(Biology I) Biomolecules
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
Biomolecules
Molecules found in organisms that are necessary for life
Types of biomolecules
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids
Main function of carbohydrates
Energy and structure for cells
Characteristics of carbohydrates
Water-soluble (hydrophilic)
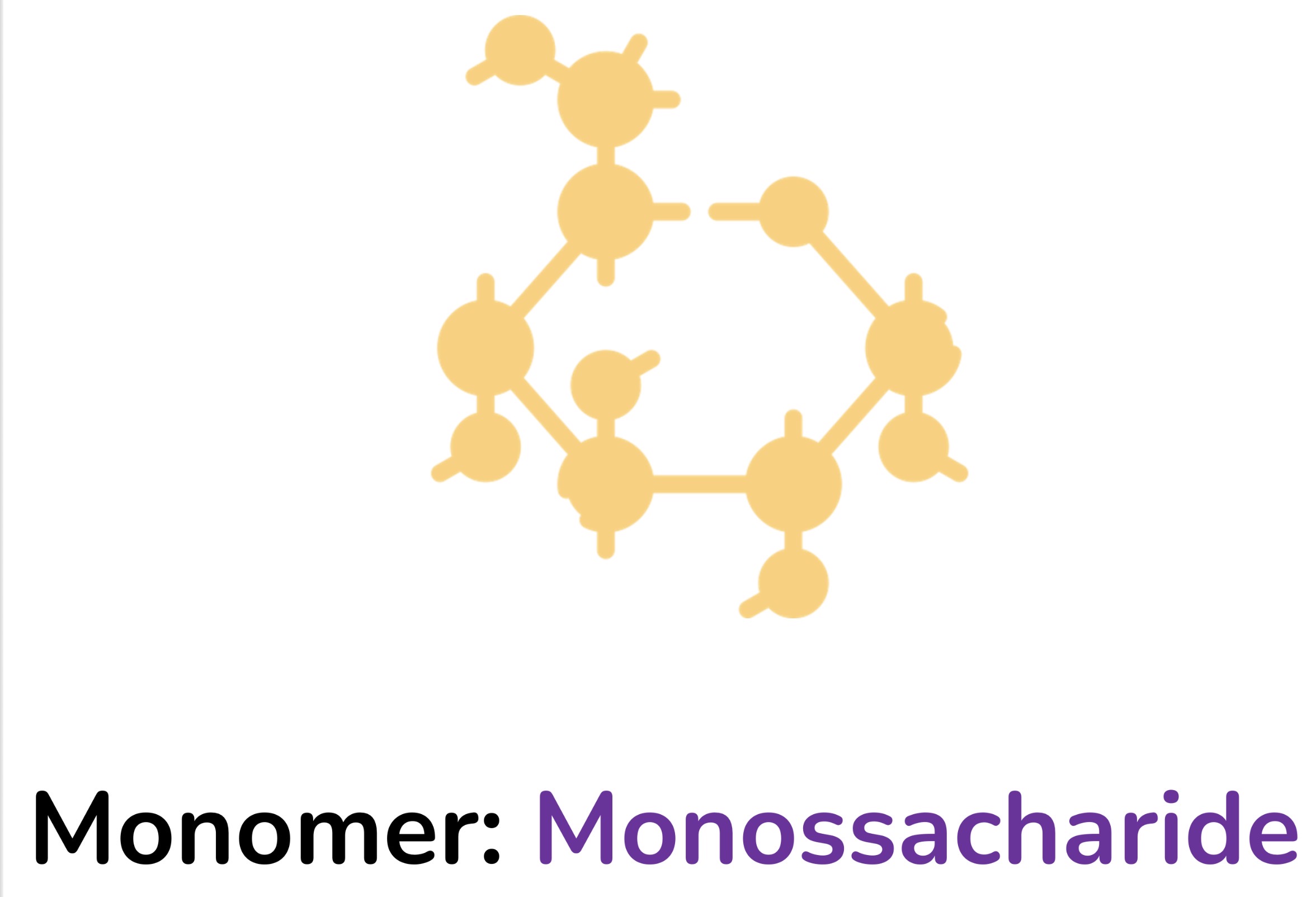
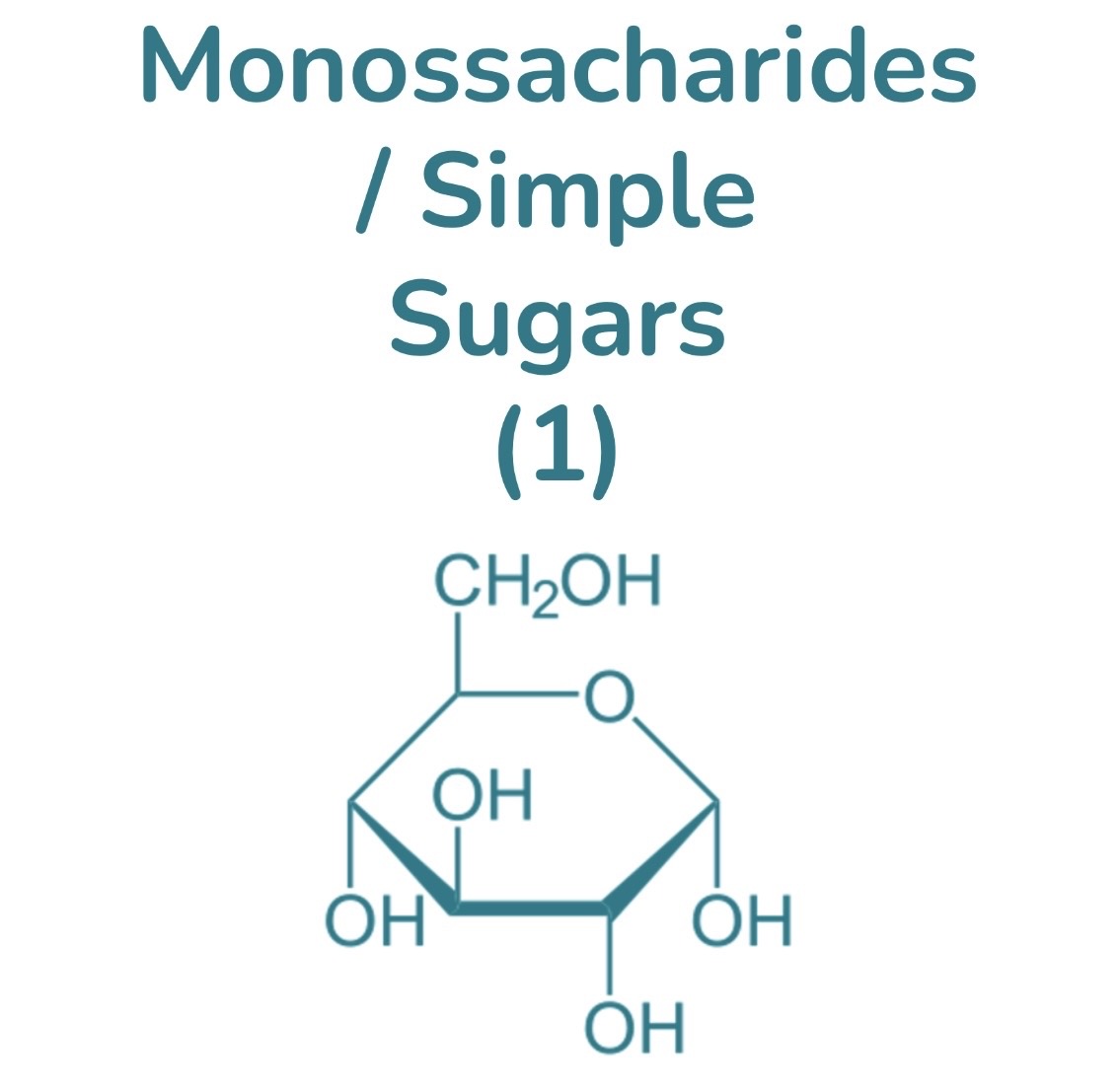
Carbohydrate monomer
Monosaccharide
Classification of Carbohydrates
Monosaccharides, dissacharide, polyssacharide
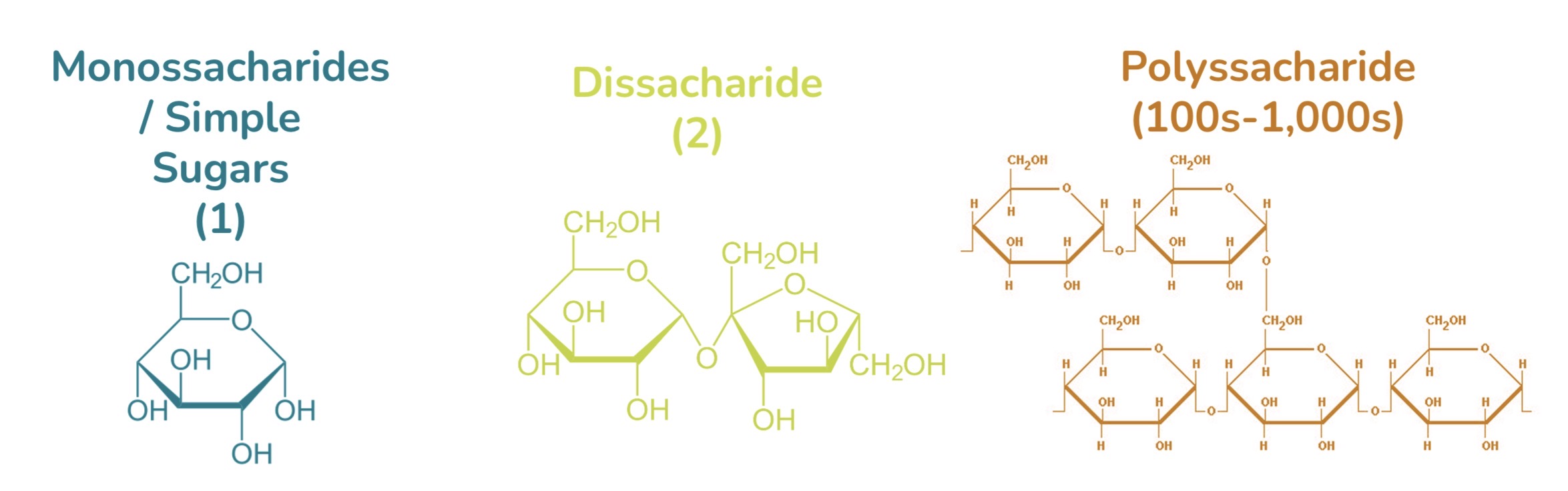
