Circulatory Physiology
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
1
New cards
Cardiac output at rest: where is the main flow going?
digestive system, kidneys, muscle, brain
BFlow changes based on metabolism
BFlow changes based on metabolism
2
New cards
Blood Flow + Pressure relationship (gradients)
High to Low (^ change in P = ^ flow)
inversely proportional to vascular resistance (^ resistance = less flow)
\
Left Ventricle creates pressure and flow
inversely proportional to vascular resistance (^ resistance = less flow)
\
Left Ventricle creates pressure and flow
3
New cards
Blood Pressure moving through vessels (high to low)
Aorta
Arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Veins
Vena Cava
Arteries
Arterioles
Capillaries
Venules
Veins
Vena Cava
4
New cards
Resistance to BFlow
resistance factor (it -- resistance --)
viscosity ^^
vessel length ^^
radius v^
viscosity ^^
vessel length ^^
radius v^
5
New cards
@@Radius impact on blood flow + by what factor?@@
smaller radius→ ^ resistance = less flow
@@radius decrease by factor of 2: r@@
@@flow decrease by factor of 16: r^4@@
@@radius decrease by factor of 2: r@@
@@flow decrease by factor of 16: r^4@@
6
New cards
What controls BFlow
vasoconstriction + dilation
7
New cards
effect of viscosity on blood flow
^ viscosity (thick) = less blood flow
8
New cards
blood doping
example of effect of viscosity: excessive RBC’s will increase viscosity (thick) = decrease blood flow = decrease O2 delivery
9
New cards
Order of size of vessels
arteries →arterioles → capillaries → venules (dont need to know) → veins
10
New cards
Layers of Vasculature (blood + lymph vessels)
tunica intima = endothelium (+ areolar connective tissue)
tunica media = **muscle** + elastin
tunica externa = connective tissue - collagen, elastin
tunica media = **muscle** + elastin
tunica externa = connective tissue - collagen, elastin
11
New cards
What layer of vasculature arterioles have the most of
smooth muscle -- tunica media
12
New cards
what layer of vasculature capillaries are
single endothelium
13
New cards
what layer of vasculature arteries mainly have
collagen + elastin -- tunica externa
14
New cards
when there is a large section between arterioles and capillaries… what happens to diffusion?
larger section = more diffusion time/ time for exchange = less speed thru capillaries
\*\*pulse through arterioles to capillaries is non existent for smooth movement
\*\*pulse through arterioles to capillaries is non existent for smooth movement
15
New cards
ARTERIES - fibres? what do they do?
high flow rate + high pressure (pressure reservoir when heart relax)
large radius = low resistance
collagen →strength for tension
elastin →stretch/recoil
pulsate flow
systolic (contract) pressure = 120 mmHg
diastolic (relax) pressure = 80 mmHg
large radius = low resistance
collagen →strength for tension
elastin →stretch/recoil
pulsate flow
systolic (contract) pressure = 120 mmHg
diastolic (relax) pressure = 80 mmHg
16
New cards
atherosclerosis
cholesterol build up within arteries
17
New cards
Atherosclerosis - atheroma
fatty plaques within vessel WALLS
harden into plaques
restrict blood flow… clot
Causes:
* obesity
* inactivity
* smoking + alcohol
* genetics
* diabetes
Risk factor for:
* ischemia, infarct, stroke
harden into plaques
restrict blood flow… clot
Causes:
* obesity
* inactivity
* smoking + alcohol
* genetics
* diabetes
Risk factor for:
* ischemia, infarct, stroke
18
New cards
Pulse Pressure
dif btwn systolic + diastolic pressures
increase as age
increase as age
19
New cards
ARTERIOLES - main function? applications?
change blood flow + resistance + control flow
smooth out pulsatile flow (from arteries to capill.)
RADIUS:
* adjusted to distribute CO to organs based on needs
* @@**blood flow to brain stays constant**@@
* - regulate arterial BP
vasoconstrict + vasodilate (triggered by local + central factors)
smooth out pulsatile flow (from arteries to capill.)
