The Control Of Gene Expression
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/105
Last updated 11:07 AM on 5/20/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
1
New cards
Gene Mutation
A change to the base sequence of DNA through errors made in DNA and increased by mutagenic agents.
Usually random.
Usually random.
2
New cards
Frame shift mutation
A change in the number of nucleotides which alters the base triplets so the code is read in a different way. Has a large effect on protein structure.
Examples: Deletion, Addition, Duplication
Examples: Deletion, Addition, Duplication
3
New cards
Silent mutations
A mutation that does not always change the amino acid sequence due to the degenerate nature of coding (some AA are coded for by 1+ triplet codes.
Examples: Substitution, Inversion, Base Translocation
Examples: Substitution, Inversion, Base Translocation
4
New cards
Inversion mutation
Codon triplet is reversed. The order goes back to front.
5
New cards
Base Translocation
Base sequence is moved from one location to another. 9(can be same chromosome or different).
6
New cards
Mutagenic agents
Enviro factors that increases rate of mutations.
Examples: UV radiation, ionizing radiation or chemicals.
Examples: UV radiation, ionizing radiation or chemicals.
7
New cards
How do mutagenic agents work?
1. Act as a base (substitution) \~ change base sequence
2. Alters the base (deletion)
3. Changes DNA structure \~ problems during replication
8
New cards
Stem cells
Unspecialised cells that have ability to replicate themselves or differentiate into other (specialized cells).
9
New cards
Embryonic Stem Cells
Stem cells extracted from embryos (usually from developing eggs during IVF that are donated).
Illegal in many countries (including most of USA & Germany).
Can differentiate into any type of cell - totipotent or pluripotent. After embryonic period, stem cells loose their potency.
ETHICAL ISSUES
Illegal in many countries (including most of USA & Germany).
Can differentiate into any type of cell - totipotent or pluripotent. After embryonic period, stem cells loose their potency.
ETHICAL ISSUES
10
New cards
Adult tissue stem cells
E.g. from adult bone marrow or umbilical chord \~ operation needed to extract these cells.
Can only differentiate into cells of the tissue they are found in - multipotent or unipotent.
Can only differentiate into cells of the tissue they are found in - multipotent or unipotent.
11
New cards
Totipotent stem cells
Differentiate into any cell type in human body.
Found in embryos up to 32 cell state (first 4 days after fertilisation).
Toti = whole (cell types)
Found in embryos up to 32 cell state (first 4 days after fertilisation).
Toti = whole (cell types)
12
New cards
Pluripotent stem cells
Differentiate into any body cell apart from placenta cells, cannot generate a new individual.
Found in blastocyst (day 5 embryo).
Pluri = several (apart from 1)
Found in blastocyst (day 5 embryo).
Pluri = several (apart from 1)
13
New cards
Multipotent stem cells
Limited in cell type differentiation, only divide into related families of cells. Used by body to replace + repare damaged tissues.
Found in bone marrow.
Multi = multiple (of related fams)
Found in bone marrow.
Multi = multiple (of related fams)
14
New cards
Unipotent stem cells
Differentiate (divide) into only 1 type of cell / tissue.
Examples: skin epidermal cells and cardiomyocytes
Examples: skin epidermal cells and cardiomyocytes
15
New cards
Crdiomyocytes
Heart muscle unipotent cells that form when heart tissue / cells are damaged.
Shows hearts have some regenerative capacity.
Shows hearts have some regenerative capacity.
16
New cards
How do stem cells become specialised?
Determined by what parts of DNA are transcribed and translated.
Transcription factors turn on and off cells which determines what cell the stem cell becomes.
Transcription factors turn on and off cells which determines what cell the stem cell becomes.
17
New cards
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPS cells)
Stem cells created in a lab; reprogrammed cells from unipotent (e.g. skin cells) to pluripotent cells by adding in 4 genes.
Pluripotency is turned off by transcription factors in adult body cells when they differentiate and turning them into iPS cells requires infection with a modified virus that contains genes for coding transcription factors.
NO ETHICAL ISSUES.
Can be used to grow new organs (from individuals unipotent cells) w/out rejection issues.
Pluripotency is turned off by transcription factors in adult body cells when they differentiate and turning them into iPS cells requires infection with a modified virus that contains genes for coding transcription factors.
NO ETHICAL ISSUES.
Can be used to grow new organs (from individuals unipotent cells) w/out rejection issues.
18
New cards
Use of stem cells in medicine
1. Bone marrow transplants
Leukaemia (blood cancer), Lymphoma, Sickle cell, SCID
2. Potential uses
New brain cells => Parkinson’s. Replace faulty neurones => paralysis. Insulin-producing cells => diabetes.
19
New cards
Ethics of stem cells
Embryos right to live \~ is it killing human life?
George W Bush banned stem cell use whilst in presidency.
Adult stem cells > ESC as don’t destroy embryos.
iPS>>>> as increased potency, less controversial than ESC w/ similar properties.
George W Bush banned stem cell use whilst in presidency.
Adult stem cells > ESC as don’t destroy embryos.
iPS>>>> as increased potency, less controversial than ESC w/ similar properties.
20
New cards
Gene expression
When DNA is transcribed into mRNA and translated into proteins due to genes being ‘turned on’.
What genes are turned on and off determines cell structure and cell processes.
What genes are turned on and off determines cell structure and cell processes.
21
New cards
Transcription Factors
Proteins which bind to genes on specific promoter regions and act as a binding site for RNA polymerase to attach which initiates gene transcription.
Multiple transcription factors may bind to promoter region before RNA polymerase can attach.
Multiple transcription factors may bind to promoter region before RNA polymerase can attach.
22
New cards
Promoter region
Sequence of nucleotides on a gene marking the start of transcription of mRNA.
The area which transcription factors and RNA polymerase attach.