Examples of Carbohydrate monossacharide
Glucose, fructose
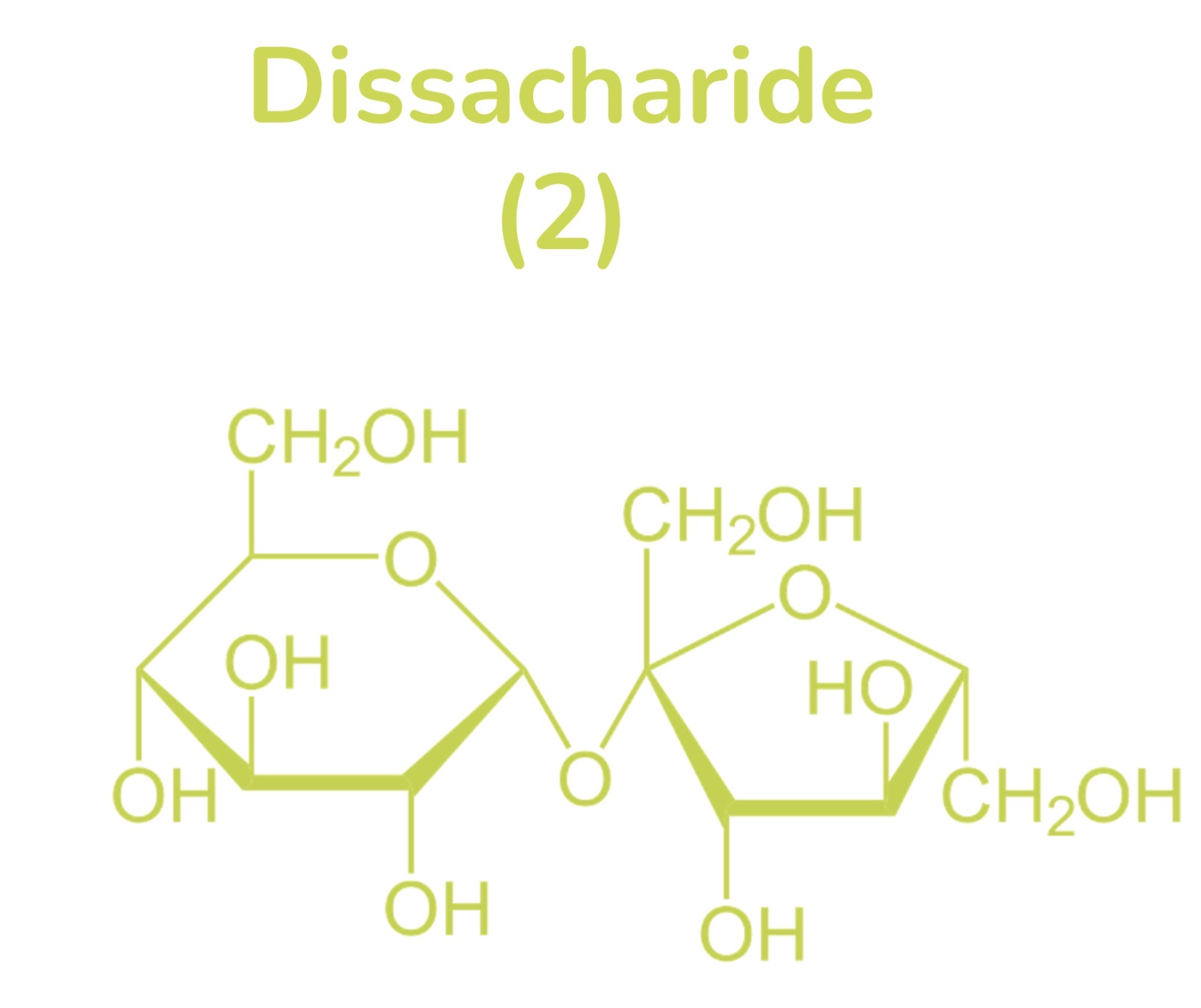
Examples of Carbohydrate dissacharide
Sucrose, lactose
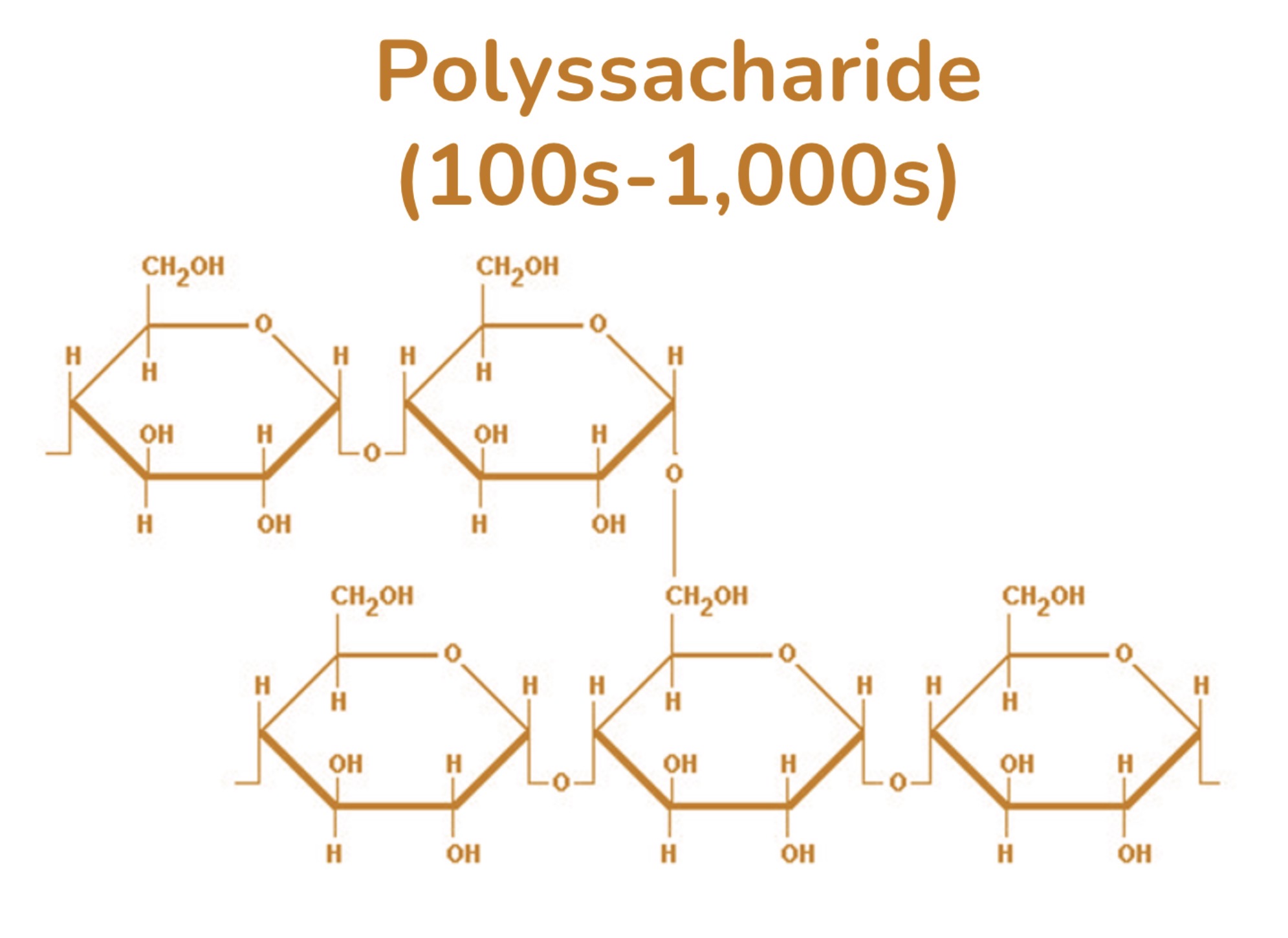
Carbohydrates: Starch (poly)
Storages sugar in plant cells
Carbohydrates: Glycogen (poly)
