Lab 7 - Chemical Digestion and Anatomy of the Accessory Structures of the Digestive System
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
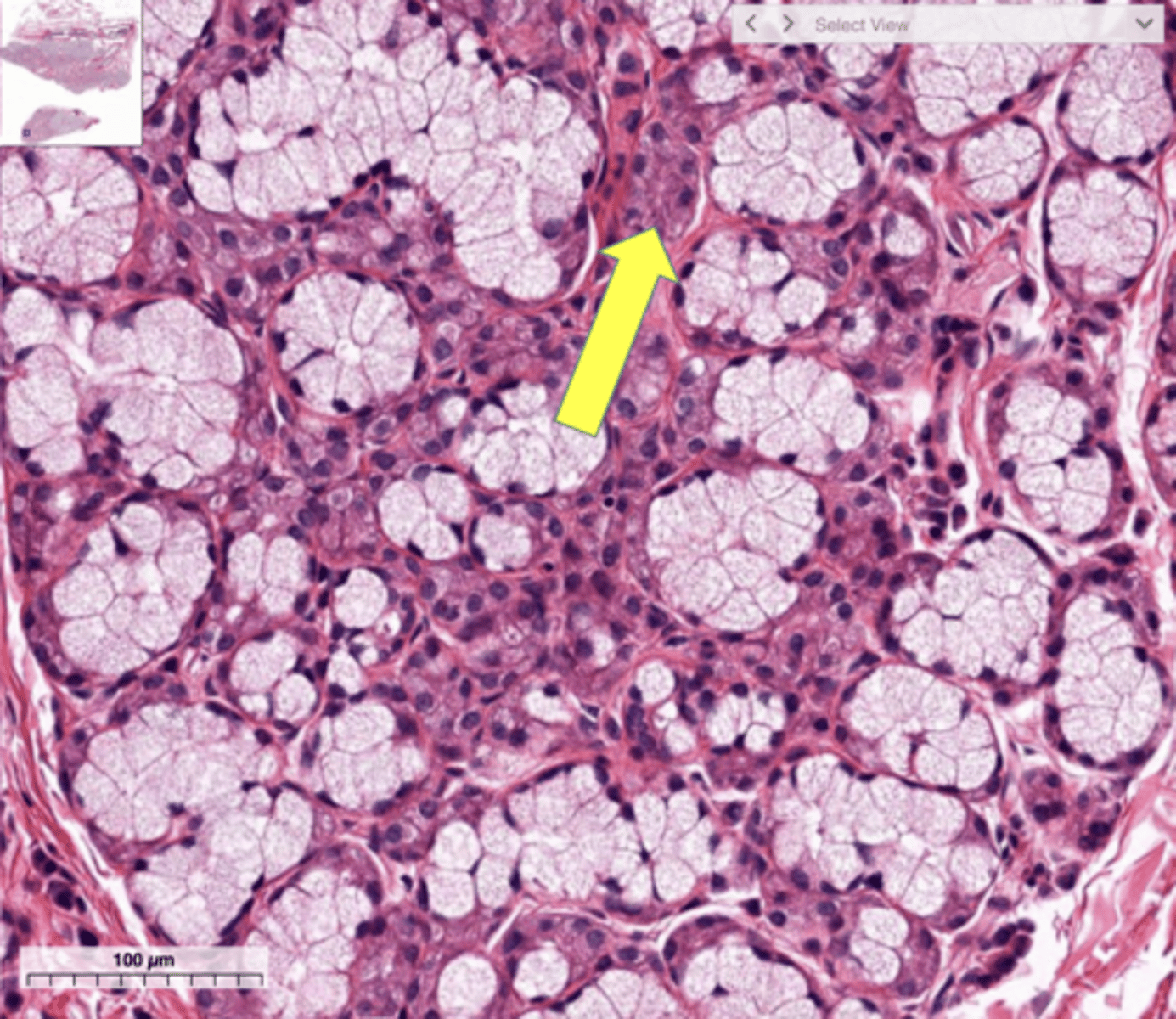
