3.9 DNA Replication & the Genetic Code
1/37
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
38 Terms
In what stage of the cell cycle does DNA replication occur?
interphase
Why must DNA be copied when cells divide?
so that each daughter cell is genetically identical
Why must the copying of DNA be accurate? Why might it not be accurate?
To conserve the genetic information. A mutation can cause differences in copied DNA
What is a mutation?
a random and spontaneous change in the formation of DNA base sequences
What is the term given to the process by which DNA replicates?
semi-conservative replication
What does the term semi-conservative replication mean?
for every 2 molecules of DNA produced/formed, each molecule contains 1 parent strand and one new strand
What enzyme unzips the DNA molecule before replication?
DNA helicase
In what part of the cell are free, activated nucleotides found?
nucleoplasm
What enzyme joins adjacent nucleotides in the new strand of DNA?
DNA polymerase
What is the term describing the part of DNA where free nucleotides joins once it has been unzipped?
replication fork
Describe how DNA replicates by semi-conservative replication
The DNA helix unwinds and the enzyme DNA helicase unzips the molecule by breaking the hydrogen bonds between the CBP at the replication fork.
Free, activated nucleotides form CBP with each parent template strand - A→T by 2 H bonds, C→G by 3 H bonds, always purine to pyrimidine
DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides on each new strand by phosphodiester bonds in condensation reactions (releasing water molecules) to create a sugar phosphate backbone
2 genetically identical DNA molecules are formed, each containing one parent strand that acted as a template strand for a new, complementary strand
Where does the energy to form the phosphodiester bonds come from?