The area which transcription factors and RNA polymerase attach.
23
New cards
Activator transcription factor
Stimulates rate of transcription, aid RNA polymerase to bind to DNA and activate transcription.
24
New cards
Represor transcription factor
Inhibits rate of transcription. Binds to target gene (promoter region) and prevents RNA polymerase from binding to stop transcription.
25
New cards
Oestrogen; role and production etc.
A steroid hormone which is secreted by the ovaries. Stimulates protein synthesis in target tissue, e.g. breasts.
Crucial to immunity, bone developments and female reproduction.
Crucial to immunity, bone developments and female reproduction.
26
New cards
Oestrogen as an activator transcription factor
As Oestrogen is lipid soluble and small, it diffuses through the cell membrane, into cytoplasm.
Oestrogen then binds to an Oestrogen receptor on the transcription factor. This causes the Oestrogen-Oestrogen receptor (aka Oestrogen bound to TF) to change shape and become activated.
The complex then diffuses into the nucleus and attaches to the promoter region of the target gene to facilitate the attachment of RNA polymerase and initiate transcription.
Oestrogen then binds to an Oestrogen receptor on the transcription factor. This causes the Oestrogen-Oestrogen receptor (aka Oestrogen bound to TF) to change shape and become activated.
The complex then diffuses into the nucleus and attaches to the promoter region of the target gene to facilitate the attachment of RNA polymerase and initiate transcription.
27
New cards
Oestrogen’s role in developing breast cancer
Oestrogen receptors are overexpressed OR there is increased exposure to oestrogen (through early menstruation, consuming oestrogen-containing drugs HRT, post-menopausal fat cell oestorgen production) and so oestrogen activates more TF which may activate (transcribe) a gene related to cell division which will cause more breast tissue division and therefore increase the chances of a mutation occurring and breast tissue production will become out of control and eventually forma tumor.
28
New cards
Breast cancer treatments
Patients undergo drug therapy where drugs are selective to oestrogen receptor molecules (as has similar shape to oestrogen) so bind to receptor TF and blocks oestrogen from forming a complex and preventing transcription (as no longer facilitating RNA polymerase attachment).
29
New cards
RNAi
RNA interference (of translation). A small, double stranded RNA molecule which prevents gene expression through breaking down mRNA before translation (to protein) occurs.
30
New cards
siRNA
small interfering RNA. A type of RNAi which acts on mRNA travelling through the cytoplasm.
31
New cards
How does siRNA inhibit translation
An enzyme cuts a double stranded RNA molecule into smaller sections (= siRNA).
ATP then acts on siRNA and splits it into single-stranded molecules.
A protein complex, RISC, combines w/ 1 single-stranded siRNA whilst the other (single stranded siRNA) is broken down.
The protein complex + siRNA strand then binds to complementary bases on target mRNA.
Once integrated, the siRNA + RISC cuts the mRNA into sections, making the mRNA useless, meaning translation cannot occur.
The mRNA fragments are then degraded.
ATP then acts on siRNA and splits it into single-stranded molecules.
A protein complex, RISC, combines w/ 1 single-stranded siRNA whilst the other (single stranded siRNA) is broken down.
The protein complex + siRNA strand then binds to complementary bases on target mRNA.
Once integrated, the siRNA + RISC cuts the mRNA into sections, making the mRNA useless, meaning translation cannot occur.
The mRNA fragments are then degraded.
32
New cards
miRNA
microRNA. A type of RNAi which can target multiple different RNA strands as it is not 100% complimentary (induced fit). Does not breakdown mRNA to never use again, just blocks it temporarily, therefore less effective at stopping translation.
33
New cards
Uses of siRNA (2)
1. To observe effects and highlight the role of the blocked gene. (Done through blocking certain target genes).
2. To determine whether a disease has a genetic bases or caused through certain gene expression. Suspect gene is blocked by siRNA which may then prevent disease development.
34
New cards
Epigenome
The total chemical compounds (epigenetic markers) **inherited** by an organism which modify or mark the genome to control gene expression, without altering the base sequence of DNA.
Controls whether a gene is switched on or off.
Can be influenced by the enviro (e.g. food availability or pollution).
Controls whether a gene is switched on or off.
Can be influenced by the enviro (e.g. food availability or pollution).
35
New cards
Epigenetic markers funtion
Control whether genes are turned on or off through adding or removing chemical groups to the DNA or histone proteins. Influences how easily enzymes and proteins (TF) can interact with the DNA for transcription + translation.
36
New cards
Methylation of DNA through epigenetic markers
ADDING A METHYL GROUP TO SILENCE A GENE.
A -CH3 (methyl) group is added to DNA at CpG or GpC sites via enzymes. This alters the DNA structure and prevents transcription from occurring through blocking the transcription factor from binding to promoter regions or making the DNA more complex / further wrapping it around histone, meaning the DNA sequence is not easily accessible. This causes the gene silencing.
A -CH3 (methyl) group is added to DNA at CpG or GpC sites via enzymes. This alters the DNA structure and prevents transcription from occurring through blocking the transcription factor from binding to promoter regions or making the DNA more complex / further wrapping it around histone, meaning the DNA sequence is not easily accessible. This causes the gene silencing.