Salivary gland
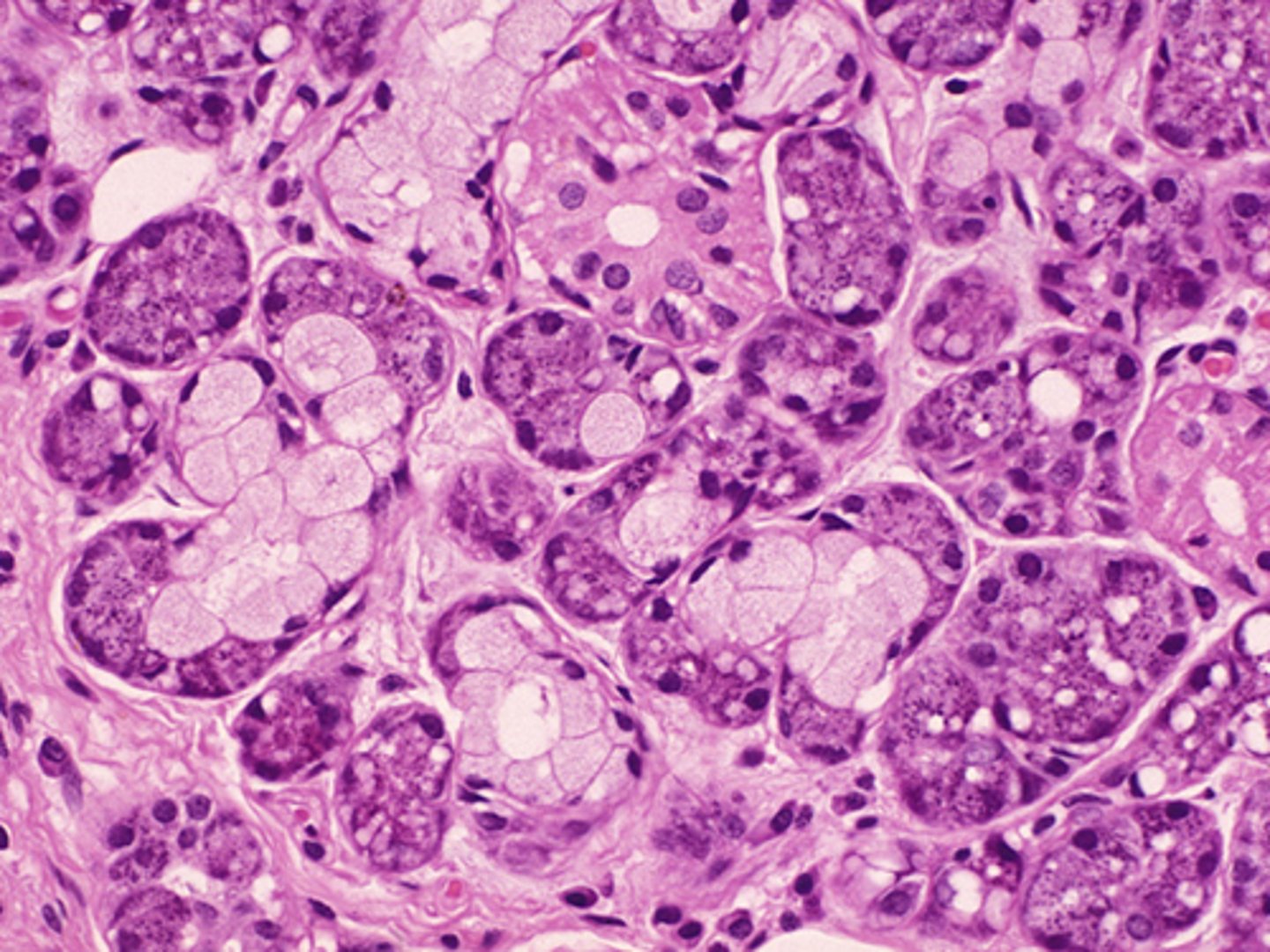
Mucous cell
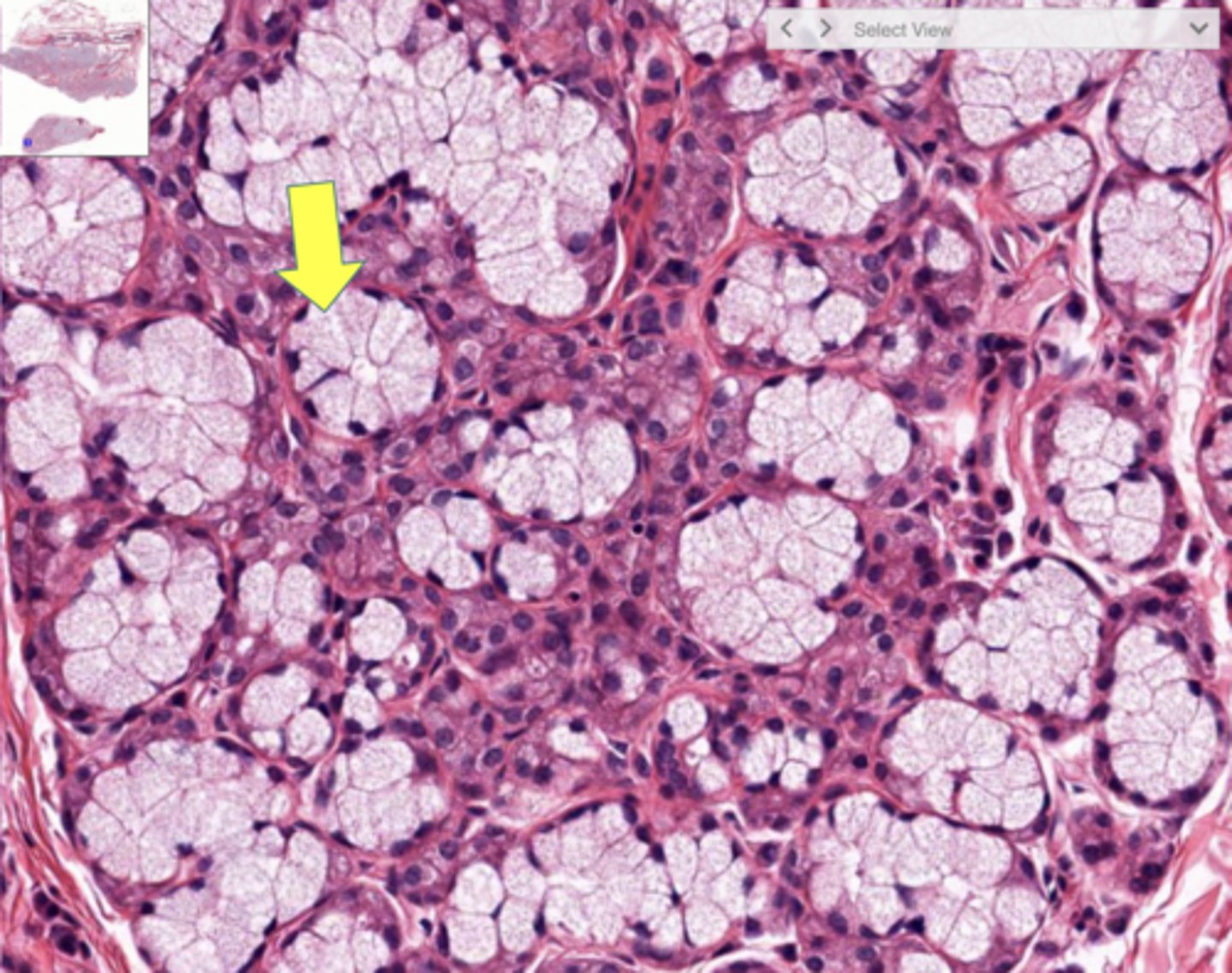
Serous cell
Soften food to ease digestion
What is the function of the salivary glands?