the extra phosphate groups of the free activated nucleotides, which are hydrolysed off
How are free nucleotides activated in the nucleoplasm?
with extra phosphate groups
True or false? DNA in prokaryotes also replicates semi-conservatively
true
Describe how DNA replicates in prokaryotes, and inside mitochondria and chloroplasts
A bubble sprouts from the loops of DNA, unwinding and unzipping it so complementary nucleotides can join the exposed area until the entire loop is copied
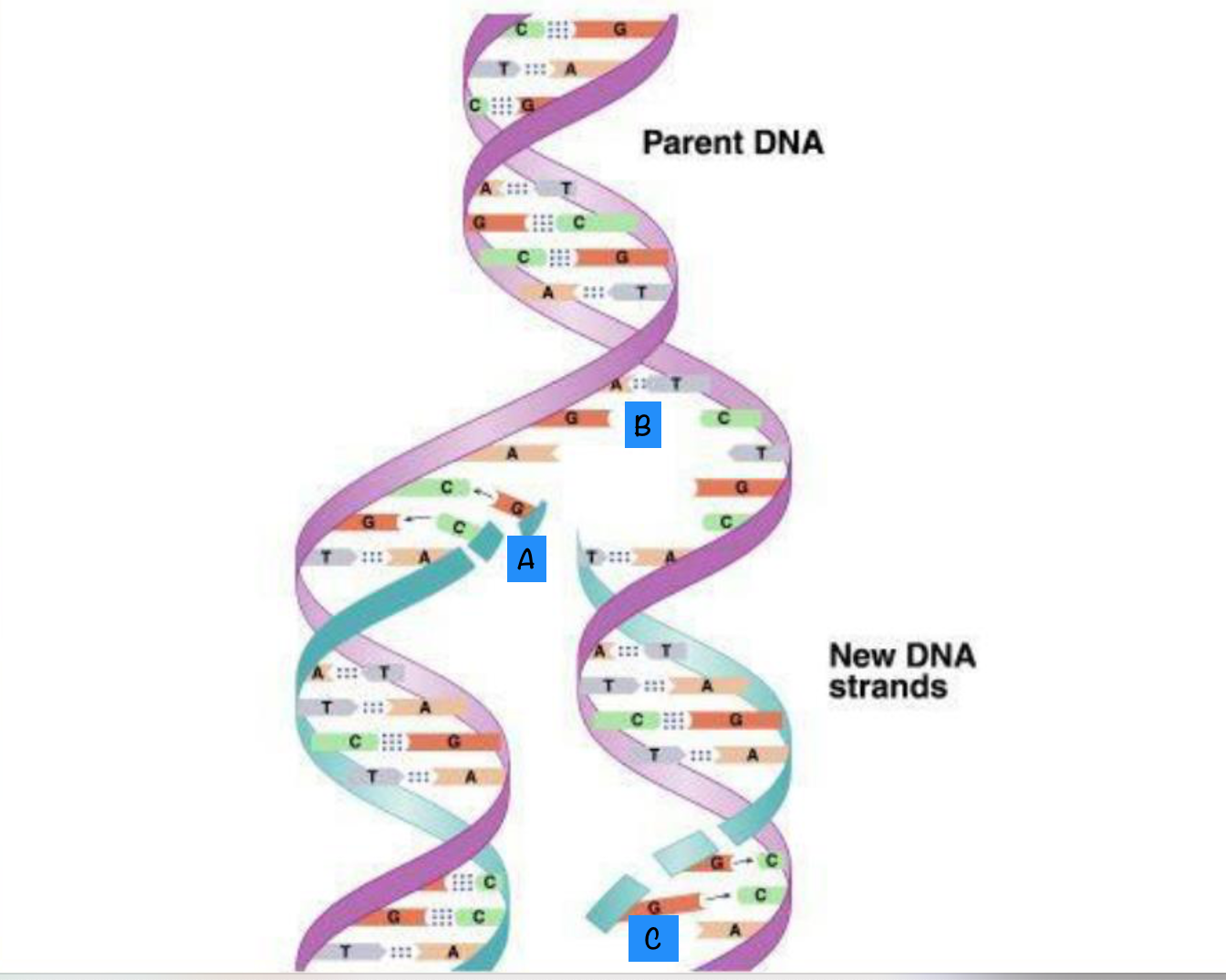
This image shows semi-conservative replication. Which letter represents the replication fork?
B
What were the 3 theories of how DNA self-replicated called?
conservative, semi-conservative, dispersive
What was the theory of conservative DNA replication?
original molecules act as templates and new molecules are made
What was the theory of dispersive DNA replication?
original molecules break into nucleotides and each one joins to a complementary nucleotide, which join into strands
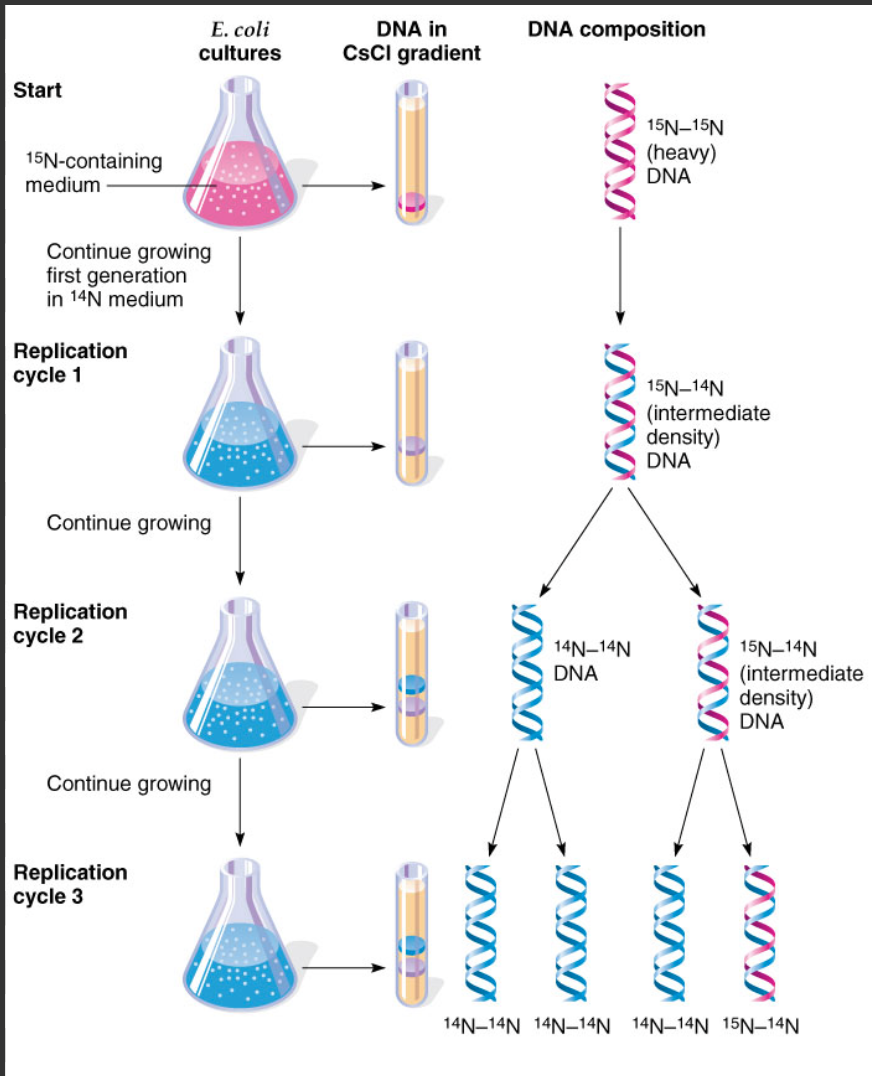
Using the diagram, briefly describe the Meselson and Stahl experiment that provided evidence of semi-conservative replication
nucleotides contain nitrogen, so free nucleotides in heavy nitrogen isotopes contain N15, and the ones formed in light nitrogen contain N14
bacteria was grown in a heavy (N15) nitrogen medium
it was transferred to a medium of light nitrogen (N14) and after a single replication the DNA has a medium density, being made from both N15 (parental strand) and N14 (new strand)
the next replication lead to some DNA only containing N14 isotopes and some contain N15-N14, forming 2 bands when spun in a centrifuge
for future replications, the band at N15-N14 will get thinner, while the band at N14 gets thicker
