Pharm Pharacokinetics & Pharmacodynamics
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/177
Earn XP
Last updated 3:33 PM on 9/19/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
178 Terms
1
New cards
Increasing natural hormone
How can competitive inhibition be overcome?
2
New cards
inverse agonist (direct)
Agonist that produces less activity than baseline
3
New cards
drug C
Which drug(s) have the lowest potency?
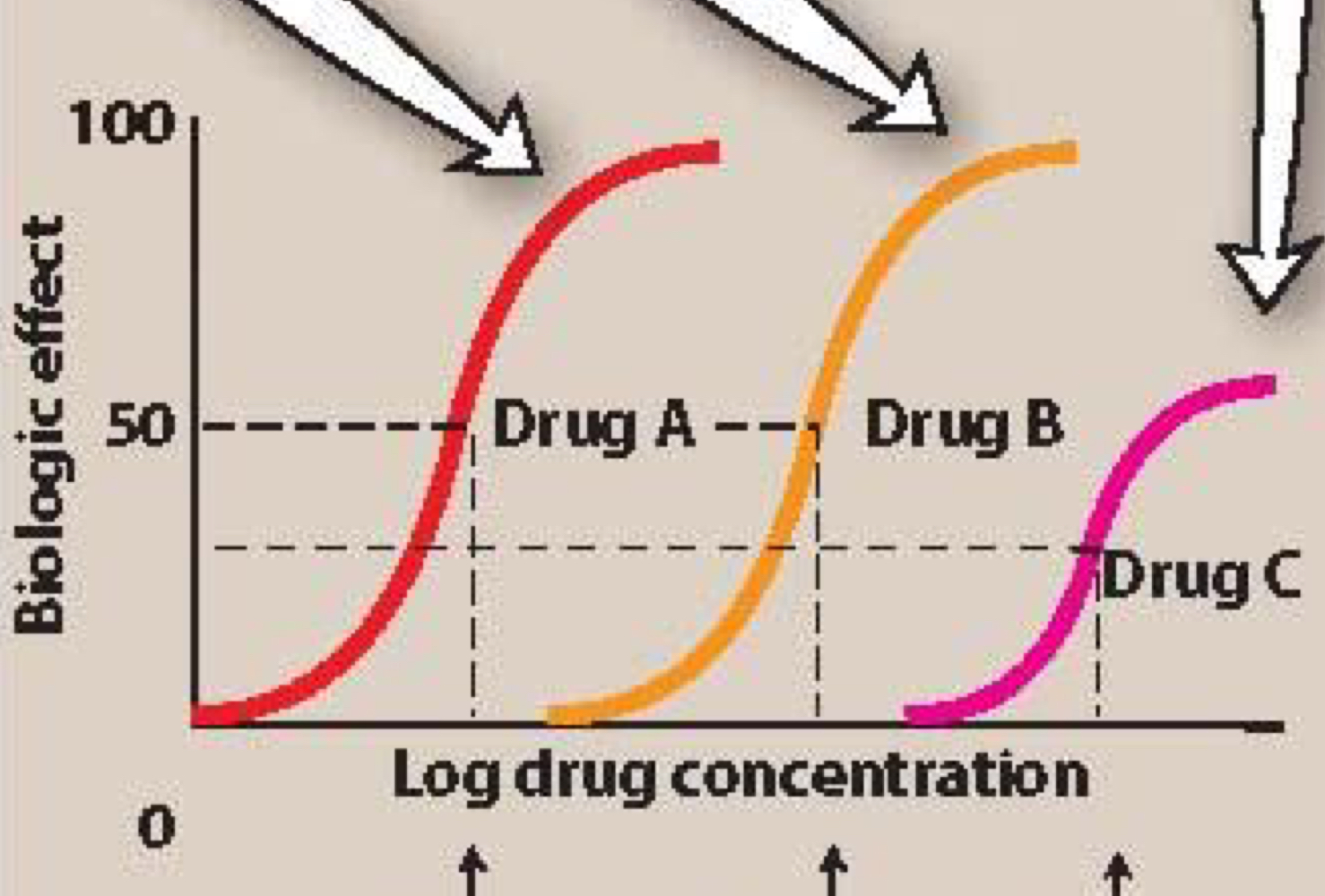
4
New cards
increase
Drug binding the receptor may (increase/decrease) activity of receptor.
5
New cards
cranberry juice
Acidification by _______________ increases trapping of weak base.
6
New cards
sprays
Topical ophthalmic drug administration method used to administer mydriatic drops to closed eyes
7
New cards
ADME
What is the pneumonic to remember the varying pharmacokinetics of how the body acts on the medication?
8
New cards
1. Absorption
2. Distribution
3. Metabolism
4. Excretion
What are the 4 ways in which the body acts on medications?