Salivary amylase
What enzyme is secreted by the salivary glands
Serous cells
What cells secrete salivary amylase?
-Parotid Glands
-Submandibular Glands
-Sublinguinal Glands
What are the 3 pairs of salivary glands?
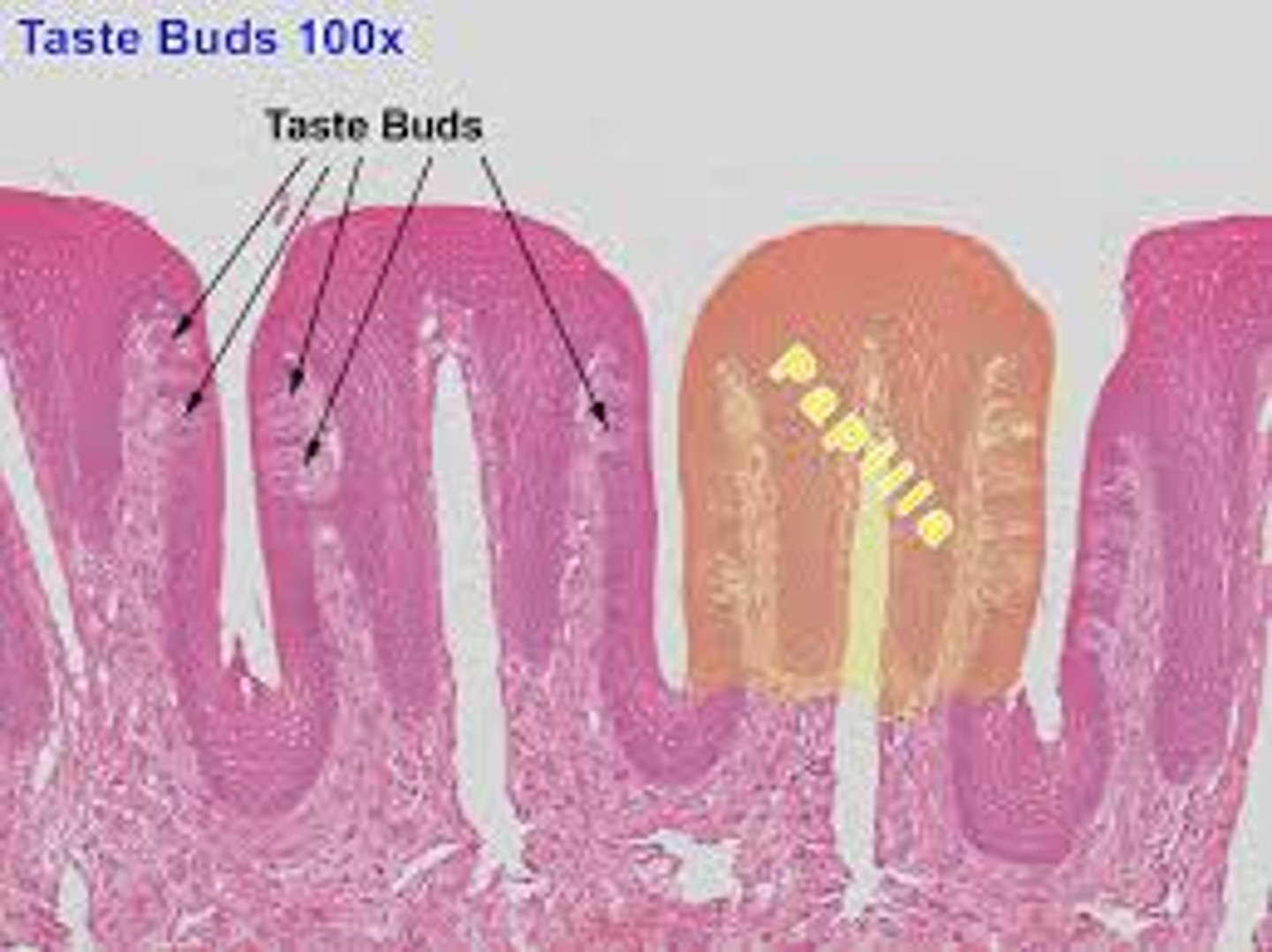
Tongue
Papillae
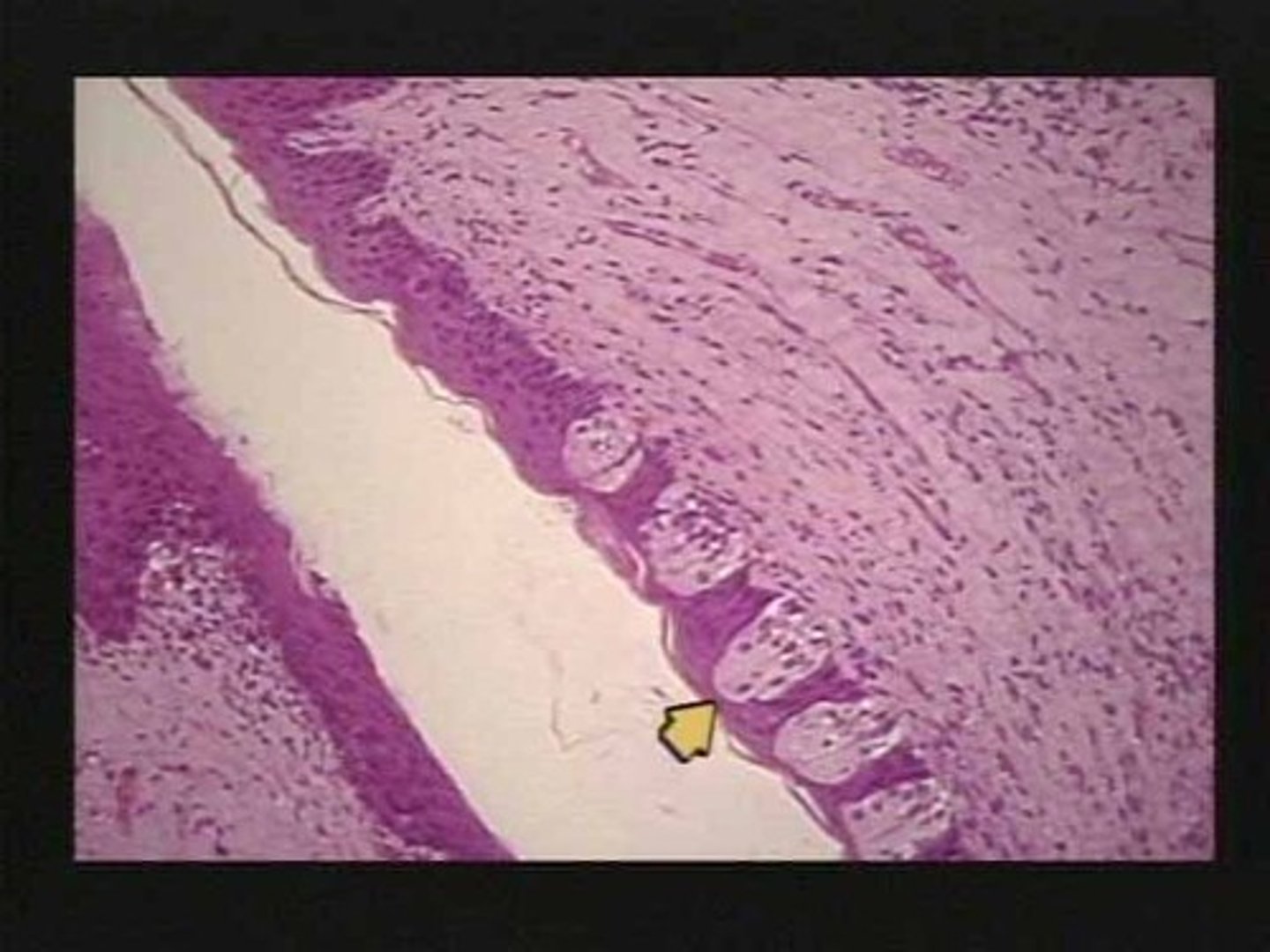
Taste buds
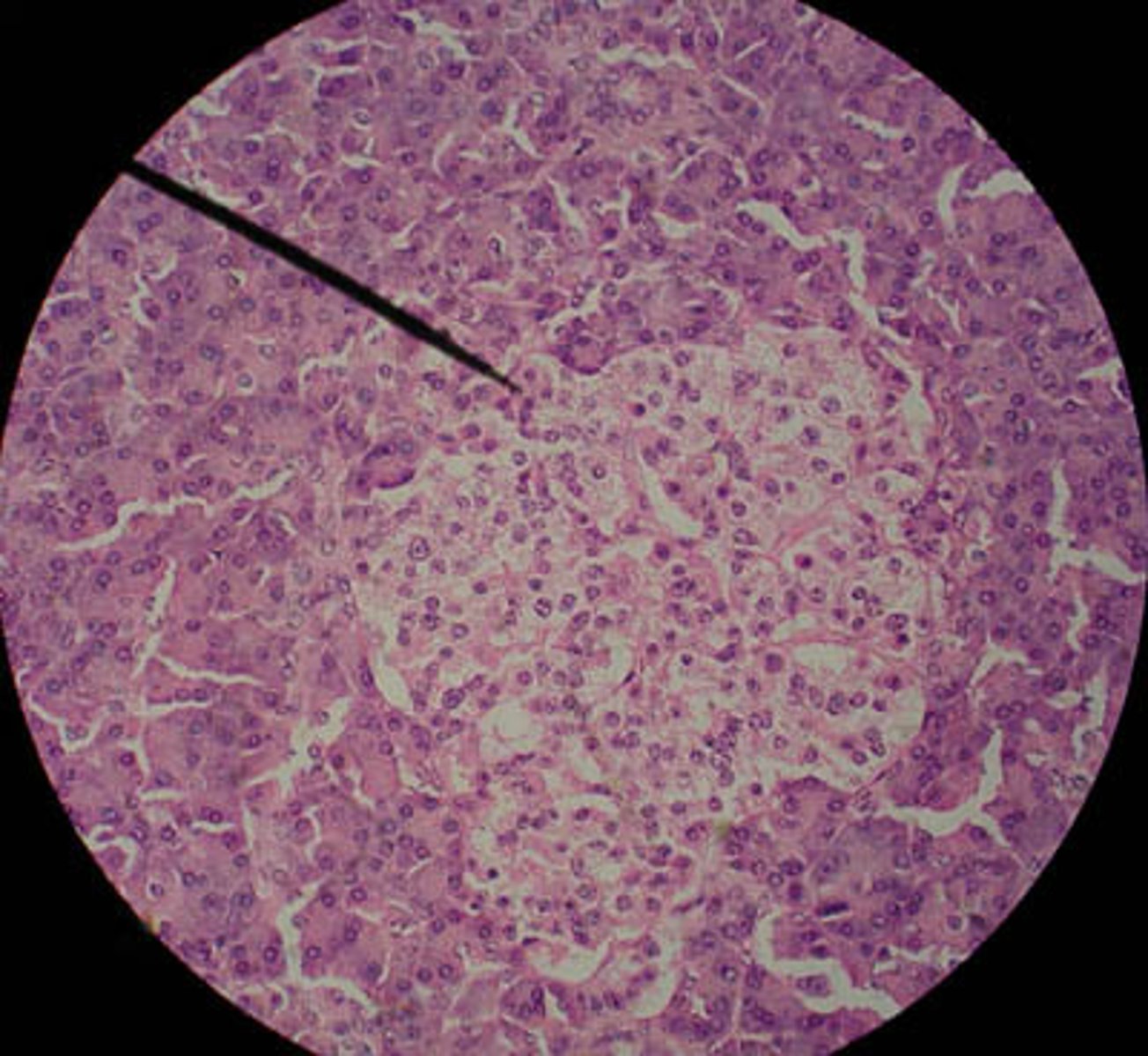
Liver lobule
