HLTH 4011 FINAL
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Which specific persons were mentioned as being vulnerable to this specific outbreak of whooping cough?
Latino farm workers
Children/infants under the age of 3 months (latino background)
Which specific places were mentioned as being vulnerable to this specific outbreak of whooping cough?
Fresno County, California (central valley)
Which specific times of the year were mentioned as being vulnerable to whooping cough?
May, July, August (peak season in the summer)
What are the factors impacting the public health importance of the problem for surveillance?
Volatility (or changes) of incidence/prevalence
Severity of sequela (or consequences)
Virulence/mortality
Communicability
Potential for outbreak
Public concern
ability to ______, ______, or ______ the problem.
prevent, control, treat
Capacity of the health system to implement ______ ________ for the problem.
control measures
Disease outbreaks are more likely to be investigated when…
number of affected persons is large
health-related event is severe
control measures exist
outbreak has the potential to spread
What is the method for documenting or tracking events or persons over time?
Registries
What is the name of the permanent record of persons or events?
Registries
What do diseases registries usually include?
diagnostic, treatment, and outcome information
What are registries of vital events?
birth, marriage, death
what are registries used to track in preventative medicine?
immunizations
Disease-specific registries
blindness, birth defects, cancer, psychiatric cases
Registries of persons at-risk or exposed
atomic bomb survivors, World Trade Center survivors
what is reporting of certain diseases as specified by law, regulation, or agreement that is made to a state or local health agency?
Notification
Reporting/underreporting of notifiable diseases:
For rare, serious diseases of public health importance (e.g., rabies, plague, botulism) reporting approaches 100%
what are other non-life threatening diseases (e.g., shigellosis) can be as low as 9%
Non-symptomatic
Did not see a physician
Not reported to the health department
What does it mean by the CDC MMWR?
CDC Morbidity and Mortality weekly report
The proportion of people with a health condition (i.e., cases) that are correctly identified by a screening or case definition
Sensitivity
What is the ability of surveillance to detect (and exclude) persons not having the health problem (i.e., non-cases) it is intended to detect?
Specificity
Which term in our text/slides refers to the proportion of persons without a health condition (non cases) that are correctly identified by a screening or case definition?
Specificity
What is a true positive, and what cell does it go in?
A positive test for a person who has the condition
Cell A
What is a false positive, and what cell does it go in?
A positive test for a person who actually does not have the condition
Cell B
What is a false negative, and what cell does it go in?
A negative test for a person who actually has the condition
Cell C
What is a true negative, and what cell does it go in?
A negative test for a person who does not have the condition
Cell D
What are the treatment implications of a false positive?
Doesn’t have asthma, unnecessary treatment
What are the treatment implications of a false negative?
Has asthma, not getting treated when they should
For a sensitivity rate calculation, what goes in the numerator? denominator?
numerator - those with the condition who were correctly identified (true positives)
denominator - all those with the condition, regardless of whether they were identified correctly
All cases: True positives & False negatives
what is the formula for sensitivity rates?
A/(A+C)
true positives divided by the sum of true positives and false negatives
what are sensitivity rate ranges?
Can range between 0% and 100%
The higher the rate, the more accurate the test is in detecting cases
Higher sensitivity = fewer false negatives
For a specificity rate calculation, what goes in the numerator? denominator?
Numerator: those without the condition who were correctly identified (True negatives)
Denominator: all those without the condition, regardless of whether they were identified correctly
All non-cases: True negatives & False positives
What is the formula for specificity rates?
D/(B+D)
True negatives divided by the sum of true negatives and false positives
what are specificity rate ranges?
Can range between 0% and 100%
The higher the rate, the more accurate the test is in detecting non-cases
Higher specificity = fewer false positives
What does it mean when either sensitivity or specificity is 80% or lower?
poor/unacceptable
Low sensitivity = too many false negatives
Low specificity = too many false positives
What is the primary way that clusters (suspected outbreaks) are detected?
Reviewing ________ data.