RADIUS:
* adjusted to distribute CO to organs based on needs
* @@**blood flow to brain stays constant**@@
* - regulate arterial BP
vasoconstrict + vasodilate (triggered by local + central factors)
20
New cards
vaso**constrict**ion - what is it? what causes it?
narrow vessels
^ resistance = reduce flow
smooth muscle **contrac**tion
\
causes:
* ^ O2 in tissues
* less CO2 in tissues
* \*endothelin + stretch
^ resistance = reduce flow
smooth muscle **contrac**tion
\
causes:
* ^ O2 in tissues
* less CO2 in tissues
* \*endothelin + stretch
21
New cards
vasodilation - what is it? what causes it?
enlargement of vessel
less resistance = ^ flow
smooth muscle relaxation
\
causes:
* @@less O2@@ in tissues (want more, so send more blood)
* @@^ CO2@@ in tissues
* @@Nitric oxide@@
* ^ lactic acid
* ^ K+
* ^ osmosis
* ^ adenosine release (coronaries)
* ^heat
less resistance = ^ flow
smooth muscle relaxation
\
causes:
* @@less O2@@ in tissues (want more, so send more blood)
* @@^ CO2@@ in tissues
* @@Nitric oxide@@
* ^ lactic acid
* ^ K+
* ^ osmosis
* ^ adenosine release (coronaries)
* ^heat
22
New cards
Vascular tone - what is it? what @@influences@@ it?
contractile activity
* local influences:
* metabolic changes
* histamine release (vasodilate)
* endothelial factors (protein regulating BVessel constriction) -- nitric oxide (dilate) + endothelin (constrict)
* local physical influences
* heat (dilate)
* cold (constrict)
* myogenic response to stretch -- reflex contraction
* constriction of vessel due to pressure
* local influences:
* metabolic changes
* histamine release (vasodilate)
* endothelial factors (protein regulating BVessel constriction) -- nitric oxide (dilate) + endothelin (constrict)
* local physical influences
* heat (dilate)
* cold (constrict)
* myogenic response to stretch -- reflex contraction
* constriction of vessel due to pressure
23
New cards
Arterioles →extrinsic control
maintain Mean Arterial Pressure + redistribute blood
SNS input (vasoCONSTRICT)
Hormones
* Alpha 1 receptors
* norepi
* vasoCONSTRICT
* Beta 2 receptors
* epi
* heart/skeletal muscle
* vasoDILATE
* Angiotensin II
* vasoCONSTRICT
* ^ BP
\
SNS input (vasoCONSTRICT)
Hormones
* Alpha 1 receptors
* norepi
* vasoCONSTRICT
* Beta 2 receptors
* epi
* heart/skeletal muscle
* vasoDILATE
* Angiotensin II
* vasoCONSTRICT
* ^ BP
\
24
New cards
CAPILLARIES --
gas exchange
thin wall = %%less diffusion distance%%
small radius = slow velocity of BFlow = large cross-sectional area = ^ gas exchange time
^ SA
thin wall = %%less diffusion distance%%
small radius = slow velocity of BFlow = large cross-sectional area = ^ gas exchange time
^ SA
25
New cards
Pre-capillary Sphincters
constrict sphincter = close capill. bed (@rest are often closed)
relax sphincter = open capill. bed
metarteriole - btw arteriole + venule
relax sphincter = open capill. bed
metarteriole - btw arteriole + venule
26
New cards
Types of Capillaries
Continuous
* common
* least permeable
* muscle, lungs, brain, CT
Fenestrated
* pores
* kidneys (bc filter blood), small intestine
Sinusoids
* large for RBC + proteins
* liver, bone marrow, spleen
* common
* least permeable
* muscle, lungs, brain, CT
Fenestrated
* pores
* kidneys (bc filter blood), small intestine
Sinusoids
* large for RBC + proteins
* liver, bone marrow, spleen
27
New cards
Capillary Bulk Flow - Causes
GIST: hydrostatic pressure (cap) + osmotic pressure (tissue) regulate bulk flow
\
Starling Forces (physical forces) determine fluid flow btwn capillaries + tissues: PRESSURE GRADIENTS
\
* capillary BP
* Hydrostatic pressure: regular pressure of fluids
* encourage fluid flow into tissue
* interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
* pushes things out + opposes hydrostatic capill. pressure
* plasma colloid osmotic pressure
* encourage fluid into capillaries
* interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure
* opposes plasma colloid osmotic pressure
\
Starling Forces (physical forces) determine fluid flow btwn capillaries + tissues: PRESSURE GRADIENTS
\
* capillary BP
* Hydrostatic pressure: regular pressure of fluids
* encourage fluid flow into tissue
* interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure
* pushes things out + opposes hydrostatic capill. pressure
* plasma colloid osmotic pressure
* encourage fluid into capillaries
* interstitial fluid colloid osmotic pressure
* opposes plasma colloid osmotic pressure
28
New cards
pressure of capillary end close to arteries
high BP inside
lower osmotic pressure outside
more want to move out
lower osmotic pressure outside
more want to move out
29
New cards
pressure of capillary end close to veins
low BP inside
higher osmotic pressure outside
more want to move in
higher osmotic pressure outside
more want to move in
30
New cards
what is the lymphatic system? functions?
