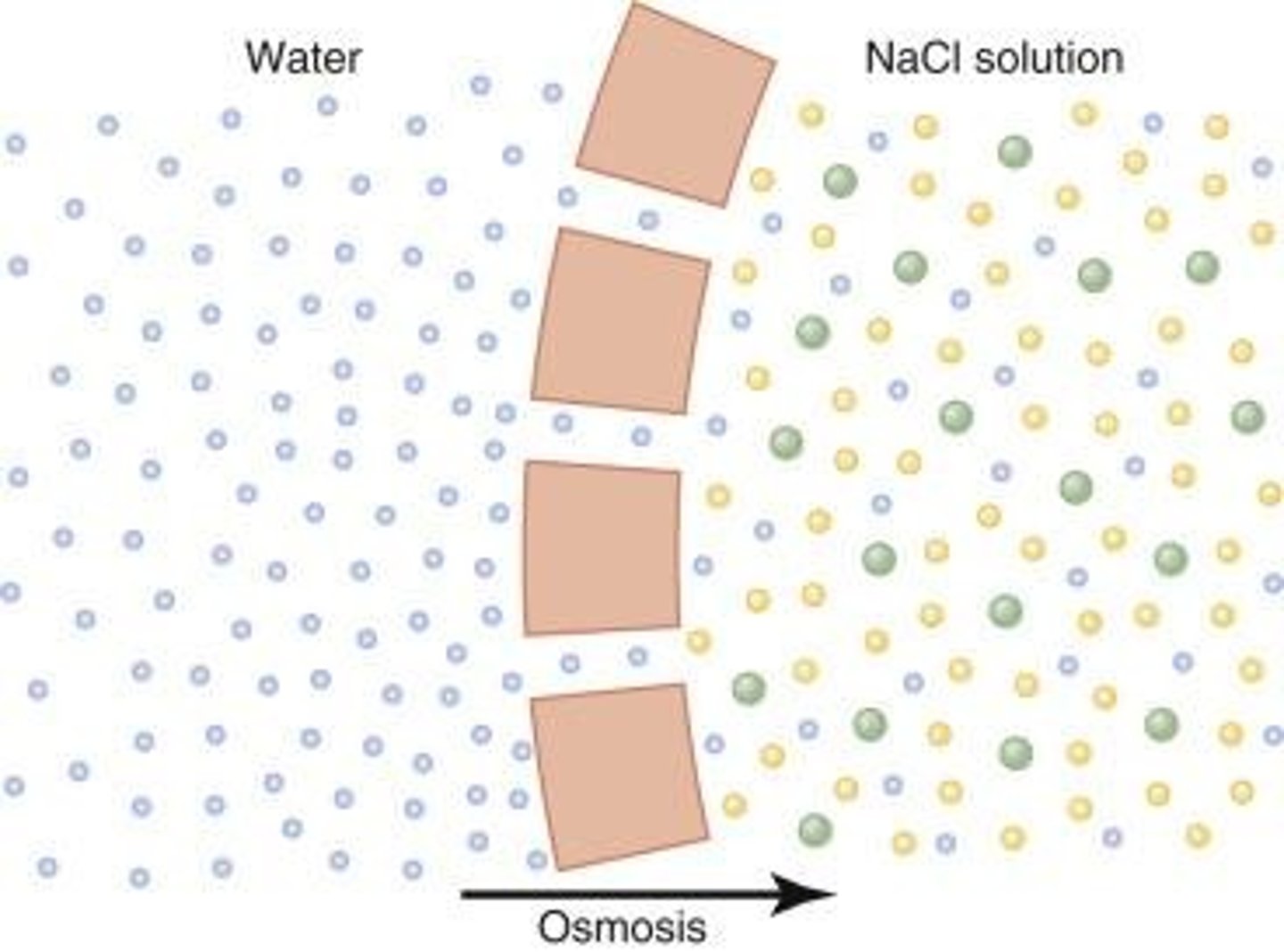
Osmosis
Water movement across a semi-permeable membrane.
Osmolality
Osmoles per kilogram of fluid.
Osmolarity
Osmoles per liter of fluid.
Molarity
Moles of solute per liter of solution.