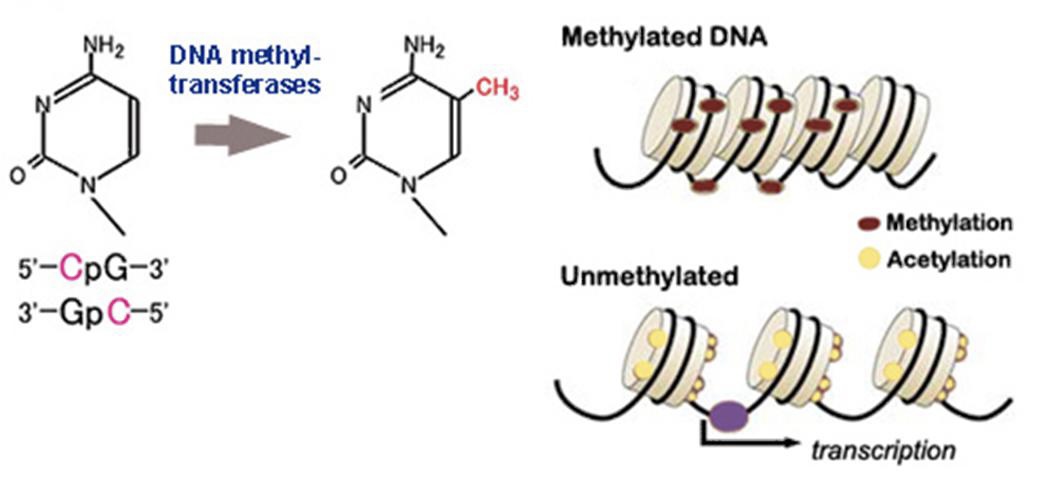
37
New cards
De-methylation
Epigenetic re-programming that occurs when gametes are made; most epigenetic factors are removed to allow the fertilized egg to be totipotent.
38
New cards
Histone
A protein that DNA is wrapped around to form chromatin. Condenses DNA. How condensed they are determines if transcription can occur and if transcription factors can access the DNA or not.
39
New cards
Increased acetylation modification on histones
ADDITION OF ACETYL GROUPS TO TURN ON GENES.
When an acetyl group (-CH3CO) attaches to a histone, this relaxes the chromatin structures and they become less condense (partially unwound = euchromatin), meaning DNA code is more accessible to transcription factors, the gene is turned on and transcription occurs.
When an acetyl group (-CH3CO) attaches to a histone, this relaxes the chromatin structures and they become less condense (partially unwound = euchromatin), meaning DNA code is more accessible to transcription factors, the gene is turned on and transcription occurs.
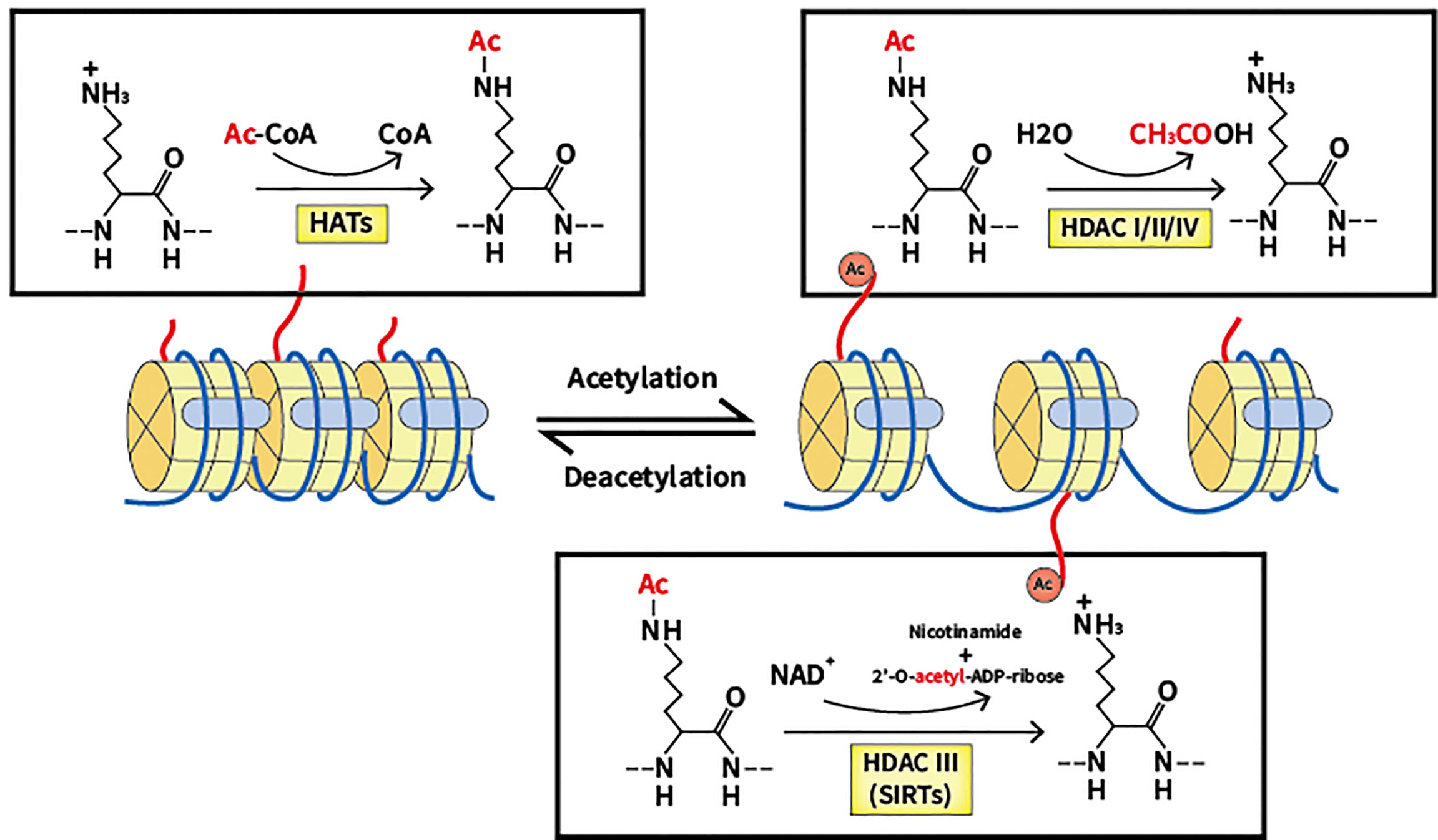
40
New cards
Decreases acetylation modification on histones
Enzymes remove acetyl (-CH3CO) groups from histones, chromatic becomes highly condensed (compact = heterochromatin) making it inaccessible to transcription factors, transcription cannot occur therefore the gene is silenced.