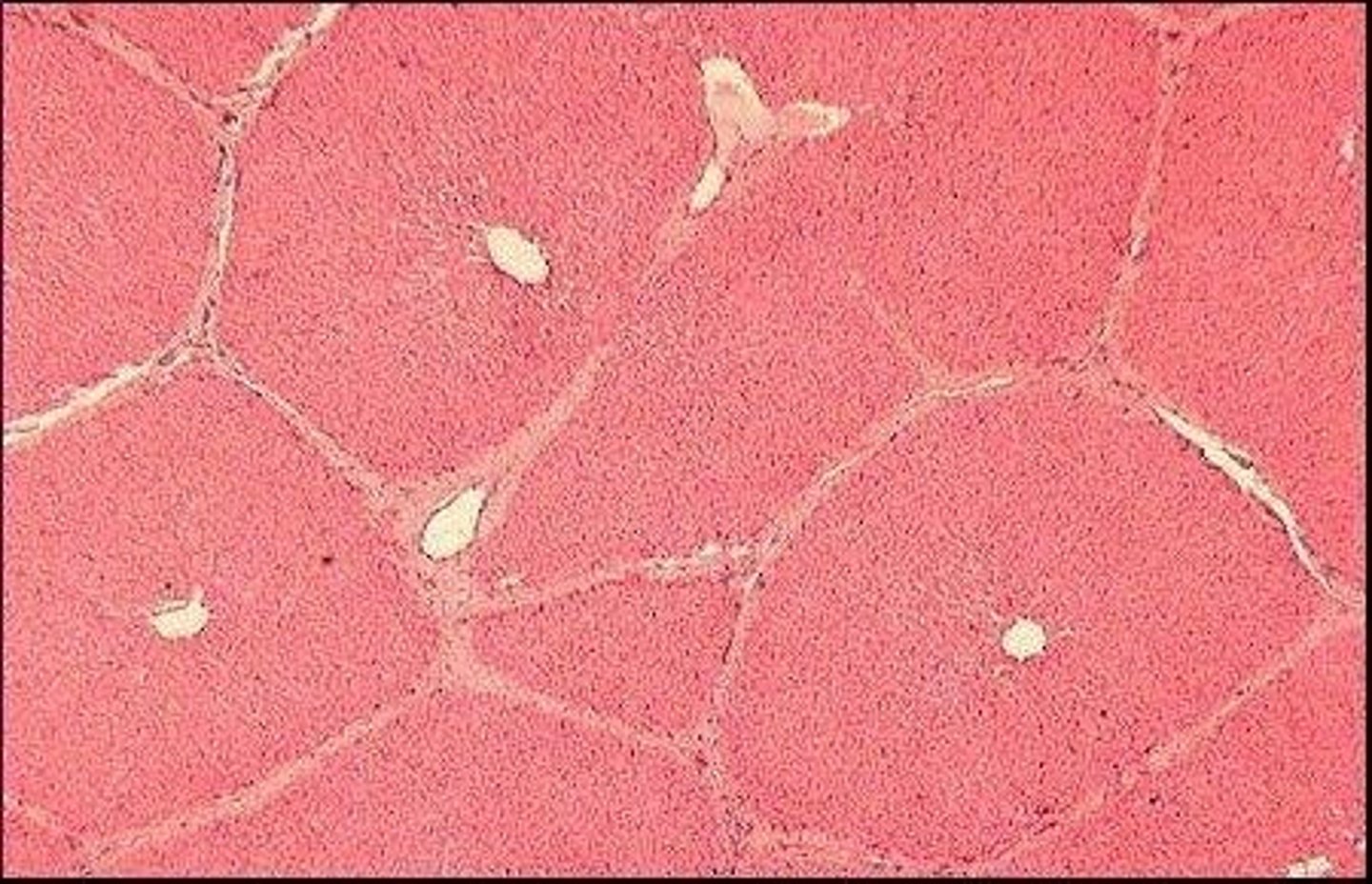
Hepatocytes
Central vein
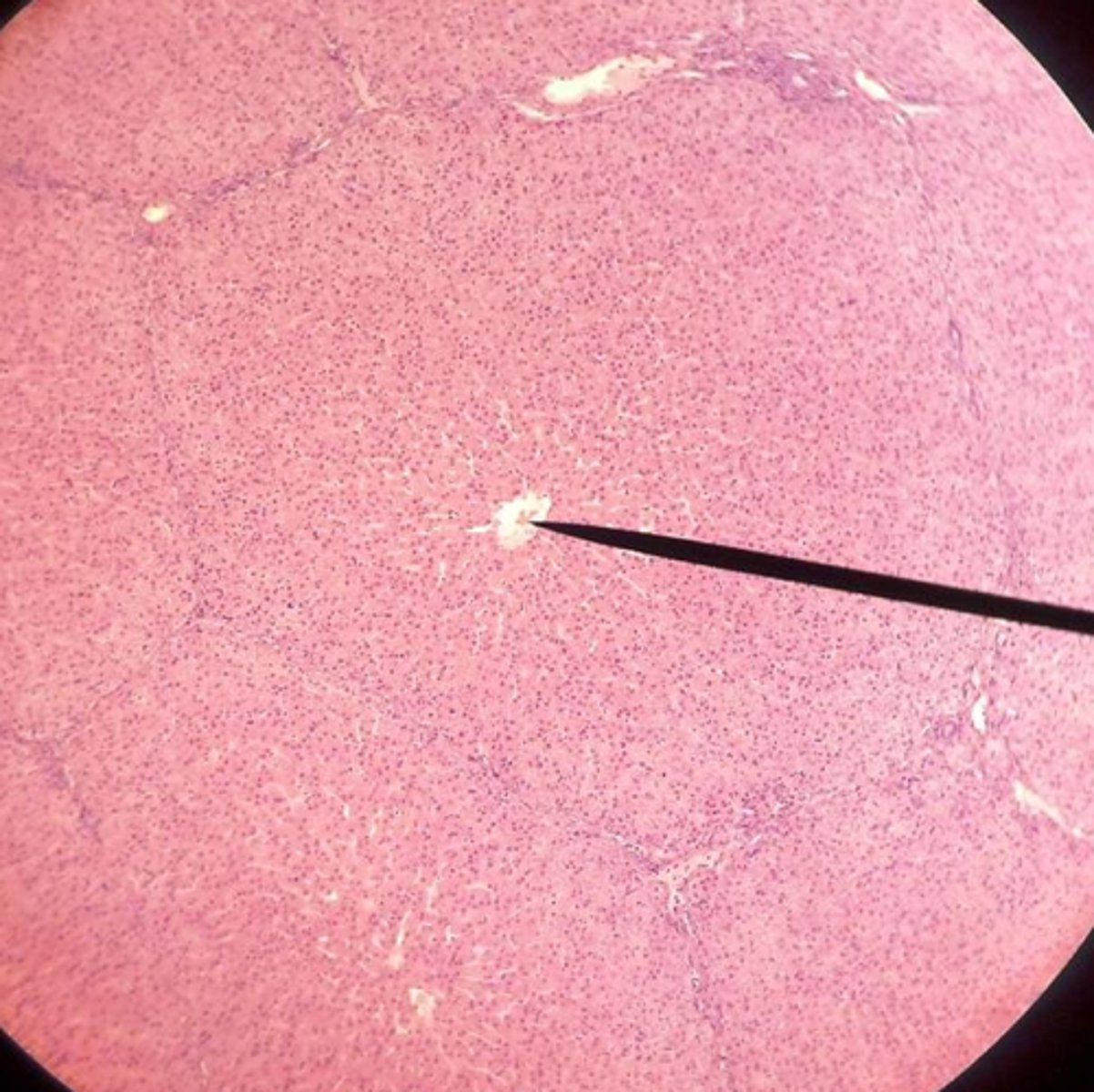
Sinusoids
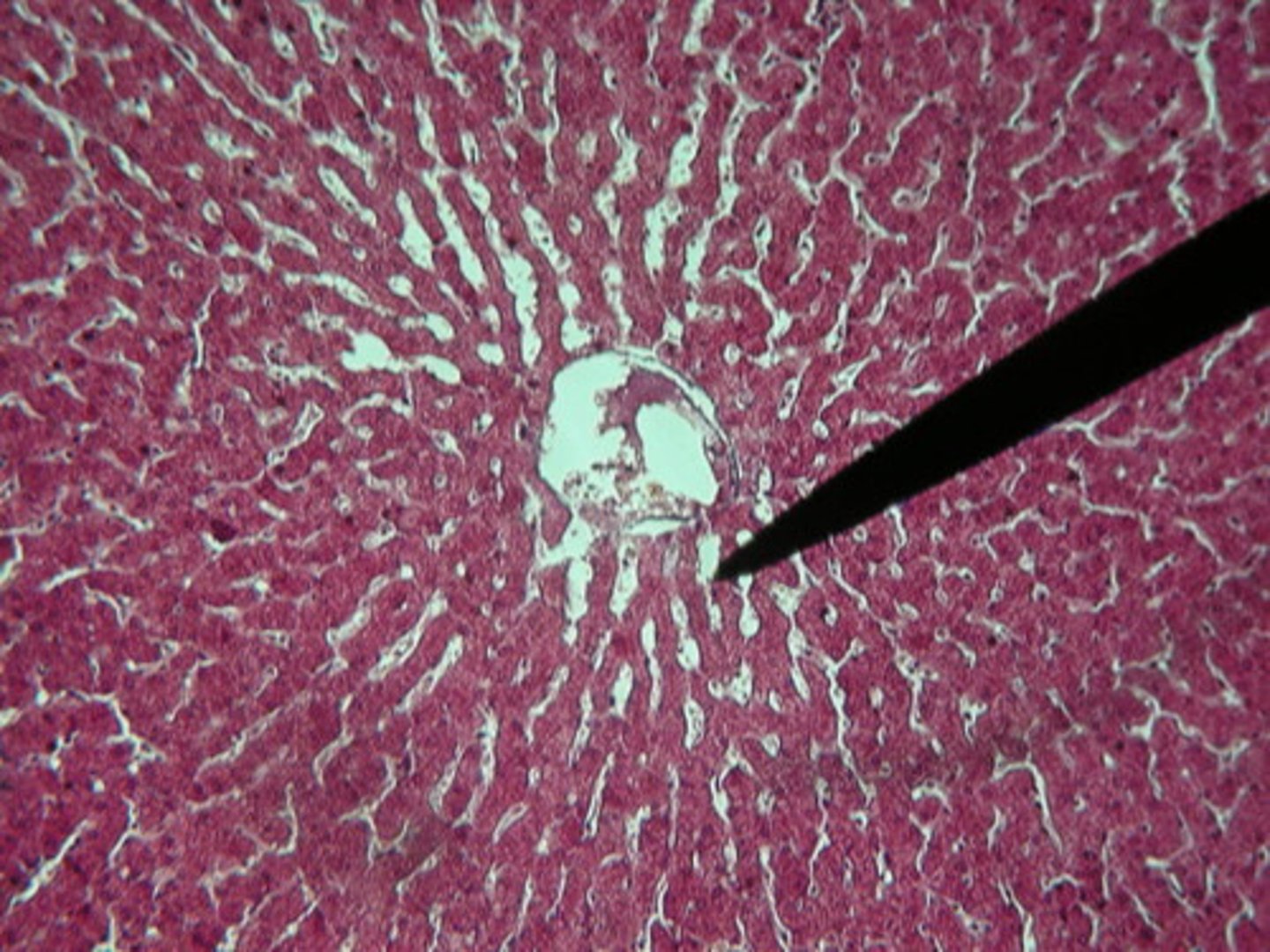
Lobule
What is the functional unit of the liver?