Fill in the blanks: DNA contains the ___ ___ which codes for the synthesis of all ____
genetic code, polypeptides
What is a gene?
the sequence of DNA that codes for the synthesis of a specific polypeptide
Why is the genetic code contained in the nucleus?
so it can be conserved/protected
Fill in the blanks: polypeptides are chains of ___ ___ joined by ____ bonds
amino acids, peptide
How many different amino acids are there?
20
What is a genome?
the entire sequence of DNA in an organism
What is the position of a gene of a chromosome called?
locus (loci)
What is found in between genes of DNA?
non-coding DNA
Give 5 words/phrases to describe the genetic code
triplet code, degenerate, widespread (but not universal), contains punctuation, is non-overlapping
Why is the genetic code a triplet code?
the sequence of DNA nucleotide bases found within a gene is determined by a triplet code, with each sequence of three bases, a codon, coding for 1 amino acid
How many different codons are there if 4 DNA bases are grouped into triplets?
64 (4³)
Why is the genetic code degenerate?
there are 64 different codons that code for only 20 amino acids, so multiple codons can code for the same amino acid
Why is it important that the genetic code is degenerate?
it helps to limit the number of mutations that have an serious effect
Fill in the blanks: the genetic code is (w)____ but not (u)_____
widespread, universal
Why is the genetic code not completely universal?
a few organisms have different nitrogenous bases
How is the genetic code said to have punctuation?
it has a universal start codon (AUG) and stop codons
True of false? the start codon of the genetic code also codes for an amino acid, but the stop codons don’t
true
What is meant by the term gene expression?
the sequence of bases expressed as an amino acid through the processes of transcription and translation