41
New cards
How are epigenetic factors inherited and influenced?
Passed on through gametes during meiosis and are vital for development.
Influenced by environment.
Influenced by environment.
42
New cards
Adaptations on epigenetics through environmental influence.
Chemical tags (methyl and acetyl groups) respond to enviro changes (e.g. diet or drugs) to provide offspring with advantage after birth \~ e.g. if starvation occurs bc lack of food, epigenetic markers adapt child to survive in this environment after birth.
Time a developing mammal spends in womb is where enviro factors have the most effect on epigenetic factors.
Time a developing mammal spends in womb is where enviro factors have the most effect on epigenetic factors.
43
New cards
Cancer
Uncontrolled cell division, forming tumors that may invade and destroy surrounding tissue.
44
New cards
Benign tumors
Grow slowly
Forms a ‘primary tumor’ \~ cells stick tog in one big clump
May cause blockages but less likely to be life threatening.
Usually only requires 1 surgery to remove.
Cell nucleus often unaffected / normal.
Forms a ‘primary tumor’ \~ cells stick tog in one big clump
May cause blockages but less likely to be life threatening.
Usually only requires 1 surgery to remove.
Cell nucleus often unaffected / normal.
45
New cards
Malignant tumors
Grows rapidly and uncontrollably
Cells tend to spread to other parts of body and form ‘secondary tumors’ = metastasis.
Abnormal tissues may replace normal tissues = life threatening.
Treatment usually long term; chemotherapy + radiotherapy + (multiple) surgery.
Cell nucleus often effected; larger and darker due to more DNA.
Cells tend to spread to other parts of body and form ‘secondary tumors’ = metastasis.
Abnormal tissues may replace normal tissues = life threatening.
Treatment usually long term; chemotherapy + radiotherapy + (multiple) surgery.
Cell nucleus often effected; larger and darker due to more DNA.
46
New cards
Cause of Cancer
Random mutation in genes which control cell division (initiates apoptosis is replication produces a damaged cell), leads to uncontrolled mitosis (as no apoptosis).
47
New cards
Role of tumor suppressor gene in normal mitosis
1. Regulates mitosis and restrains it at a slow speed.
2. Produces proteins that:
a. Inhibit cell proliferation (cell division) if damaged cell is produced
b. Act as check points during cell cycle to make sure DNA is not damaged.
c. Promote and induce apoptosis (cell death) when recognize DNA is damaged.
Acts as break and inhibits cell division to maintain it. Works tog with proto-oncogene. Controls mitosis.
48
New cards
Role of tumor suppressor genes in cancer (abnormal) cell division
A mutation may occur which inactivated and switched of the tumor suppressor gene, meaning no measures (protein production or cell division speed maintenance) for cell division will be controlled and tumor formation is promoted.
For a tumor suppressor gene to be switched off, both alleles must be lost \~ if 1 is lost, no effect will occur on the gene.
For a tumor suppressor gene to be switched off, both alleles must be lost \~ if 1 is lost, no effect will occur on the gene.
49
New cards
Role of proto-oncogenes in normal cell division
Acts as a silenced oncogene. Stimulates cell divisions through coding for proteins that activate and regulate cell growth and division.
Acts as controlled accelerator to stimulate mitosis. Works tog with tumor suppressor gene. Drives mitosis.
Acts as controlled accelerator to stimulate mitosis. Works tog with tumor suppressor gene. Drives mitosis.
50
New cards
Role of proto-oncogenes in cancer (abnormal) cell division
A random mutation causes proto-oncogene to become an oncogene through making it overactive and constantly stimulate cells to divide uncontrollably, driving uncontrollable mitosis.
51
New cards
Abnormal methylation (epigenetics) and it’s effect on tumor growth
1. Hypermethylation (too much methyl) of tumor suppressor genes inactivates them through preventing the transcription of the gene, therefore silencing the gene, meaning no mitosis maintenance = cells divide uncontrollably and form a tumor.
2. Hypomethylation (too little methyl) of proto-oncogenes means transcription will turn on the proto-oncogenes = oncogenes, which increases protein production, increasing cell division = tumors.
52
New cards
Genetic risk factors
Some cancers are linked with specific inherited alleles, if offspring inherits that allele they have increased likelihood of developing cancer. E.g. inheriting a mutation on the BRCA 1 gene (tumor suppressor protein producing gene) means stops production or dysfunctional protein production. Increases woman’s likelihood of breast cancer.
53
New cards
Environmental risk factors
Often exposure to carcinogens.
* Ionising radiation (X-rays)
* UV-light
* Smoking
* Increased alcohol consumption
* High-fat diet
* Ionising radiation (X-rays)
* UV-light
* Smoking
* Increased alcohol consumption
* High-fat diet
54
New cards
WHEN INTERPRETING CORRELATIONAL DATA OF CANCER, IDENTIFY IF ENVIRO OR GENETIC.
Correlation =/= causation
Positive or negative correlation
Positive or negative correlation
55
New cards
Tumor suppressor genes role in cancer treatment.
Hint: Drug treatments
Hint: Drug treatments
Drug (AZACITIDINE) taken which inhibits the methylation of tumour suppressor genes so they are not switched off.
Drug inhibits the enzyme needed for methylation which means the tumor suppressor gene functions normally and controls (/ prevents uncontrollable) cell division.
Drug usually used in chemotherapy.
Drug inhibits the enzyme needed for methylation which means the tumor suppressor gene functions normally and controls (/ prevents uncontrollable) cell division.
