chapter 26- seed plants
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
seed plants
spermatophytes (vascular)
what are the 2 categories under spermatophytes
gynosperms and angiosperms
seed plants first appeared
305-465 mya, gymnosperms THEN angiosperms
timeline
first land plants, first vascular plants, first seed plants, first gymnosperms, gymnosperm forests replace fern forests, cycads and conifers dominate, flowering plants
embryophytes
land plants
embryo
produced from the diploid zygote, grows into sporophyte (2n) when seed germinates
seed
offers embryo protection and nourishment
female gametophyte
develops in ovule (has egg and endosperm producing cell-supports growth), enclosed within diploid sporophyte tissue in angiosperms
male gametophyte
within pollen grains (has sperm of the plant), protected from desiccation, not dependent on water to reach female organs
desiccation
extreme no water
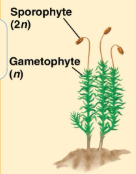
mosses and nonvascular plants reproduction
gametophyte- dominant, sporophyte- reduced and dependent on gametophyte for nutrition, sporophyte (2n) and gametophyte (n) grows on top of main plant body
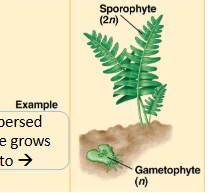
ferns and other seedless vascular plants reproduction
gametophyte- reduced and independent (free living n), sporophyte- dominant (2n)
seed plants reproduction (gymnosperm)
gametophyte- reduced (microscopic) dependent on sporophyte for nutrition, sporophyte- dominant, female gametophytes- inside ovulate cone, male gametophytes inside pollen cones
seed plants reproduction (angiosperm)
same as gymnosperm, female gametophyte- inside bulb of flower, male gametophyte- inside tall stalks of flowers
seed plants are
heterosporous- megaspores for female gametophytes and microspores for male gametophytes happens in sporangium
what is the advantage of gametophytes maturing in sporangia?
highly reduced in size, protected from drying and UV
seed
develops in fertilized ovule= integument+megasporangium+megaspore
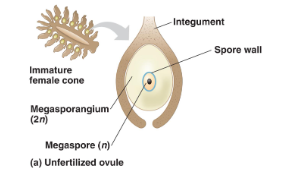
megaspore germinates inside ovule to develop
tiny female gametophyte, produces eggs then will be fertilized
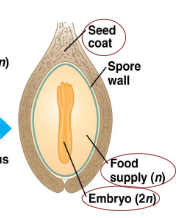
seed structure
embryo, food supply, seed coat (embryo is 2n)
pollen grains
male gametophyte surrounded my pollen wall (partly from sporophyte), long dispersal, tough and resistant, does not need water for fertilization
sporopollenin
protects pollen grains (inside pollen wall)
pollination
transfer of pollen to part of the seed plant that has ovule
fertilization process from pollen grains side
pollen grain germinates, pollen tube, sperm discharged into female gametophyte
gymnosperm characteristics
naked seeds (kinda protected by sporophyls), pollination by wind, vascular system (tracheids), alternation of generations, reduced gametophytes, dominant sporophyte, heterosporous, reproductive organs are cones or strobili, monoecoius or dioecious
where do female and male cones grow on gymnosperms (conifers)
males on lower branches and females on upper branches
gymnosperms phyla
coniferophyta, cycadophyta, gnetophyta, ginkophyta, non flowering and naked seed (ex- conifers, cycad, ginkgos)
angiosperm phyla
anthophyta, flowering and covered seed (ex-all flowering plants)
coniferophyta
conifers, most diverse, have cones (pollen and ovulate cones), high altitudes, evergreen with needles
examples of coniferophyta
pine, fir, spruce, sequoia
cycadophyta
cycads, fern like, radiate from central stem, central female and male cones, flagellated sperm, beetles are involved for polination
ginkgophyta
ginkgos, one tree- ginkgos biloba, herbal medicine, flagellated sperm, fan shaped leaves, strobili
gnetophyta
gnetophytes, 3 genera: Ephedra (U.S deserts), Gnetum (tropics), Welwitchia (deserts), strobili, male sperm not mobile
ephedera (gntephyta)
used for herbal medicine
angiosperms key innovations
flowers and fruits
flowers
structure to facilitate sexual reproduction (due to pollinators)
male part of flower
anther and filament
female part of flower
stigma, style, ovary
sepals
green petals close to flowers
stamen
male part (filament and anther)
carpel
female part (stigma-sticky tip, style, ovary, and ovules)
angiosperm male life cycle
microsporangia, male sporocytes (2n), microspores (1n), pollen grain (n)
pollen grains
1 generative cell, 1 tube cell
angiosperm female life cycle
ovule, megasporangium, megasporocyte (2n), 4 megaspores(n), only large megaspore survives, 3x mitosis to get 3 cells at one pole to become egg and 2 synergids (the other 3 cells are antipodal cells)
center cell
2 polar nuclei
double fertilization with 2 sperm nuclei
one fuses with egg to get zygote (2n) and one fuses with polar nuclei to get endosperm (3n) for food supply in seed
fruit
mature ovary of flower thickens around seeds, protects seeds and enhances seed dispersal
monocots examples
orchids, palms, lillies, grasses
eudicots examples (dicots)
oaks, peas, roses, potatoes
tissues rarely found in monocots
true woody tissues
eudicots can be
non woody (herbaceous) or woody tissues called xylem cells
monocot characteristics
one cotyledon, parallel veins, vascular tissue scattered, fibrous foots (no main root), pollen grain with one opening, flower organs in multiple of 3
eudicot characterisitcs
2 cotyledons, veins are netlike, vascular tissue arranged in a ring, taproot (main root), pollen grain with 3 openings, flower organs in multiple of 4 or 5