WCHS Mr. Alasti HBS Human Body Systems 2.2.1 The Endocrine System
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What does the endocrine system control?
Communication in the body
Endocrine System
The glands and parts of glands that produce endocrine secretions, which help to integrate and control bodily metabolic activity, and include especially the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenals, islets of Langerhans, ovaries, & testes
What does the endocrine system work with the nervous system to do?
Regulate & control all the actions of the human machine
How does the endocrine system communicate?
Using chemical signals, or hormones, to regulate body functioning
Hormone
A signaling molecule produced by glands. A hormone induces a specific effect on the activity of cells
What do hormones carry messages between and what are they responsible for?
They carry messages between organs and cells and are responsible for your body’s energy level, growth & development, mood, and sleep

Label the glands within the brain
Pineal Gland
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
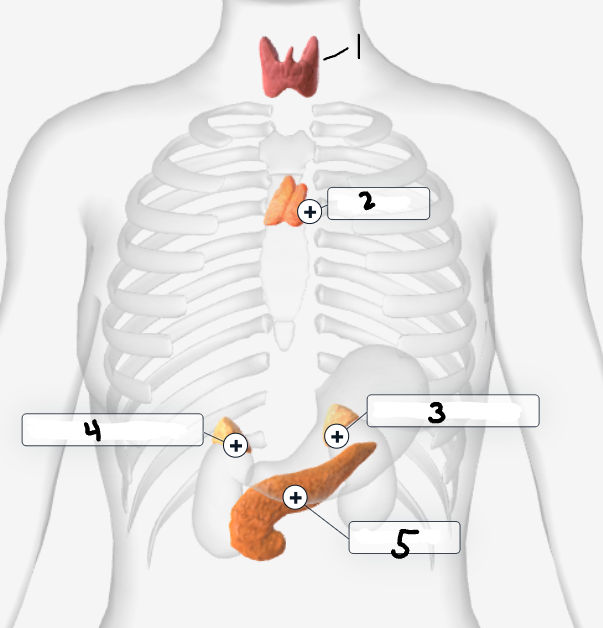
Label the image
Thyroid Gland
Thymus
Left Adrenal Gland
Right Adrenal Gland
Pancreas
Pineal Gland Function
Regulates sleep/wake cycles and secretes the hormone melatonin
Hypothalamus Function
Releases hormones to help with reproduction, thyroid regulation, growth, emotions, water levels in the body, & our response to stress
Pituitary Gland Function
Releases several hormones that relate to growth, metabolism, reproduction, stress or trauma response, lactation, water balance, & childbirth
Thyroid Gland Function
Plays a major role in growth and development of the human body and metabolism
Thymus Function
Makes white blood cells up until puberty, when all the T-cells you need have been made. It also releases hormones that control the pituitary gland
Adrenal Glands Functions
The adrenals release hormones that help regulate the body’s response to stress as well as metabolism, blood pressure, & the immune system
Ovaries Functions
Produce the hormones estrogen and progesterone which regulate reproduction and menstruation

Label the image
Secreting Gland
Hormone
Blood Vessel
Target Cells
Basic function of a hormone in the endocrine system
Regulating and coordinating vital body functions like growth, metabolism, mood, reproduction, & maintaining homeostasis
Basic function of the endocrine system
Regulate & coordinate essential body functions like growth, metabolism, reproduction, mood, & stress response by producing & secreting chemical messengers (hormones)
Basic function of a gland in the endocrine system
Produce & secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream
Basic function of a receptor in the endocrine system
Recognize a specific hormone and, upon binding, initiate a series of cellular events that ultimately produces a characteristic biological response in the target cell
Basic function of target cells in the endocrine system
Receive specific chemical signals from the bloodstream via protein receptors, initiating a specific response to maintain bodily balance or triggering processes like growth, metabolism, or reproduction
What do feedback mechanisms in the endocrine system regulate?
Body functions such as temperature, heart rate, & concentration of sugar in the blood
Insulin
A protein hormone secreted by the pancreas. It is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates & the regulation of glucose levels in the blood
Glucagon
A hormone secreted by pancreatic endocrine cells that raises blood glucose levels; an antagonistic hormone to insulin
How do you get your body back on track if you are close to being diagnosed with diabetes?
Focus on nutrition (eat balanced meals, limit sugary drinks & sweets, & eat your meals at a regular time), incorporate physical activity, & limit harmful habits such as smoking and/or drinking
Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune disease where the immune system destroys insulin producing cells in the pancreas, leading to little to no insulin production, causing high blood sugar since glucose can’t enter cells for energy
Type 2 Diabetes
A chronic condition where the body either doesn’t make enough insulin, or doesn’t use it properly, leading to high blood sugar levels
Hyperglycemia
High blood sugar
What allows blood sugar to go down?
Hormones (specifically insulin) get secreted into the bloodstream, travel through the entirety of it, and attach to receptors specific to insulin. Glucose receptors then allow glucose into the bloodstream, into a target cell, and allowing the blood sugar to go down
Hypoglycemia
Low blood sugar
What happens when the body’s blood sugar is too low (hypoglycemia)?
Glucagon gets released from the pancreas, goes into the bloodstream, travels to the liver (where glycogen is stored), to release glucose into the blood, & tells skeletal muscles to release their stored glucose
How does insulin lower blood sugar?
By getting glucose into cells instead of the bloodstream
How does glucagon raise blood sugar?
By telling the liver & skeletal muscles to release stored glucose
What error causes Type 1 Diabetes?
The immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas, leading to little or no insulin production
What error causes Type 2 Diabetes?
Insulin resistance, meaning the body’s cells don’t respond well to insulin, and the pancreas struggles to produce enough to compensate, leading to high blood sugar