Drug usually used in chemotherapy.
56
New cards
Oncogenes role in cancer treatment.
Hint: Drug treatments
Hint: Drug treatments
Drugs (HDAC inhibitor drugs) taken which decrease the acetylation of histones which prevent transcription of genes, aka switch them off.
These drugs inhibit enzyme activity which causes acetylation so oncogenes remain switched off and make sure cell division is not constantly stimulated by oncogenes (turned on proto-oncogenes).
Drug usually used in chemotherapy.
These drugs inhibit enzyme activity which causes acetylation so oncogenes remain switched off and make sure cell division is not constantly stimulated by oncogenes (turned on proto-oncogenes).
Drug usually used in chemotherapy.
57
New cards
The Human Genome Project and Sequencing Genomes
The process by which DNA strands are broken down into smaller fragments, the sequence of nucleotide bases is recorded, the fragment is aligned with overlapping segments and then returned back in order to record the sequence of the whole genome.
The Human Genome Project used this process to map all of the genes of the human genome, both from a physical and functional standpoint.
The Human Genome Project used this process to map all of the genes of the human genome, both from a physical and functional standpoint.
58
New cards
What is the use of the Human Genome Project (3)
1. Diagnosis: Development of genetic testing via screening (using gene probes) to identify genes.
2. Prediction: If an errant gene is detected in the genome, the linked disease can be predicted and doctors can advise patients on next steps and risks of genetic disorders (genetic counselling).
3. Treatment: Development of gene therapy through gene replacement, supplementing or adding genes.
59
New cards
Evaluations of the Human Genome Project (4)
Ethical, Legal and Social Issues
Ethical, Legal and Social Issues
* Who has access to the genetic information \~ if health insurance insurance providers have access of the info they may increase costs of insurance for those who need it.
* Who has control over the genetic information \~ power holder??
* Who actually owns the genes and genetic info \~ ppl who discover it or the people it comes from??, grey area
* What regulations do the gov have to put in place to secure the genetic info
* Who has control over the genetic information \~ power holder??
* Who actually owns the genes and genetic info \~ ppl who discover it or the people it comes from??, grey area
* What regulations do the gov have to put in place to secure the genetic info
60
New cards
Sequencing proteomes
Recording all of the proteins the genome (DNA) can code for via identification of all coding DNA and what that DNA codes for.
61
New cards
Proteomes in simple organisms - e.g. bacteria
Only contain coding DNA so its much easier to determine the proteome from the genome as they are likely to be the same.
If we identify the proteome in simple organisms, as AA code is universal, we can identify much of the proteome in more complex organisms.
If we identify the proteome in simple organisms, as AA code is universal, we can identify much of the proteome in more complex organisms.
62
New cards
Proteomes in complex organisms
Contain both exons and introns (non-coding DNA) and regulatory genes so its more difficult to translate the genome to the proteome as we don’t know what sections code for functional proteins and which are non-coding \~ 99% non-coding.
So far, 30,000< human proteins have been identified.
So far, 30,000< human proteins have been identified.
63
New cards
What is the uses of knowing the proteome of a bacteria?
Practical Application
Practical Application
Allows the identification of proteins acting as antigens on the surface of pathogens which can be used to generate vaccines faster without before the bacteria infects humans.
64
New cards
Sanger sequencing (for genome and proteome)
* Expensive
* Labour intensive and requires lots of effort
* Small scale
* A slow process
* Labour intensive and requires lots of effort
* Small scale
* A slow process
65
New cards
Pyrosequencing (for genome and proteome)
* Cost-effective
* Automated so doesnt require loads of work
* Large scale operation
* Faster (produces 400 mil base pairs in 10 hrs)
* Automated so doesnt require loads of work
* Large scale operation
* Faster (produces 400 mil base pairs in 10 hrs)
66
New cards
Recombinant DNA tech
Used to transfer DNA fragments from one organisms to another, from doner organism to transgenic organism.
Steps: Isolation, Insertion, Transformation / Identification (transfer to host) and Growth.
There are many different ways of gene isolation and insertion of fragments.
Steps: Isolation, Insertion, Transformation / Identification (transfer to host) and Growth.
There are many different ways of gene isolation and insertion of fragments.
67
New cards
What are the 3 ways of gene isolation / DNA fragment production?
1. Reverse Transcriptase
2. Restriction Endonuclease Enzyme~~s~~
3. Gene Machine
68
New cards
What are the 2 ways of insertion + what is in insertion?
Insertion = Amplification (increasing amnt) of DNA fragments and insertion into vector.
1. Invivo cloning
2. Invitro cloning
1. Invivo cloning
2. Invitro cloning
69
New cards
How does reverse transcriptase contribute to making cDNA fragments?
Desired proteins are usually manufactured in specific cells in the body, meaning those cells will contains large amounts of mRNA for protein production.
Reverse Transcriptase is added to the cell and drives DNA production by matching specific DNA bases with complimentary mRNA bases to produce complimentary DNA (cDNA).
DNA polymerase then acts on the cDNA template to pair complementary DNA bases, forming a double cDNA strand (gene) which codes for the required protein.
mRNA used as only contains exons / no introns so cDNA produced is all coding.
Reverse Transcriptase is added to the cell and drives DNA production by matching specific DNA bases with complimentary mRNA bases to produce complimentary DNA (cDNA).
DNA polymerase then acts on the cDNA template to pair complementary DNA bases, forming a double cDNA strand (gene) which codes for the required protein.
mRNA used as only contains exons / no introns so cDNA produced is all coding.
70
New cards
How does using restriction endonuclease enzymes create DNA fragments?
Via use on palindromic sequences (usually 4-8 bases long) as specific recognition sites.
* Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific recognition sequences to cut out the desired gene from rest of genome.
* The recognition site is complementary to the enzyme active site so diff enzymes cut diff recognition sites.
