The Nervous System
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Cerebrum
Telencephalon
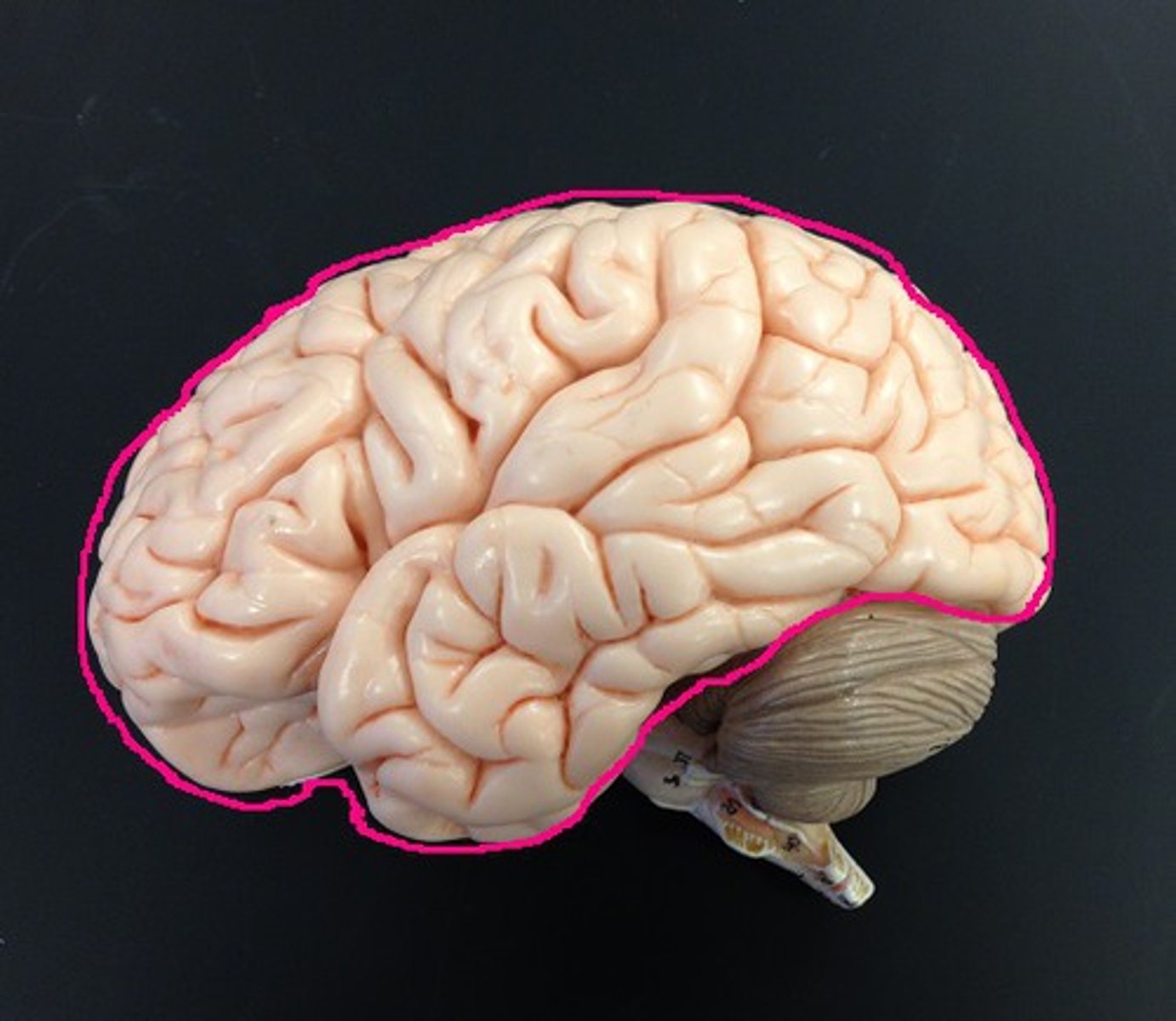
lateral ventricles
What is the largest ventricle?
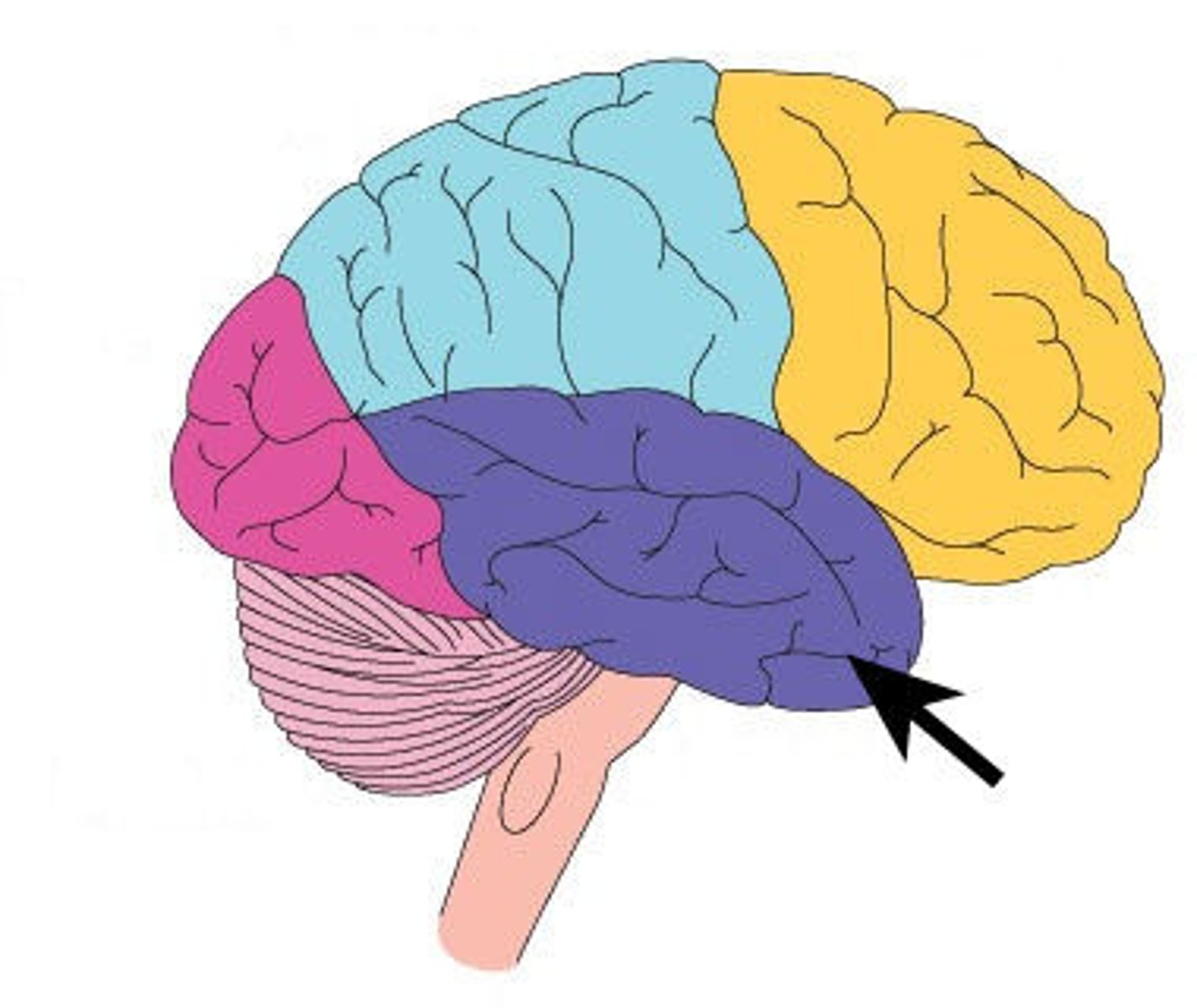
Frontal lobe
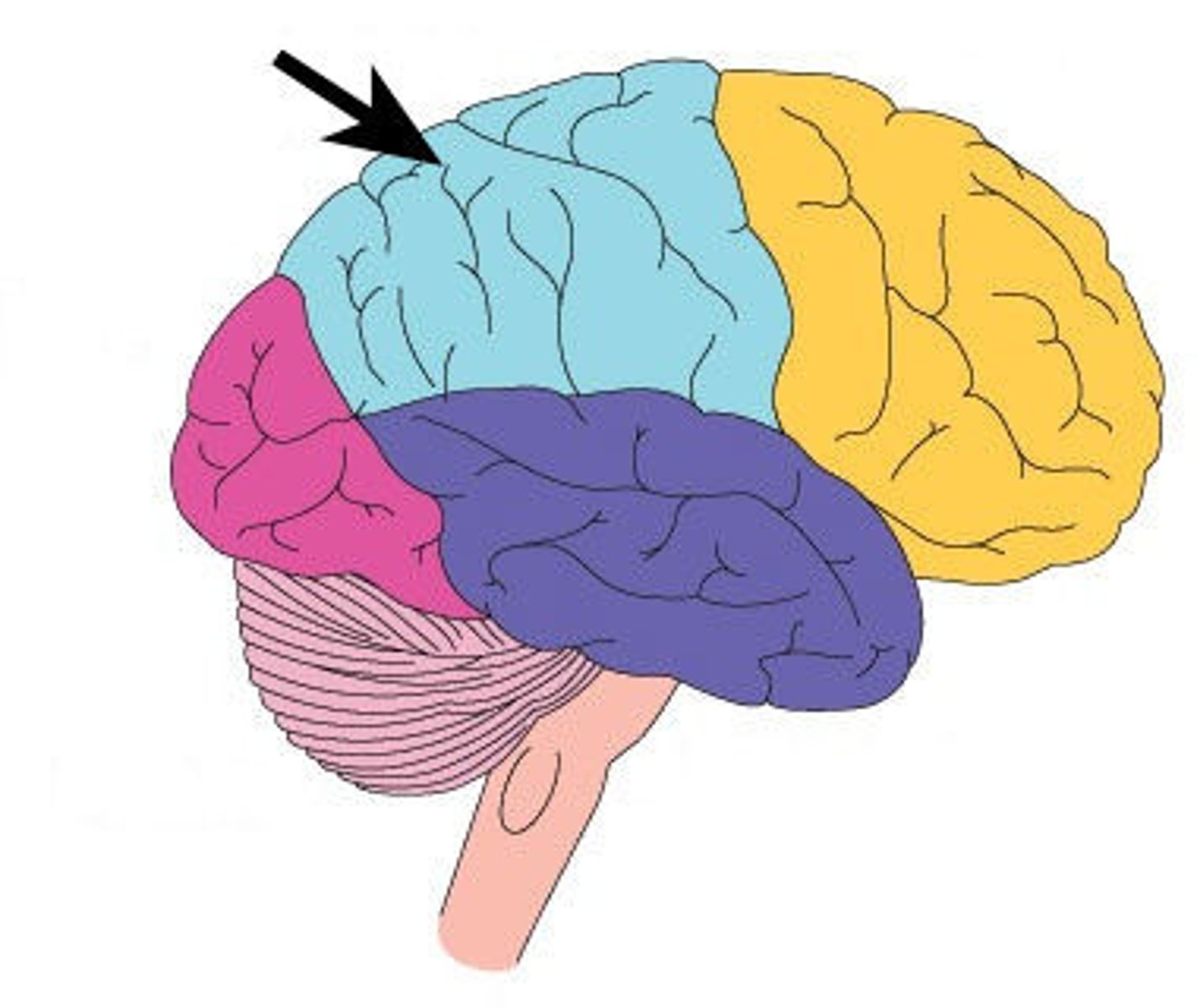
Parietal lobe
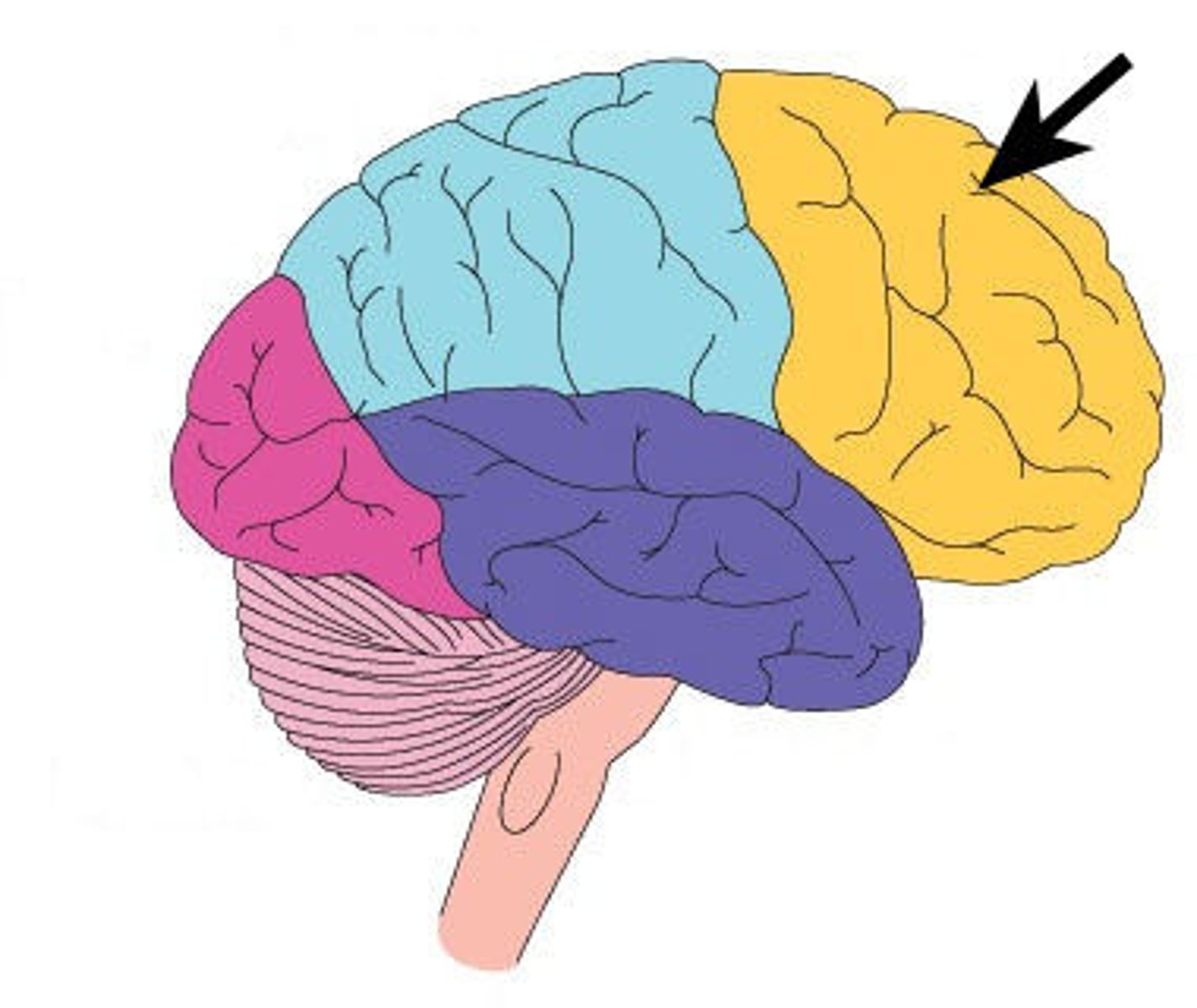
Occipital lobe
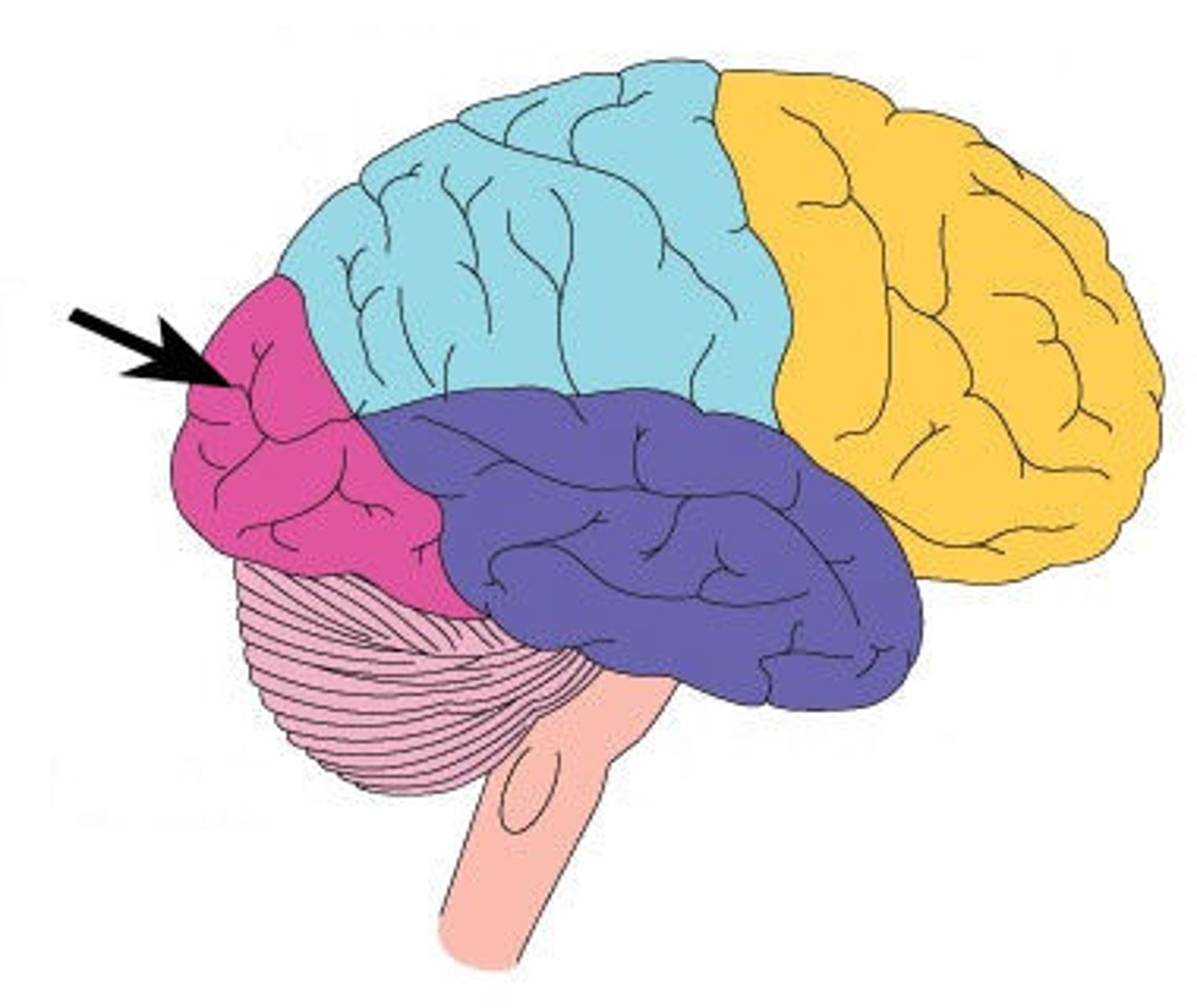
Temporal lobe
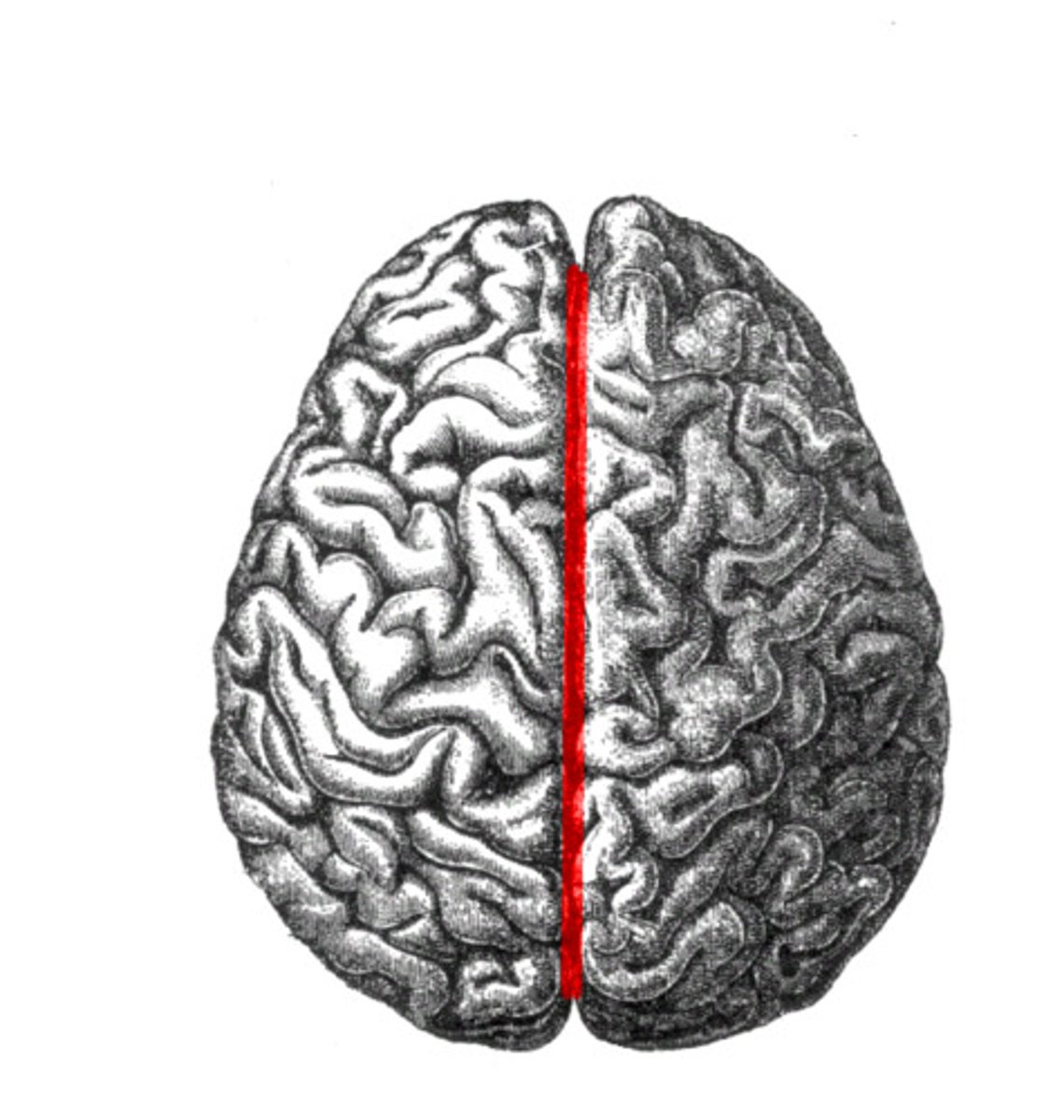
