MLS 2214 Exam 1
1/240
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 4, 5 and 6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
241 Terms
What is an antimicrobial?
A chemical that kills or inhibits a disease causing organism
What’s the difference in the cell membrane between eukaryotes and prokaryotes?
Cholesterol
What is an antibiotic?
A metabolic product of mold or bacteria
What is a synthetic drug?
Chemical drugs that are manufactured
What are semi-synthetic drugs
Antibiotics that have been chemically modified, most antimicrobials modernly are semi-synthetic
What is selective toxicity
Effectively kills or inhibits an organism AND
has no side effect to the host
What does selective toxicity target in bacteria?
The differences in prokaryotes and eukaryotes
What are the differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
Eukaryotes have a nucleus while prokaryotes don’t
Eukaryotes have cell bound organelles while prokaryotes don’t
Prokaryotes have a cell well (peptidoglycan) while eukaryotes don’t
Eukaryotes have 80s ribosome (60s+40s) and prokaryotes have 70s ribosome (50s+30s)
Why is the presence of a cell wall so important when it comes to antimicrobials?
It allows for something that antimicrobials can attack against that do not exist in eukaryotic cells, the peptidoglycan layer
What does s stand for in 40s and 60s
Svedburg unit, a measurement of the sedimentation rate in an ultracentrifuge. When two ribosomal subunits are combined they sediment at a faster rate than when alone
Explain selective toxicity in regards to fungus and parasites
Funus and parasites are cells that
Define narrow spectrum antibiotics
Effects only specific type of organism
Best used when causative agent is known
Define broad spectrum antibiotics
Effects wide range of organisms
used when causative agent is unknown
How do super infections happen?
Antimicrobials kill off susceptible normal flora and so opportunistic pathogens are able to grow and cause infection due to lack on competition
What are the effects of broad spectrum antibiotics on normal flora?
Wipes out all normal flora that susceptible
Creates a lack of competition - E. coli
Can result in a super infection from opportunistic pathogens
What are some examples of super infections
Ear infections - dirrhea
Yeast infections - skin rashes and vaginitis
Antibiotic associated enteritis - C. diff
Define susceptible, sensitive
An organism is inhibited or killed
Define resistant
The antimicrobial has no effect on the
Define MIC
The lowest concentration of a drug required to inhibit an organism
Define MBC
Minimum bactericidal concentration
The minimum concentration of a drug required to kill an organism
Define bacteriostatic
Suppresses an organism’s growth, if the drug is removed then the organism will continue to grow
Define bactericidal
The drug makes an irreversible lethal effect and kills the bacteria
Define broth dilution test
A method used to determine the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of an antimicrobial agent by diluting it in a liquid growth medium.
Define anaphylactic shock
A severe, life-threatening allergic reaction characterized by rapid onset, often involving difficulty breathing, swelling, and a drop in blood pressure. It requires immediate medical attention and intervention.
Define probiotics
Probiotics are live microorganisms, usually bacteria or yeast, that provide health benefits when consumed in adequate amounts. They help maintain a healthy balance of gut microbiota and can support immune function.
What are the 6 modes of antimicrobial action?
Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
Inhibition of cell membrane synthesis
Inhibition of protein synthesis
Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis
Inhibition of metabolic pathways
Inhibition of recognition or attachment
What drugs work by inhibiting cell wall synthesis?
Penicillin
ethambutol
echinocandins
carbapenems
cycloserine
Cephalosporins
Vancomycin
isoniazid
monobactams
bacitracin
How do penicillins, cephalosporins, vancomycin, monobactams and carbapenems work?
They inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
What are the two steps that are blocked in cell wall synthesis
Blocks the final step in cross linking of the peptidoglycan mesh
Blocks early peptidoglycan synthesis
What drugs work by blocking the final steps in cross linking of the peptidoglycan mesh?
Penicillin
Cephalosporins
How do penicliins’s and cephalosporins work?
work by blocking the final steps in cross linking of the peptidoglycan mesh
What drugs work by blocking the early steps in peptidoglycan synthesis?