Stores sugars in animal cells
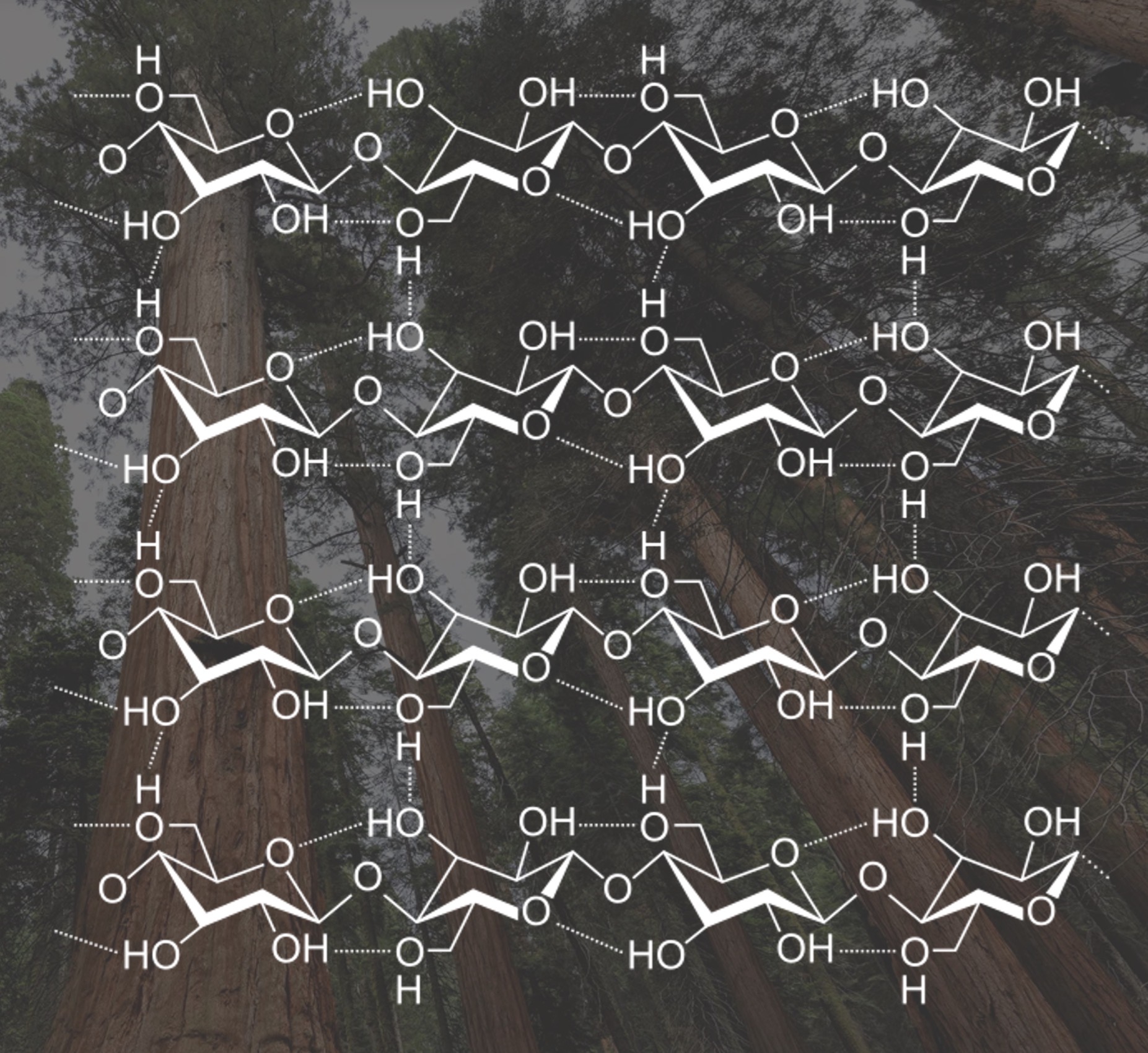
Carbohydrates: Cellulose (poly)
Main structural material of plants
Main function of Lipids (fats)
Long-term energy storage, cell membrane, body protection
Characteristics of Lipids (fats)
Water-insoluble