Longitudinal Fissure
Separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres, the falx cerebri is found here
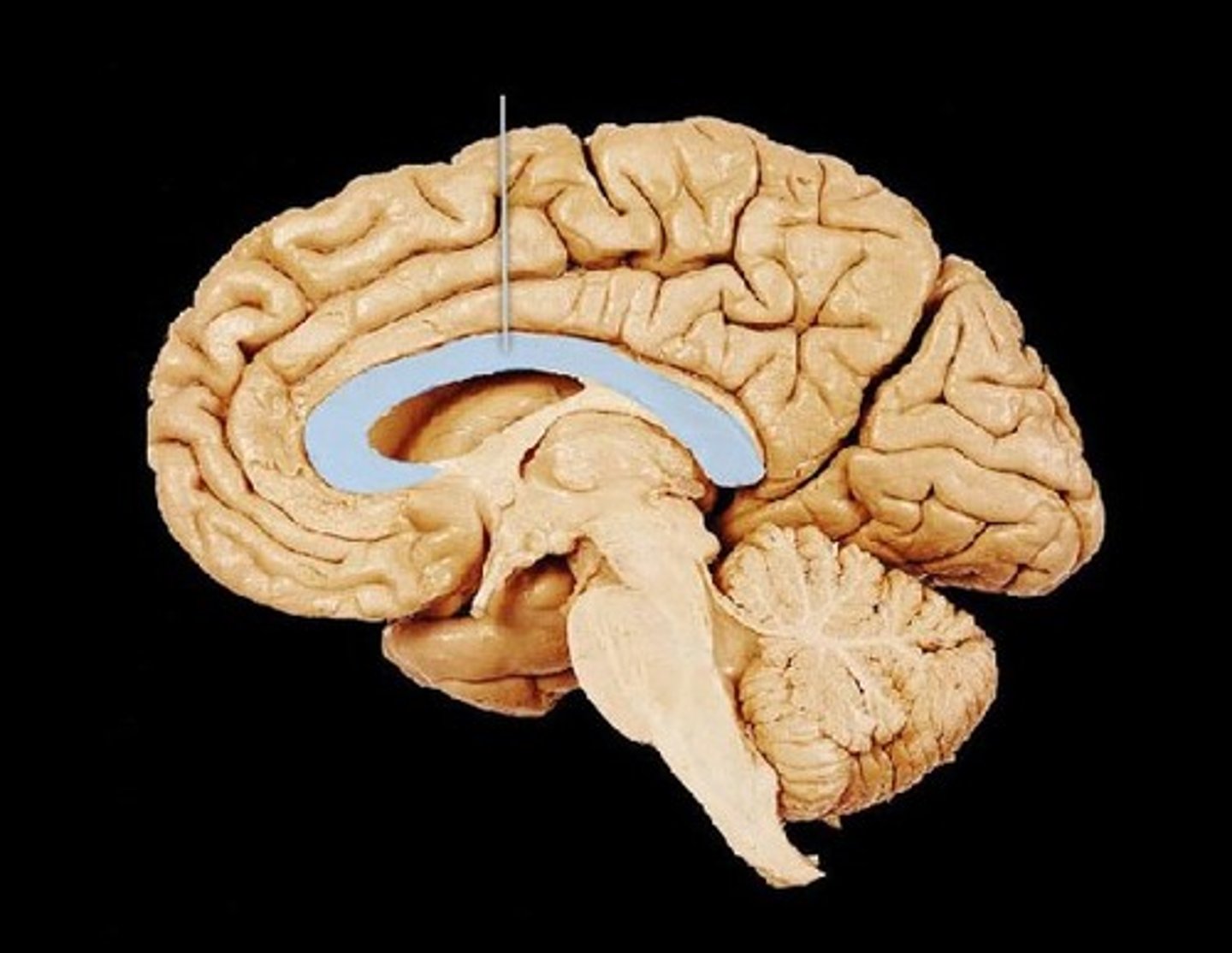
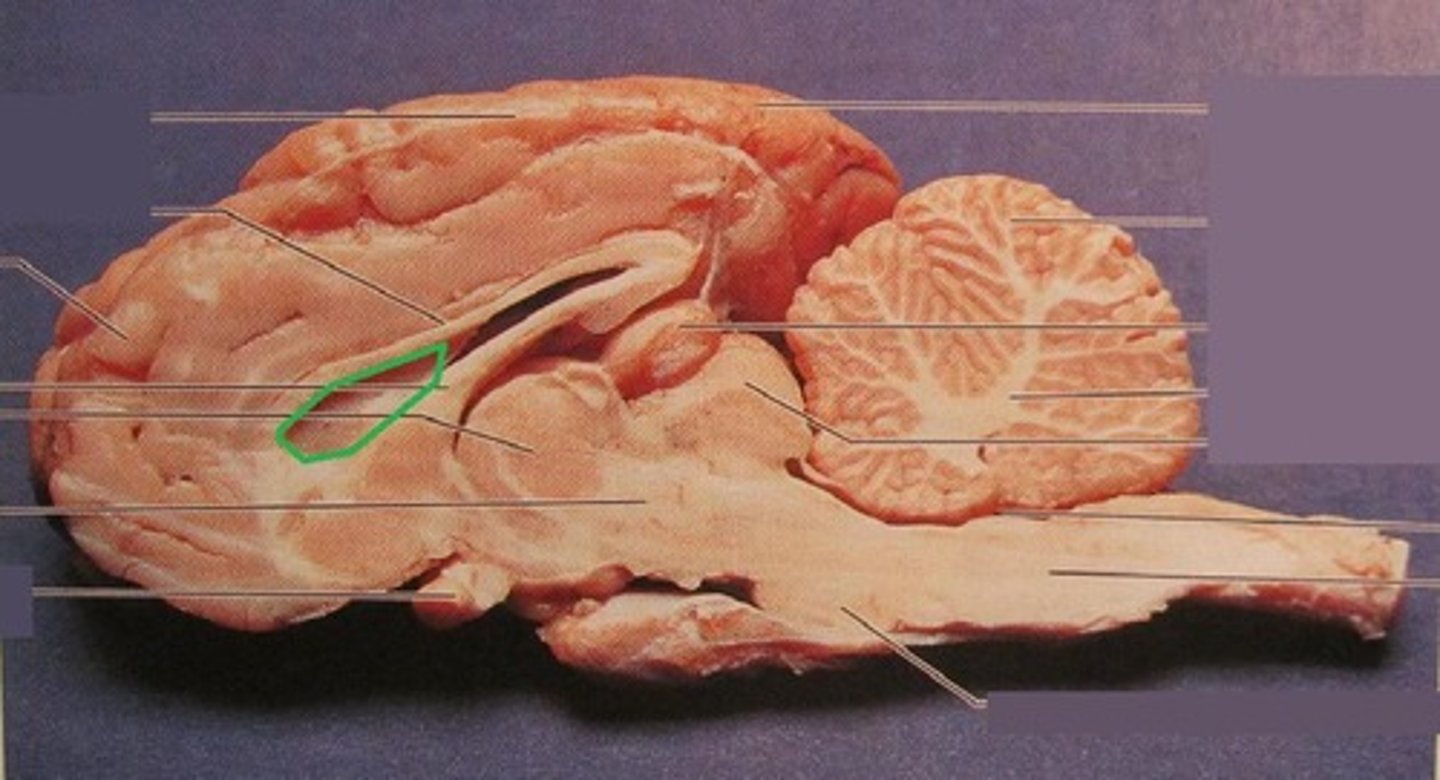
Corpus Callosum
Connects the left and right cerebral hemisphere and is their main mode of communication
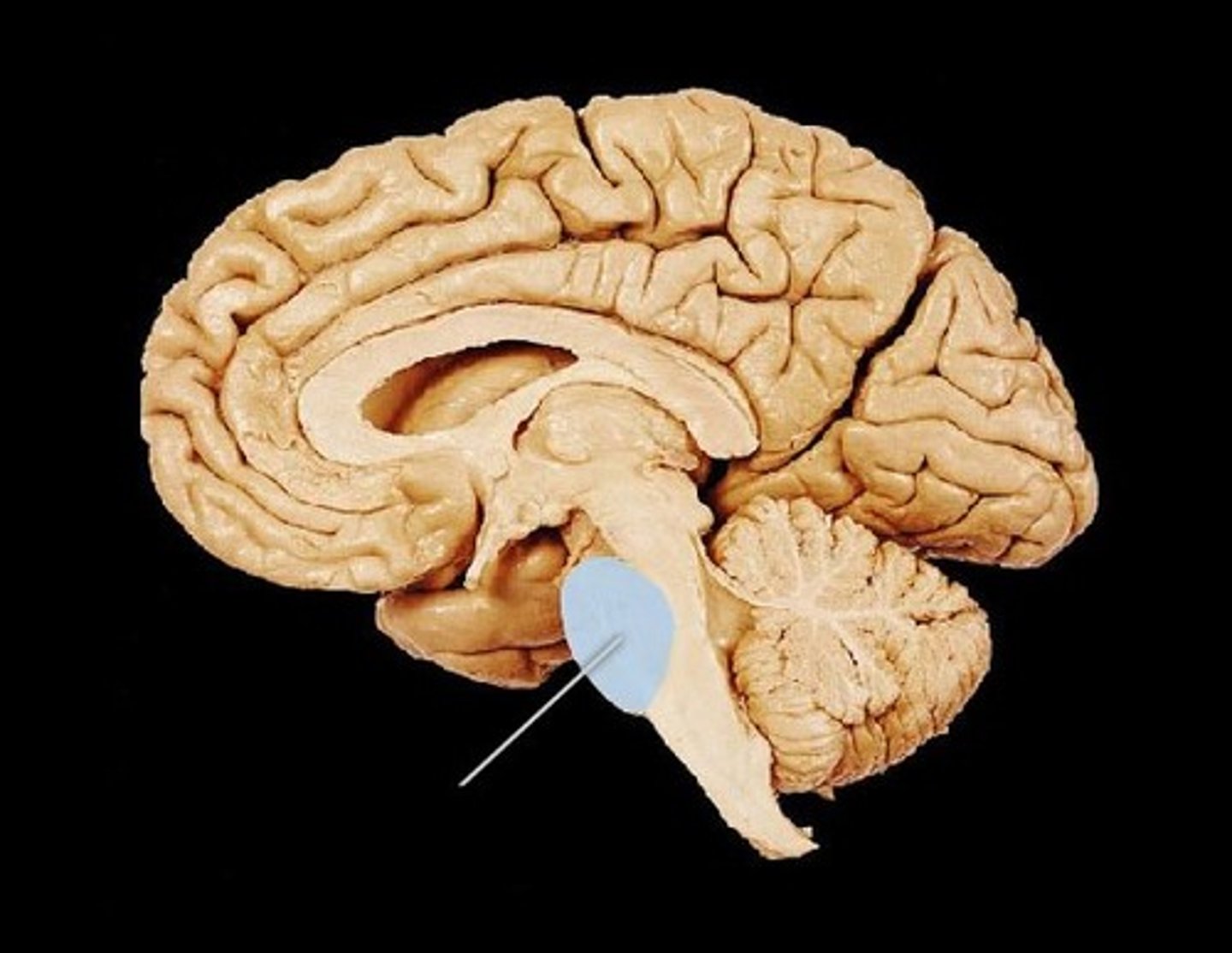
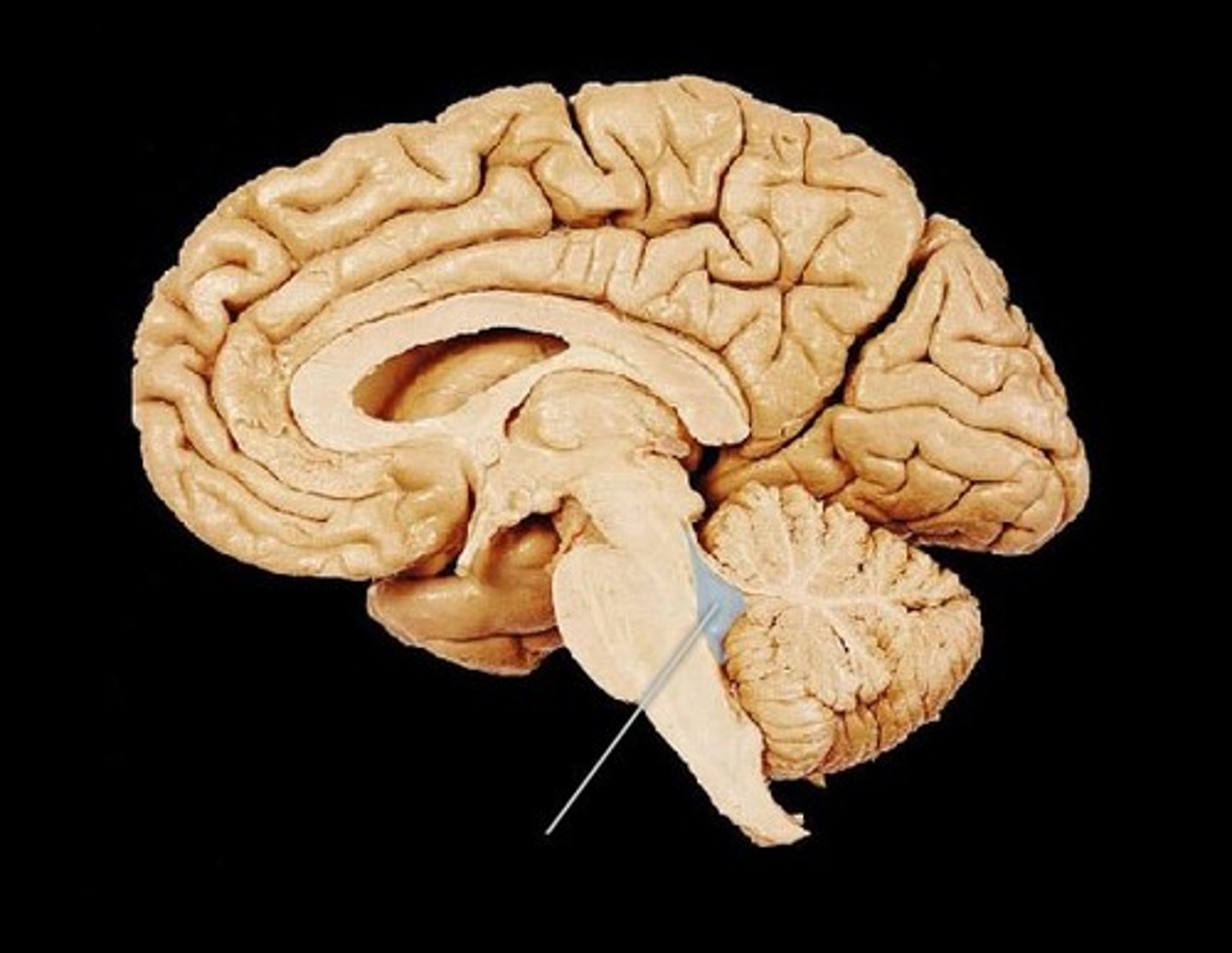
Cerebellum
muscle memory, equilibrium, posture, proprioception