Concentration Gradient
Difference in solute concentration across a membrane.
Diffusion
Molecules moving from high to low concentration.
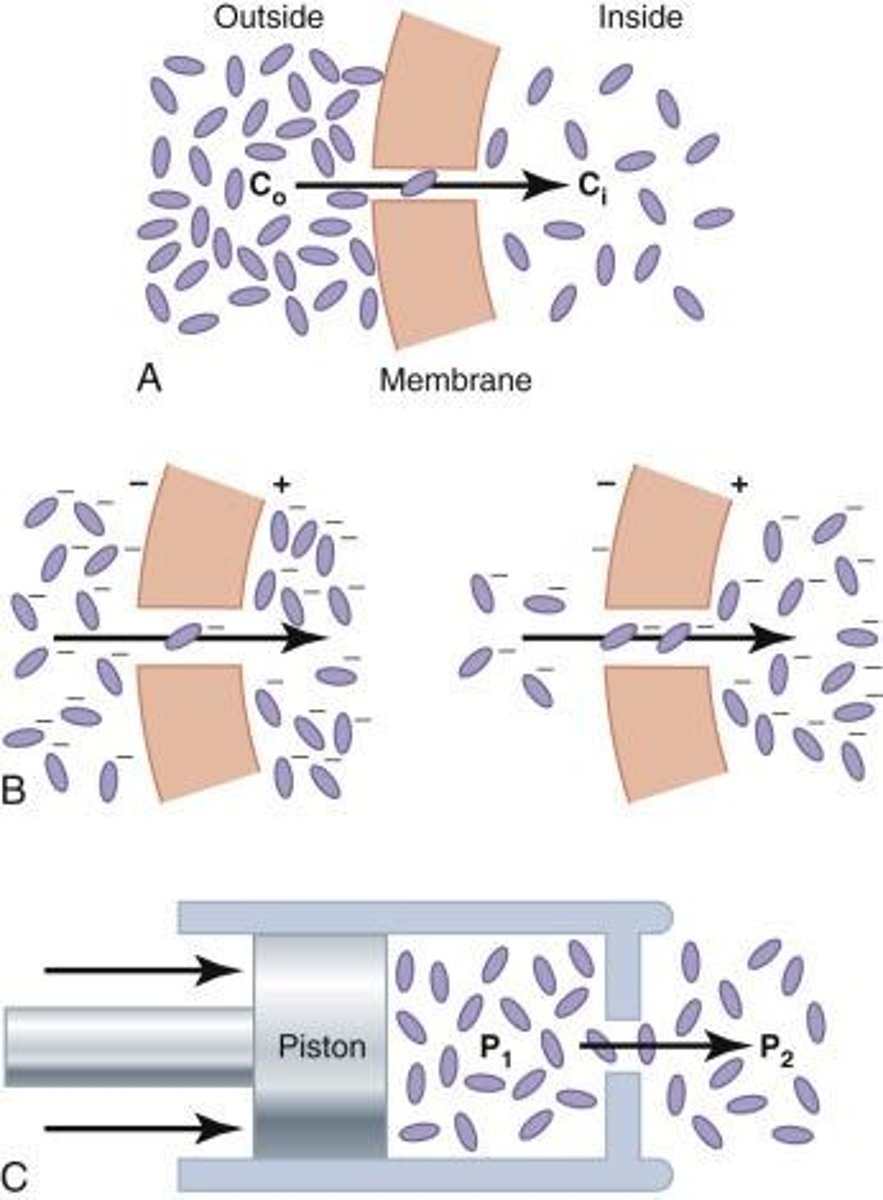
Osmotic Pressure
Force needed to equalize solute concentration.
Net Movement of Water
Water movement changes cell shape and volume.
Isotonic Environment
Equal solute concentration inside and outside cell.
Valence
Charge of an ion affecting its reactivity.
Primary Active Transport
Energy-dependent movement against concentration gradients.