Lipids (fats) monomers [kinda]
Glycerol (yes wawa) and fatty acids (no wawa)

Classification of Lipids (fats)
Triglycerides, phospholipids, waxes, steroids
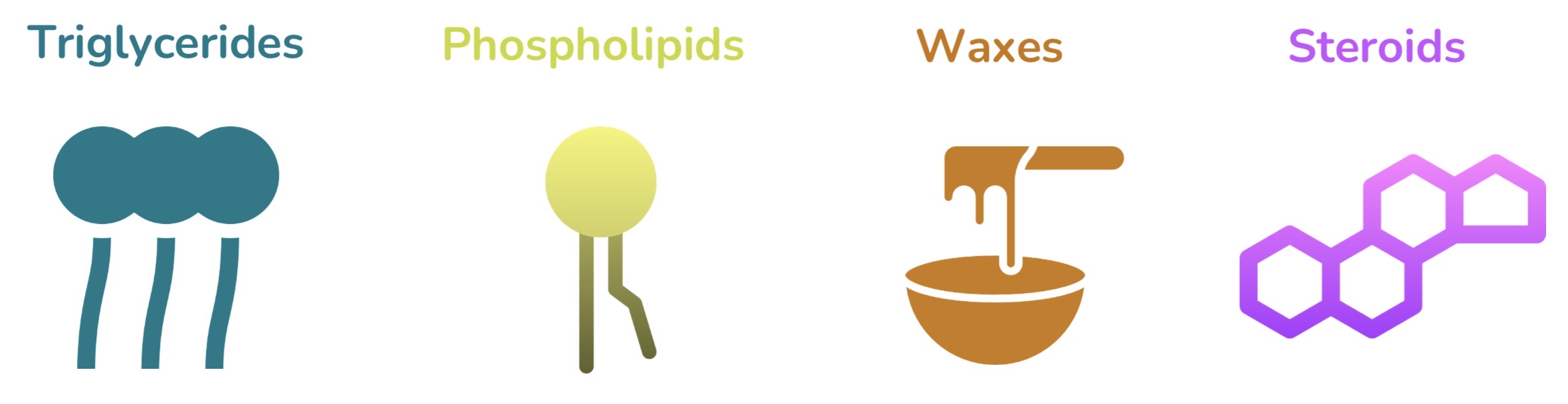
Types of lipids (fats)
Saturated, unsaturated
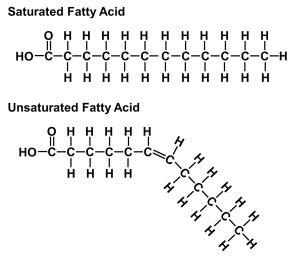
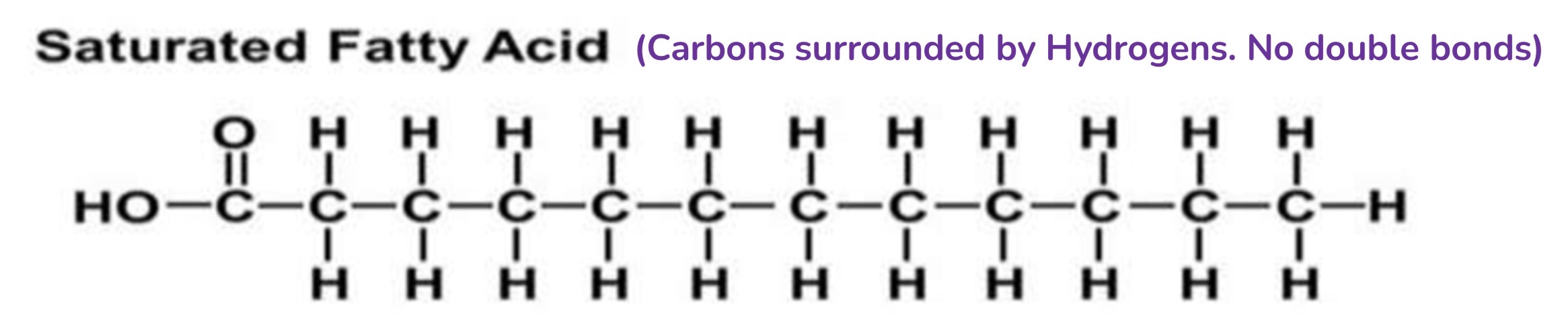