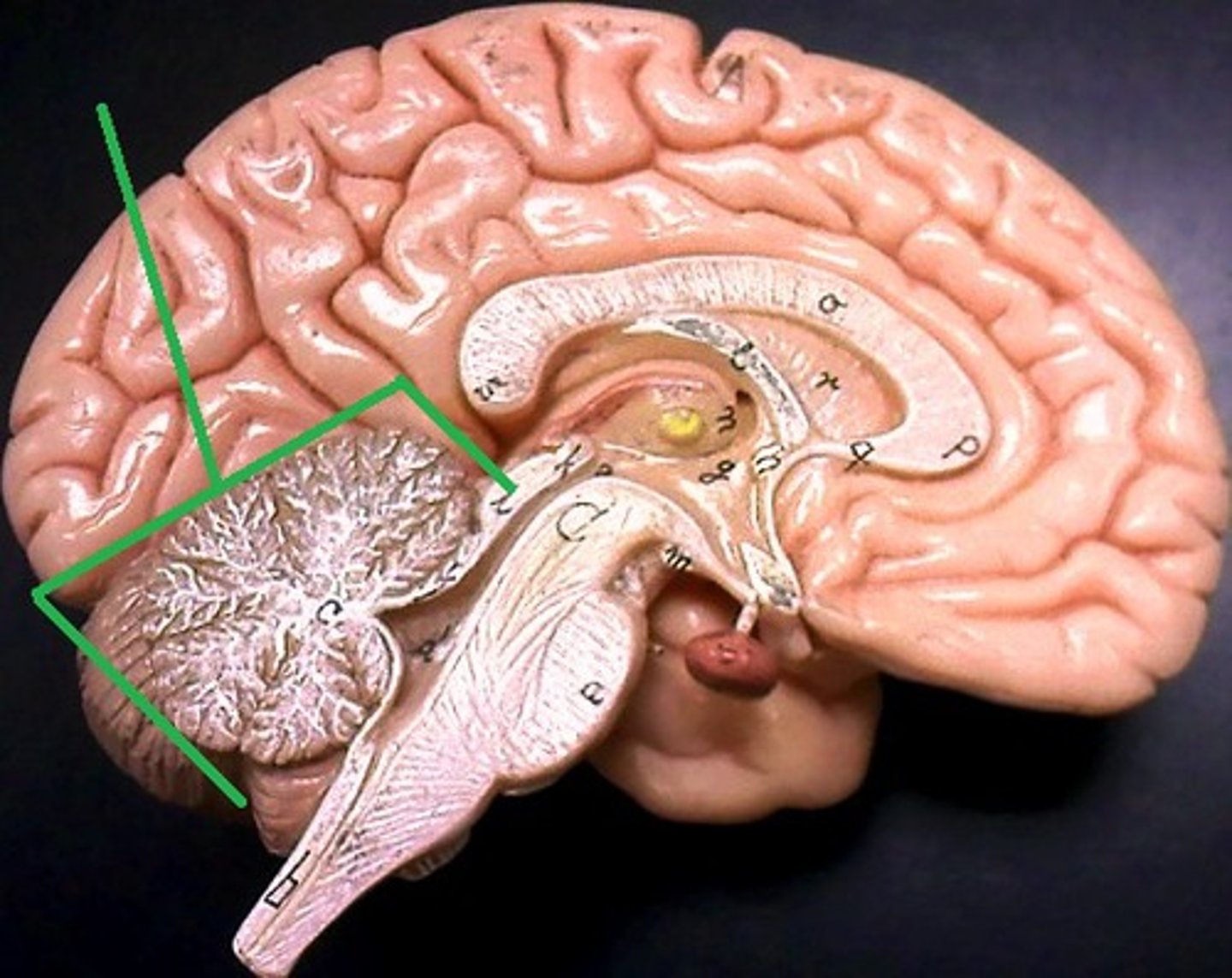
Arbor Vitae
Tree of life
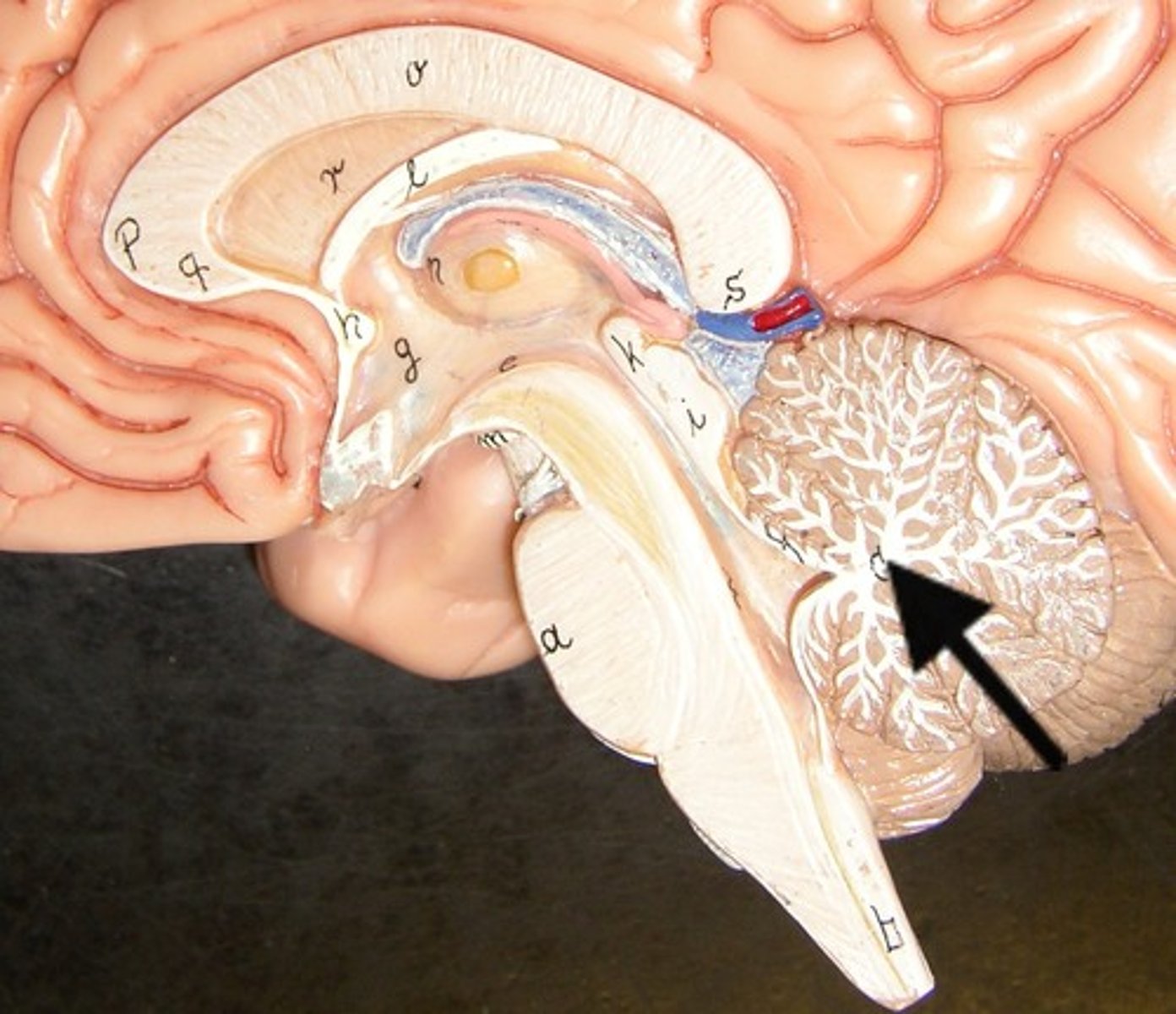
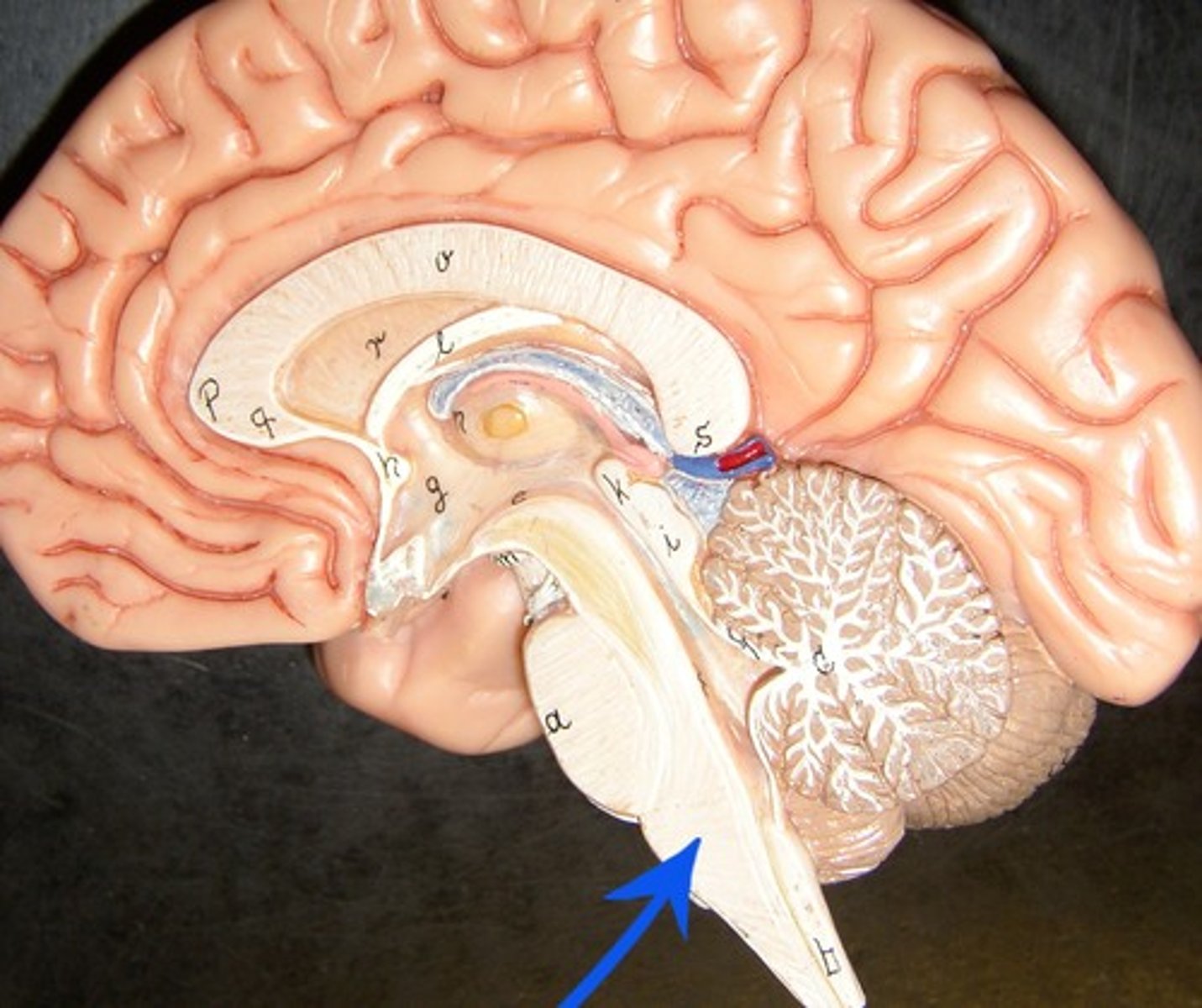
midbrain, pons, medulla oblongata
The brainstem includes (rostral to caudal)
midbrain
pons
Bridge
relays impulses and helps to regulate breathing
Medulla Oblongata
Functions include sensory relay for cranial nerves, relay for thalamus, cardiac center,vasomotor center, respiratory center