network of open-ended vessels
drains fluid from tissues
\
return of excess **filtered** fluid
defense against disease
* lymph nodes + phagocytes
transport absorbed fat
return filtered protein
\
drains fluid from tissues
\
return of excess **filtered** fluid
defense against disease
* lymph nodes + phagocytes
transport absorbed fat
return filtered protein
\
31
New cards
@@lymph@@ @@vessels@@
@@similar structure to veins@@
lower pressure
have valves
lower pressure
have valves
32
New cards
edema
swelling of tissues
too much interstitial fluid
\
Causes:
* less concentration of plasma proteins = less osmotic pull/ pressure
* ^ permeability of capill walls
* ^venous pressure
* blockage of lymph vessels
too much interstitial fluid
\
Causes:
* less concentration of plasma proteins = less osmotic pull/ pressure
* ^ permeability of capill walls
* ^venous pressure
* blockage of lymph vessels
33
New cards
venules
capill. beds uniting
porous + allow fluids and WBC into tissues
larger ones have 1+ smooth muscle cell layers
porous + allow fluids and WBC into tissues
larger ones have 1+ smooth muscle cell layers
34
New cards
VEINS - main purpose? characteristics?
return to heart
low pressure
larger radius
low resistance to BFlow
slow flow
blood reservoir
low pressure
larger radius
low resistance to BFlow
slow flow
blood reservoir
35
New cards
Venous Return: Increased and Decreased by…?
Decrease:
* venous compliance (stretch)
Increase:
* pressure from cardiac contraction
* ^ venous pressure = ^ pressure gradient
* SNS venoconstriction
* ^ vein pressure = ^ pressure gradient = less venous capacity
* skeletal muscle movement
* ^ venous pressure = ^ pressure gradient
* venous valves impact
* respiratory activity
* less pressure in lung veins = ^ pressure gradient
* cardiac suction
* less pressure in heart = ^ pressure gradient
\
\
increase venous return = ^ EDiastolicV = ^ SV = ^ CO
* venous compliance (stretch)
Increase:
* pressure from cardiac contraction
* ^ venous pressure = ^ pressure gradient
* SNS venoconstriction
* ^ vein pressure = ^ pressure gradient = less venous capacity
* skeletal muscle movement
* ^ venous pressure = ^ pressure gradient
* venous valves impact
* respiratory activity
* less pressure in lung veins = ^ pressure gradient
* cardiac suction
* less pressure in heart = ^ pressure gradient
\
\
increase venous return = ^ EDiastolicV = ^ SV = ^ CO
36
New cards
venous valves + skeletal pump - functions?
VV: prevent backflow
SP: pushes blood upward
SP: pushes blood upward
37
New cards
Skeletal muscle contract + relax - top + bottom valves what?
SP relax - bottom valve open, top closed
SP contract - bottom closed, top open
SP contract - bottom closed, top open
38
New cards
Embolism
blockage of a blood vessel, sometimes sudden
ex. scuba diving + nitrogen
locations: pulmonary, cerebral, cardiac
… i dont think we have to know this one
ex. scuba diving + nitrogen
locations: pulmonary, cerebral, cardiac
… i dont think we have to know this one
39
New cards
STROKE:
less blood supply to brain
* ISCHEMIC: thrombus or embolus or plaque blockage
* HAEMORRHAGIC: bleeding - weak wall rupture
TIA’s: Transient Ischemic Attacks
* mini strokes (transient) temporary
CVA: Cerebrovascular accidents
* ISCHEMIC: thrombus or embolus or plaque blockage
* HAEMORRHAGIC: bleeding - weak wall rupture
TIA’s: Transient Ischemic Attacks
* mini strokes (transient) temporary
CVA: Cerebrovascular accidents
40
New cards
Stroke symptoms
depend on area of brain
\
* drooping face + drooling
* confusion
* dizziness
* loss of consciousness
* poor coordination / paralysis
* weak arms
* sudden headache
* difficulty with speech
* loss of vision
\
* drooping face + drooling
* confusion
* dizziness
* loss of consciousness
* poor coordination / paralysis
* weak arms
* sudden headache
* difficulty with speech
* loss of vision
41
New cards
controllable and non controllable risk factors of stroke
80% strokes are preventable
controllable:
* smoking/alcohol
* high-fat diet / obesity
* lack of exercise
* high BP
* diabetes
non controllable:
* age, gender, ethnicity, genetics
controllable:
* smoking/alcohol
* high-fat diet / obesity
* lack of exercise
* high BP
* diabetes
non controllable:
* age, gender, ethnicity, genetics
42
New cards
Ways to asses stroke
EEG + CT + MRI
Angiogram (measure blood vessel)
doppler flow (flow thru blood vessels)
Angiogram (measure blood vessel)
doppler flow (flow thru blood vessels)
43
New cards
Ways to treat a stroke
anticoagulants →less clotting
hypertensive meds →lower BP
carotid endarterectomy →scrape fat
\
change diet + exercise
hypertensive meds →lower BP
carotid endarterectomy →scrape fat
\
change diet + exercise
44
New cards
BP - main causes
CO
total peripheral resistance (all vessels together… force against flow)
\
mean arterial pressure = CO x total peripheral resistance
total peripheral resistance (all vessels together… force against flow)
\
mean arterial pressure = CO x total peripheral resistance
45
New cards
Short + Long Term control for BP
short: seconds
* baroreceptors (relay info from BP in ANS)
* cardiovascular system (epi, change HR, contract… etc.)