Lipids (fats): Saturated
C surrounded by H. No double bonds
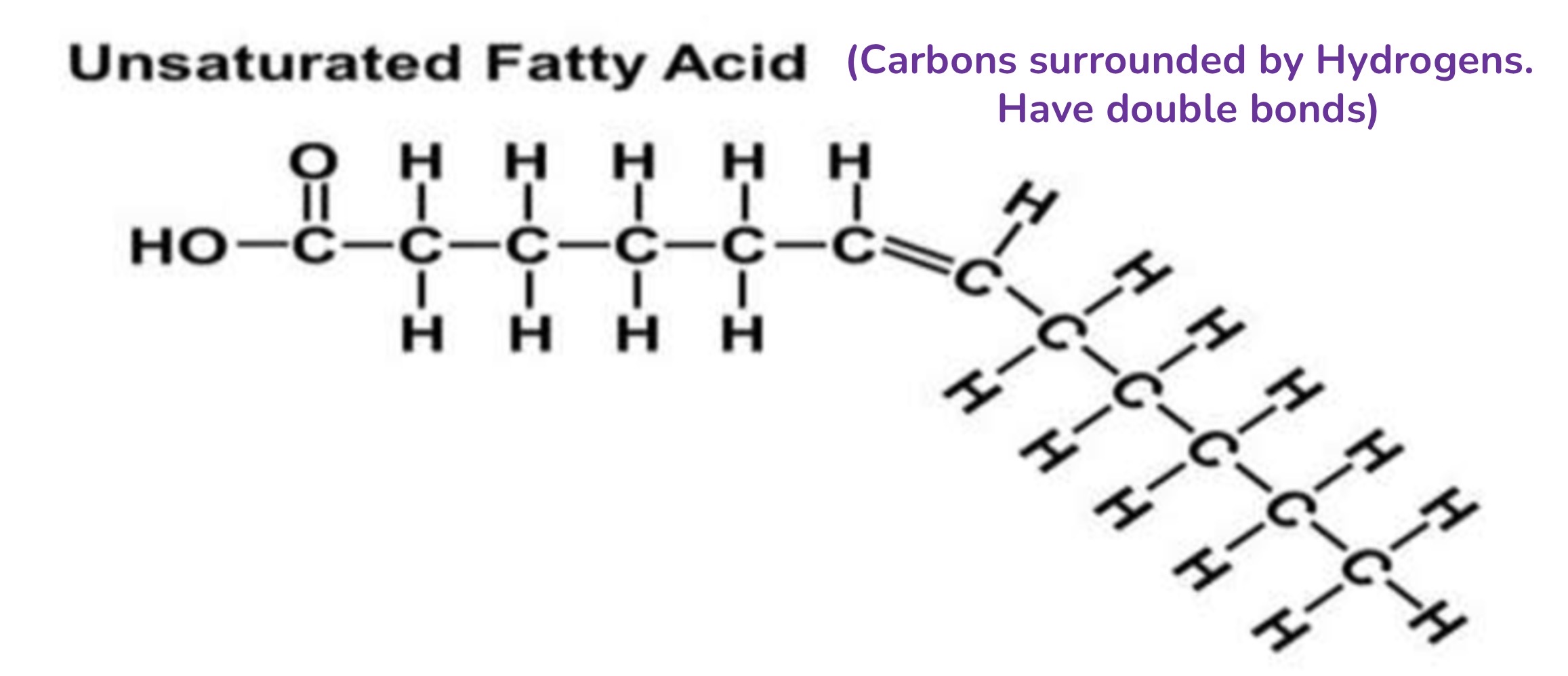
Lipids (fats): Unsaturated
C surrounded by H. With double bonds
Types of unsaturated fats (Lipids)
Cis, trans
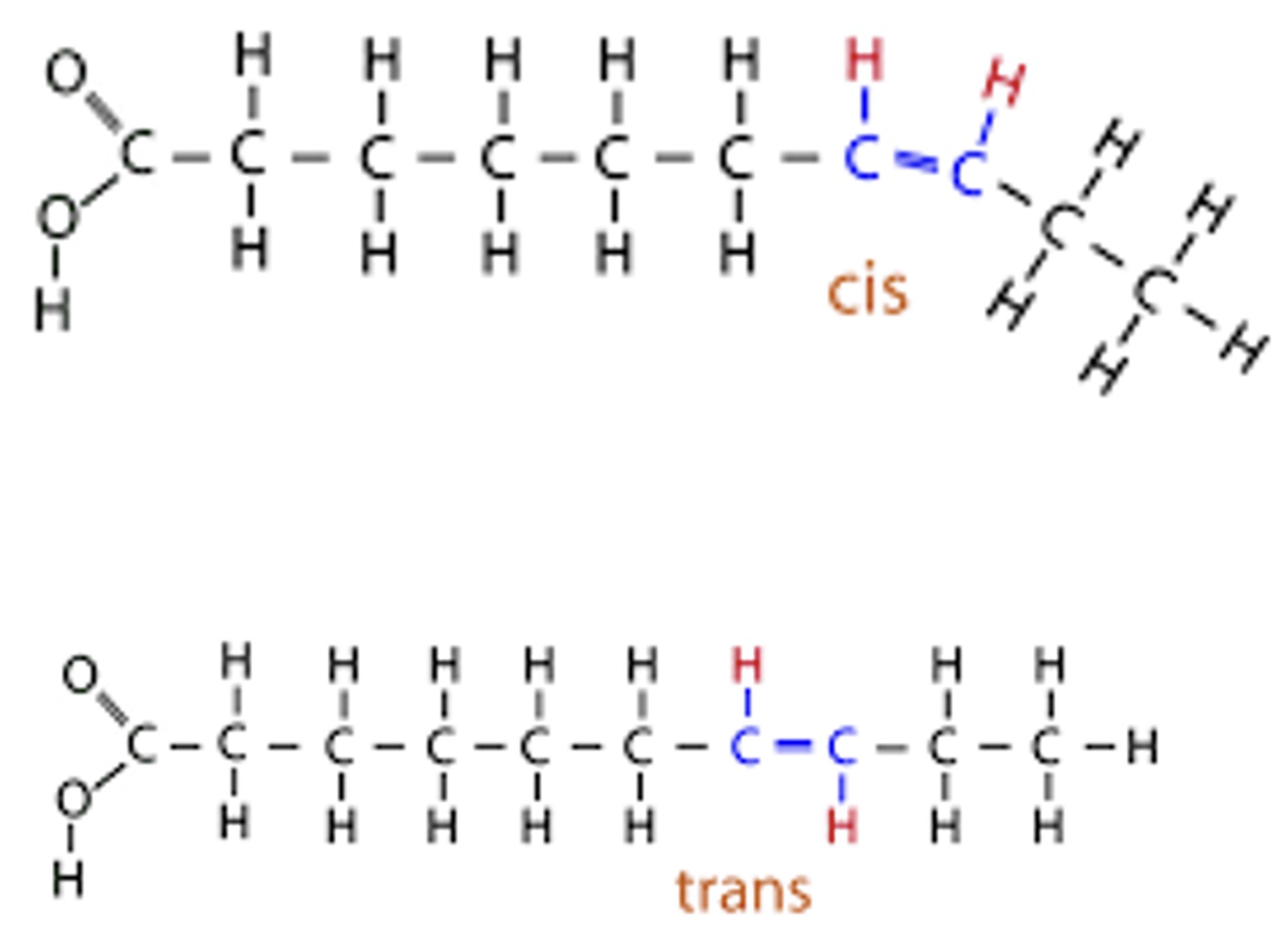
Cis unsaturated fats (Lipids):