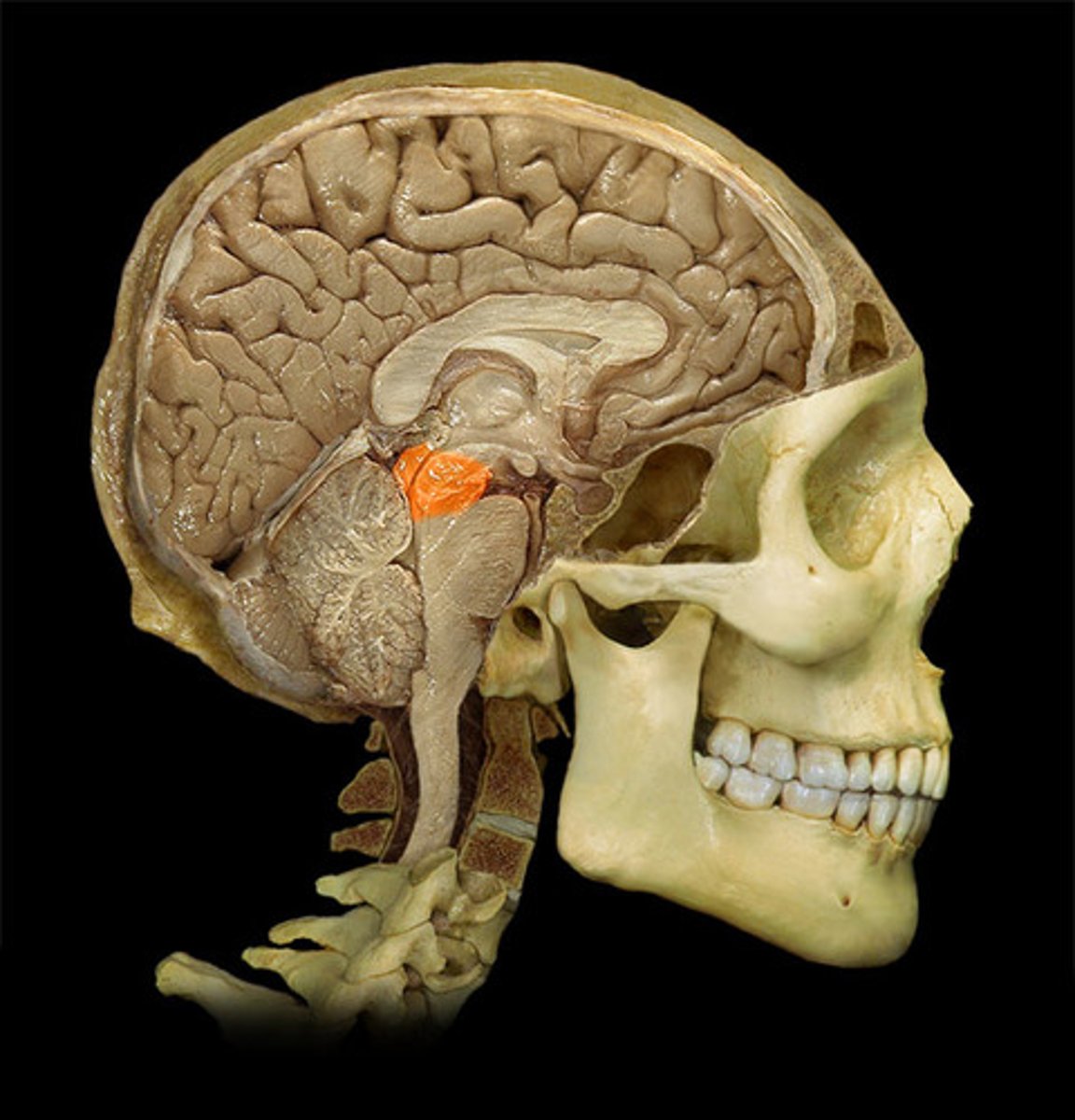
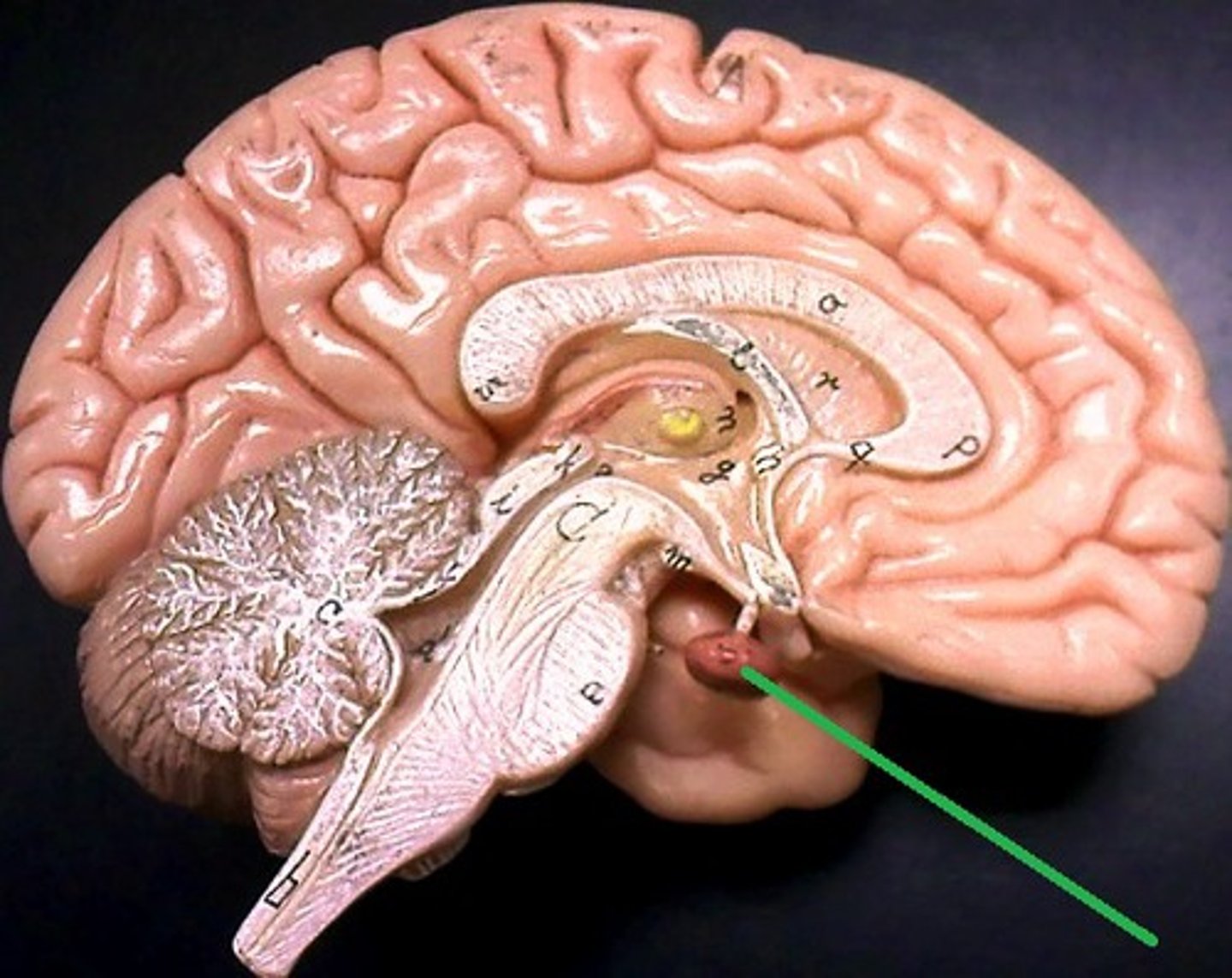
Pituitary gland
sella turcica
Lateral Ventricles
Third Ventricles
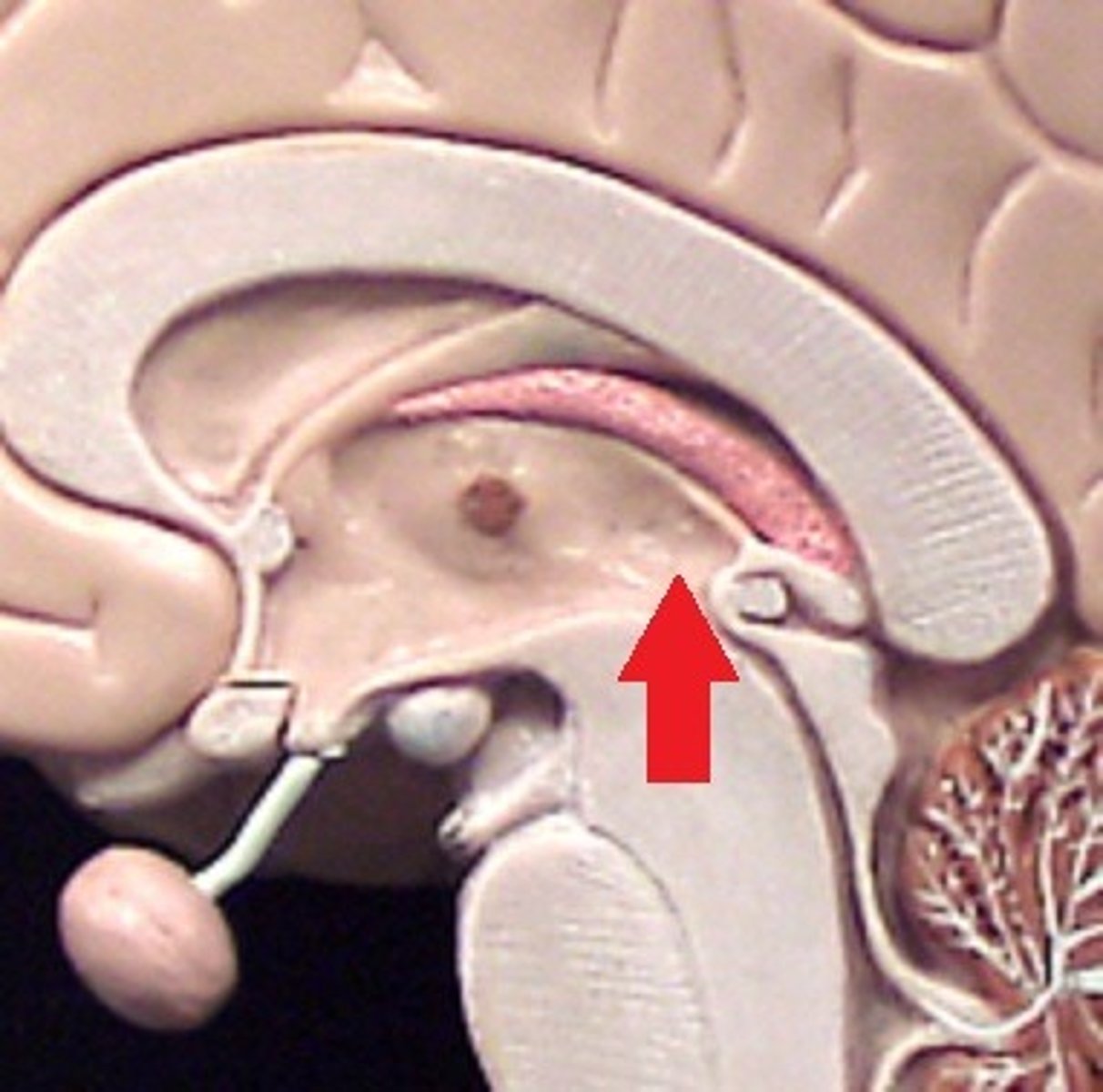
Fourth Ventricle
Choroid Plexi
found in each ventricle
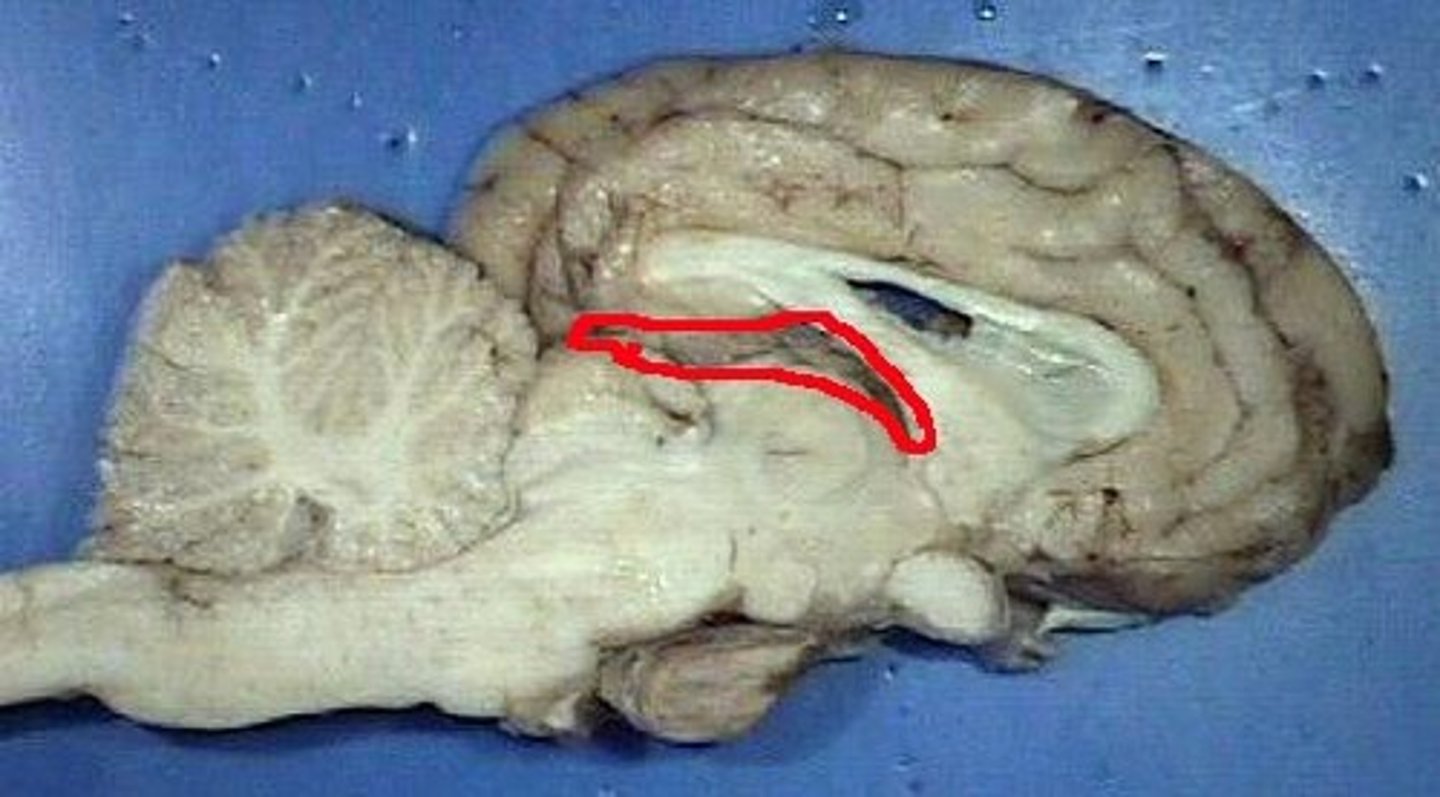
Meninges
Connective tissue membranes that surround and separate portions of the brain.
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