* Cuts are done via hydrolysis \~ create either sticky or blunt ends cut.
* Restriction endonucleases cut DNA at specific recognition sequences to cut out the desired gene from rest of genome.
* The recognition site is complementary to the enzyme active site so diff enzymes cut diff recognition sites.
* Cuts are done via hydrolysis \~ create either sticky or blunt ends cut.
71
New cards
What is a sticky ends cut?
A staggered cut across a palindromic sequence, leaving fragments of exposed DNA w/ unpaired bases.
The unpaired bases can then re-join another palindromic sequence sticky ends to complete whole genome with desired gene removed.
The unpaired bases can then re-join another palindromic sequence sticky ends to complete whole genome with desired gene removed.
72
New cards
How does a Gene Machine produce DNA fragments?
No requirement for a DNA template as uses a database of discovered DNA fragments to synthesise any nucleotide sequence inputted into connected computer / the machine.
Much faster process as no template needed.
Much faster process as no template needed.
73
New cards
Describe **In Vivo** cloning as a method of amplification.
Gene copies are made within a living organism (vector) who replicates the DNA and creates multiple copies.
Restriction endonucleases cut open the vector to create sticky ends.
The same restriction endonucleases cut the target gene to produce the same sticky ends to be complementary to the vector DNA.
The gene is then inserted into the vector (usually a plasmid from bacteria), hydrogen bonds are formed between complementary bases and DNA ligase seals the strands via connecting the sugar phosphate backbones).
Promoter and Terminator regions are also added to / already present in the vector = make sure the transformed host cell produces protein coded by recombinant DNA.
Restriction endonucleases cut open the vector to create sticky ends.
The same restriction endonucleases cut the target gene to produce the same sticky ends to be complementary to the vector DNA.
The gene is then inserted into the vector (usually a plasmid from bacteria), hydrogen bonds are formed between complementary bases and DNA ligase seals the strands via connecting the sugar phosphate backbones).
Promoter and Terminator regions are also added to / already present in the vector = make sure the transformed host cell produces protein coded by recombinant DNA.
74
New cards
Promoter region
A sequence of nucleotides which tells the RNA polymerase to stop transcribing.
Similar to a stop codon.
Similar to a stop codon.
75
New cards
What happens after In Vivo amplification?
\~ transformation of the cells and identification of transformed cells
\~ transformation of the cells and identification of transformed cells
__Cell transformation__
The vector (usually plasmid) containing the recombinant DNA is then transferred into a host cell (usually bacteria). When host cell takes in vector = transformed cell.
__Transformed Cell Identification__
As not all host cells take up the vector, a marker gene is added to identify the transformed cell, such as a **GFP gene** which turns the cell fluorescent under UV or a gene for antibiotic resistance.
Enviros are then created to test flourencence and/or antibiotic resistance.
The vector (usually plasmid) containing the recombinant DNA is then transferred into a host cell (usually bacteria). When host cell takes in vector = transformed cell.
__Transformed Cell Identification__
As not all host cells take up the vector, a marker gene is added to identify the transformed cell, such as a **GFP gene** which turns the cell fluorescent under UV or a gene for antibiotic resistance.
Enviros are then created to test flourencence and/or antibiotic resistance.
76
New cards
How does transferal of recombinant DNA containing vector occur? (3 ways)
1. Host cell placed in Calcium Chloride to make its cell wall more permeable for insertion.
2. Electroporation \~ electric shocks given to host cell to create a hole(s) for recombinant vector to pass through.
3. Bacteriophage injects vector into host cell (injects recombinant plasmid DNA into bacteria).
77
New cards
How do marker genes work?
Marker gene added into the vector (plasmid) w/ the target gene.
Host cells are then grown on an agar plate (culture) where cell division and DNA replication occurs \~ colony is created.
Transformed cells then show signs of marker gene if successfully accepted recombinant DNA.
Those cells are then identified, removed and allowed to grow more, cloned and used.
Host cells are then grown on an agar plate (culture) where cell division and DNA replication occurs \~ colony is created.
Transformed cells then show signs of marker gene if successfully accepted recombinant DNA.
Those cells are then identified, removed and allowed to grow more, cloned and used.
78
New cards
Describe In Vitro cloning as a method of amplification + PCR definition.
Copies of DNA fragments are produced outside a living organism, using the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR).
PCR produces large amounts of identical DNA from a very small sample via repeated replication of DNA in a test tube, doubling DNA amount each time (exponential growth). Each cycle = 5 mins and 20-30 cycles processed to analysed.
PCR produces large amounts of identical DNA from a very small sample via repeated replication of DNA in a test tube, doubling DNA amount each time (exponential growth). Each cycle = 5 mins and 20-30 cycles processed to analysed.
79
New cards
DNA Primers
Artificially synthesised single stranded DNA (abt 20 bases) complementary to the bases at the start of the region to be replicated (desired fragment).
Provides starting sequence for Taq Polymerase to begin copying.
Provides starting sequence for Taq Polymerase to begin copying.
80
New cards
DNA Polymerase used in PCR
Taq polymerase which lines up free nucleotides along each template strand & joins them together. Can withstand high temperatures so when reaction mixture is heated, it doesn’t denature.
81
New cards
Describe the Polymerase Chain Reaction \~ PCR (4)
1. DENATURING: Hydrogen bonds are broken and double helix is separated through heating DNA to 95°. Reaction Mixture is added (containing DNA Polymerase, multiple of 4 diff nucleotides and DNA primers).
2. ANNEALING: Primers then anneal (bind) to 2 exposed separated DNA strands through allowing the mixture to cool between 50°-65°. Primers facilitate the binding of DNA Polymerase which starts to attach nucleotides to the existing chain \~ DNA replication.