Vancomycin
Cycloserine
Bacitracin (Neosporin)
How do vancomycin, cycloserine, and bacitracin work?
work by blocking the early steps in peptidoglycan synthesis
What is transpeptidase?
An enzyme involved in the cross-linking of peptidoglycan layers in bacterial cell walls, crucial for maintaining structural integrity
Convert the peptide chain from nag to nam
What are penicillin binding proteins
A group of proteins that bind penicillin and are important for the synthesis and maintenance of the bacterial cell wall, particularly in peptidoglycan cross-linking.
Whats another term for transpeptidase?
Penicillin-binding protein
How do drugs work by blocking the final steps in cross linking of the peptidoglycan mesh?
They bond to the transpeptidase enzymes which stop the cross linking
How do drugs work by blocking the early steps in peptidoglycan synthesis?
They interfere with enzymes used in the transfer of building blocks to cell wall from cytoplasm
Prevent peptide crossbridge from being made
What are the first two antimicrobial drugs that were put into large scale production?
Sulfa drugs
Penicillin
What are the disadvantages of Penicillin G
Most stable, but unstable in acidic solutions - cannot be taken orally
Only effective against gram pos
Not effective against penicillinase
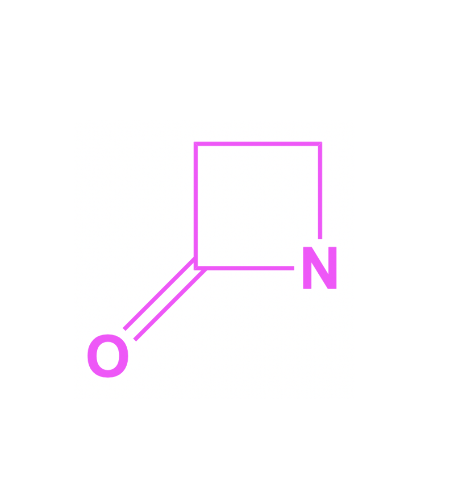
What structure is this?
Beta lactam ring
What enzymes can break down the beta lactam ring?
Penicillinase or beta lactamase
What is the end product of a Beta lactam ring that has been broken down?
Penicilloic acid, which is inactive against bacteria.
What is the difference between Penicillin G and Penicillin V?
Penicillin G is more effective against gram-positive bacteria and must be given via injection
Penicillin V is more stable in acidic environments, allowing for oral administration.
What are the advantages of using ampicillin
It is broad spectrum and acid resistant
What are the advantages of using ticarcillin?
More actively used against GNRs like pseudomonas but not as effective against some gram pos organisms
What are the common beta lactam antimicrobials?
Penicillin
Cephalosporins
Monobactams
Carbapenems
What class of antibiotics are penicillin, cephalosporins, monobactams, and carbapenems?
Beta lactam antibiotics
What are some examples of penicillins
Penicillin G, Penicillin V, methicillin, dicloxacillin, ampicillin, amoxicillin, ticarcillin and piperacillin
How are cephalosporins classified
Classified by the generation they were made
Newer generations have more effectiveness against GNRs and beta lactamase producers
What is an example of a monobactam?
Aztreonam
What is an example of a carbapenem
Imipenem
What is impenem an example of?
a carbapenem antibiotic
What is the broadest antimicrobial?
Imipenem
Why should imipenem only be used in emergencies?
Because it is so broad it will kill off NF and may lead to resistant infections
What are beta lactamase inhibitors?
Have a high affinity for beta lactamase
Best used in combo with B lactam drugs
Clavulanic acid
Amoxicillin + clavulanate
Ticarcillin + clavulanate
How do antimicrobials inhibit the synthesis of the cell membrane?
Attaches to phospholipids
Combines with sterols (cholesterol)
Why do antimicrobials inhibit the synthesis of the cell membrane work?
They increase the permeability and reduce the osmotic integrity of the plasma membrane
Why is the selective toxicity low for cell membrane synthesis inhibitors?
Because they are only used as topical treatment and not used orally
Eukaryotes have a cell membrane with minimal differences from prokaryotes
What are some examples of antimicrobials that inhibit cell membrane synthesis
Polymyxin B
Bacitracin
Ergosterol
Azoles
How do polymyxin B, bacitracin, ergosterol and azoles work?