3 layers of meninges (outer to inner)
dura mater
most superficial layer of meninges
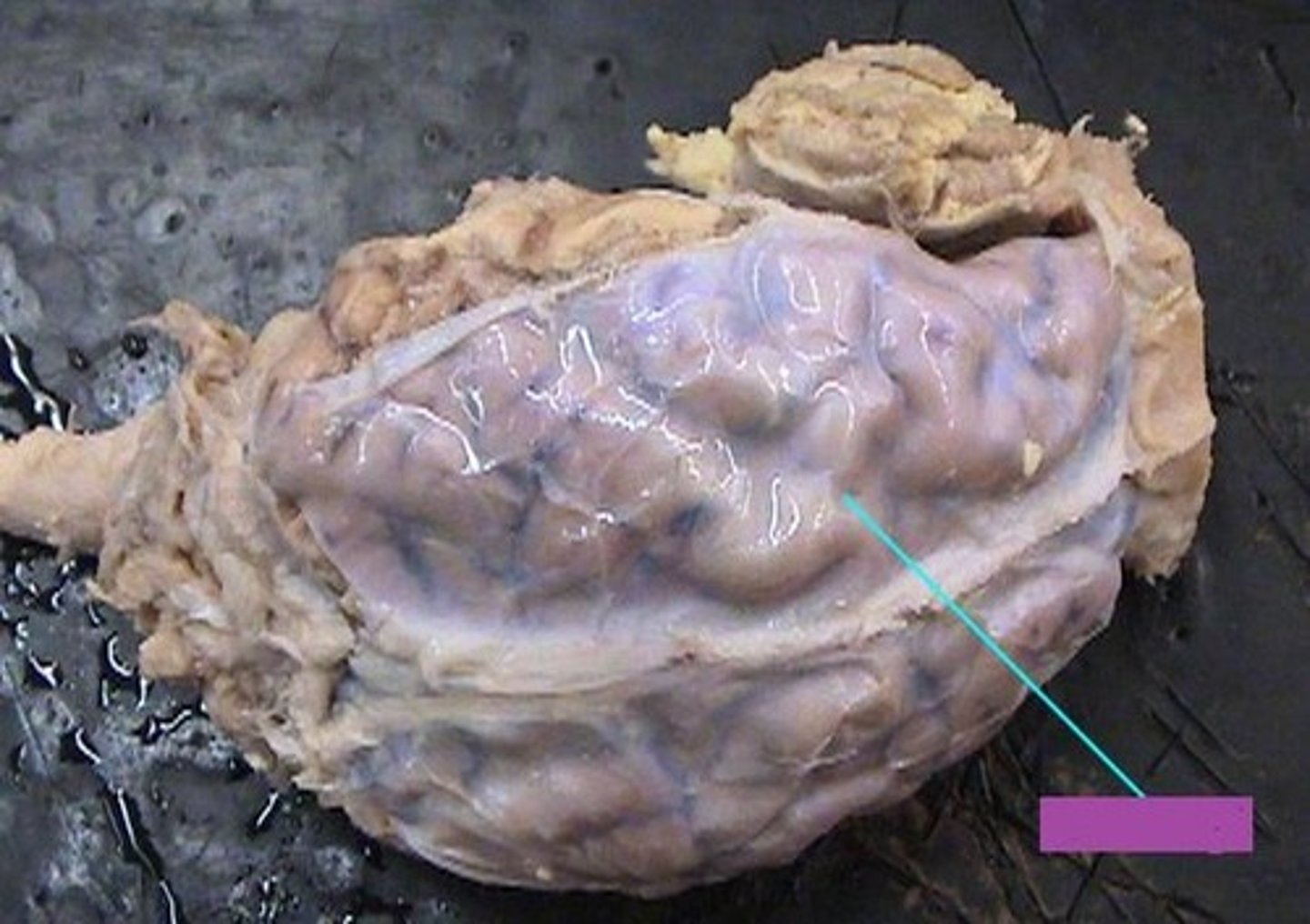
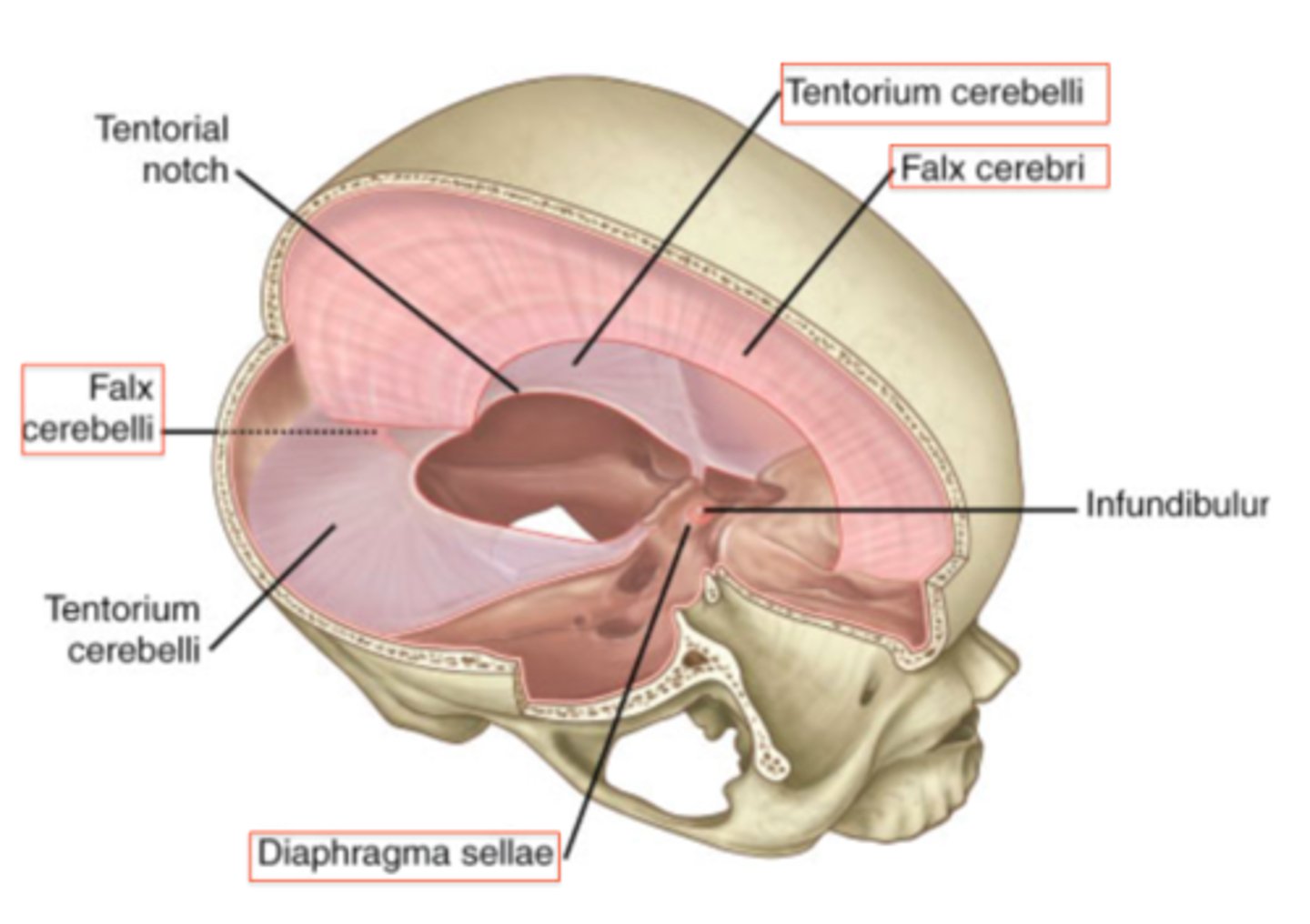
falx cerebri
in the midsagittal plane
Where is the dura mater and falx cerebri located?
anterior: crista galli - posterior: superior portion of the tentorium cerebelli
Where is the dura mater and falx cerebri anterior attachment and posterior attachment?