Liquid at room temperature, generally heatlhy
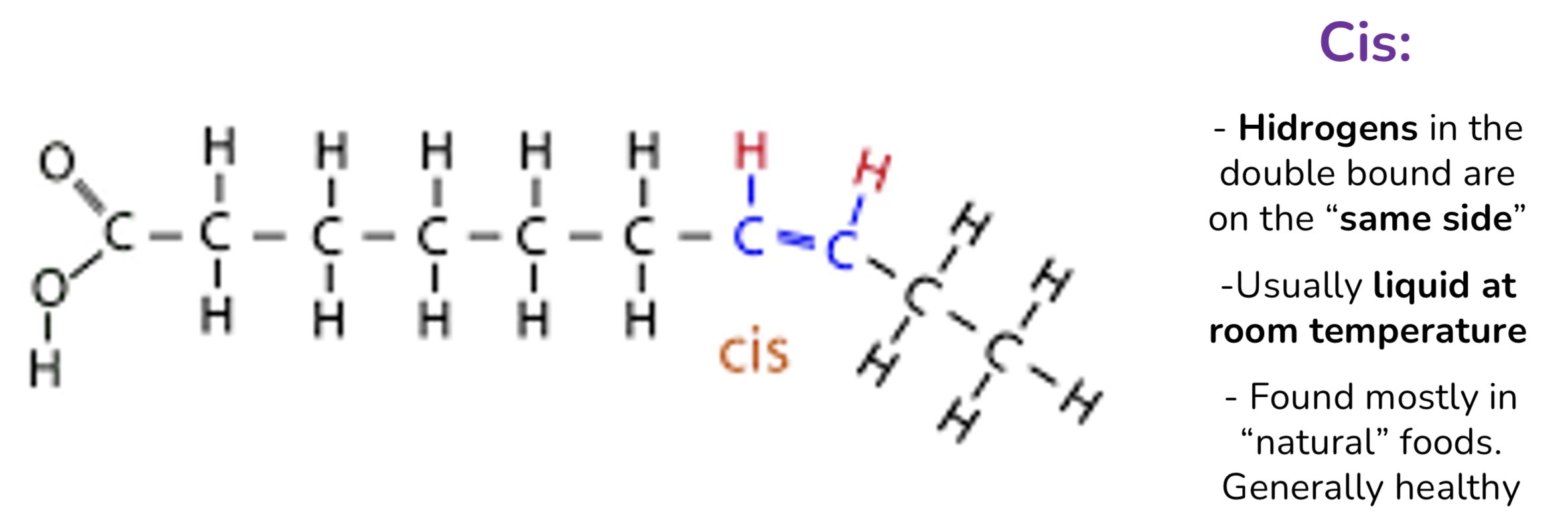
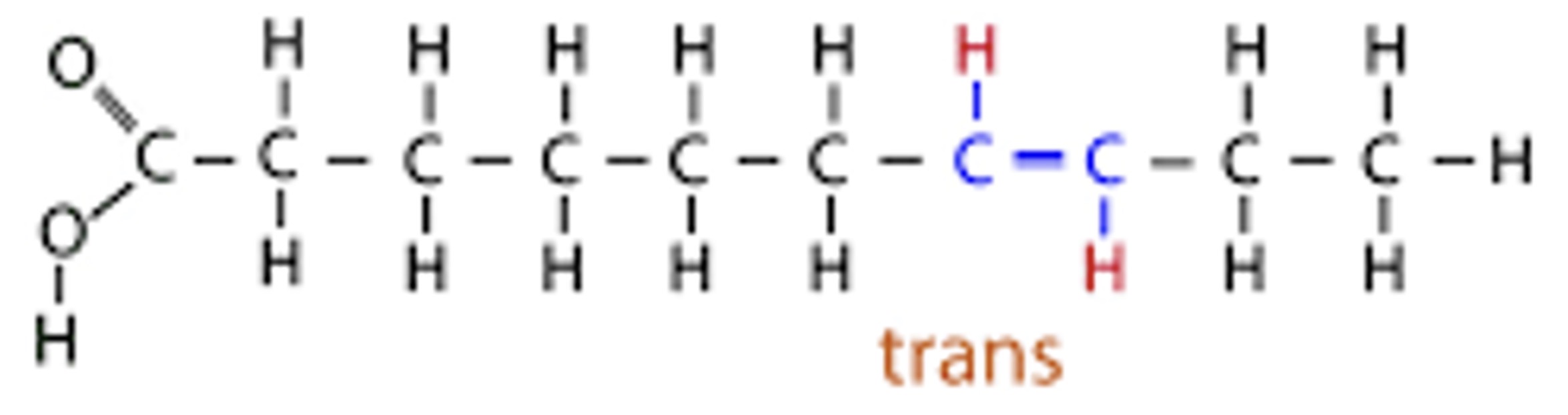
Trans unsaturated fats (Lipids):
Solid at room temperature, mostly artificial
Main function of proteins
Major building block of the body
Protein monomer