long: mins-hrs
* kidneys
* \*\*blood volume
* baroreceptors (relay info from BP in ANS)
* cardiovascular system (epi, change HR, contract… etc.)
long: mins-hrs
* kidneys
* \*\*blood volume
46
New cards
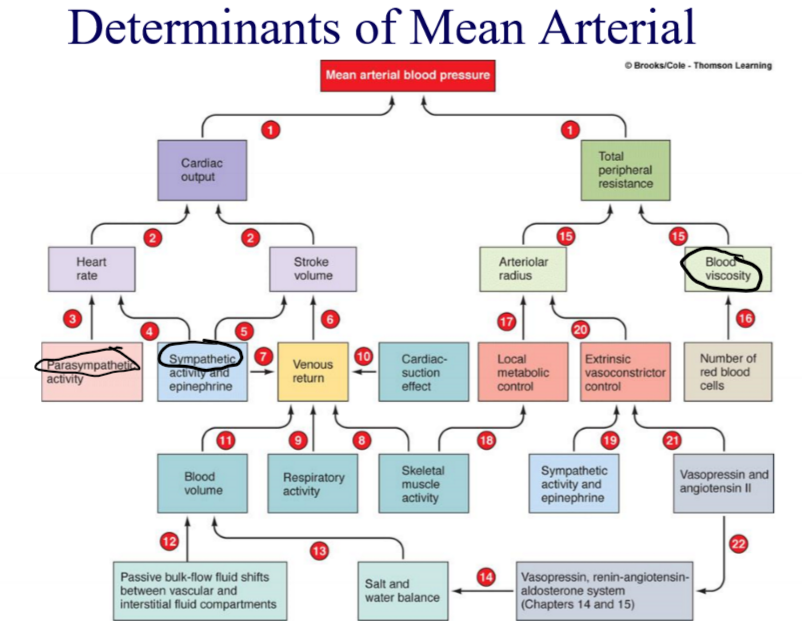
Things contributing to MAP (flow chart)
\
47
New cards
Baroreceptors
fast + cardiovascular
pressure receptors (exp. in blood)
* send input to cardiovascular center
* output to heart + vessels
\
^ BP = stimulated
low BP = inhibited
pressure receptors (exp. in blood)
* send input to cardiovascular center
* output to heart + vessels
\
^ BP = stimulated
low BP = inhibited
48
New cards
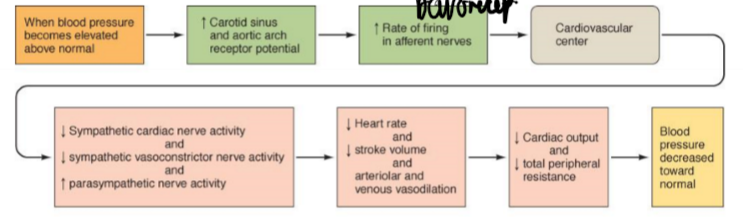
HIGH BP response
everything decrease EXCEPT PNS + baroreceptors firing
\
less SNS:
→vasodilation →less TPR →less BP
→less contractility →less SV →less CO →less BP
→ venodilation →less VR →less SV →less CO →less BP
\
less SNS:
→vasodilation →less TPR →less BP
→less contractility →less SV →less CO →less BP
→ venodilation →less VR →less SV →less CO →less BP
49
New cards
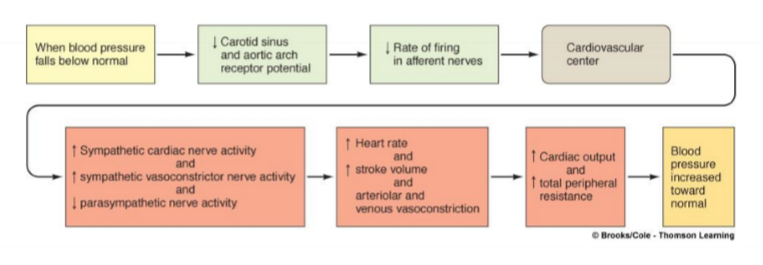
LOW BP response
everything increase EXCEPT PNS + baroreceptors firing
\
^ SNS:
→vasoconstriction →^ TPR →^ BP
→^ contractility →^ SV →^ CO →^ BP
→ venoconstriction →^ VR →^ SV →^ CO →^ BP
^HR
TPR: total peripheral resistance
\
^ SNS:
→vasoconstriction →^ TPR →^ BP
→^ contractility →^ SV →^ CO →^ BP
→ venoconstriction →^ VR →^ SV →^ CO →^ BP
^HR
TPR: total peripheral resistance
50
New cards
Renal Regulation
long term BP control by altering BVolume
kidneys
* direct renal
* indirect renal (renin-angiotensin)
kidneys
* direct renal
* indirect renal (renin-angiotensin)
51
New cards
Direct Renal Mechanism in Renal Regulation
change BV indep. of hormone
* ^BP or BV
* ^ filtration
* eliminate ^ urine
* THEREFORE reduce BP
* decrease BP or BV
* kidney preserve water + fluid retention
* less filtration
* less urine
* BP ^
* ^BP or BV
* ^ filtration
* eliminate ^ urine
* THEREFORE reduce BP
* decrease BP or BV
* kidney preserve water + fluid retention
* less filtration
* less urine
* BP ^
52
New cards
Indirect Renal Mechanism in Renal Regulation
Renin-angiotensin
* controls BV + arterioles
* controls BV + arterioles
53