3. EXTENSION: Mixture is re-heated to DNA Polymerase (Taq) optimum working temp, 72°, to speed up process of attaching complementary base pairs tog via specific base pairings.
4. REPEAT: Whole process starts again when mixture is (re-)heated to 95° and amount of DNA continues to grow exponentially by doubling each time.
82
New cards
How to calculate the amount of DNA produced?
Amnt of DNA = 2^no. of cycles / no. of times doubled.
83
New cards
Graph to show DNA production by In Vivo Amplification.
DNA doubles each cycle, to a point where it plateaus. The plateau is caused due to Primers being a limiting factor as it is used up, causing DNA replication to stop.
Nucleotide abundance can also be a limiting factor but less likely.
Nucleotide abundance can also be a limiting factor but less likely.
84
New cards
Examples of Genetic Modification via In Vivo Amplification (2)
1. Plants: Gene coding for desirable protein inserted into plasmid. Plasmid added to bacteria vector w/ correct promoter region for correct integration into plant. bacteria inserted into plant and new desired protein produced.
2. Gene coding for desirable protein inserted into early animal embryo or egg cell. This means all body cells created from embryo / egg will be transformed and contain desired gene. Promoter regions in specific body cells will facilitate transcription of desired gene at specific locations where needed and organism is not damaged.
All transformed organisms = Genetically Modified (GM).
85
New cards
Advantages and Disadvantages for using recombinant DNA in agriculture
\+ Crops transformed to give higher yield and be more nutritious \~ reduce famine and malnutrition.
\+ Genetically Modified to have drought, herbicide and pest resistance so there is less need for pesticides and reduces costs and enviro problems (e.g. eutrophication via pesticide runoff).
\- Promotes monoculture, only grows 1 type of genetically identical crop which increases vulnerability to disease and reduced biodiversity.
\- Threat of superweeds if resistance to herbicide recombinant DNA spreads to weeds. Unknown consequences.
\- Organic farmer crop contamination, via wind blown seeds from GM crops = farmers can’t sell as no longer organic = reduced income.
\+ Genetically Modified to have drought, herbicide and pest resistance so there is less need for pesticides and reduces costs and enviro problems (e.g. eutrophication via pesticide runoff).
\- Promotes monoculture, only grows 1 type of genetically identical crop which increases vulnerability to disease and reduced biodiversity.
\- Threat of superweeds if resistance to herbicide recombinant DNA spreads to weeds. Unknown consequences.
\- Organic farmer crop contamination, via wind blown seeds from GM crops = farmers can’t sell as no longer organic = reduced income.
86
New cards
Advantages and Disadvantages for using recombinant DNA in industry
\+ Enzymes can be extracted from transformed organisms to be used in industry, e.g. GM enzymes used in cheese-making = less animal death to obtain it + cheaper production for more.
\+ Large quantities of proteins can be produced efficiently and with reduced costs.
\- GM used to purify proteins may lead to intro of toxins in food industry if GM is not labeled (some strict labeling rules).
\- If GM tech increases use in large corporations, smaller businesses may be out-competed and run out of business and large companies further increase power over others.
\+ Large quantities of proteins can be produced efficiently and with reduced costs.
\- GM used to purify proteins may lead to intro of toxins in food industry if GM is not labeled (some strict labeling rules).
\- If GM tech increases use in large corporations, smaller businesses may be out-competed and run out of business and large companies further increase power over others.
87
New cards
Advantages and Disadvantages for using recombinant DNA in medicine
\+ Drugs and vaccines extracted from transformed organisms using recombinant DNA tech. E.g. insulin = transformed microorganism > animal pancreas.
\+ Quick, cheap and large production scale vaccines = more available and affordable to population.
\- GE tech owning companies may limit use in order to gain more profit, not as many lives saved.
\- Endless possibilities for GM, may be used unethically. E.g. Designer babies = pick and choose best traits.
\- Grey area as to who owns the genetic material from humans once removed from body.
\- Use and construction of technology is expensive.
\+ Quick, cheap and large production scale vaccines = more available and affordable to population.
\- GE tech owning companies may limit use in order to gain more profit, not as many lives saved.
\- Endless possibilities for GM, may be used unethically. E.g. Designer babies = pick and choose best traits.
\- Grey area as to who owns the genetic material from humans once removed from body.
\- Use and construction of technology is expensive.
88
New cards
What is genetic fingerprinting?
The process of identification of DNA sequences through using exon and intron comparison between different organisms
89
New cards
5 uses if genetic fingerprinting
* To determine a genetic relationship (paternity tests); inherit VNTRs from parents so half the sequencing comes from 1 parent and other half comes from another parent.
* Determine genetic variability within a population; greater number of bands not matching between genetic fingerprints = more genetically different / more variation.
* In forensic science; compare DNA samples from crime scene to database for id.
* Medical diagnosis; Genetic fingerprint = unique pattern of several alleles which can be used to identify cancers.
* Animal + plant selective breeding; Prevention of inbreeding as id which organisms are closely related so that gene pool is varied. + pedigree (animal parent test).
* Determine genetic variability within a population; greater number of bands not matching between genetic fingerprints = more genetically different / more variation.
* In forensic science; compare DNA samples from crime scene to database for id.
* Medical diagnosis; Genetic fingerprint = unique pattern of several alleles which can be used to identify cancers.
* Animal + plant selective breeding; Prevention of inbreeding as id which organisms are closely related so that gene pool is varied. + pedigree (animal parent test).
90
New cards
What are VNTRs and functions
Variable number tandem repeats which are base sequences that don’t code for a protein (introns) and repeat next to each other multiple times. Number of repeats varies between individuals.
91
New cards
How do VNTRs contribute to genetic fingerprinting?
Through the comparison of number of repeats at different places in an organism used as identification for that organism.
92
New cards
Names overview of 3 process contribute to genetic fingerprinting?
