NHM 340 - Healthcare Systems and Policy (M5)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 7:33 PM on 3/12/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
1
New cards
Categories of Health Insurance and Percentage of U.S. Population Enrolled
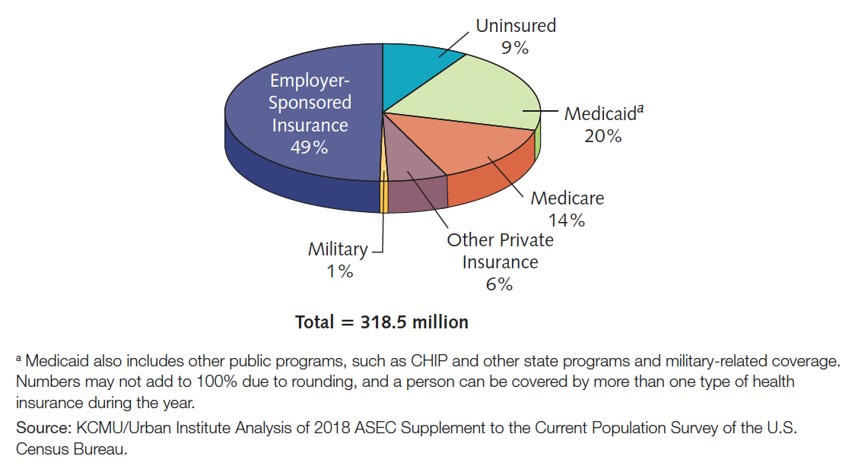
2
New cards
What are the two general categories of health insurance in the U.S.?
Private and Government/public health insurance
3
New cards
What type of private health insurance includes indemnity or traditional fee-for-service insurance?
Indemnity or traditional fee-for-service insurance
4
New cards
What type of private health insurance focuses on managed care?
Managed-care insurance
5
New cards
What type of private health insurance allows consumers to direct their own health care spending?
Consumer-directed health plans
6
New cards
What is the Medicare Program?
A government/public health insurance program for individuals aged 65 and older or with certain disabilities
7
New cards
What is the Medicaid Program?
A government/public health insurance program for low-income individuals and families
8
New cards
What is the Military Health System?
A government/public health insurance program for military personnel and their families
9
New cards
What does CHIP stand for?
Children's Health Insurance Program
10
New cards
What are individual state health plans?
Health insurance programs managed by individual states
11
New cards
What are indemnity or traditional fee-for-service plans?
They are insurance plans that charge for each service rendered.
12
New cards
What percentage of insurance coverage today is accounted for by private insurance?
Only a small percentage.
13
New cards
What do proponents of private insurance prefer?
Greater flexibility and unrestricted access to health care providers and facilities.
14
New cards
What do critics claim about fee-for-service plans?
They encourage physicians to provide unnecessary services.
15
New cards
What is managed-care insurance?
Insurance that tries to limit the use of health services, reduce costs, or both.
16
New cards
What are some types of managed-care insurance?
Health maintenance organizations (HMOs), Preferred provider organizations (PPOs), Point-of-service plans (POSs), Exclusive provider organizations (EPOs).
17
New cards
What is the presumed goal of managed care?
Improved quality of care with decreased costs.
18
New cards
What percentage of coverage for employees is accounted for by managed care?
Around 99%.
19
New cards
What are consumer-directed health plans?
Plans that combine a high-deductible health plan (HDHP) with a tax-advantaged health reimbursement arrangement (HRA) or health savings account (HSA).
20
New cards
How do enrollees use a health savings account (HSA)?
To pay for a portion of their health expenses.
21
New cards
What do proponents of consumer-directed health plans contend?
Enrollees seek lower-cost care and only seek care when necessary.
22
New cards
What do critics state about consumer-directed health plans?
Employers may use these to shift the cost of coverage to employees.
23
New cards
What are the two major public health insurance plans in the United States?
Medicare and Medicaid
24
New cards
Which federal agency is responsible for administering Medicare and Medicaid?
The Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
25
New cards
What does CHIP provide?