Inhibit cell membrane synthesis
Where is ergosterol found?
In fungal cell membranes.
Why does ergosterol increase selective toxicity of amphotericin B?
Because amphotericin binds selectively to ergosterol in fungal membranes, disrupting their integrity without affecting human cell membranes that contain cholesterol
How do antimicrobials that inhibit protein synthesis work?
Bind to the 50S subunit or bind to the 30S subunit
How does an antimicrobial that binds to the 50S subunit work?
Inhibits the formation of peptide bonds in growing poly peptide chains
Inhibits peptide chain elongation
What antimicrobial inhibits the formation of peptide bonds in growing poly peptide chain?
Chloramphenicol
What antibiotic inhibits peptide chain elongation?
-rythromycin
Azithromycin
Linezolid
How do azithromycin, linezolid and -rythromycin work?
They inhibit peptide chain elongation during protein synthesis.
How do antimicrobials that attach to the 30S subunit work?
Interferes with the attachment of tRNA
Causes misreading of mRNA by changing the shape of 30S
What is an antimicrobial that interferes with the attachment of tRNA
Tetracycline
How does tetracycline work?
It inhibits protein synthesis by preventing the attachment of tRNA to the ribosome.
What are antimicrobials that cause a misreading of mRNA by changing the shape of the 30S
Aminoglycosides
Streptomycin, gentamicin, neomycin, tobramycin, amikacin
How do aminoglycosides work?
cause a misreading of mRNA by changing the shape of the 30S
How do nucleic acid synthesis inhibitors work?
Targets enzymes or precursors used in DNA and RNA synthesis
Selective toxicity is limited to slight differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
How does polymerase work?
An enzyme that synthesizes DNA and RNA
The antimicrobial target mRNA synthesis
What antibiotic targets mRNA synthesis
Rifampin
R N A
How does rifampin work?
Rifampin works by inhibiting RNA polymerase, preventing bacterial RNA synthesis, which ultimately stops bacterial growth.
What is topoisomerase and DNA gyrase
Topoisomerase - helps unwind DNA and RNA
DNA gyrase - winds DNA back into a super coil
What antibiotics target topoisomerase and DNA gyrase?
Quinolones + nalidixic acid
Fluroquinolones
Ciprofloxacin, floxacin, norfloxacin, ofloxacin, and levofloxacin
How do quinolones and fluoroquinolones work?
Quinolones and fluroquinolones work by inhibiting bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV, leading to interference with DNA replication and transcription
What antibiotics work by targeting nucleotide analogs?
Flucytosine - antifungal
How does flucytosine work?
It blocks the ability to create uracil in RNA
What are the modes of action in antimicrobials that inhibit the metabolic pathway
Is a competitive analogue to PABA (Para amino benzoic acid)
Competitive analogue to dihydrofolic acid
Where to bacteria get their folic acid?
They synthesize it themselves
What are the steps in the folic acid pathway?
PABA
Dihydrofolic acid
Tetrahydrofolic acid
Purine and pyrimidine nucleotides
DNA and RNA
What drugs compete and PABA?
Sulfonamides
What drugs compete with dihydrofolic acid
Trimethoprim used with Sulfamethoxazole
What are two genetic changes that can lead to drug resistance?
Chromosome mediated resistance
Transfer of genetic material
Define transformation?
A recipient cell takes up DNA from the environment
Define conjugation?
A fertility plasmid forms a conjugation pili that attaches to another cell and transfers genes
Define transduction
DNA is transferred from one cell to another via a virus
What is plasmid mediated resistance
An extra chromosomal DNA part has a gene that codes for higher resistance
What is MRSA
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
What is ORSA
Oxacillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
What is VRSA
Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
What is VISA
Vancomycin-intermediate Staphylococcus aureus
What is VRSE
Vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis
What is VRE
Vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus
What is CRAB
Carbapenem-resistant Acinetobacter baumannii
What is MDR TB
Multidrug-resistant tuberculosis