1. Restriction enzymes used to make DNA fragments containing VTNRs + amplification using PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction)
2. DNA fragments places in gel electrophoresis
3. DNA fragments / proteins compared to known samples / ladders.
93
New cards
Detailed overview of Genetic Fingerprinting (4)
STEP 1 (Extraction): Obtaining a sample of DNA
* Sample of blood, hair, caliva, semen etc. obtained
* PCR initiated to make copies containing desired VNTRs.
* Primers are then added which bind to either side of VNTRs
\
STEP 2: Add fluorescent tags + cut
* Fluorescent tag added so they’re visible under UV light.
* OR radioactive probes are added which bind to specific VNTR sequences
* Restriction enzymes are then added which cuts DNA into different sized fragments, determined by number of repeats (of VNTR) the person has at each specific enzyme cutting position.
\
STEP 3: Gel electrophoresis
* Fragments are then separated using GE.
* DNA fragments injected into wells of gel and electric current is applied.
* DNA = -ve charged so is attracted to positive end of gel.
* Shorter + lighter fragments move towards +ve electrodes faster. Longer + heavier fragments move slower.
* Patterns of bands are formed; shorter = further along in set time than longer.
\
STEP 4: View under UV + comparison
* Fluorescence tag added prev allows fragments to be viewed under UV which allows comparison of 2 fingerprints. Same binding = match.
* OR radioactive probes used prev means fragments viewed using x-ray film.
* Sample of blood, hair, caliva, semen etc. obtained
* PCR initiated to make copies containing desired VNTRs.
* Primers are then added which bind to either side of VNTRs
\
STEP 2: Add fluorescent tags + cut
* Fluorescent tag added so they’re visible under UV light.
* OR radioactive probes are added which bind to specific VNTR sequences
* Restriction enzymes are then added which cuts DNA into different sized fragments, determined by number of repeats (of VNTR) the person has at each specific enzyme cutting position.
\
STEP 3: Gel electrophoresis
* Fragments are then separated using GE.
* DNA fragments injected into wells of gel and electric current is applied.
* DNA = -ve charged so is attracted to positive end of gel.
* Shorter + lighter fragments move towards +ve electrodes faster. Longer + heavier fragments move slower.
* Patterns of bands are formed; shorter = further along in set time than longer.
\
STEP 4: View under UV + comparison
* Fluorescence tag added prev allows fragments to be viewed under UV which allows comparison of 2 fingerprints. Same binding = match.
* OR radioactive probes used prev means fragments viewed using x-ray film.
94
New cards
What are gene (DNA) probes? + use
Simple, short, single-stranded sections of DNA which have a specific base sequence complementary to a specific target allele and are radioactively of fluorescently labeled.
Probes hybridise (bind) to complementary sequence on target allele meaning it is easily identifiable under x-ray film or UV light.
Probes hybridise (bind) to complementary sequence on target allele meaning it is easily identifiable under x-ray film or UV light.
95
New cards
DNA hybridisation
2 complementary single stranded DNA molecules form a double stranded molecule through base pairings.
96
New cards
How are DNA probes used? (to identify presence of mutated allele)
* DNA sample is broken up into smaller fragments via restriction enzymes and separated via gel electrophoresis.
* DNA probe sequenced (synthesised) to be complimentary to mutant allele of gene trying to be identified. + Probe fluorescently labelled.
* PCR used to produce multiple copies of probe.
* Sample DNA heated to separate strands. Probe is then added to the single stranded DNA. Probe then hybridises to complementary bases of mutated allele, if present.
* UV light shone on membrane and if mutated sequence present, fluorescent band will show.
* DNA probe sequenced (synthesised) to be complimentary to mutant allele of gene trying to be identified. + Probe fluorescently labelled.
* PCR used to produce multiple copies of probe.
* Sample DNA heated to separate strands. Probe is then added to the single stranded DNA. Probe then hybridises to complementary bases of mutated allele, if present.
* UV light shone on membrane and if mutated sequence present, fluorescent band will show.
97
New cards
Uses of DNA probes.
Screening for genetic diseases:
* Identify inherited conditions (huntingtons or cystic fibrosis)
* Determine how patient may respond to drugs (cancer tratements)
* Identification of health risks, presence of particular mutated alleles (risk of developing cancer??)
* Development of specific drug therapies or treatments that suit patient
\
Genetic counselling: used with screenings
* Patients advised by specialists about next steps if at risk of a genetic disorder.
* Aid in decision makings over treatments and childbirth.
* Identify inherited conditions (huntingtons or cystic fibrosis)
* Determine how patient may respond to drugs (cancer tratements)
* Identification of health risks, presence of particular mutated alleles (risk of developing cancer??)
* Development of specific drug therapies or treatments that suit patient
\
Genetic counselling: used with screenings
* Patients advised by specialists about next steps if at risk of a genetic disorder.
* Aid in decision makings over treatments and childbirth.
98
New cards
Examples of types of advice given by genetic counselors after a cancer screening.
* Oncogene mutations; determines the type of cancer so advice given about best type of drug or radiotherapy to use.
* Gene alterations; predicts whether patients are more likely to benefit from certain treatment types.
* Tumor suppressor allele mutations; Advice on lifestyle changes to reduce cancer risk.
* Gene alterations; predicts whether patients are more likely to benefit from certain treatment types.
* Tumor suppressor allele mutations; Advice on lifestyle changes to reduce cancer risk.
99
New cards
Risks of DNA probes
Discrimintation by insurance companies and if employers have to declare results.
100
New cards
What is gene therapy?
Insertion of functional alleles into gametes and zygotes (fertilized egg).
Insertion of functional alleles into body cells.
Insertion via use of vectors (viruses, plasmids or liposomes)
Insertion of functional alleles into body cells.
Insertion via use of vectors (viruses, plasmids or liposomes)