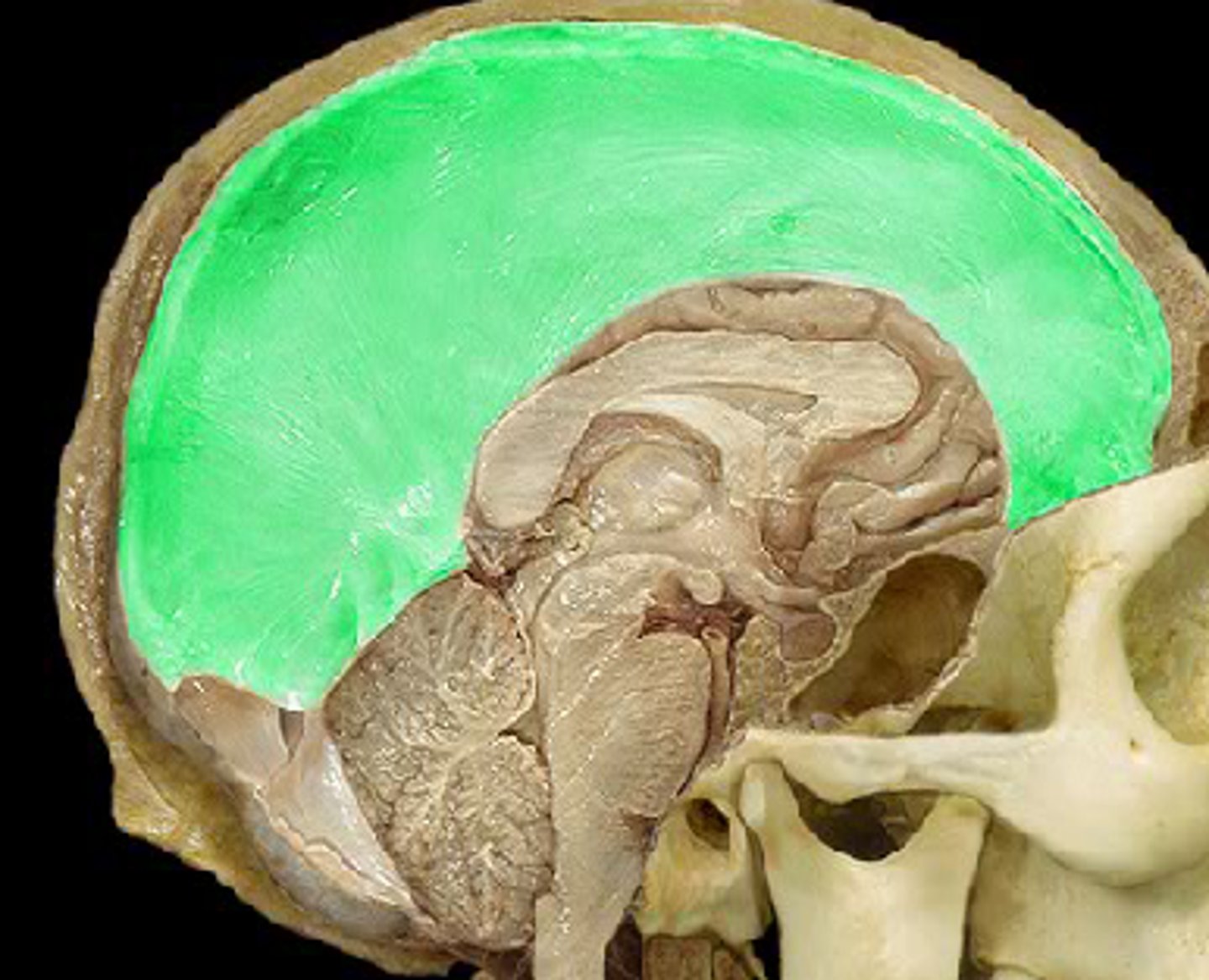
tentorium cerebelli
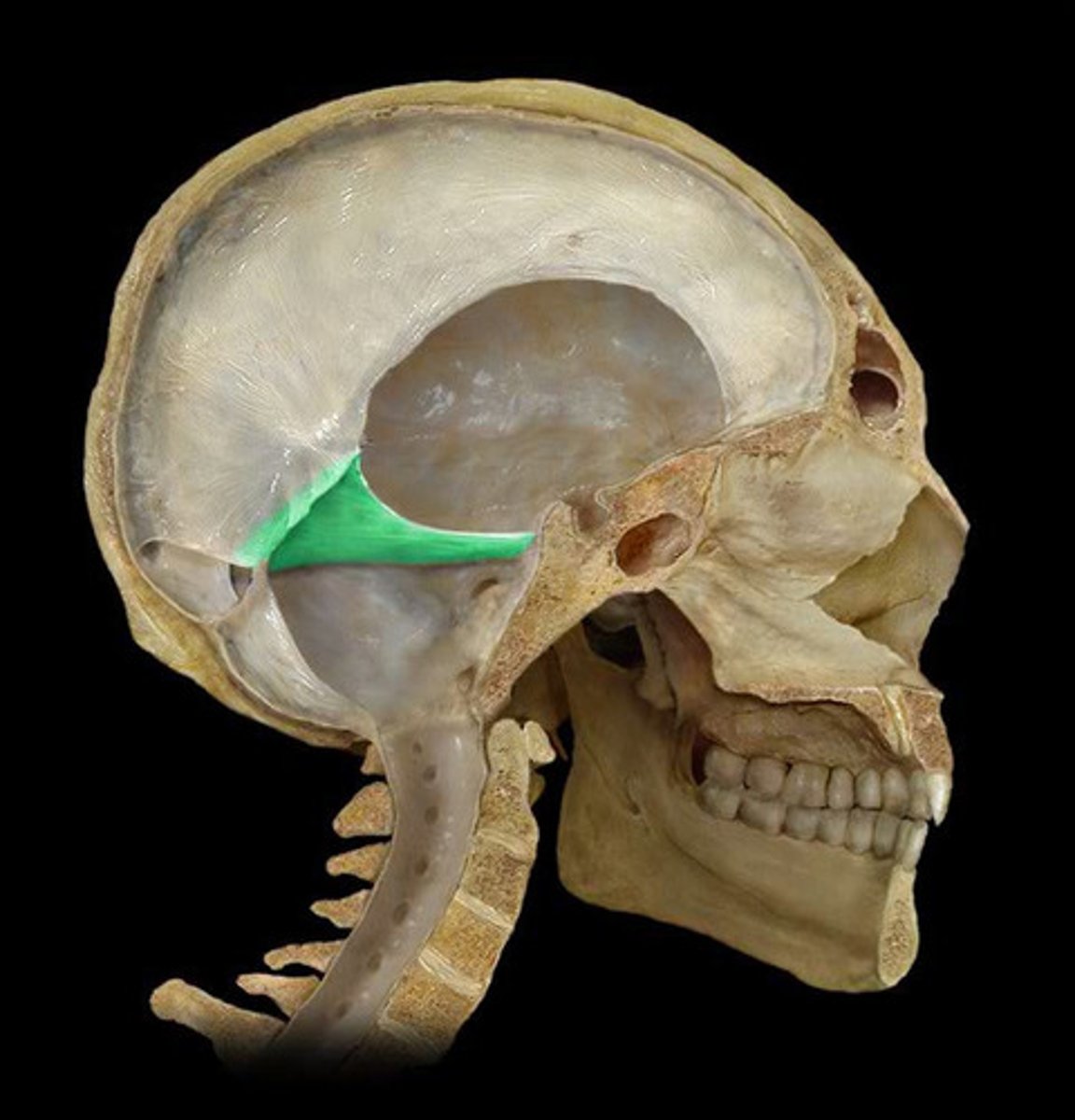
tentorial notch
the space in the tentorium through which the brainstem passes
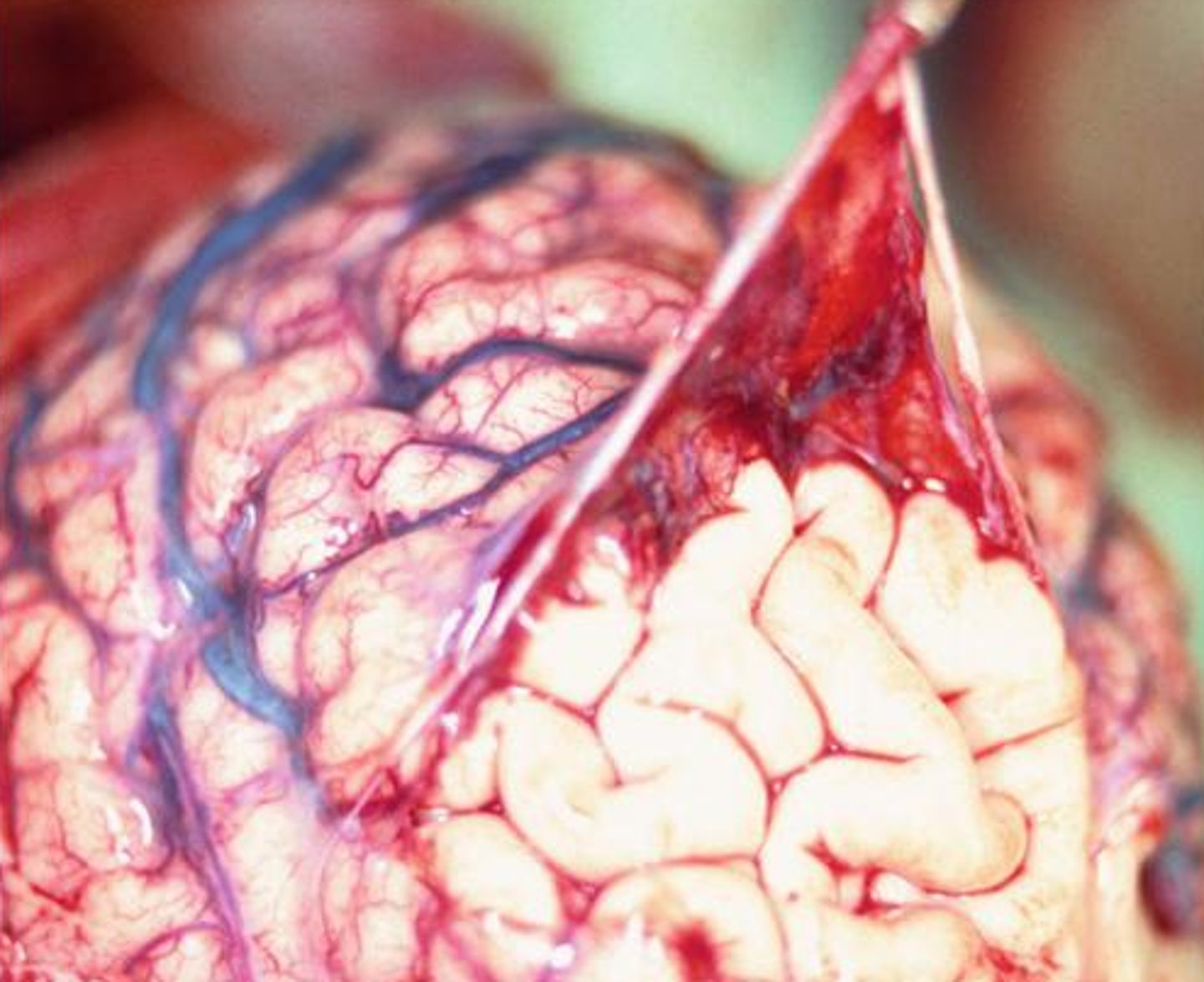
arachnoid mater
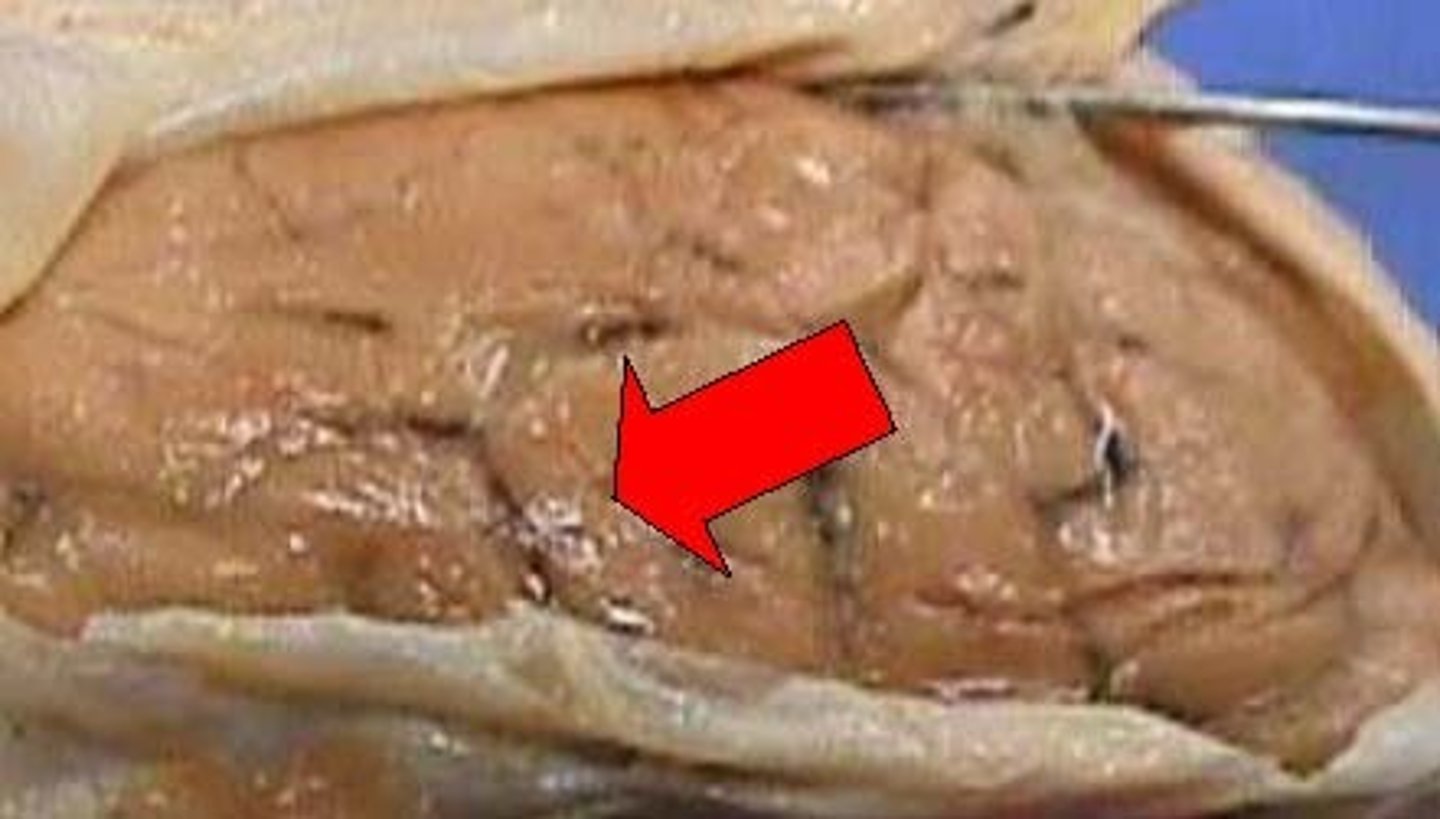
pia mater