Surveillance
what is the most important purpose/reason of field investigation?
control the outbreak and prevent additional cases
What are surveillance related changes that should be considered and controlled for in suspected outbreaks (clusters)?
changes in:
reporting (notification)
population (size, demographics)
diagnosis (# tested, type of tests)
case definition (AIDS in 1993)
analyzing by person:
Age, gender, race/ethnicity, school or workplace, presence of risk factors (e.g., cigarette smoking, recent travel)
analyzing by place:
Spot maps (small outbreaks) and area maps (larger outbreaks), demonstrate clusters and patterns
analyzing by time:
Display in a table by day, week, month, year, decade, etc.
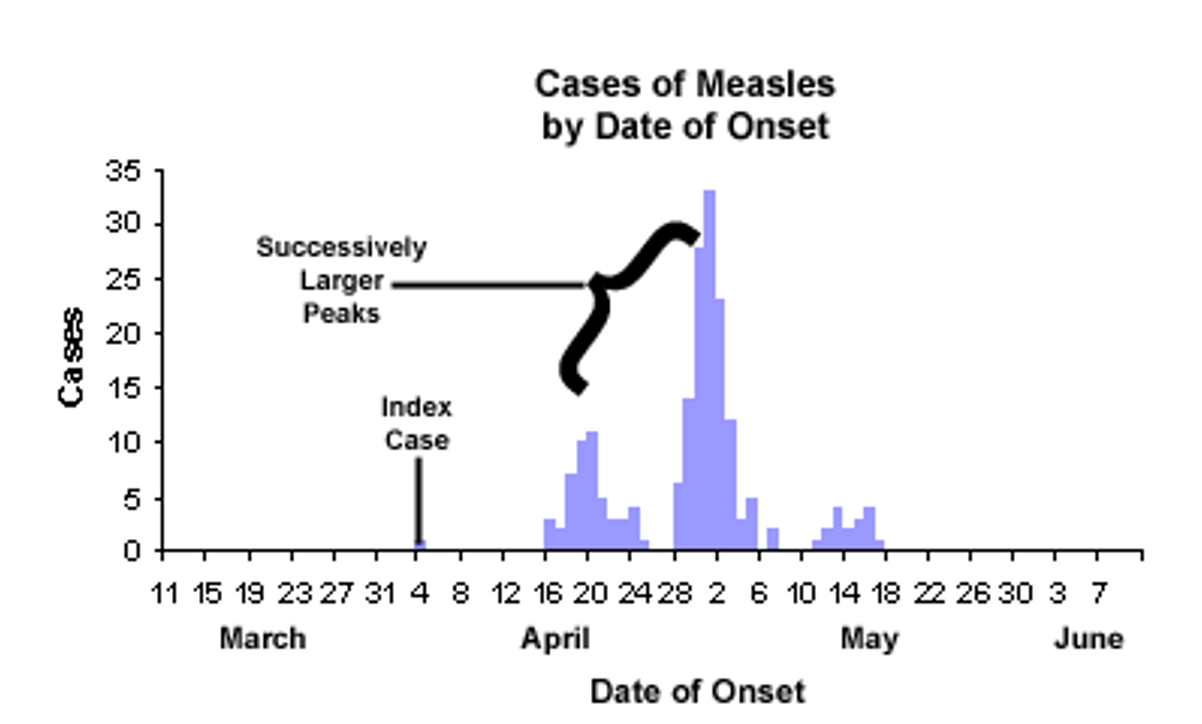
The illustration of a measles outbreak is most consistent with which epi-curve type?
Propagated
What is the type of outbreak that might occur in a point source outbreak?