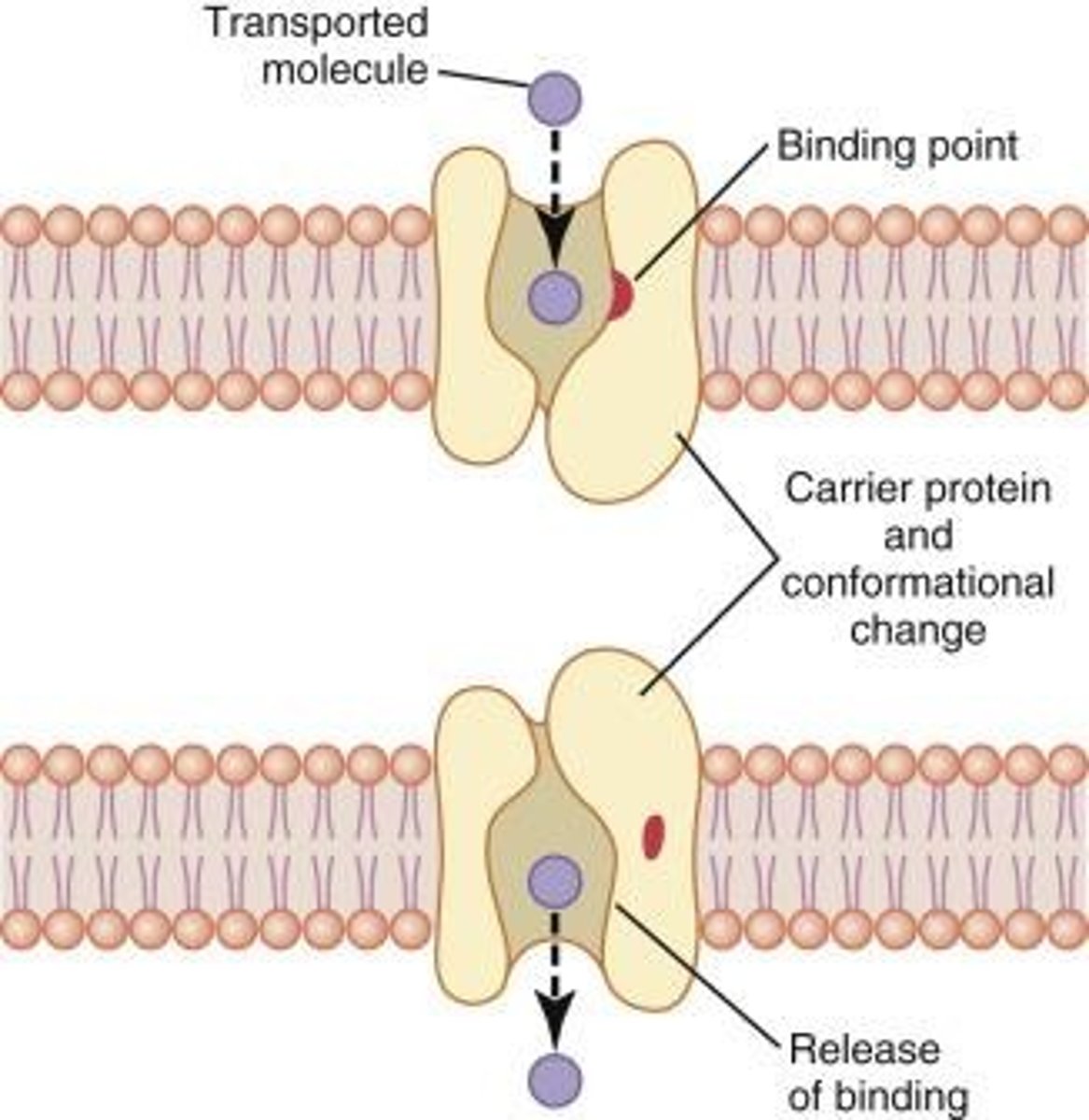
Facilitated Diffusion
Transport requiring a carrier protein, no ATP.
Simple Diffusion
Lipid-soluble molecules pass through the membrane.