Liver Hepatic Portal Triad
Bile ductule
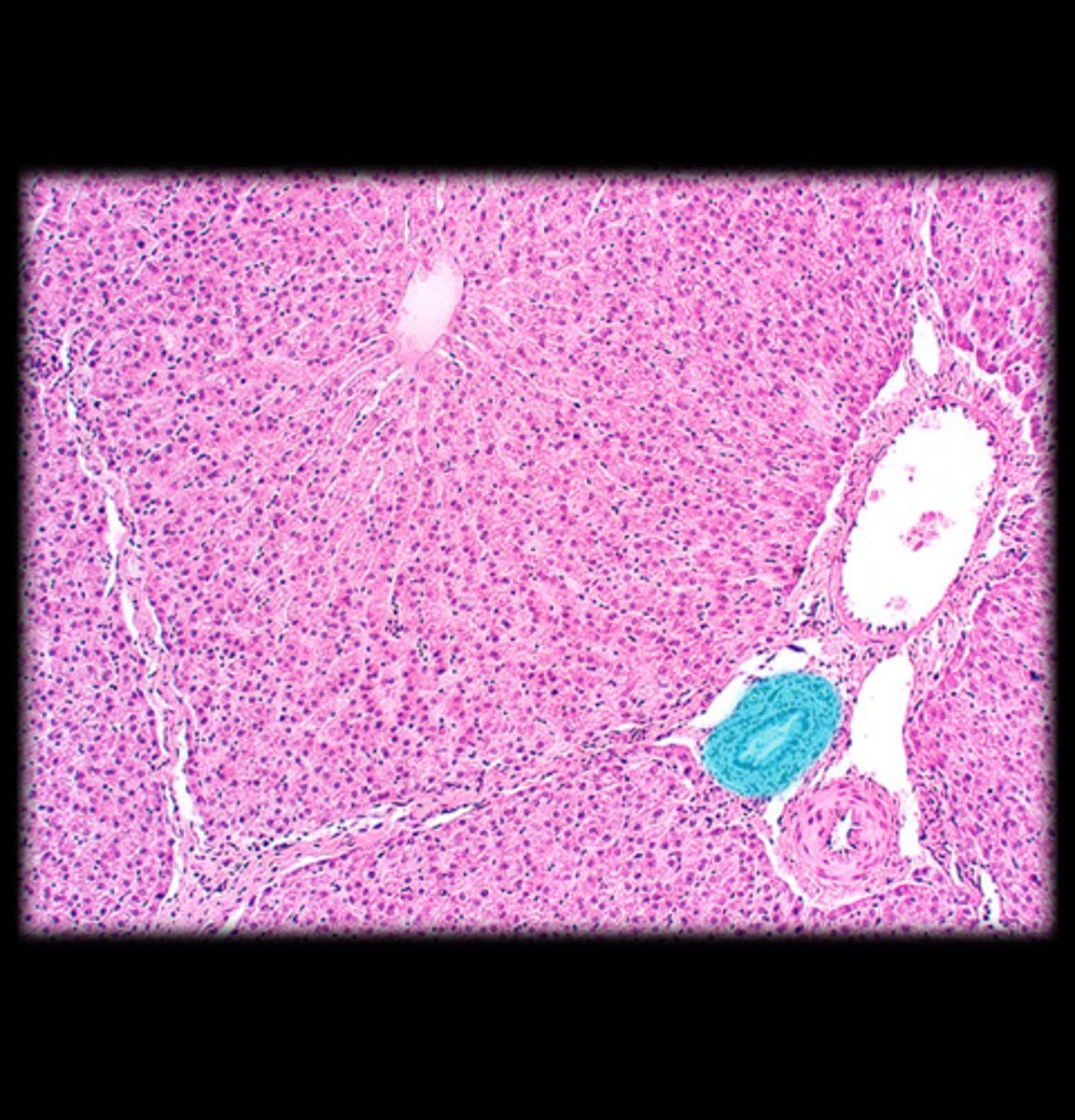
Hepatic arteriole
C
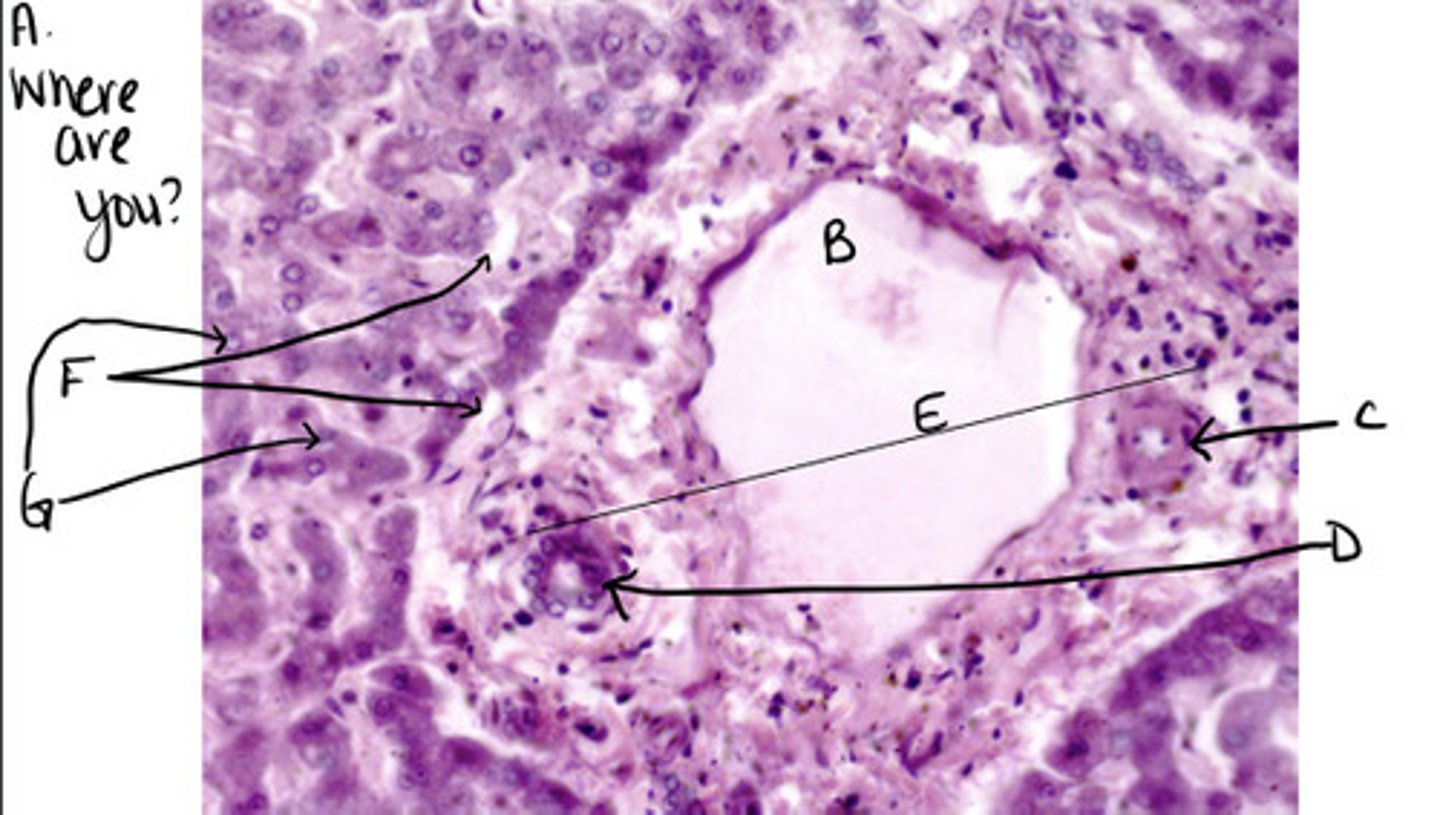
Bile
What flows through the bile ductule?
Oxygen rich blood
What flows through the hepatic arteriole?
Nutrient rich blood
What flows through the hepatic portal venule
Bile production
What is the digestive function of the liver?