foodborne outbreaks
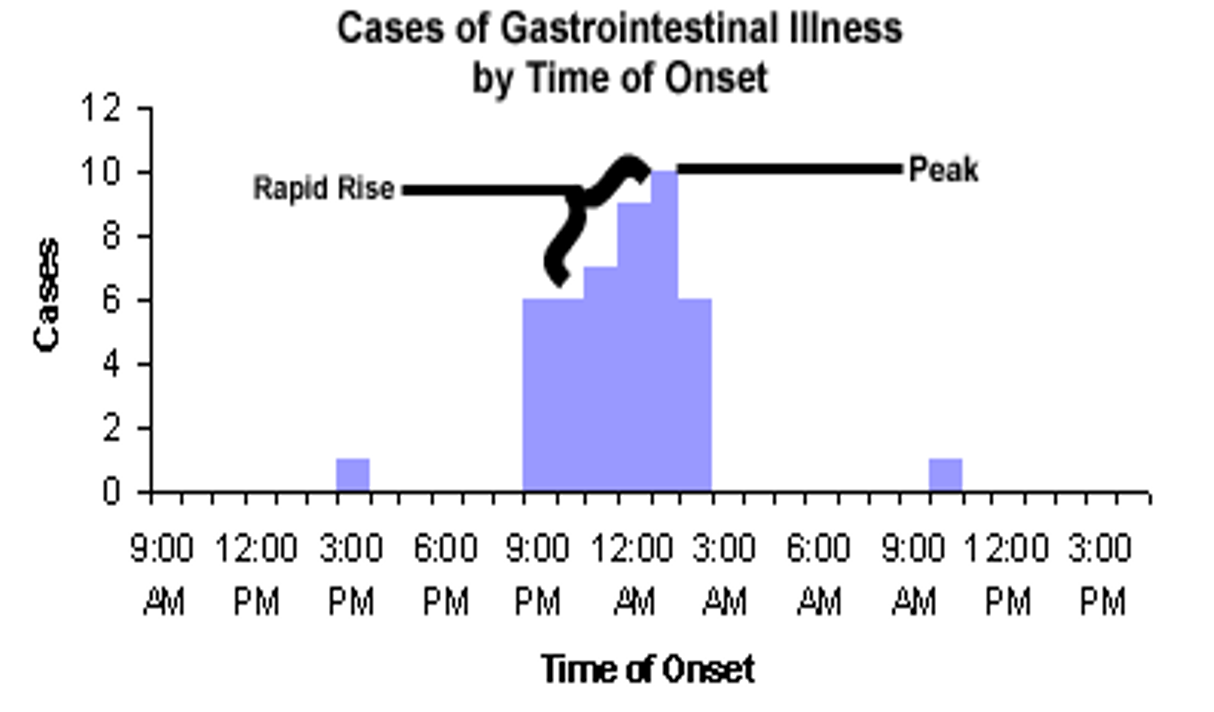
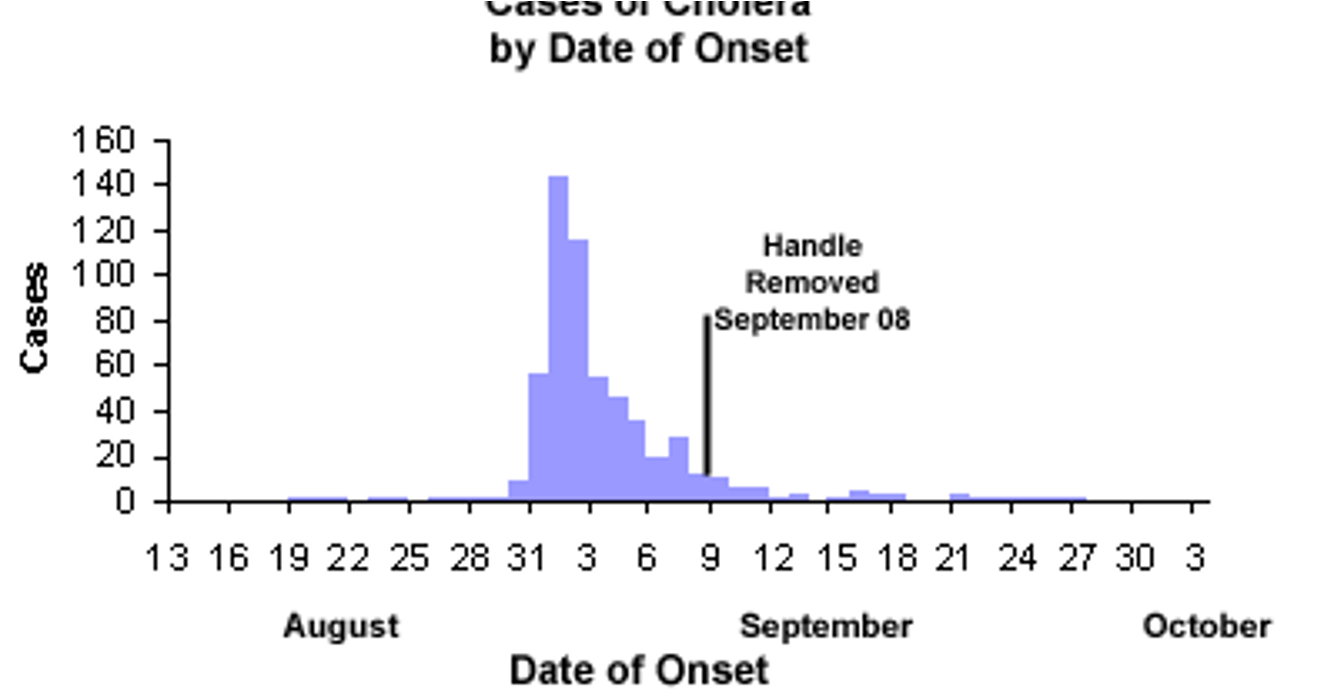
what is the example of a continuous common source?