Health coverage to uninsured children
26
New cards
What government agency provides health care services to veterans?
The Department of Veterans Affairs (VA)
27
New cards
What service includes the Indian Health Service?
The Public Health Service
28
New cards
Which department provides health care services to military personnel and their families?
The Department of Defense (including TRICARE)
29
New cards
What types of facilities provide health care services in the public sector?
Public hospitals and community health centers
30
New cards
What programs provide health services at the state and local level?
State and local public health programs
31
New cards
What program pays benefits to workers injured on the job?
Workers' compensation
32
New cards
What are common coverage gaps in public health insurance?
Prescription drug coverage and skilled nursing/long-term institutional care
33
New cards
What type of policy helps cover gaps in Medicare?
Medigap policy from private insurance companies
34
New cards
What is Medicare, Part C also known as?
Medicare Advantage
35
New cards
What are the eligibility requirements to join Medicare Part C?
The individual must have Medicare Part A and Part B
36
New cards
Who are the uninsured in America?
Working poor, self-employed, early retirees, and unemployed
37
New cards
What percentage of all Americans are uninsured?
13%
38
New cards
What type of medical care do uninsured individuals often use?
Hospital emergency room care
39
New cards
What do uninsured individuals often do regarding treatment?
Delay getting treatment
40
New cards
What is a consequence of uninsured individuals delaying treatment?
They later require more expensive medical services
41
New cards
How much was spent on health care services and products in the U.S. in 2013?
$2.9 trillion
42
New cards
What is a major contributor to the high cost of health care related to managing insurance?
Administration of insurance process
43
New cards
What practice in medicine contributes to the high cost of health care by avoiding potential legal issues?
Practice of defensive medicine
44
New cards
What type of costs contribute to the high cost of health care related to legal accountability?
Professional liability costs
45
New cards
What are the three trends characterizing efforts at cost containment in healthcare?
Move away from traditional fee-for-service to managed care models.
Companies managing employee healthcare through self-insured plans.
Payers setting reimbursement restrictions and limitations.
46
New cards
What is the Prospective Payment System (PPS) based on?
Diagnosis related groups (DRGs).
47
New cards
What factors are used to classify patients in the Prospective Payment System (PPS)?
Principal diagnosis, secondary diagnosis, age, sex, and surgical procedures.
48
New cards
What does each Diagnosis Related Group (DRG) have assigned to it?
A relative weight reflecting the cost of care.
49
New cards
What coding system is used in the Prospective Payment System (PPS) to classify diseases and diagnoses?
ICD 10-CM.
50
New cards
What has the Prospective Payment System (PPS) resulted in an increased focus on?
Outpatient services and preventive medicine.
51
New cards
Why are outpatient services emphasized in the Prospective Payment System (PPS)?
They are less costly than inpatient care.
52
New cards
What percentage of the population do baby boomers make up?
More than one-fourth
53
New cards
What percentage of the population is expected to be over 65 by 2030?
21%
54
New cards
What can be expected to rise due to demographic trends?
Demand for care
55
New cards
What type of disparities are highlighted in demographic trends?
Racial and ethnic disparities
56
New cards
Which population is expected to increase according to demographic trends?
Hispanic population
57
New cards
What is one of the goals of Healthy People 2030?
To eliminate health disparities
58
New cards
What does Healthy People 2030 aim to achieve in addition to eliminating health disparities?
Health equity
59
New cards
What is a key factor that Healthy People 2030 aims to improve?
Health literacy
60
New cards
What do most industrialized countries, except the U.S., have regarding health care?
National health care programs
61
New cards
How is health care coverage characterized in most industrialized countries?
It is universal and uniform
62
New cards
How are health care costs typically covered in most industrialized countries?
By tax revenues or a combination of individual/employer premiums and government subsidization
63
New cards
What is the goal of Healthy People 2030?
To decrease racial/ethnic and other health disparities
64
New cards
What types of outcomes will Healthy People 2030 track in relation to demographic factors?
Rates of illness, death, chronic conditions, behaviors, and other types of outcomes
65
New cards
Which demographic factors will Healthy People 2030 consider when tracking health outcomes?