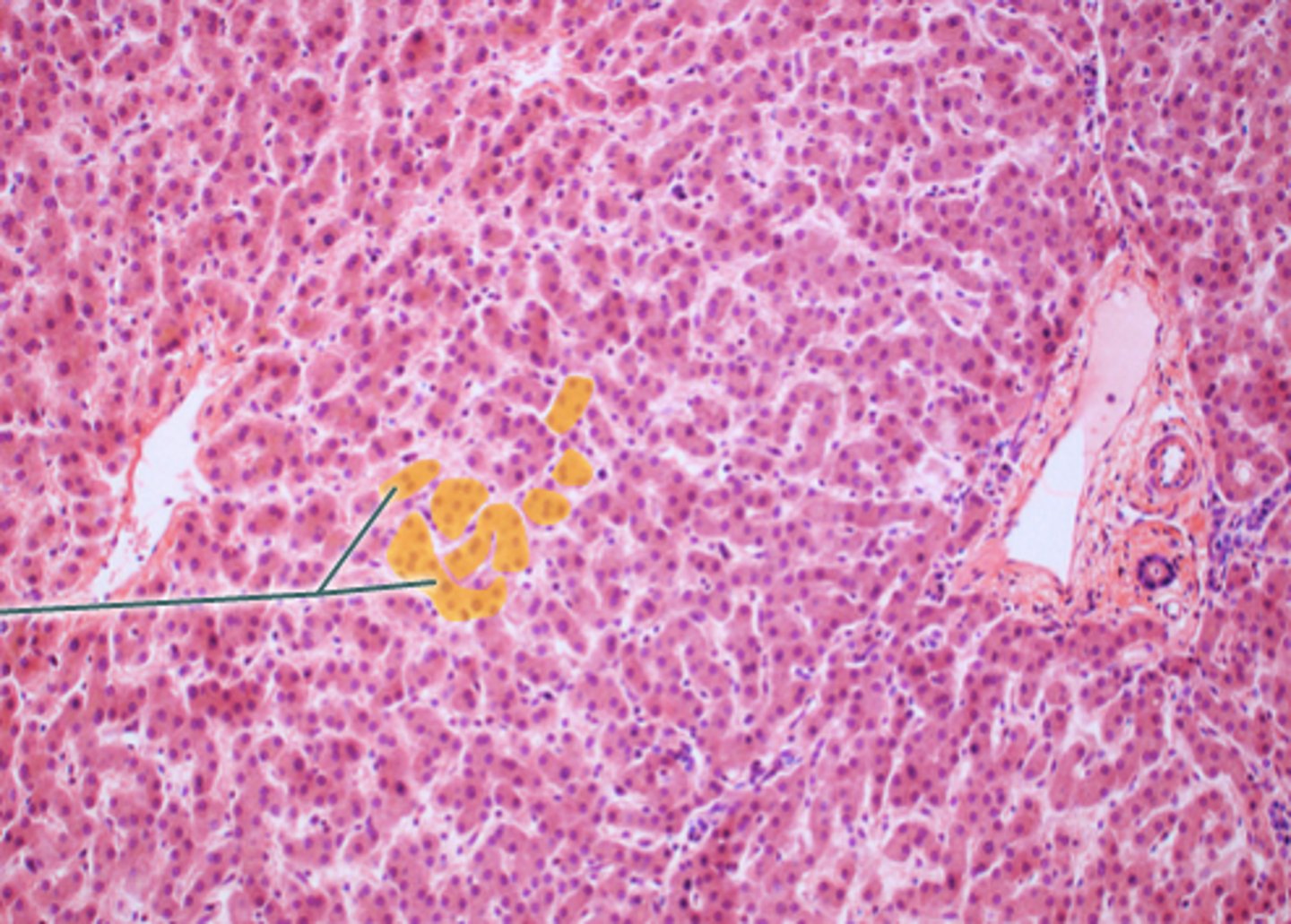
Pancreas
Acinar cells
Blue circle
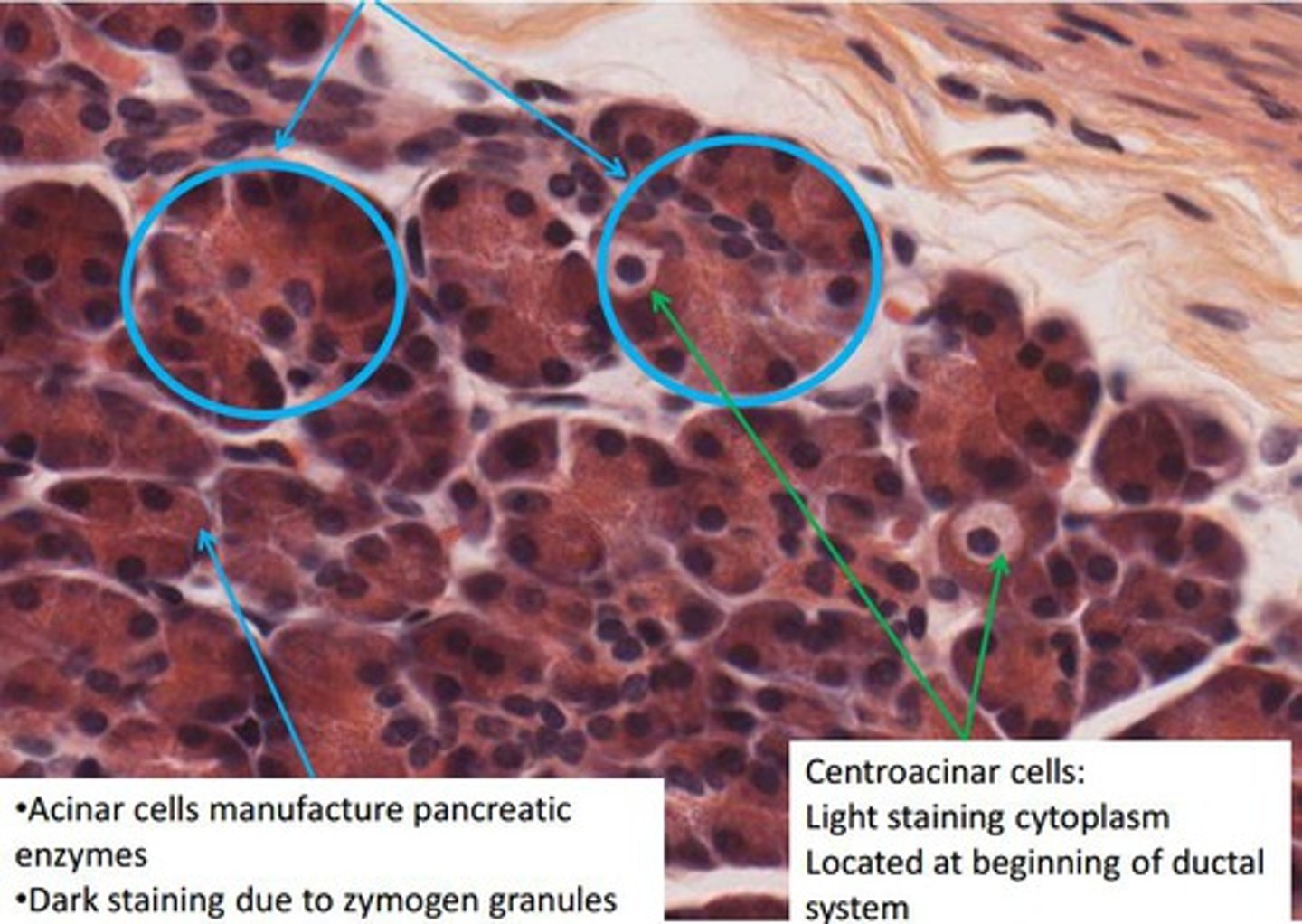
Pancreatic islet
Acinar cells
What cells make up the exocrine portion of the pancreas?
Dump digestive enzymes in the small intestine
What is the function of the pancreas?
Pancreatic islets
What structure contains the endocrine portion of the pancreas?