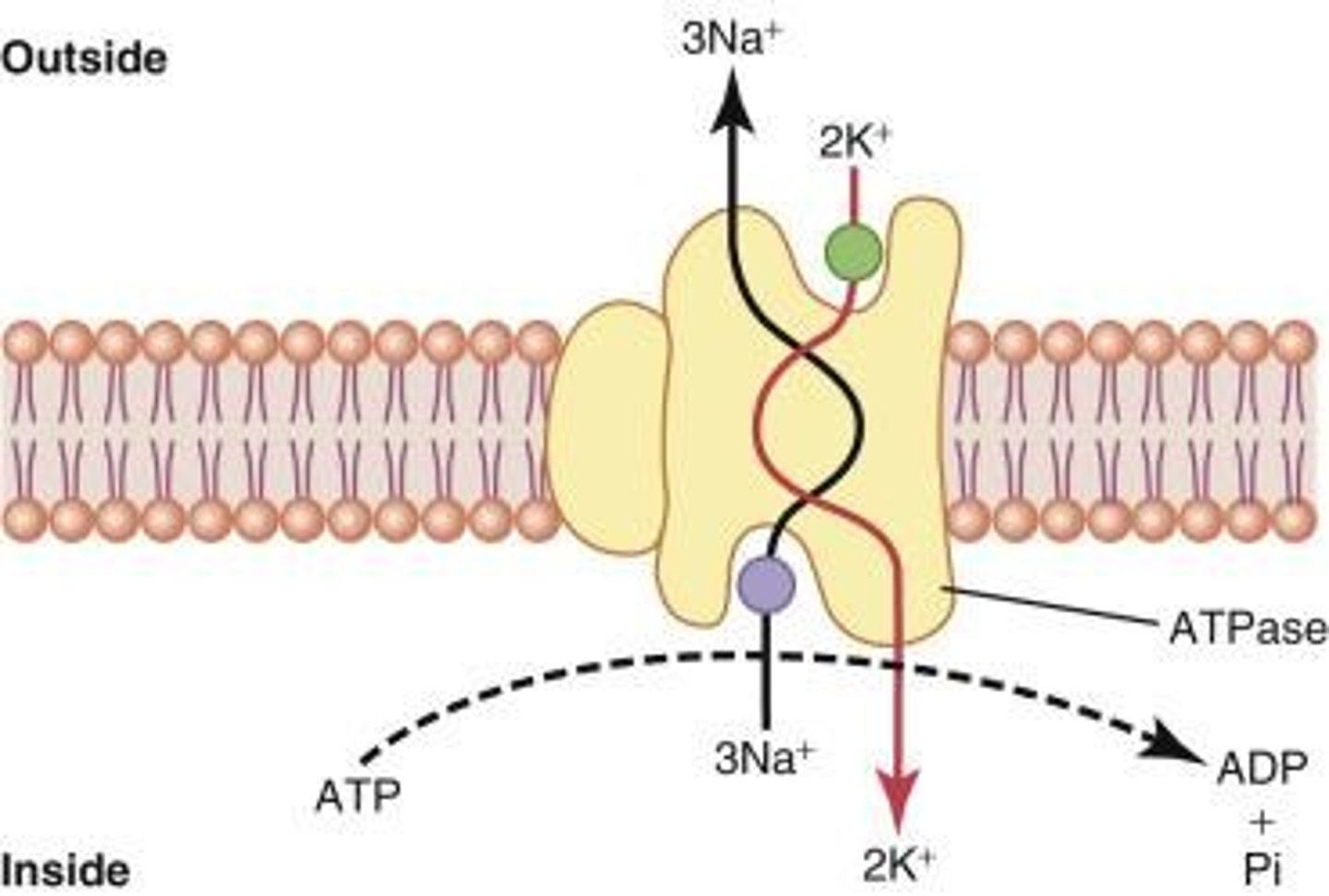
Sodium-Potassium Pump
Maintains Na and K concentration gradients using ATP.
Electrochemical Gradient
Combined concentration and electrical gradients across membranes.
Carrier Membrane Proteins
Control transport of nutrients and ions.
Cell Differentiation
Specialization of cells based on structure.
Membrane Fluidity
Phospholipid composition affects membrane flexibility.
Heat Tolerance in Camelids
Can lose 25% body water without harm.
Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter
Uses sodium gradient to absorb glucose.
Concentration of Ions
Varies inside and outside the cell.
Homeostatic Mechanisms
Regulate isotonic environments in the body.