9
New cards
absorption
Way in which the body acts on medication that involves entry of the drug into the body
10
New cards
distribution
Way in which the body acts on medication that involves the spreading of the drug throughout the body
11
New cards
metabolism
Way in which the body acts on medication that involves the transformation of a drug to a more active form & involves the modification of the drug for elimination
12
New cards
excretion
Way in which the body acts on medication that involves the removal of the drug via urine, feces, or bile
13
New cards
1. Enteral
2. Parenteral
3. Inhalation
4. Intrathecal/Intraventricular
5. Transdermal
6. Rectal
7. Topical
What are the 7 routes of drug administration?
14
New cards
enteral
Route of drug administration defined as either “by mouth” or “by using the GI tract”
15
New cards
1. Oral
2. Sublingual
3. Buccal
What are the 3 methods of enteral route drug administration?
16
New cards
oral
Enteral drug administration where the drug is swallowed by mouth
17
New cards
sublingual
Enteral drug administration where the drug is placed under the tongue
18
New cards
buccal
Enteral drug administration where the drug is placed between the cheek and gum
19
New cards
parenteral
What route of drug administration involves injection?
20
New cards
1. Intravenous (IV)
2. Intramuscular (IM)
3. Subcutaneous (SC)
What are the 3 parenteral types of injection drug administration?
21
New cards
intravenous (IV)
Which route of injection drug administration is very rapid & is completely absorbed?
22
New cards
intramuscular (IM)
What route of injection drug administration may either be rapidly or slowly absorbed?
23
New cards
subcutaneous (SC)
What route of injection drug administration is slower than IV absorption?
24
New cards
larger
A (smaller/larger) gauge indicates a smaller needle.
25
New cards
30-gauge
Ocular/intraocular injections are usually performed using what gauge of needle?
26
New cards
19-23 G
What gauge range of needle is used for intramuscular injections?
27
New cards
25-26 G
What gauge range of needle is used for subcutaneous injections?
28
New cards
25-28 G
What gauge range of needle is used for intravenous injections?
29
New cards
26-28G
What gauge range of needle is used for intradermal injections?
30
New cards
intrathecal/intraventricular
What route of drug administration involves direct administration into the brain?
31
New cards
transdermal
What route of drug administration involves patches being applied to the skin?
32
New cards
topical
What route of drug administration involves local application of medication, often on the skin?
33
New cards
inhalation
What route of drug administration involves oral or nasal drug administration, often with an inhaler?
34
New cards
topical
What route of drug administration is most used in optometry?
35
New cards
rectal
What route of drug administration is involved with suppository use?
36
New cards
oral
What is the safest & most common form of drug administration?
37
New cards
oral
What route of drug administration is susceptible to first pass metabolism (GI tract works on it)?
38
New cards
sublingual administration
What route of oral drug administration bypasses first pass metabolism?
39
New cards
intravenous (IV)
What route of injection drug administration involves direct insertion into the venous system, allowing full absorption into the vascular system?
40
New cards
intravenous (IV)
What route of injection drug administration has no absorption phase?
41
New cards
intramuscular (IM)
What route of injection drug administration has fast absorption, but has a slow, sustained release & works better for patient self administration?
42
New cards
intradermal (ID)
What route of injection drug administration is usually diagnostic & is involved with anesthetic drugs?
43
New cards
subcutaneous (SC)
What route of injection drug administration has a fast absorption & slow, sustained release & may cause local necrosis/inflammation?
44
New cards
subcutaneous (SC)
Insulin is a classic example of drug administration using what injection method?
45
New cards
transdermal
What route of drug administration is slow & sustained & bypasses first past metabolism?
46
New cards
transdermal
What route of drug administration is encompassed with motion sickness and nicotine patches?
47
New cards
inhalation
What route of drug administration has rapid absorption & may lead to systemic absorption?
48
New cards
inhalation
What route of drug administration is very effective for respiratory problems?
49
New cards
inhalation
What route of drug administration is the most addictive drug route?
50
New cards
topical
What route of drug administration has variable absorption, minimizes systemic absorption, and includes ophthalmic & otic?
51
New cards
epidural
What route of drug administration involves spinal injection?
52
New cards
ointment
Abbreviation “ung”
53
New cards
1. Topical
2. Periocular
What are the 2 main ophthalmic drug administration routes?
54
New cards
1. Subconjunctival
2. Sub-Tenon’s
3. Retrobulbar
What are the 3 types of periocular administration of drugs?
55
New cards
1. Sub-conjunctival
2. Sub-Tenon’s capsule
3. Retrobulbar
Identify the labeled methods of periocular drug administration in the figure.