deepest layer of meninges
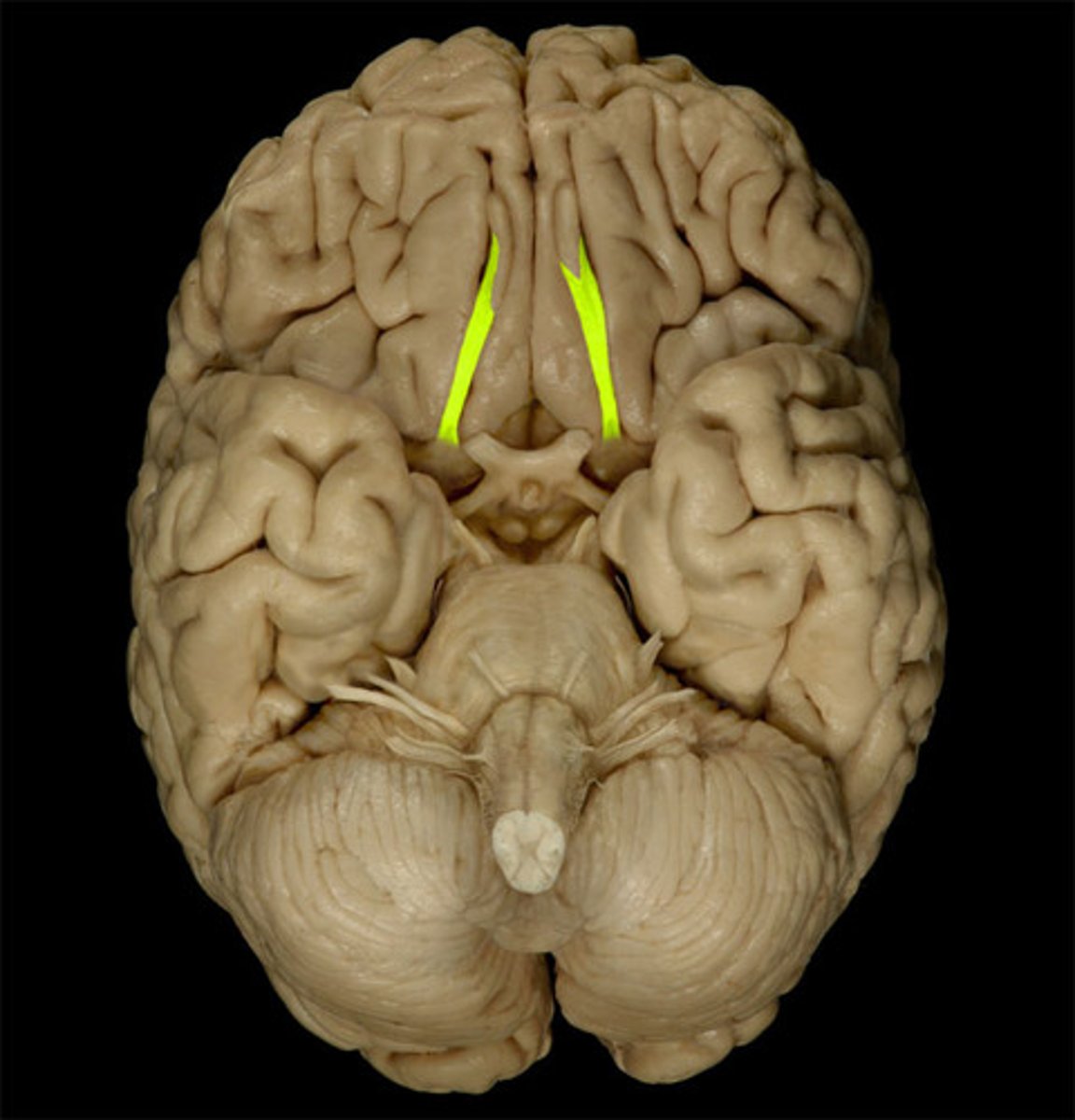
optic nerves
runs through optic foramen
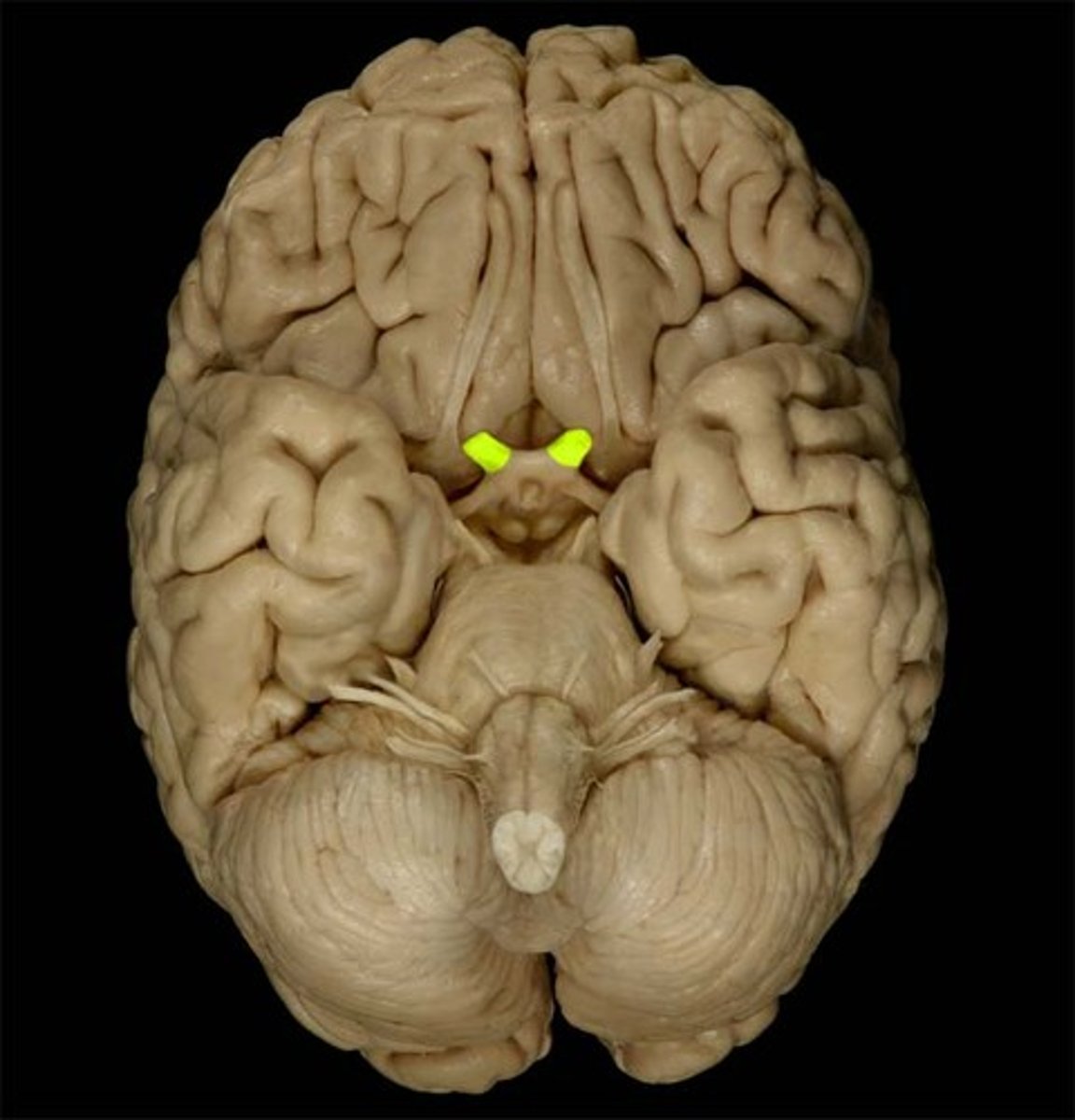
optic chiasm
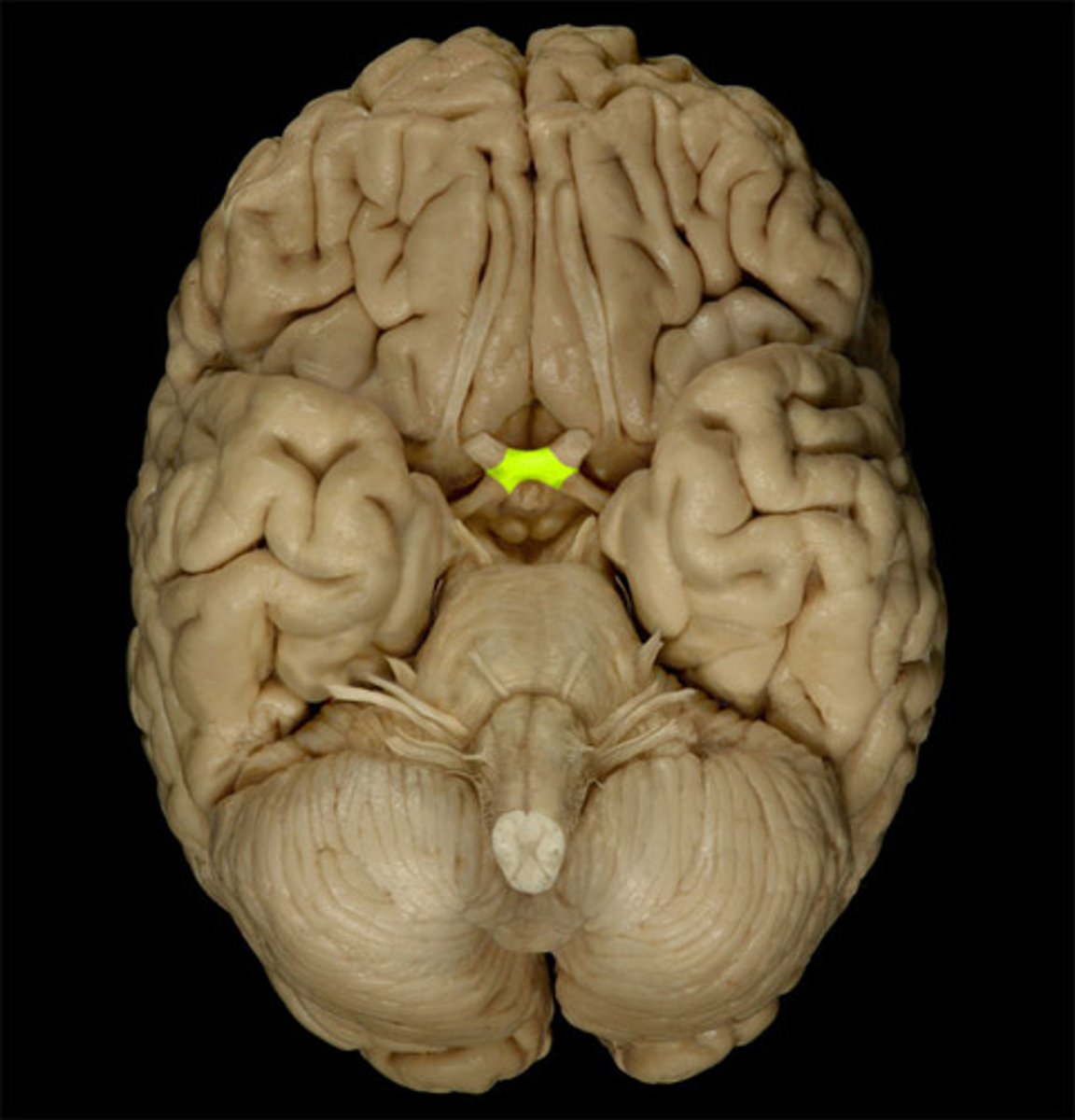
olfactory bulb
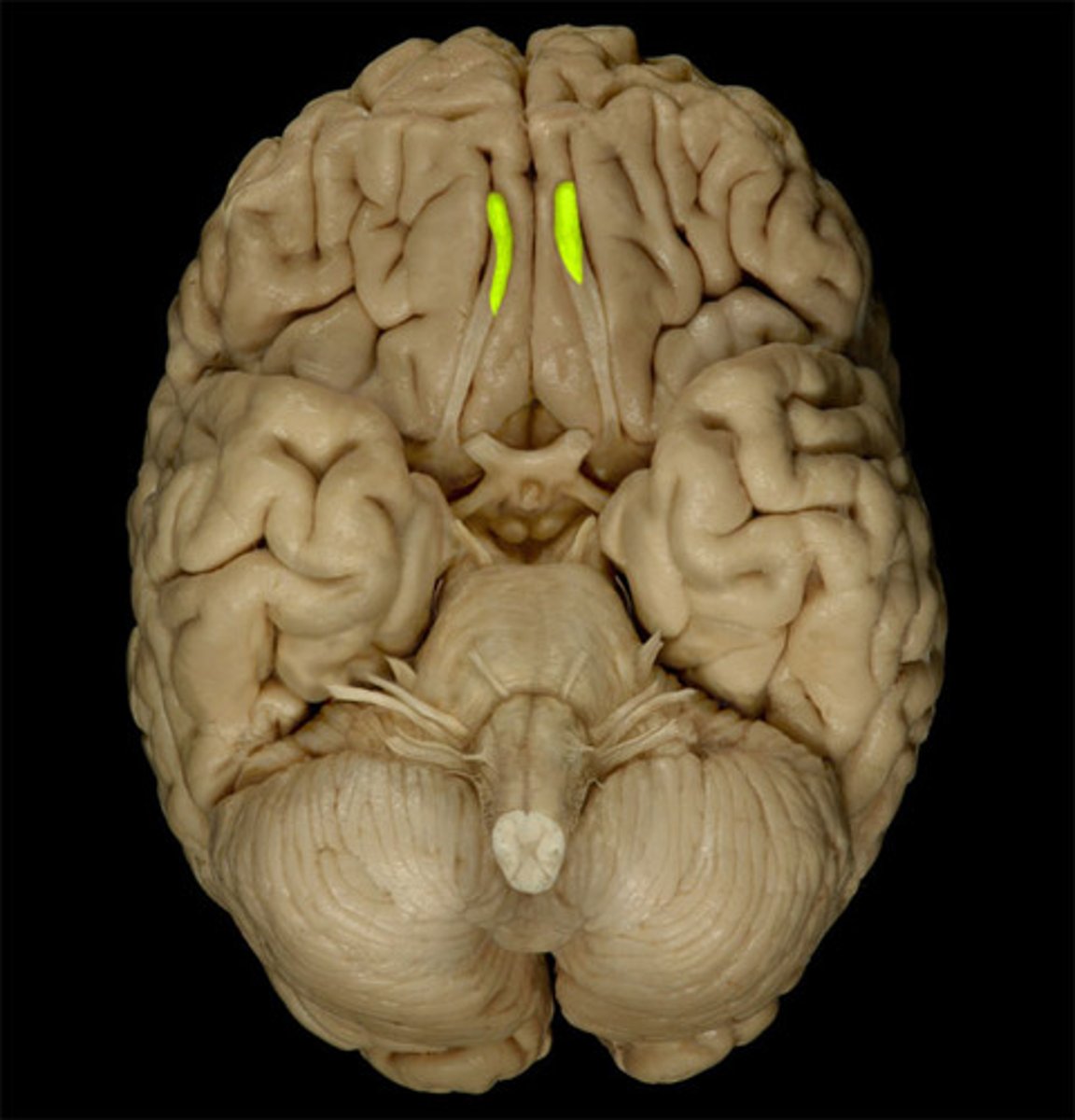
olfactory tract
spinal nerves