Blood sugar levels
What homeostatic variable is regulated by the endocrine portion of the pancreas?
The molecule is too bog and needs to be broken down
Why can't the small intestine absorb starches?
Saliva
What kind of digestive juice is in the mouth?
Serous cells of the salivary glands
What is the source of saliva?
Salivary amylase
Enzyme in saliva
Starches
Substrate for salivary amylase
Dextrin and maltose
Products from salivary amylase
Gastric juice
What digestive juice is in the stomach?
-Chief cells
-Parietal cells
-Mucous cells
What are the sources for gastric juice production?
Pepsin (as pepsinogen)
What does chief cells secrete?
Proteins
What is the substrate for pepsin?
Peptides
What is the product for pepsin?
HCl
What does parietal cells secrete?
Pepsinogen activation
What is the purpose for parietal cells secreting HCl?
Pepsin
What is the product of parietal cells secreting HCl?
Intrinsic factor
What else does parietal cells secrete? (besides HCl)
Vitamin B12 absorbtion
What is the function of intrinsic factor?
Mucous
What substance is secreted from gastric mucous cells?
Protection
What is the function of gastric mucous?
-Bile
-Pancreatic juice
-Intestinal juice
What are the 3 digestive juices in the small intestine?
Liver
What is the source for bile?
Bile salts
What is secreted from bile?
Emulsification of fats
What is the function of bile salts?
-Pancreatic amylase
-Pancreatic lipase
-Proteases
What substances are secreted from the acinar cells of the pancreas?
Starches
Substrate for pancreatic amylase
Dextrins and maltose
Products of pancreatic amylase
Lipids
Substrate of pancreatic lipase
Fatty acids and monoglycerides
Products of pancreatic lipase
Proteins and peptides
Substrate of proteases
Amino acids
Product of proteases
NaHCO3 (sodium bicarbonate)
What is secreted by the tubule cells of the pancreas?
Neutralize acidic chyme
What is the function of NaHCO3?
Acinar cells and tubule cells
What are the sources for pancreatic juice?
-Intestinal glands
-Duodenal glands
-Goblet cells
What are the sources for intestinal juice?
-Dipeptidases
-Maltase
-Sucrase
-Lactase
-Dextrinase
What enzymes are secreted from intestinal glands?
Dipeptides
What is the substrate for dipeptidases?
Amino acids
What is the product of dipeptidases?
Maltose
What is the substrate for maltase?
Glucose
What is the product for maltase?
Sucrose
What is the substrate for sucrase?
Glucose and fructose
What are the products of sucrase?
Lactose
What is the substrate for lactase?
Glucose and galactose
What are the products for lactase?
Dextrins
What is the substrate for dextrinase?
Maltose
What is the product of dextrinase?
Mucous
What is secreted from the duodenal glands?
Protection and neutralization
What is the function of the mucous from the duodenal glands?
Mucous
What do goblet cells secrete (small and large intestine)?
Protection
What is the purpose of the mucous in the small and large intestine?
-Common bile duct
-Pancreatic Duct
What 2 ducts release into the duodenum from the haepatopancreatic sphincter?
pH
What does phenolphthalein measure?
Presence of peptide bonds
What does biuret's reagent indicate?
Presence of starches
What does iodine indicate?
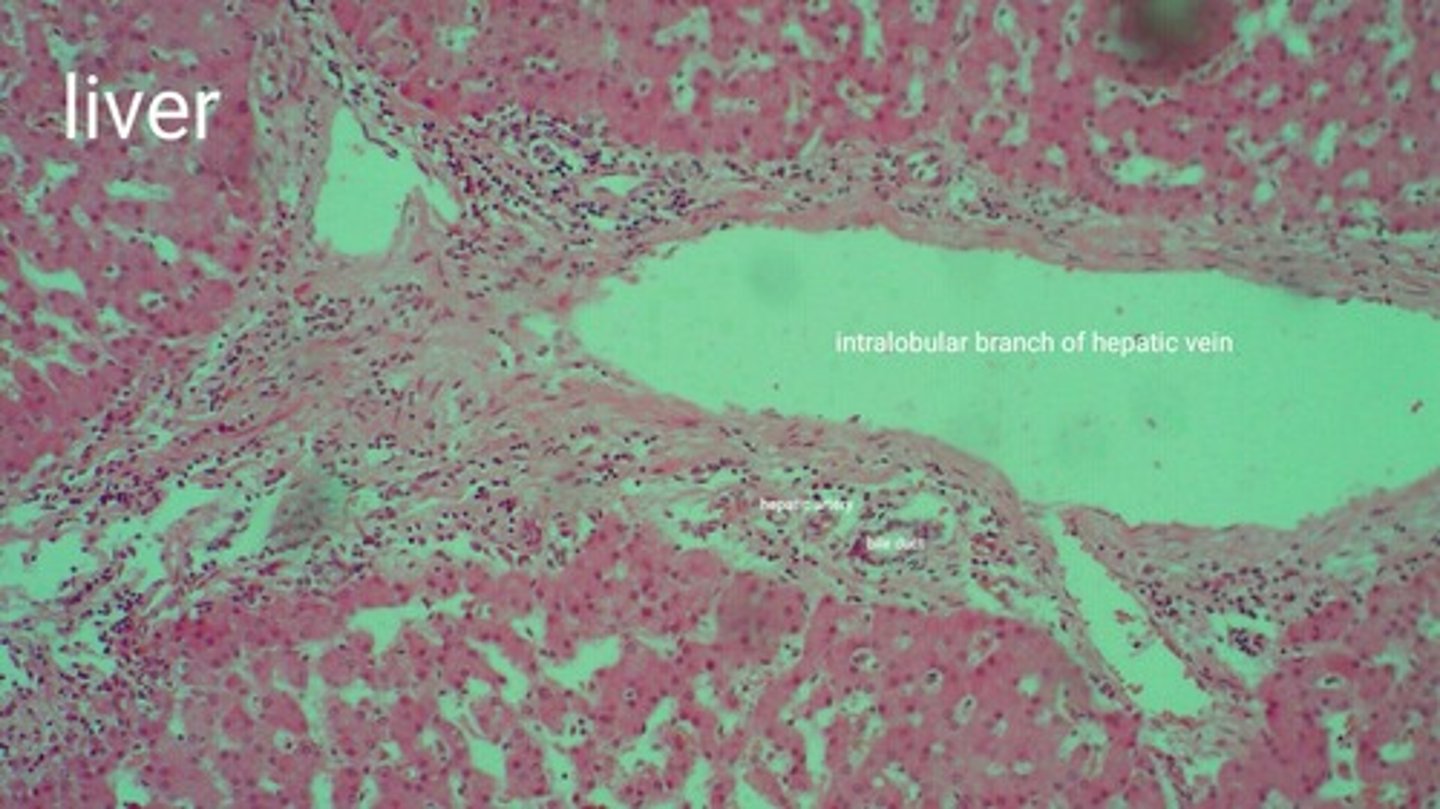
Hepatic vein
Where does blood flow after it exits the sinusoids of the liver?
Fatty acids
In the chemical digestion experiment with lipids, with caused the pH to decrease in tube 2?
pH was not acidic, pepsin was inefficient
In the chemical digestion experiment with proteins, why didn't digestion occur in tube 3?
It was the control tube
In the chemical digestion experiment with starch, why didn't digestion occur in tube 2?