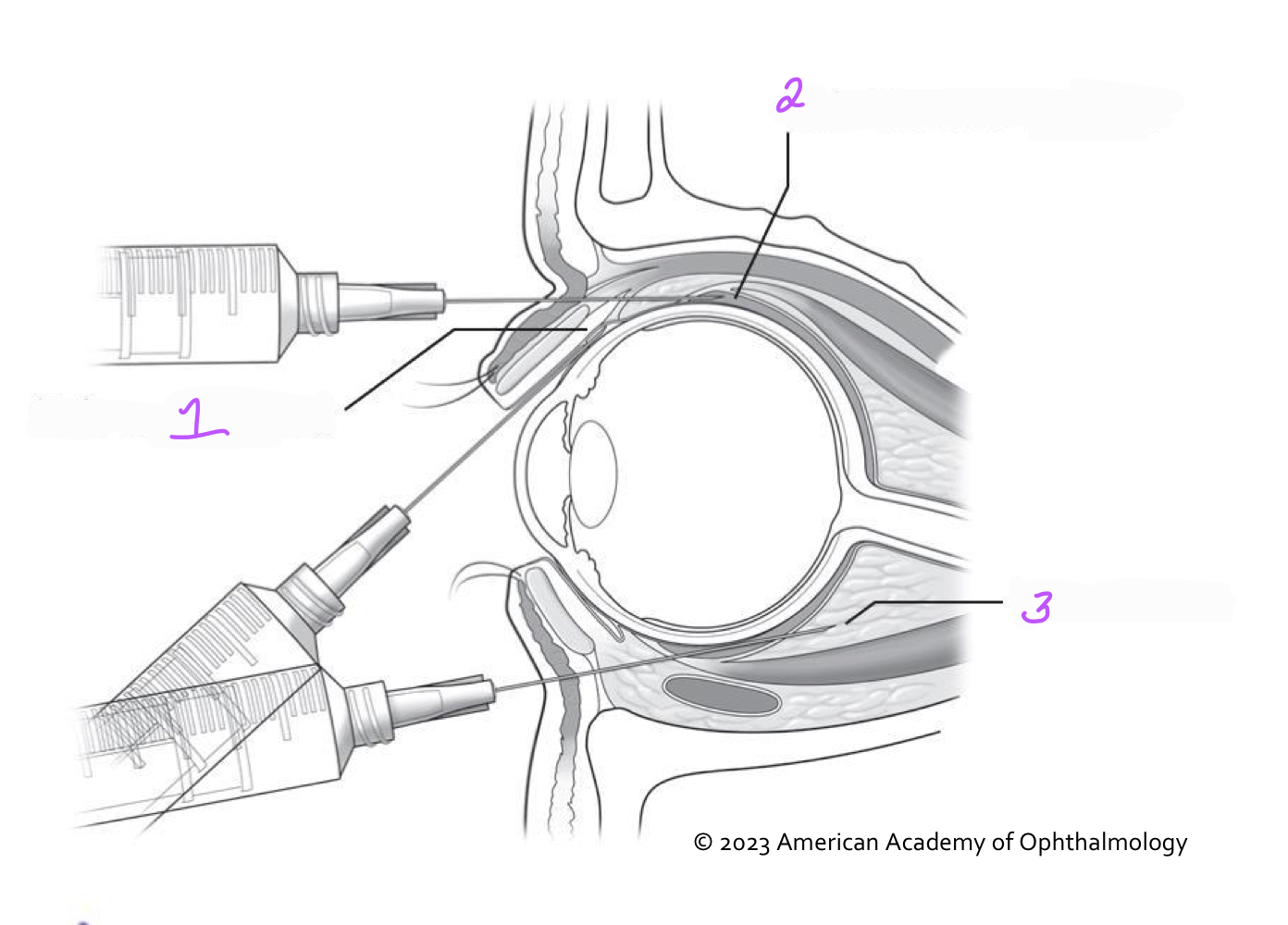
56
New cards
RPE & photoreceptors
Between what 2 layers of the retina is a subretinal injection administered?
57
New cards
topical
What method of ophthalmic drug administration is convenient & has poor systemic absorption?
58
New cards
1. Solutions
2. Suspensions
3. Emulsions
4. Ointments
5. Gels
6. Lid scrubs
7. Sprays
What are the 7 types of topical ophthalmic drug administration methods?
59
New cards
suspensions
Topical ophthalmic drug administration that must be shaken before use and has a longer contact time
60
New cards
solutions
Topical ophthalmic drug administration method that has inconsistent deliver, short contact time, and risk of contamination
61
New cards
emulsions
Topical ophthalmic drug administration method that is not shaken and has a longer contact time
62
New cards
ointments
Topical ophthalmic drug administration method that dissolves quickly, has longer contact time, and an increased chance of blurred vision
63
New cards
Gels
Topical ophthalmic drug administration method that increases contact time but causes less bluirred vision
64
New cards
lid scrubs
Topical ophthalmic drug administration commonly used to treat eye lid infections
65
New cards
Gel/Ointments; solutions
What topical ophthalmic drug administration method has the greatest approximate contact time? Least contact time?