Race and ethnicity, gender, sexual orientation, disability status or special health-care needs, and geographic location (rural and urban)
66
New cards
What is the Affordable Care Act?
A health care reform law enacted in 2010.
67
New cards
What does the Affordable Care Act aim to reduce?
The number of people who are uninsured.
68
New cards
How does the Affordable Care Act improve the health insurance system?
It makes the system work better for all consumers.
69
New cards
What transformation does the Affordable Care Act promote in health care?
It transforms delivery and payment systems to get better value.
70
New cards
What is the focus of health care reform according to the Affordable Care Act?
It reorients focus to prevention and primary care.
71
New cards
What role do nutrition protocols play in health care reform?
They serve as frameworks to help practitioners in the assessment, development, and evaluation of nutrition interventions.
72
New cards
What are the components of the scope of dietetics practice?
Nutrition assessment, counseling, and education.
73
New cards
What is involved in the research aspect of dietetics practice?
Development and evaluation of nutrition guidelines.
74
New cards
What administrative tasks are included in dietetics practice?
Management of time, finances, personnel, etc.
75
New cards
What is evaluated in community nutrition programs?
The effectiveness of nutrition counseling/education and community nutrition programs.
76
New cards
What do community nutritionists need to compete for?
A fair share of the health-care dollar.
77
New cards
Conflicting Healthcare Expectations Figure
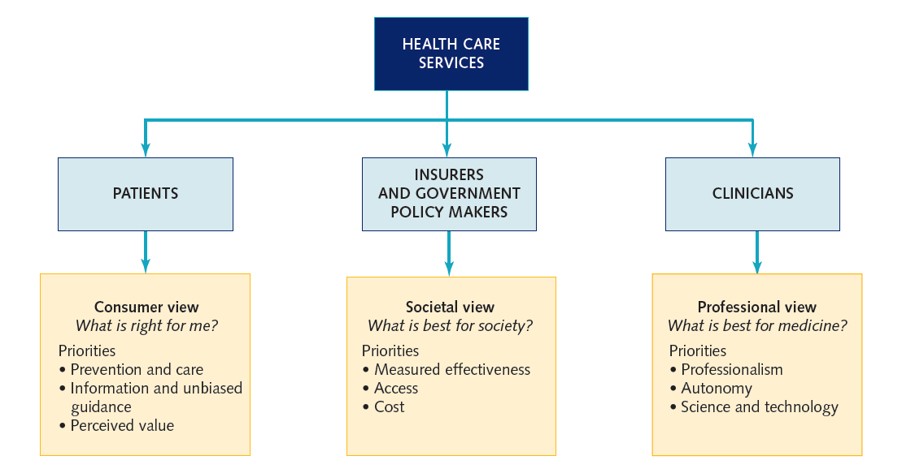
78
New cards
What has been the legislative priority of the Academy since 1992?
Inclusion of medical nutrition therapy as a covered benefit in health care delivery.
79
New cards
What is the focus of the Academy regarding medical nutrition therapy?
Securing reimbursement under existing federal insurance programs.
80
New cards
Under which part of Medicare is medical nutrition therapy currently covered for selected recipients?
Part B.
81
New cards
For which conditions is medical nutrition therapy covered under Medicare for selected recipients?
Diabetes and renal disease.
82
New cards
What is the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics actively trying to do regarding medical nutrition therapy coverage?
Increase coverage through legislation for other conditions, including prediabetes, obesity, hypertension, and eating disorders.
83
New cards
What will be one of the strongest factors affecting health care?
The paradigm shift from sickness to wellness.
84
New cards
What will medical education need to do in the future?
Medical education will have to change.
85
New cards
How must health care change in the future?
It must change from a system based on treatment of acute conditions to disease prevention and health promotion.
86
New cards
What role must nutrition services play in future health care?
Nutrition services must be part of preventive care.
87
New cards
What should all practitioners document regarding their nutrition programs?
They should document cost-effectiveness to support the integration and utilization of nutrition services in preventive care.