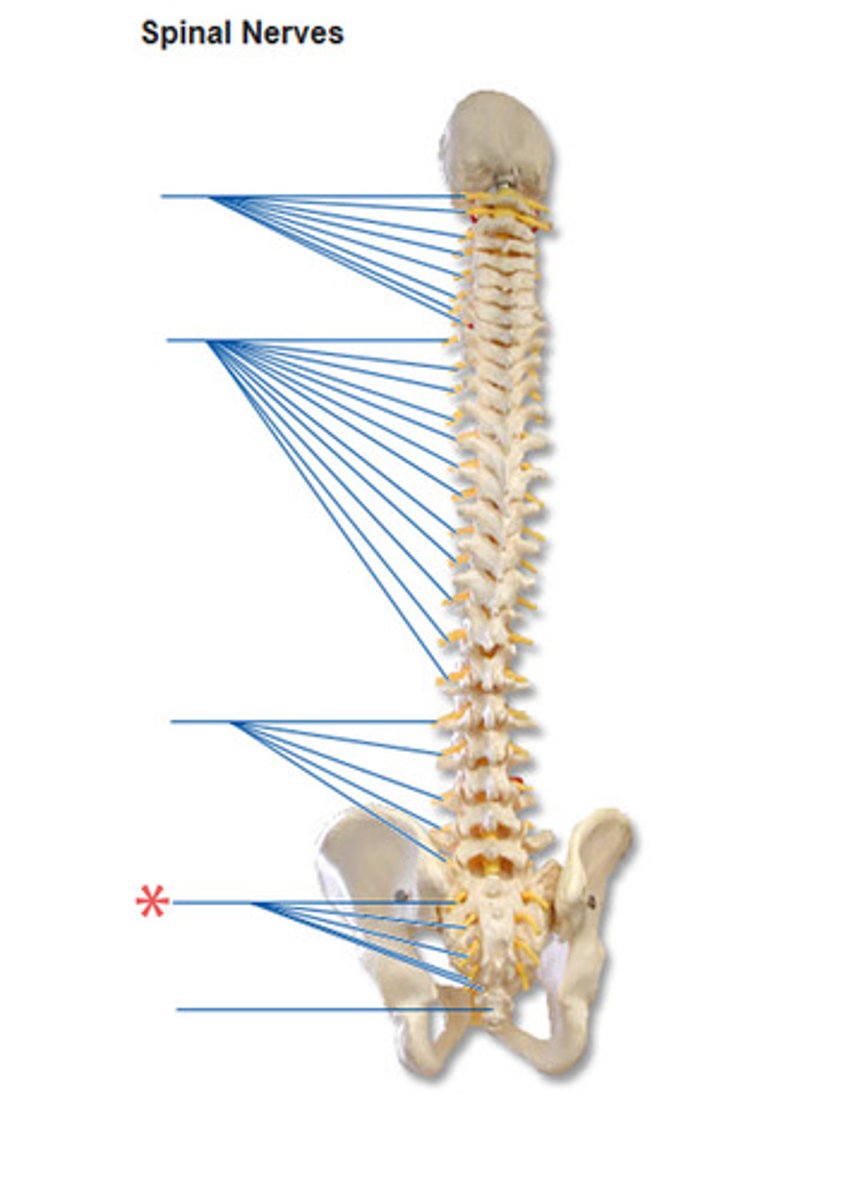
conus medullaris
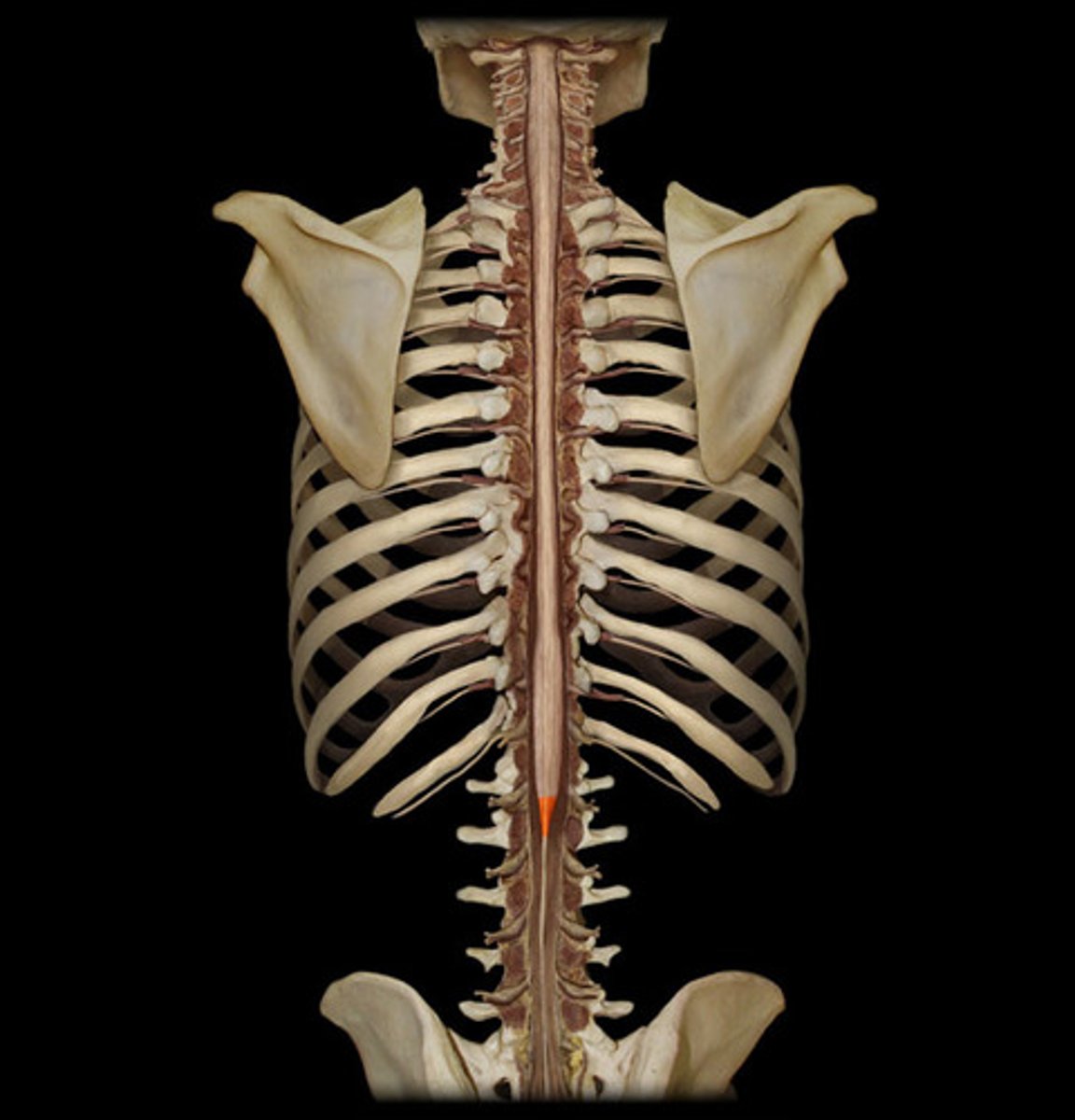
cauda equina
thicker fibers / horse tail
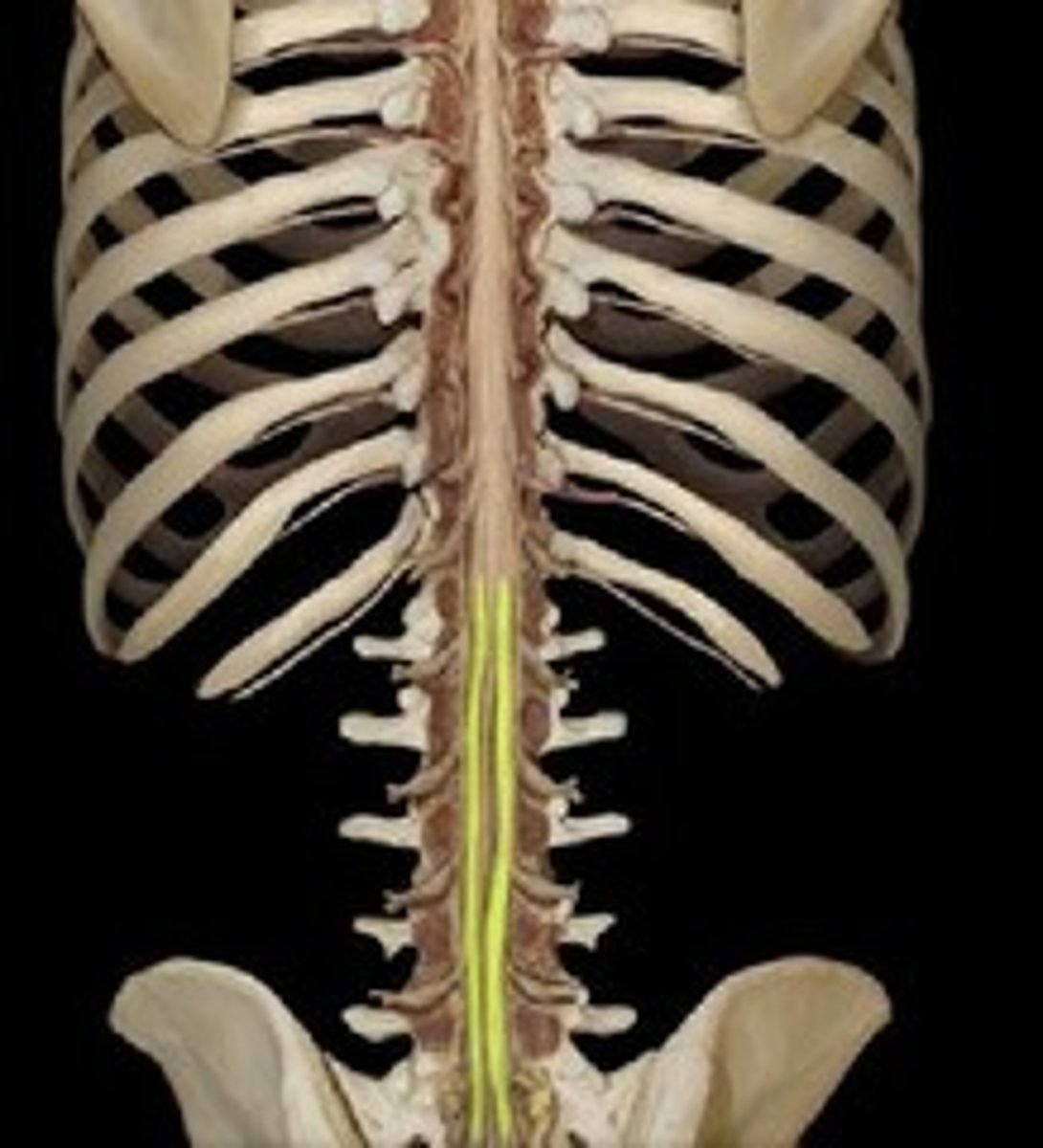
Filum Terminale
thin fibers
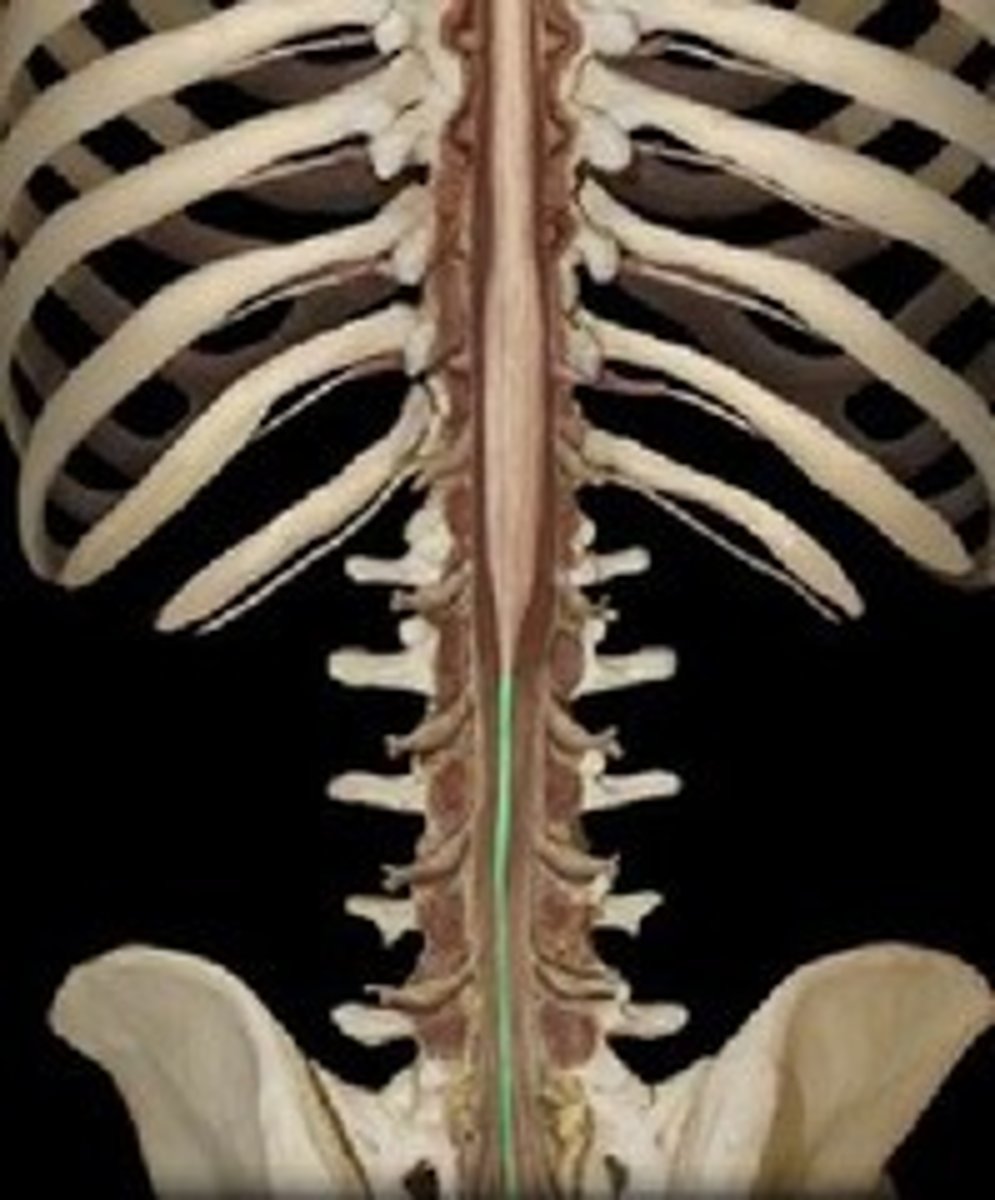
corpus callosum
what do you cut for the last resort to end seizures