New cards
Renin-Angiotensin System with less BP
less arterial BP →
release renin →
trigger production of angiotensin II → (vasoconstrictor)
aldosterone + ADH secretion →
conserve fluid→
\
\*\*BP decreases, everything else increases
release renin →
trigger production of angiotensin II → (vasoconstrictor)
aldosterone + ADH secretion →
conserve fluid→
\
\*\*BP decreases, everything else increases
54
New cards
Renin-Angiotensin System with ^ BP
\*\*BP increases, everything else decreases
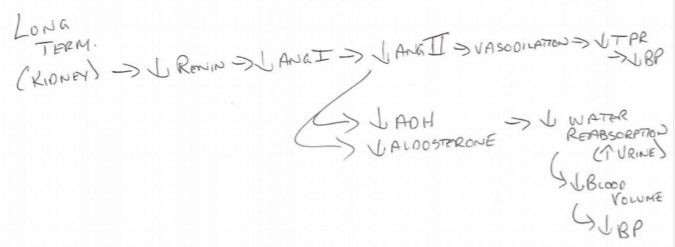
55
New cards
Hypotension
LOW BP
Below 100/60 (systolic/diastolic)
* too little blood to fill vessels
* heart is too weak to drive blood
\*not a condition in the list we need to know\*
Below 100/60 (systolic/diastolic)
* too little blood to fill vessels
* heart is too weak to drive blood
\*not a condition in the list we need to know\*
56
New cards
Hypertension
HIGH BP
Above 140/90 (systolic/diastolic)
\
KNOW: (on other cards)
* primary
* secondary (only 10% of cases)
* complications
* treatments
Above 140/90 (systolic/diastolic)
\
KNOW: (on other cards)
* primary
* secondary (only 10% of cases)
* complications
* treatments
57
New cards
Primary Hypertension Causes
salt
hormones
arterioles abnormalities
poor kidney function (renin-angiotensin system)
age + genetics
smoking / diet / obesity
stress
hormones
arterioles abnormalities
poor kidney function (renin-angiotensin system)
age + genetics
smoking / diet / obesity
stress
58
New cards
Secondary Hypertension Examples
10% of cases
happens secondary to other primary problems
EX.
* renal
* endocrine
* neurogenic hypertension
happens secondary to other primary problems
EX.
* renal
* endocrine
* neurogenic hypertension
59
New cards
Complications of Hypertension
congestive heart failure (muscle doesn’t pump as good)
stroke / heart attack
spontaneous hemorrhage
renal failure
retinal damage (blood vessels in eyes)
stroke / heart attack
spontaneous hemorrhage
renal failure
retinal damage (blood vessels in eyes)
60
New cards
Treatments of Hypertension
ACE inhibitors (ANG I to II) (prevents blood vessel narrowing)
beta blockers
Ca blockers
Diet + exercise (salt)
beta blockers
Ca blockers
Diet + exercise (salt)