Amino acid
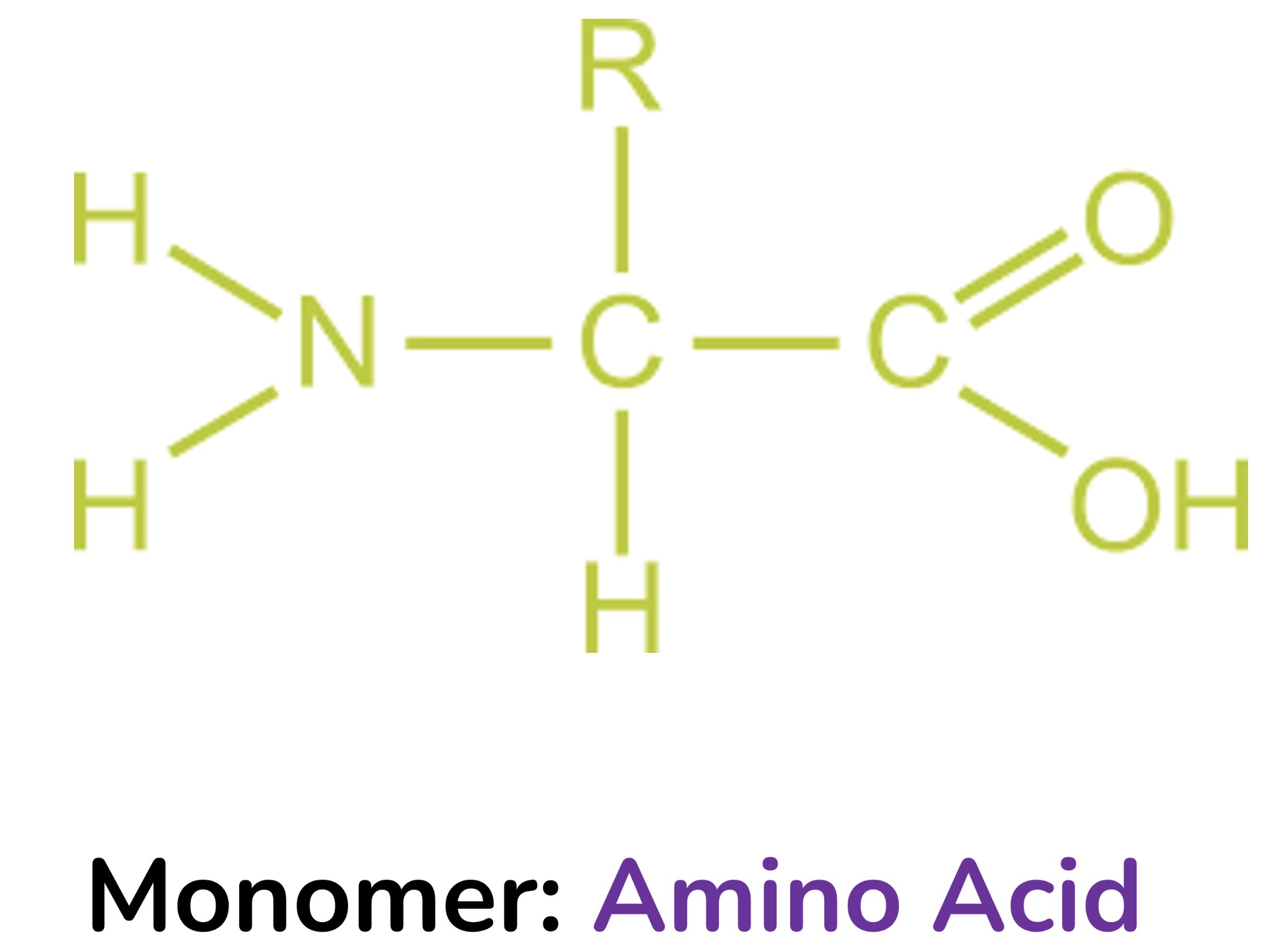
Classification of Protein
Peptide, polypeptide, protein
Protein structures
Primary, secundary, tertiary, quaternary
Main function of Nucleic acids
Store genetic information
Nucleic acids monomer
Nucleotide
Types of Nucleic acids
DNA, RNA