66
New cards
1. Paper strips
2. Cotton pledgets
What are 2 examples of solid delivery topical ophthalmic drug devices?
67
New cards
adenoviral infections
What type of infections are often treated with betadine flushing of the eye?
68
New cards
subconjunctival injections
What type of periocular ophthalmic drug administration has a high local concentration and is useful for cornea infections?
69
New cards
sub-Tenon’s injection
What periocular ophthalmic drug administration method has the greatest risk of causing glove perforation?
70
New cards
retrobulbar injection
What method of periocular drug administration is used for anesthetic delivery for ocular surgery and is contained within the muscle & fat cone?
71
New cards
peribulbar injections
What method of periocular drug administration is used for local injections of anesthetic around teh globe, is safer, and is injected outside the muscle & fat cone?
72
New cards
1. Intracameral
2. Intravitreal
3. Subretinal
What are the 3 types of intraocular ophthalmic drug administration?
73
New cards
intracameral injection
What intraocular ophthalmic drug administration route is injected directly into the anterior chamber and is used in cataract & glaucoma surgeries?
74
New cards
intravitreal injection
What intraocular ophthalmic drug administration route is injected directly into the vitreous body, is used for endophthalmitis (antibiotics), neovascularization treatments, macular edema treatments, and severe viral infection treatments?
75
New cards
subretinal injection
What intraocular ophthalmic drug administration route is more targeted than intravitreal injections & has a greater risk of complications?
76
New cards
1. Passive diffusion
2. Facilitated diffusion
3. Active transport
4. Endocytosis & exocytosis
What are the 4 mechanisms of drug absorption?
77
New cards
passive diffusion
What mechanism of drug absorption is concentration-based & will enter either through a channel or pore or by being lipid soluble?
78
New cards
facilitated diffusion
What mechanism of drug absorption moves with the concentration gradient and is drug/shape specific?
79
New cards
active transport
What mechanism of drug absorption requires ATP & moves against the concentration gradient?
80
New cards
endocytosis & exocytosis
What mechanism of drug absorption involves larger molecules and surrounded by plasma membrane?
81
New cards
1. pH
2. Blood flow
3. Total surface area
4. Contact time
5. P-glycoprotein
What 5 factors influence drug absorption?
82
New cards
a. Weak Acids
What pH is more effective with pH
a. Weak Acid
b. Weak Base
a. Weak Acid
b. Weak Base
83
New cards
b. Weak Base
What pH is more effective with pH>pKa (deprotonated) drugs?
a. Weak Acid
b. Weak Base
a. Weak Acid
b. Weak Base
84
New cards
uncharged
Drugs absorb best when (charged/uncharged).
85
New cards
Increased
(Increased/Decreased) blood flow increases drug absorption.
86
New cards
Increased
(Increased/Decreased) contact time results in greater absorption.
87
New cards
Gel/ointment
Of these options, which have the greatest contact time?
a. Solutions
b. Suspension/emulsion
c. Gel/ointment
a. Solutions
b. Suspension/emulsion
c. Gel/ointment
88
New cards
P-glycoprotein
What factor influencing drug absorption forms a pore that increases absorption of some drugs?
89
New cards
Bioavailability
Amount of uncharged drug in the body
90
New cards
IV drugs
What type of drugs have 100% bioavailability?
91
New cards
liver
Where in the body are oral drugs metabolized?
92
New cards
1. First pass hepatic metabolism
2. Solubility of drug
3. Chemical stability
4. Drug formulation
What are the 4 influencing factors of bioavailability?
93
New cards
bioequivalent
Drugs are considered _______________ if they take the same amount of time to reach peak concentration.
94
New cards
therapeutically equivalent
Generic drugs are considered to be _________ ____________ drugs.
95
New cards
90
Generic drugs have a pKa within the ____% confidence interval of the name brand.
96
New cards
1. Blood flow
2. Capillary permeability
3. Binding of drugs to plasma proteins
4. Lipophilicity
What 4 factors influence drug distribution?
97
New cards
Lipid
(Water/Lipid) soluble drugs can cross cell membranes.
98
New cards
improves
Binding of drugs to plasma proteins (improves/impairs) transport.
99
New cards
1. Continuous
2. Fenestrated
3. Discontinuous
What are the 3 types of capillary permeability?
100
New cards
discontinuous
What type of capillary permeability has the best medication distribution?