John Snow Study
What disease outbreak is related to propagated (progressive source)?
measles
when calculating relative risk, what is the formula for attack rate exposed? unexposed?
Ill exposed/Total exposed
Ill unexposed/Total unexposed
(percent, so multiply by 100)
what is the formula for calculating risk ratio?
Exposed attack rate/Unexposed attack rate (not a percent)
RR = 1
identical risk among groups (exposed and unexposed)
Hypothesis about exposure (suspected risk factor) is incorrect
RR > 1
increased risk for the exposed group (numerator)
Hypothesis about exposure is correct
RR < 1
increased risk for the unexposed group (denominator)
Finding about exposure is the opposite of the hypothesis
Any food/drink item with a Risk Ratio greater than ____ warrants further investigation
2
when to implement control and prevention measures?
As soon as possible (ASAP)
what are control measures usually directed against?
one or more chain of transmission
what is the statistical analysis program used for the project?
SPSS
Categorical variable-types
Nominal variable (no numerical ranking)
Ordinal variable (numerically ranked, not necessarily evenly ranked)
Interval variable (open-ended, assess numeric variables)
What types of questions are nominal?
Yes/no variables are nominal variables
For Yes/No questions, it is important to consider whether “not applicable” (N/A) should be an option
what types of questions are ordinal?
Likert scale variables are ordinal variables
Assessing behaviors (how often)
1. Never
2. Rarely
3. Sometimes
4. Often
5. Always
what types of questions are interval?
Open-ended questions that assess quantitative (numeric) variables are continuous variables
is this an example of categorical or continuous? What is highest number of drinks you have consumed in a day?
Continuous
What do you do in SPSS when you are addressing missing data?
leave it blank
What survey revision strategies were utilized?
part 1: added/changed 4 questions based off of existing surveys
part 2: pilot test in class (feedback)
what are measures of central location?
mean (average values)
median (middle value)
mode (most popular value(s))
what is epidemiological range?
from minimum value to maximum value (11-29)
what is statistical range?
subtract the minimum from the maximum (29-11 = 18)
what is standard deviation?
measure of spread or variability
what did column 1 have in the frequency table?
Response options
what does column 2 have in the frequency table?
frequency
what does column 3 have in the frequency table?
percentage
what are the factors that hindered control/prevention in the AIDS outbreak?
not closing the bathhouses, at the beginning they didn’t know what the disease was, lack of funding, gay stigma, blood banks pushing back (not wanting to test for the disease)
what person and place characteristics increased risk in the AIDS outbreak?
gay males, Haitian refugees, people with hemophilia
Miami, New York, Los Angeles, San Francisco
Sensitivity and/or specificity rates mentioned in the movie?
Hepatitis B, 88%
The primary purpose for conducting field investigations is to control the outbreak and prevent additional cases. In addition to this, list another purpose for conducting a field investigation that was mentioned in our slides.
address public concerns, opportunity to learn